Einstein’s photons of light were individual packets of energy having many of the characteristics of particles. Recall that the collision of an electron (a particle) with a sufficiently energetic photon can eject a photoelectron from the surface of a metal. Any excess energy is transferred to the electron and is converted to the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. Einstein’s hypothesis that energy is concentrated in localized bundles, however, was in sharp contrast to the classical notion that energy is spread out uniformly in a wave. We now describe Einstein’s theory of the relationship between energy and mass, a theory that others built on to develop our current model of the atom.
The Wave Character of Matter
Einstein initially assumed that photons had zero mass, which made them a peculiar sort of particle indeed. In 1905, however, he published his special theory of relativity, which related energy and mass according to the famous equation:

According to this theory, a photon of wavelength and frequency has a nonzero mass, which is given as follows:

That is, light, which had always been regarded as a wave, also has properties typical of particles, a condition known as wave–particle duality (a principle that matter and energy have properties typical of both waves and particles). Depending on conditions, light could be viewed as either a wave or a particle.
In 1922, the American physicist Arthur Compton (1892–1962) reported the results of experiments involving the collision of x-rays and electrons that supported the particle nature of light. At about the same time, a young French physics student, Louis de Broglie (1892–1972), began to wonder whether the converse was true: Could particles exhibit the properties of waves? In his PhD dissertation submitted to the Sorbonne in 1924, de Broglie proposed that a particle such as an electron could be described by a wave whose wavelength is given by

where
is Planck’s constant,
is the mass of the particle, and
is the velocity of the particle.
This revolutionary idea was quickly confirmed by American physicists Clinton Davisson (1881–1958) and Lester Germer (1896–1971), who showed that beams of electrons, regarded as particles, were diffracted by a sodium chloride crystal in the same manner as x-rays, which were regarded as waves. It was proven experimentally that electrons do exhibit the properties of waves. For his work, de Broglie received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1929.
If particles exhibit the properties of waves, why had no one observed them before? The answer lies in the numerator of de Broglie’s equation, which is an extremely small number. As you will calculate in Example , Planck’s constant (6.63 × 10−34 J•s) is so small that the wavelength of a particle with a large mass is too short (less than the diameter of an atomic nucleus) to be noticeable.
Standing Waves
De Broglie also investigated why only certain orbits were allowed in Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom. He hypothesized that the electron behaves like a standing wave (a wave that does not travel in space). An example of a standing wave is the motion of a string of a violin or guitar. When the string is plucked, it vibrates at certain fixed frequencies because it is fastened at both ends (Figure 2). If the length of the string is , then the lowest-energy vibration (the fundamental) has wavelength

Higher-energy vibrations are called overtones (the vibration of a standing wave that is higher in energy than the fundamental vibration) and are produced when the string is plucked more strongly; they have wavelengths given by

where n has any integral value. When plucked, all other frequencies die out immediately. Only the resonant frequencies survive and are heard. Thus, we can think of the resonant frequencies of the string as being quantized. Notice in Figure 3 that all overtones have one or more nodes, points where the string does not move. The amplitude of the wave at a node is zero.
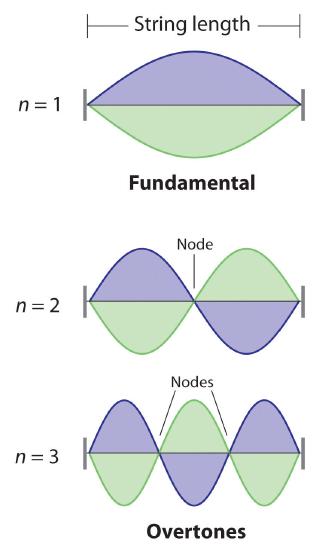
Quantized vibrations and overtones containing nodes are not restricted to one-dimensional systems, such as strings. A two-dimensional surface, such as a drumhead, also has quantized vibrations. Similarly, when the ends of a string are joined to form a circle, the only allowed vibrations are those with wavelength

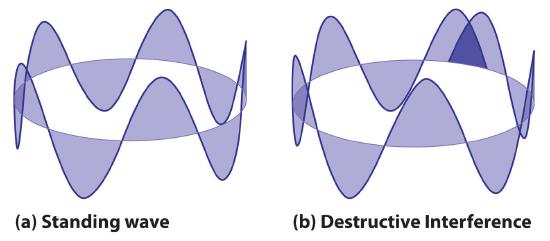
where is the radius of the circle. De Broglie argued that Bohr’s allowed orbits could be understood if the electron behaved like a standing circular wave (Figure 3). The standing wave could exist only if the circumference of the circle was an integral multiple of the wavelength such that the propagated waves were all in phase, thereby increasing the net amplitudes and causing constructive interference. Otherwise, the propagated waves would be out of phase, resulting in a net decrease in amplitude and causing destructive interference. The nonresonant waves interfere with themselves! De Broglie’s idea explained Bohr’s allowed orbits and energy levels nicely: in the lowest energy level, corresponding to in Equation 6, one complete wavelength would close the circle. Higher energy levels would have successively higher values of n with a corresponding number of nodes.
Like all analogies, although the standing wave model helps us understand much about why Bohr's theory worked, it also, if pushed too far, can mislead. As you will see, some of de Broglie’s ideas are retained in the modern theory of the electronic structure of the atom: the wave behavior of the electron and the presence of nodes that increase in number as the energy level increases. Unfortunately, his (and Bohr's) explanation also contains one major feature that we now know to be incorrect: in the currently accepted model, the electron in a given orbit is not always at the same distance from the nucleus.
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Because a wave is a disturbance that travels in space, it has no fixed position. One might therefore expect that it would also be hard to specify the exact position of a particle that exhibits wavelike behavior. A characteristic of light is that is can be bent or spread out by passing through a narrow slit. You can literally see this by half closing your eyes and looking through your eye lashes. This reduces the brightness of what you are seeing and somewhat fuzzes out the image, but the light bends around your lashes to provide a complete image rather than a bunch of bars across the image. This is called diffraction.
This behavior of waves is captured in Maxwell's equations (1870 or so) for electromagnetic waves and was and is well understood. An "uncertainty principle" for light is, if you will, merely a conclusion about the nature of electromagnetic waves and nothing new. De Broglie's idea of wave-particle duality means that particles such as electrons which exhibit wavelike characteristics will also undergo diffraction from slits whose size is on the order of the electron wavelength.
This situation was described mathematically by the German physicist Werner Heisenberg (1901–1976; Nobel Prize in Physics, 1932), who related the position of a particle to its momentum. Referring to the electron, Heisenberg stated that “at every moment the electron has only an inaccurate position and an inaccurate velocity, and between these two inaccuracies there is this uncertainty relation.” Mathematically, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that the uncertainty in the position of a particle (Δx) multiplied by the uncertainty in its momentum [Δ(mv)] is greater than or equal to Planck’s constant divided by 4π:

Because Planck’s constant is a very small number, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle is important only for particles such as electrons that have very low masses. These are the same particles predicted by de Broglie’s equation to have measurable wavelengths.
If the precise position of a particle is known absolutely (Δx = 0), then the uncertainty in its momentum must be infinite:

Because the mass of the electron at rest () is both constant and accurately known, the uncertainty in must be due to the term, which would have to be infinitely large for to equal infinity. That is, according to Equation 6., the more accurately we know the exact position of the electron (as ), the less accurately we know the speed and the kinetic energy of the electron (1/2 mv2) because . Conversely, the more accurately we know the precise momentum (and the energy) of the electron [as ], then and we have no idea where the electron is.
Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom violated the Heisenberg uncertainty principle by trying to specify simultaneously both the position (an orbit of a particular radius) and the energy (a quantity related to the momentum) of the electron. Moreover, given its mass and wavelike nature, the electron in the hydrogen atom could not possibly orbit the nucleus in a well-defined circular path as predicted by Bohr. You will see, however, that the most probable radius of the electron in the hydrogen atom is exactly the one predicted by Bohr’s model.
Summary
An electron possesses both particle and wave properties. The modern model for the electronic structure of the atom is based on recognizing that an electron possesses particle and wave properties, the so-called wave–particle duality. Louis de Broglie showed that the wavelength of a particle is equal to Planck’s constant divided by the mass times the velocity of the particle.

The electron in Bohr’s circular orbits could thus be described as a standing wave, one that does not move through space. Standing waves are familiar from music: the lowest-energy standing wave is the fundamental vibration, and higher-energy vibrations are overtones and have successively more nodes, points where the amplitude of the wave is always zero. Werner Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to precisely describe both the location and the speed of particles that exhibit wavelike behavior.



