1.1 遗传密码载体-mRNA
★碱基→氨基酸转换:遗传密码
· mRNA上的三联核苷酸构成一个密码子代表一种氨基酸,这种三联核苷酸密码为遗传密码(genetic codon),或三联体密码 (triplet codon ).
· 起始密码 (initiator codon): AUG
· 终止密码 (terminator codon): UAA、UAG、UGA
Standard Genetic codon-遗传密码表
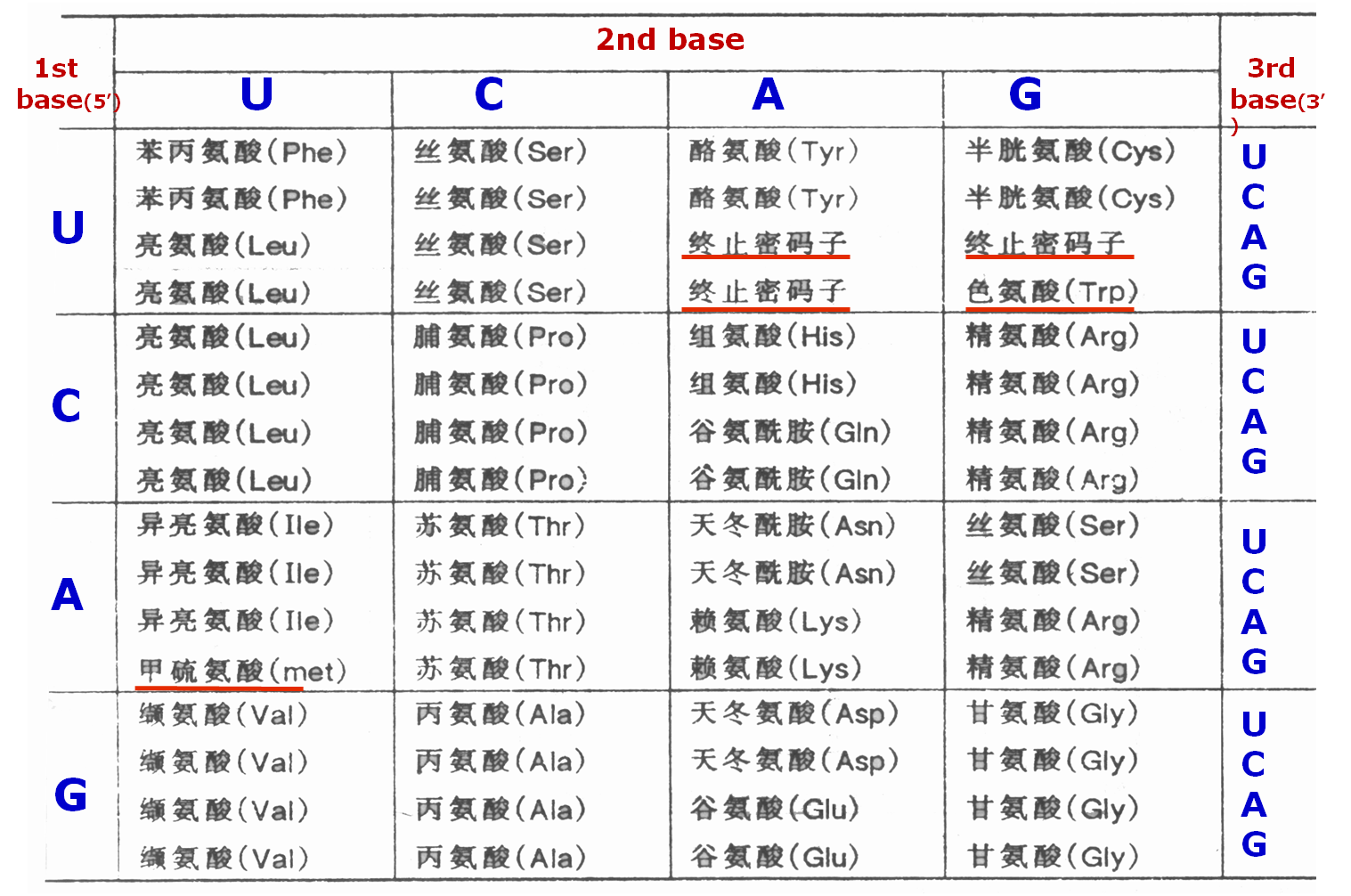
遗传密码表主要信息 
★有义密码子(Sense codon): 编码氨基酸 — 61.
★无义密码子(Nonsense codon):不编码氨基酸—
终止密码子 —UAA,UAG,UGA
★起始密码子:翻译起始信号和位点 —AUG, GUG(原核) .
遗传密码的发现 - Discovery of codons
★1. 1954, George Gamow :Triplet codon theory— a code of 3 nt codes for 64 aa.(43)
★2. 1961,Crick reconfirm triplet codon theory
★3. Nirenberg:(polyU-Phe)as template— the first experiment to demonstrate the nature of codon.
