VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory uses the basic idea that electron pairs are mutually repulsed to predict the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom (an atom that has at least two other atoms bonded directly to it). The key to correctly applying VSEPR Theory is to start with a correct Lewis dot structure. From a correct Lewis dot structure, it is a straightforward process to determine the shape of a molecule or polyatomic ion by determining the arrangement of electron pairs around every central atom in the molecule or polyatomic ion.
The step-by-step process to determine the shape around each central atom is
1. Draw the Lewis dot structure.
2. Apply the following analysis to each separate, central atom (where a central atom is an atom with two or more other atoms bonded directly to it.)
a) Find the number of "things attached" to the central atom, where a "thing attached" is either an atom or a non-bonding electron pair.
(Actually, you are counting the number of hybrid orbitals on the central atom, but that is the next theory to be discussed.)
It is important to remember that you are not counting bonds!
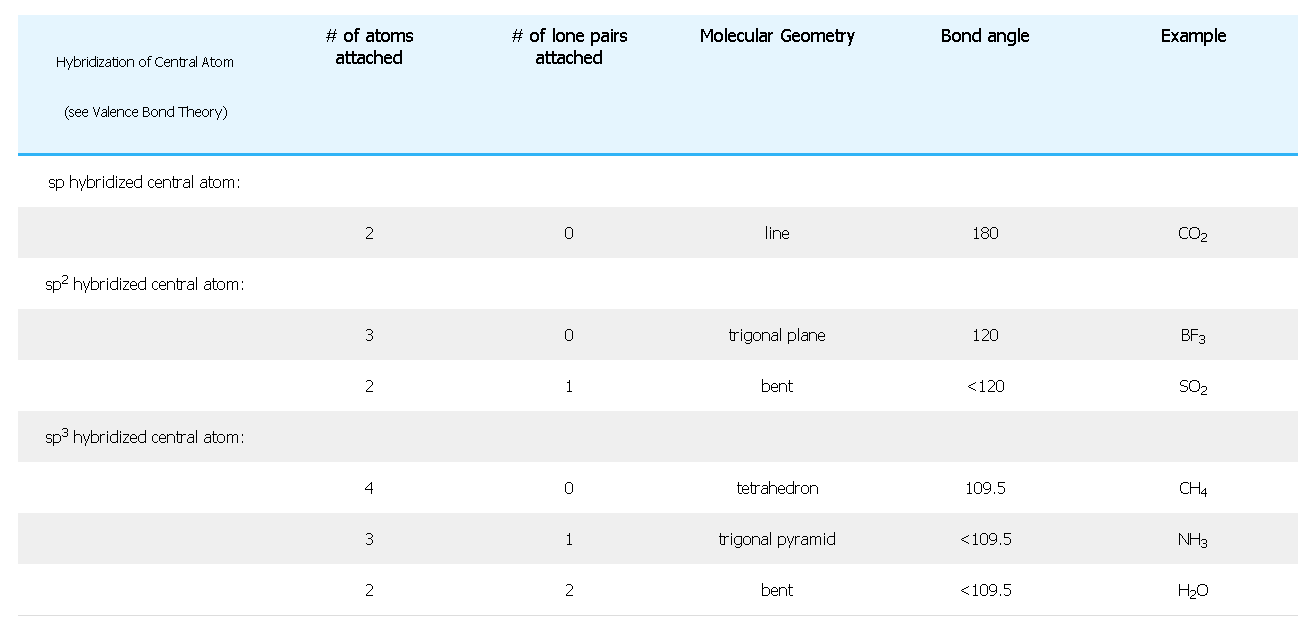
b) Find the Electron Group Arrangement (EGA) in the table below

c) Find the Molecular Geometry (MG) of the particle, determined by counting up the number of atoms and the number of lone pairs and using this table: