3.1 Primary structure modification-一级结构加工

a. Modification of N-terminus(N-末端加工)
Removing of (f)met-tRNAi(f)met/ N-terminal sequence
↑
aminopeptidase-氨基肽酶
b. Covalent modification(共价修饰)
1. Hydroxylation (羟基化)
2.Glycosylation (糖基化)
3. Phosphorylation(磷酸化)
4. Acetylation (乙酰化)
5. Carboxylation (羧化)
6. Methylation(甲基化)
7.Ubiquitinoylation (泛素化)
8. Esterification (酯化)
★Hydroxylation(羟基化)

Hydroxyproline, hydroxylysine——post-translational modification
★Case1:蛋白质翻译后修饰异常导致疾病
坏血病(Scurvy)
·原因:Vit C 缺乏致羟化异常
·发病机制:
Vit C(为羟化酶辅酶)
↓辅酶
(脯氨酸,赖氨酸)羟化酶
↓
胶原蛋白羟化
↓
胶原蛋白装配,稳定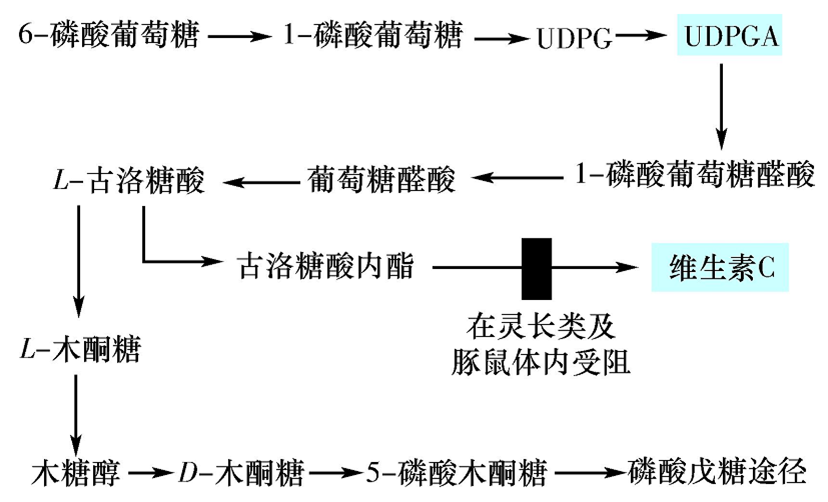
★Glycosylation(糖基化-多数功能蛋白)
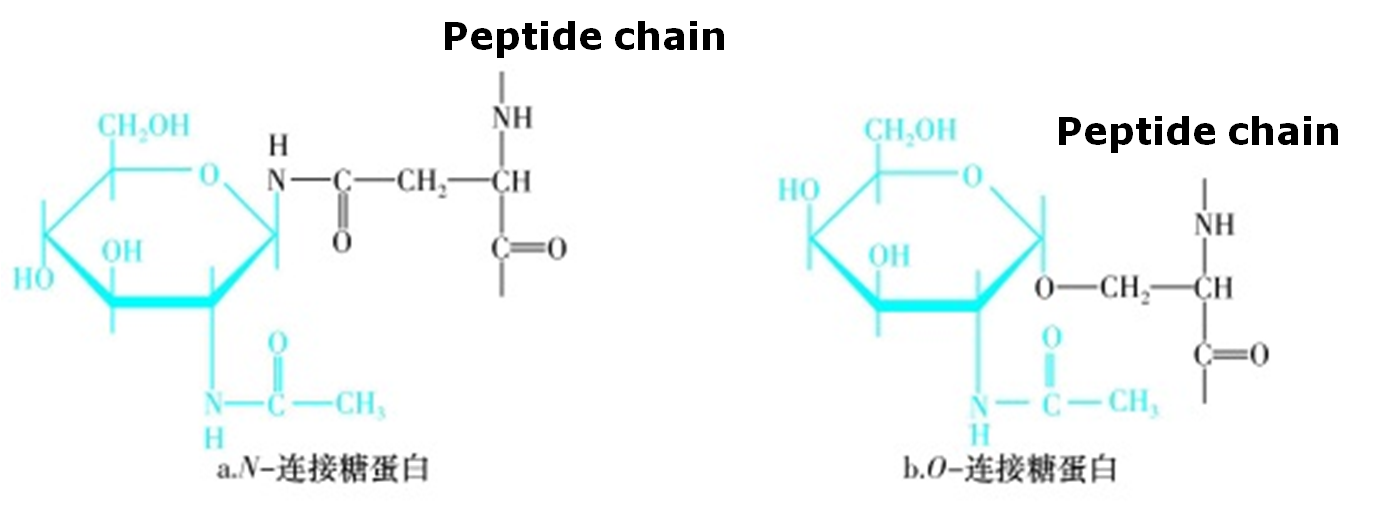
Mostglobular proteins with activity-glycoprotein
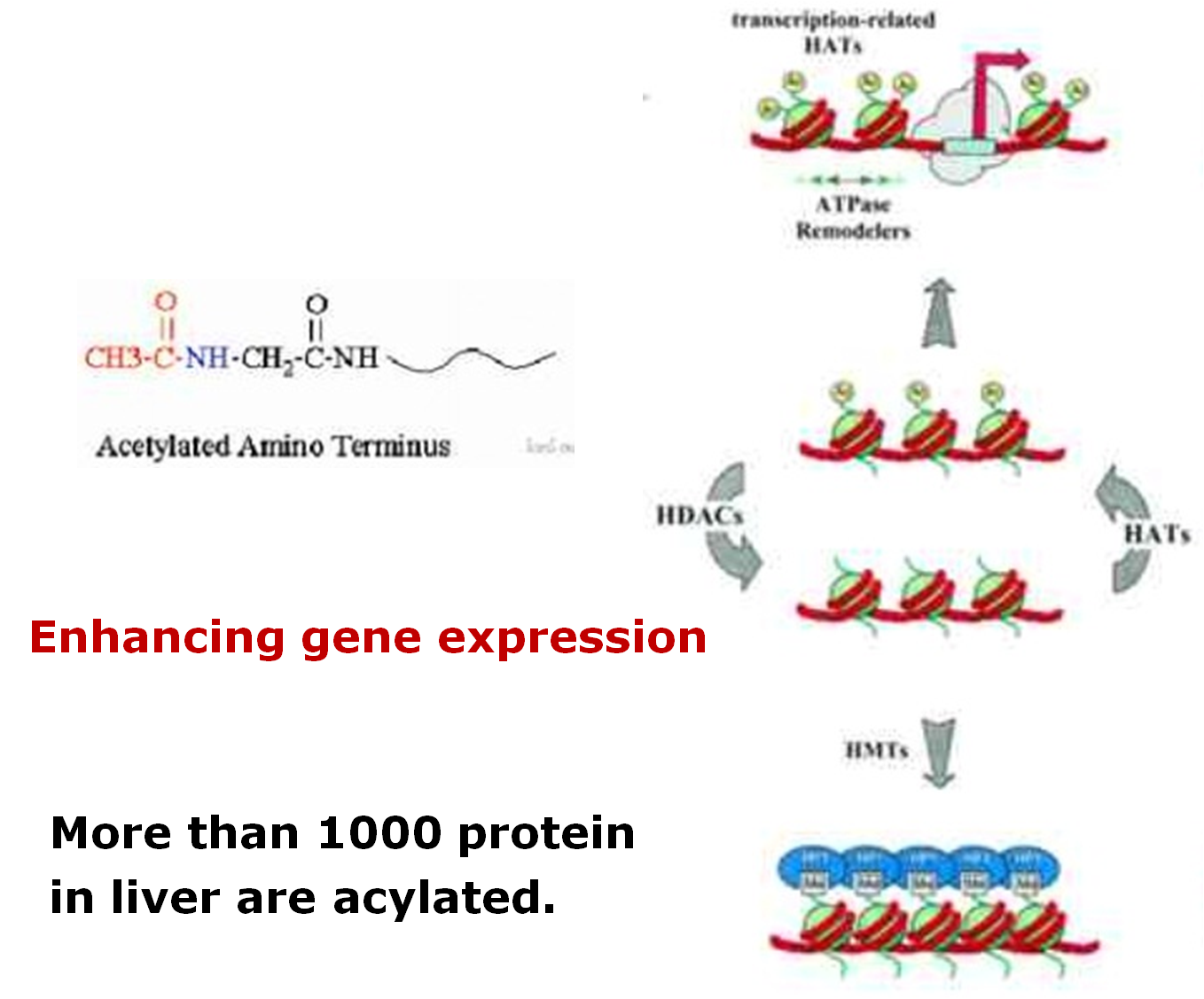
★Acylation (乙酰化)of histone-广泛的共价修饰