★4. Khorana: poly-nucleotides(UC)n(UUC)n(UUAC)n as template, and identify the rest of genetic code.
★5. 1965: complete deciphering codons of standard genetic code.
★6. 1968- Noble Prize(Robert, Nirenberg and Khorana)
§1.1 遗传密码载体-mRNA
★碱基→ 氨基酸转换:遗传密码
· mRNA上的三联核苷酸构成一个密码子代表一种氨基酸,这种三联核苷酸密码为遗传密码(genetic codon),或三联体密码 (triplet codon ).
· 起始密码 (initiator codon): AUG
· 终止密码 (terminator codon): UAA、UAG、UGA
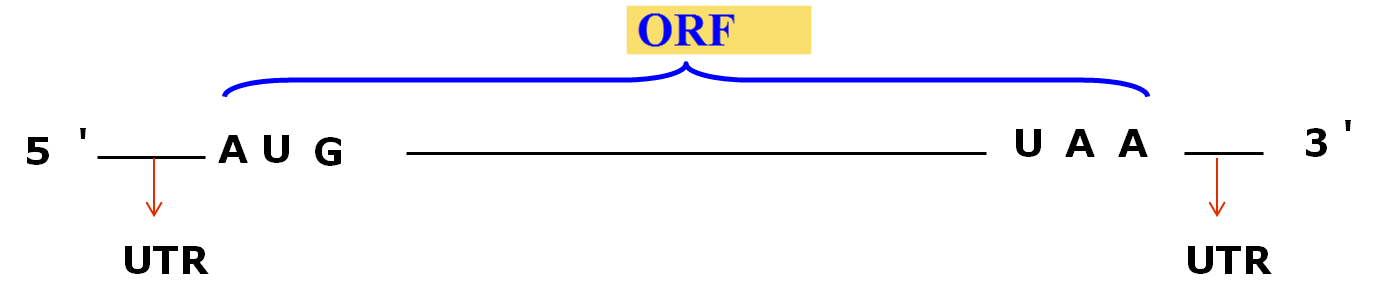
★ 完整序列的 mRNA, 从起始密码子 (AUG) 到终止密码子, 这段编码氨基酸的序列为开放阅读框架(open reading frame-ORF ), 编码多肽链的一级结构.
★各个三联体密码连续排列编码一个蛋白质多肽链。
遗传密码表特点

