-
1 CHINA'S TAX&...
-
2 China &nbs...
-
3 Individual I...
-
4 CHINA TAX&nb...
How the Tax System is Organized in China
by Qian Zhou | July 24, 2020
Taxation affects almost all aspects of doing business in China. Because China has a idiosyncratic business environment, which is significantly different to Europe or North America, business leaders need to develop a strong understanding of the country’s tax system before assessing their exposure to tax liabilities in the country. This helps businesses maximize their tax efficiency while maintaining compliance with tax laws and regulations.
In this article, we briefly touch upon the legislation and regulatory structures that are responsible for tax administration in China.
A brief history
China’s tax system was practically in chaos when the People’s Republic of China was first established in 1949. The Government Administration Council, now the State Council, promulgated the Implementation Standards of National Tax Policies in 1950, which unified the tax rules applied nationwide and laid the basic legal framework for taxation in China. Several revisions and improvements were made in the following decades. Rather than a tool to adjust the economy, China’s tax system from the 1950s to 1970s was designed solely for the purpose of collecting capital.
In 1978, two years after the death of Chairman Mao Zedong and the end of the Cultural Revolution (1966-1976), the state government led by Deng Xiaoping decided to introduce market principles to China and adopted the policy of “Reform and Opening Up” at the Third Plenary Session of the 11th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China. A series of reformative measures were adopted to facilitate the transformation to a market economy, which placed taxation in an increasingly prominent role in China’s on-going economic transition.
Several important tax laws were promulgated in the 1980s, including the Corporate Income Tax (CIT) Law for Joint Ventures, CIT Law for Foreign Enterprises, and Individual Income Tax (IIT) Law. First drafts of the regulations on value-added tax (VAT) and business tax (BT) were released in 1984.
In 1994, a significant tax reform took place, which established a new tax revenue sharing system between the central and local governments, granting greater fiscal power to the former. The Interim Regulations on VAT, BT, and consumption tax, which respectively are the blueprints of the current rules, all came into effect on January 1, 1994. The reform further integrated various income taxes into three categories: CIT on domestic enterprises, CIT on foreign enterprises and foreign-invested enterprises, and IIT; these were further synthesized into a single CIT and IIT in 2008.
China has kept reforming its tax system. Today, with the VAT reform and IIT reform essentially completed, China’s tax system is still evolving at a rapid pace as authorities seek to improve transparency, compliance, and the ease of doing business in the country.
Legislative organs
China’s tax laws and policies are mainly formulated by these state organs:
National People’s Congress (NPC) and its Standing Committee;
State Council;
Ministry of Finance (MOF);
State Taxation Administration (STA);
State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE); and
General Administration of Customs (GAC).
The legislation of new tax laws in China follows five steps: proposal, drafting, examination, voting, and promulgation by the NPC and its Standing Committee. In China, the NPC and its Standing Committee are the highest legislative organs and possess the power to formulate laws.
According to China’s Constitution, all laws passed by the NPC and its Standing Committee become effective only after they have been signed by the Chairman of the country (presented as “Chairman Order” by reference number), even though the Chairman does not actually have the power to veto decisions.
Laws promulgated by the NPC are supplemented by detailed implementing regulations formulated by the State Council – the Chinese cabinet and the highest administrative organ empowered to promulgate administrative regulations. For example, China’s IIT Law is promulgated by the Standing Committee of the NPC, while the Implementing Guidelines, which regulate the specific enforcement of the IIT Law are promulgated by the State Council.
The MOF, STA, and GAC are ministries and institutions subordinate to the State Council and are authorized to issue tax announcements, circulars, and replies in order to supplement, interpret, or clarify the laws and regulations of the NPC and State Council.
In addition, some local tax regulations and rules may be promulgated by the local iterations of the People’s Congress and government authorities at the provincial or municipal level and are only enforceable in certain regions.