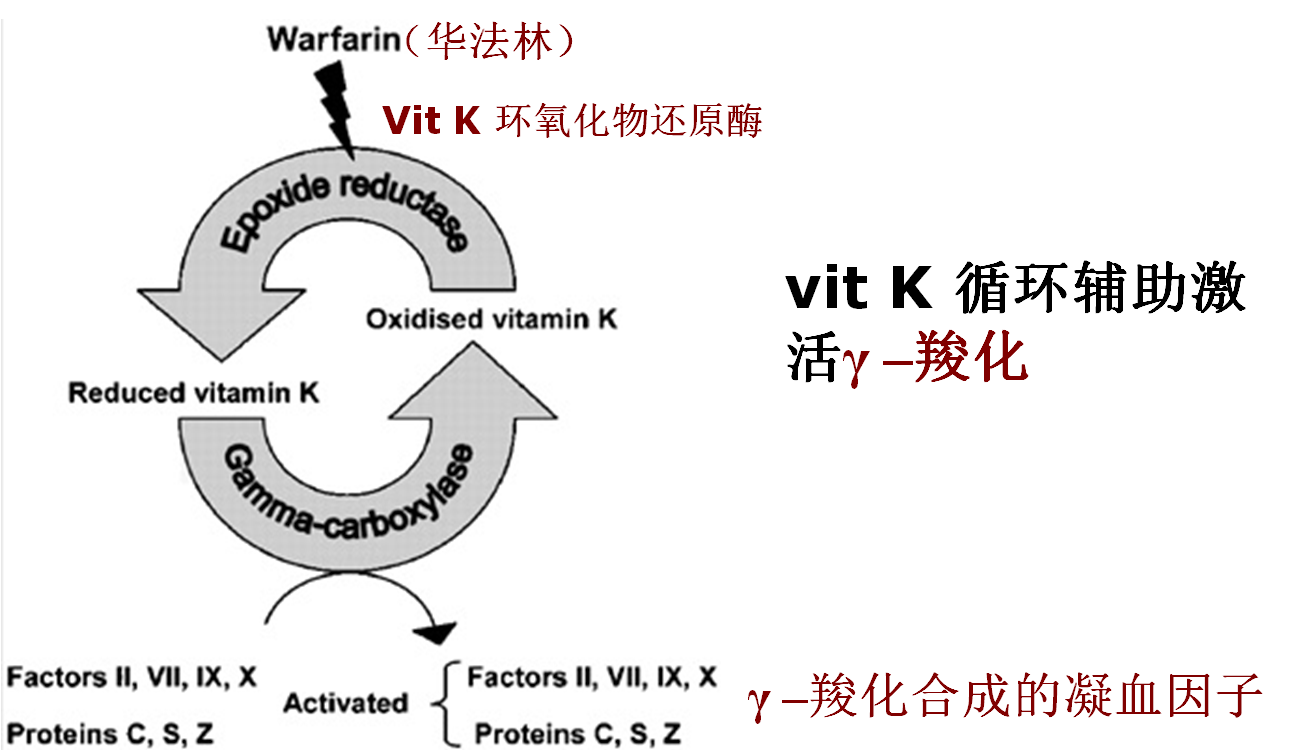
★Carboxylation(羧化)
★Carboxylation of thrombinogen(凝血酶原)

★Case2:蛋白质翻译后修饰异常导致疾病
·凝血障碍- vit K 缺乏
c. Proteolytic modification(水解修饰)
★ Removingof
N-terminal signal peptide
★Activiation of zymogen
★ Onepeptide chain is hydrolyzed to many active peptides