★1. 连续性 (Commaless)
The genetic codons should be read continuously without spacing or overlapping. —密码间既无间断也无交叉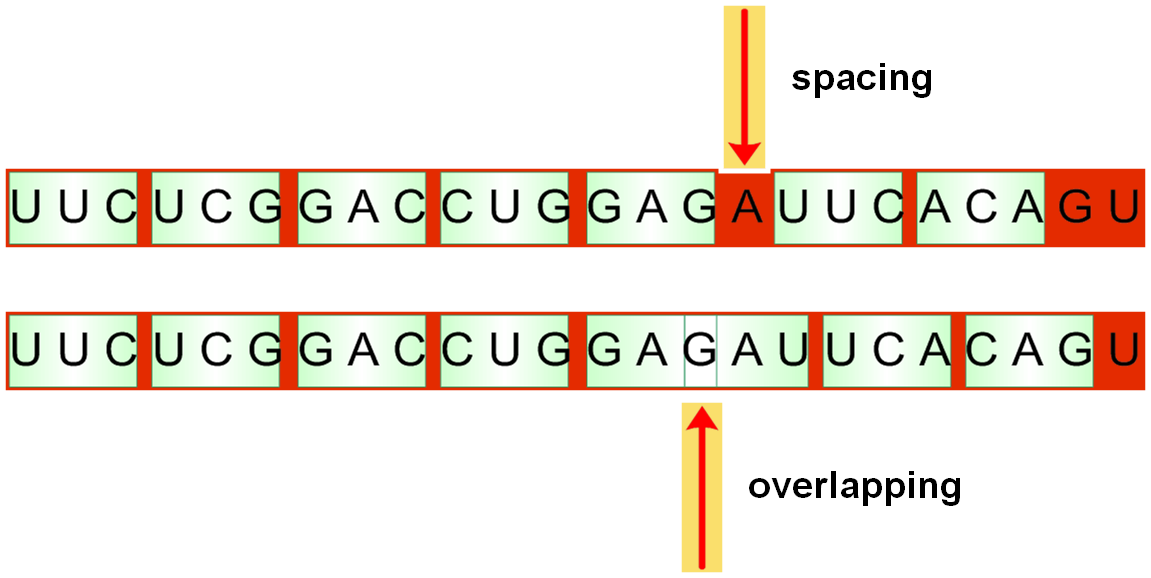
※ 翻译起始精确性的重要性
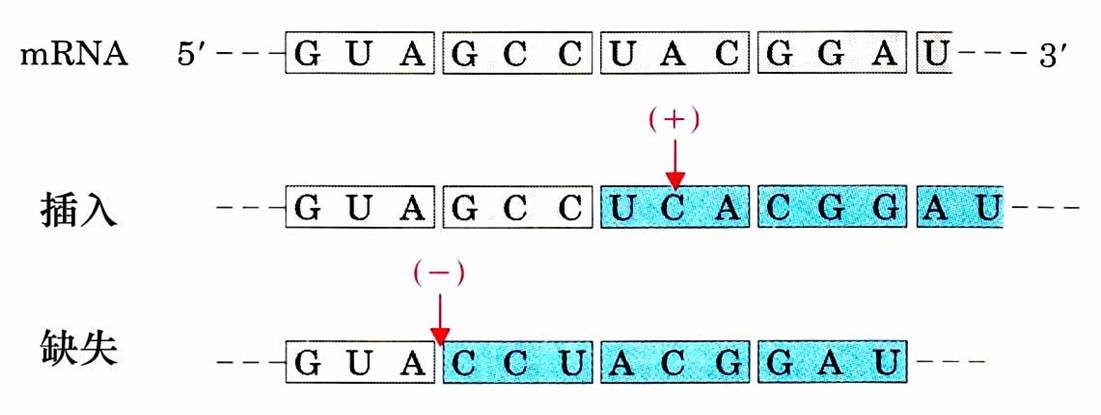
★mRNA 模板上碱基插入和缺失的突变能够导致-移码突变。
★2. 方向性 (Sideness)
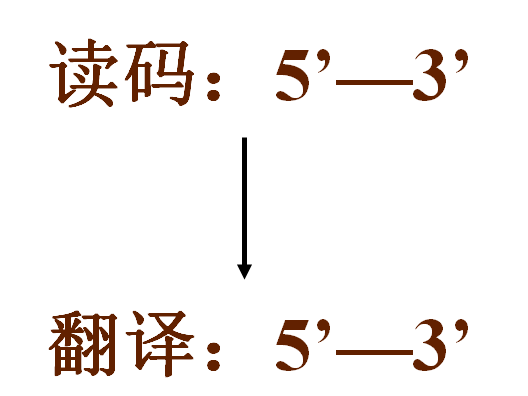
★3. 简并性 (Degeneracy)

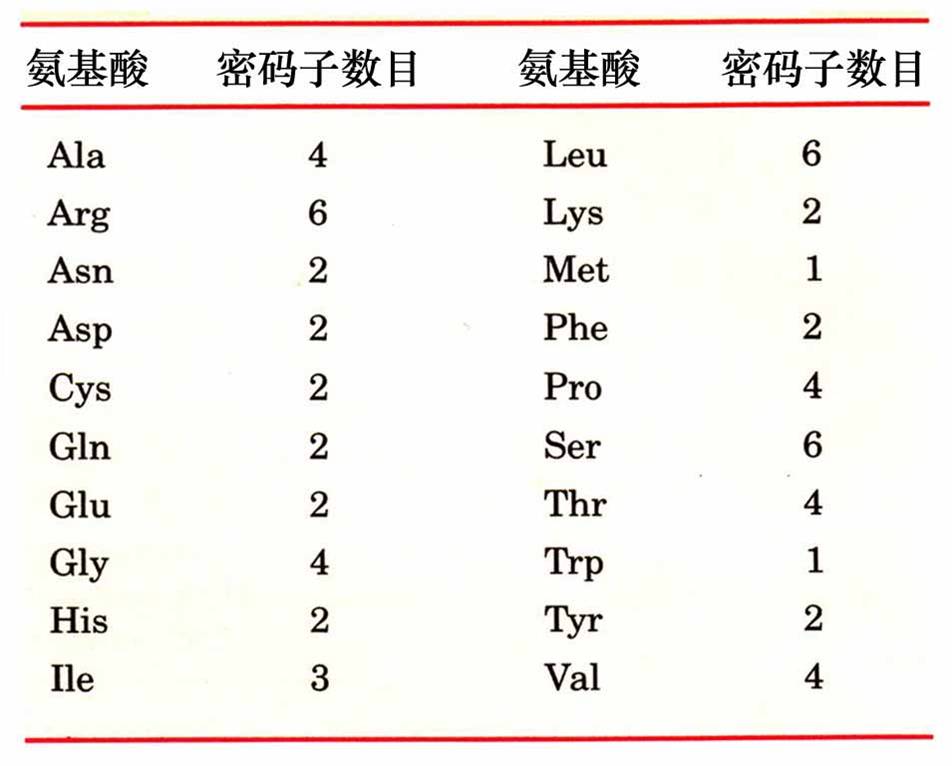
★4. 通用性 (Universal)
The genetic codons for amino acids are always the same. 从原核生物到人类都通用。(basic reason of microbial infection)
With a few exceptions : mitochondrial (线粒体)mRNA, chloroplast (叶绿体)
![]()