Tax administration
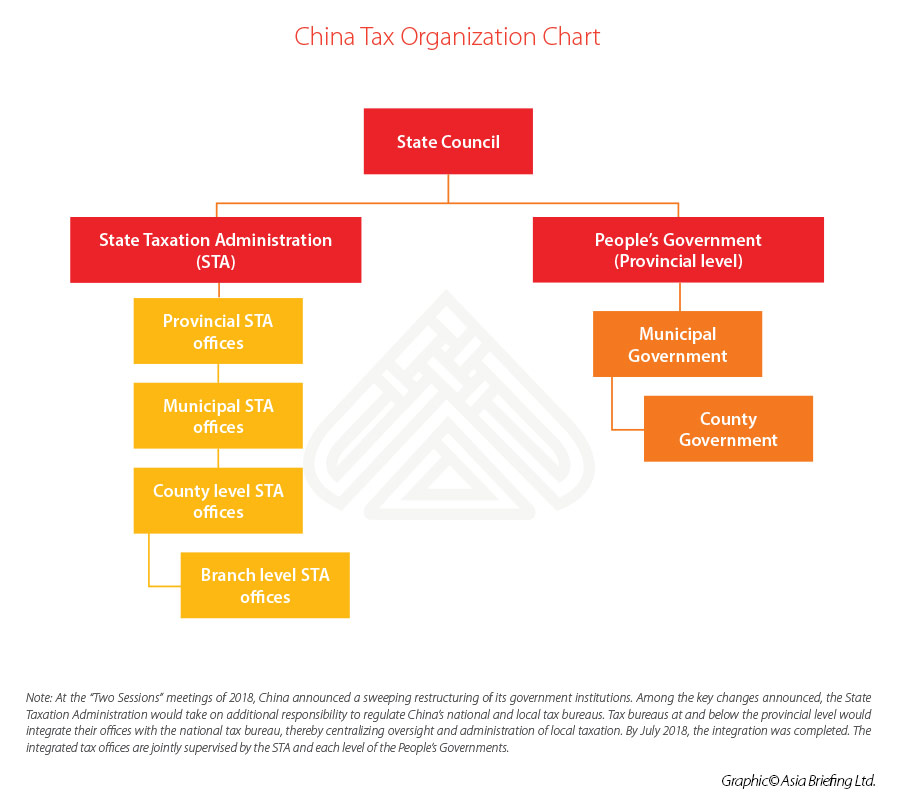
The State Taxation Administration or STA (formerly known as the State Administration of Taxation or SAT), is a government institution directly under the State Council and the highest tax authority in China. It is the equivalent of the Internal Revenue Service of the United States or HM Revenue and Customs of the United Kingdom.
The STA is authorized by the State Council to oversee the country’s tax system, draft national tax regulations (sometimes in conjunction with the MOF), support the MOF in developing national tax and economic policies, and execute the collection and administration of taxes attributed to the central government.
Previously, the state tax bureau (STB) in each municipality served as the local office of the STA. Local tax bureaus (LTB) were institutions directly subordinate to the local government, but also under the supervision of the STA. They were in charge of the administration of taxes attributed to the local government. Every business entity must have registered with both the STB and LTB.
However, at the “Two Sessions” meetings of 2018, China announced a sweeping restructuring of its government institutions. Among other changes, the SAT took on additional responsibility to regulate China’s national and local tax bureaus. Tax bureaus at and below the provincial level have now integrated their offices with the national tax bureau, thereby centralizing oversight and administration of local taxation. The integrated tax offices are jointly supervised by the STA and each level of the People’s Governments. By July 2018, this integration was completed.
Businesses must register with the customs authorities if importing or exporting. The General Administration of Customs or GAC supervises the collection of customs duties, import VAT and import consumption tax, which are all directly attributed to the central fiscal revenue. It also oversees the operation of bonded zones.
Tax registration
In September 2015, China launched a new round of business license reform, in a move to simplify companies’ registration and establishment procedures. Specifically, companies newly established after October 1, 2015 were no longer required to obtain the tax registration certificate when conducting business registration procedures. (Since January 1, 2018, the separate tax registration certificate has been invalid.)
Instead, newly established companies are issued a special business license with a unified social credit code on it. The special business license is used like the previous tax registration license when the company is dealing with tax relevant issues. However, investors are still required to apply to the tax bureau for tax clearance when they decide to shut down their operations in China.
SOURCE: https://www.china-briefing.com/news/tax-system-organized-china/