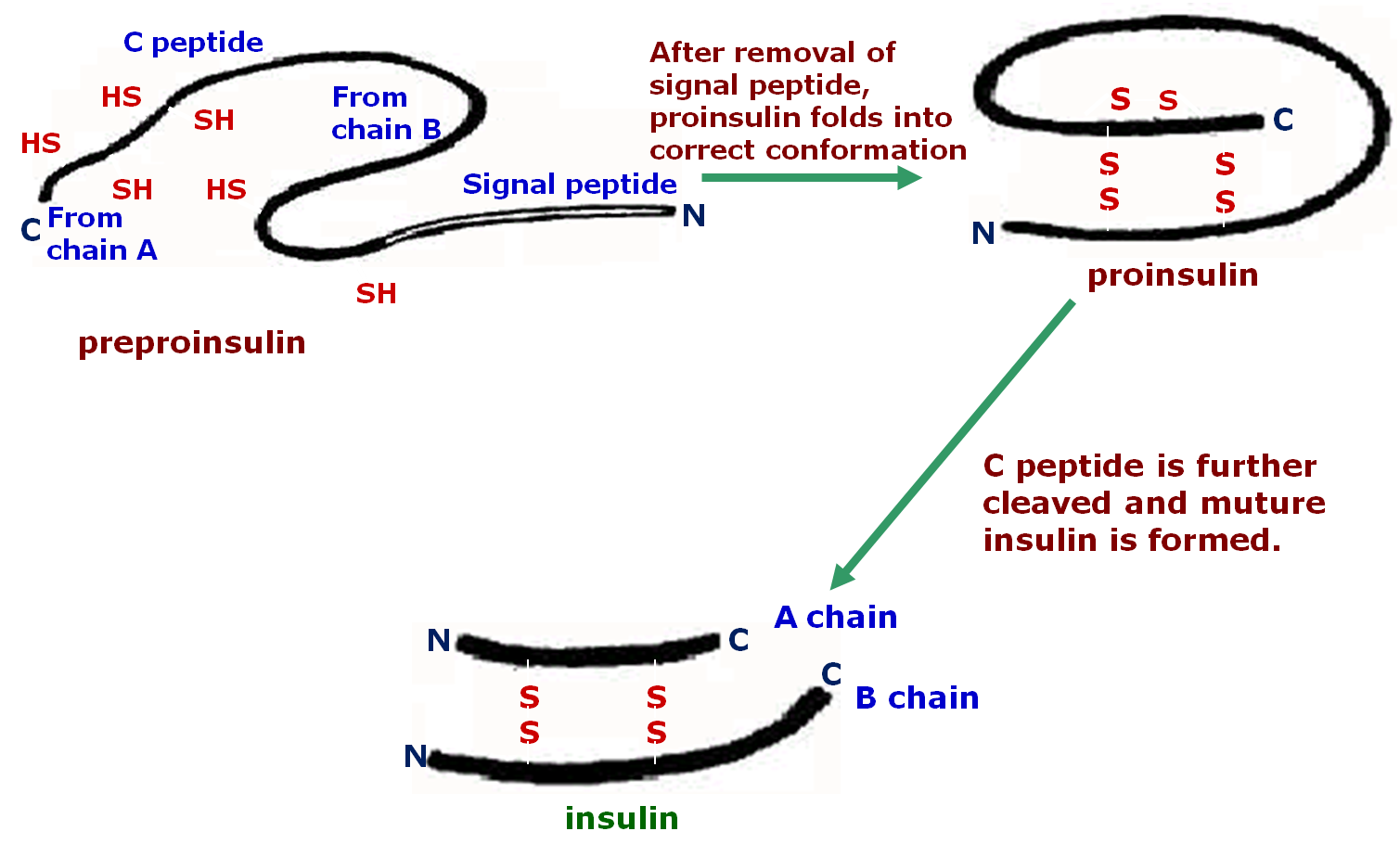
d. Formation of disulfide bond
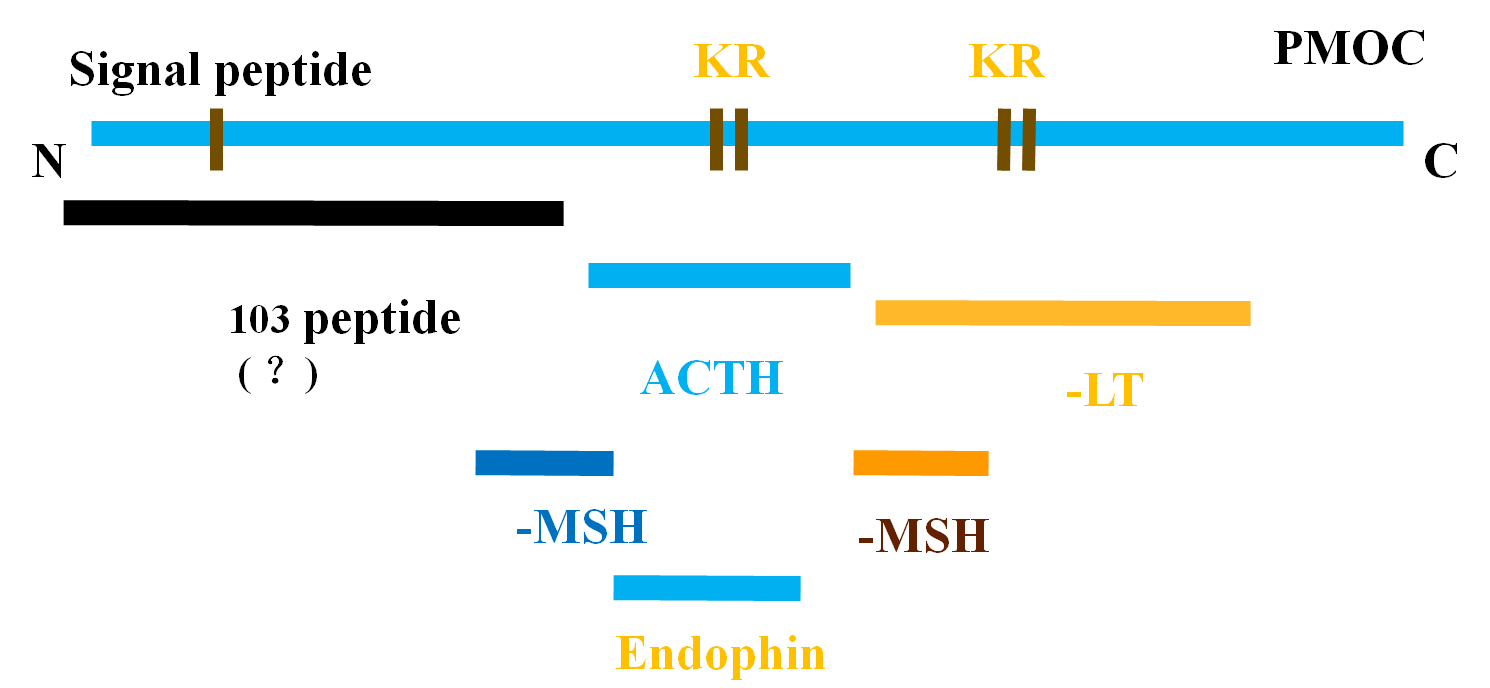
★ Proteolytic modification of pro-opiomelanocortin,POMC(鸦片促黑皮质素原)
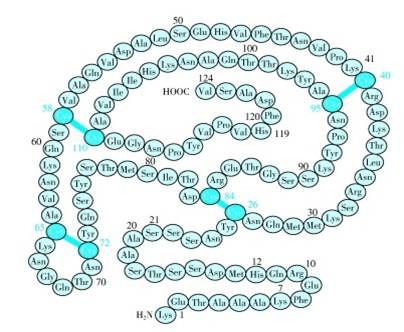
★Processing of proinsulin(胰岛素翻译后加工)