The quantum mechanical model allowed us to determine the energies of the hydrogen atomic orbitals; now we would like to extend this to describe the electronic structure of every element in the Periodic Table. The process of describing each atom’s electronic structure consists, essentially, of beginning with hydrogen and adding one proton and one electron at a time to create the next heavier element in the table; however, interactions between electrons make this process a bit more complicated than it sounds. All stable nuclei other than hydrogen also contain one or more neutrons. Because neutrons have no electrical charge, however, they can be ignored in the following discussion. Before demonstrating how to do this, however, we must introduce the concept of electron spin and the Pauli principle.
Orbitals and their Energies
Unlike in hydrogen-like atoms with only one electron, in multielectron atoms the values of quantum numbers n and l determine the energies of an orbital. The energies of the different orbitals for a typical multielectron atom are shown in Figure 1. Within a given principal shell of a multielectron atom, the orbital energies increase with increasing l. An ns orbital always lies below the corresponding np orbital, which in turn lies below the nd orbital.
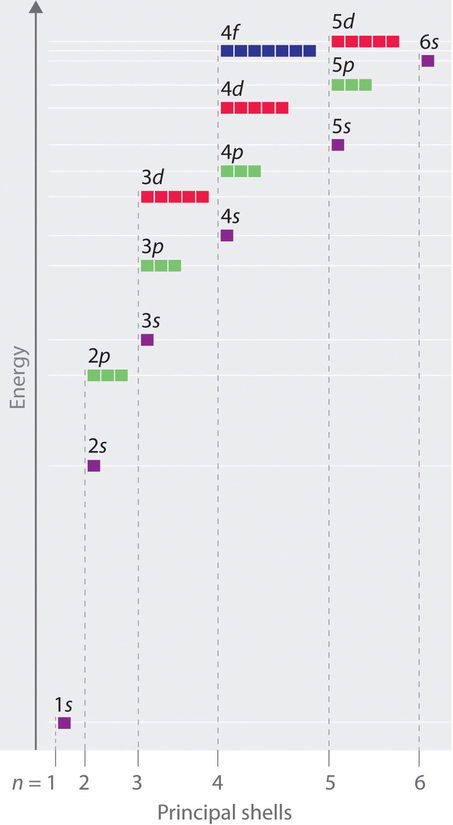
These energy differences are caused by the effects of shielding and penetration, the extent to which a given orbital lies inside other filled orbitals. For example, an electron in the 2s orbital penetrates inside a filled 1s orbital more than an electron in a 2p orbital does. Since electrons, all being negatively charged, repel each other, an electron closer to the nucleus partially shields an electron farther from the nucleus from the attractive effect of the positively charged nucleus. Hence in an atom with a filled 1s orbital, the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) experienced by a 2s electron is greater than the Zeff experienced by a 2p electron. Consequently, the 2s electron is more tightly bound to the nucleus and has a lower energy, consistent with the order of energies shown in Figure 1.
Due to electron shielding, increases more rapidly going across a row of the periodic table than going down a column.
Notice in Figure 1 that the difference in energies between subshells can be so large that the energies of orbitals from different principal shells can become approximately equal. For example, the energy of the 3d orbitals in most atoms is actually between the energies of the 4s and the 4p orbitals.
Electron Spin: The Fourth Quantum Number
When scientists analyzed the emission and absorption spectra of the elements more closely, they saw that for elements having more than one electron, nearly all the lines in the spectra were actually pairs of very closely spaced lines. Because each line represents an energy level available to electrons in the atom, there are twice as many energy levels available as would be predicted solely based on the quantum numbers , , and . Scientists also discovered that applying a magnetic field caused the lines in the pairs to split farther apart. In 1925, two graduate students in physics in the Netherlands, George Uhlenbeck (1900–1988) and Samuel Goudsmit (1902–1978), proposed that the splittings were caused by an electron spinning about its axis, much as Earth spins about its axis. When an electrically charged object spins, it produces a magnetic moment parallel to the axis of rotation, making it behave like a magnet. Although the electron cannot be viewed solely as a particle, spinning or otherwise, it is indisputable that it does have a magnetic moment. This magnetic moment is called electron spin.
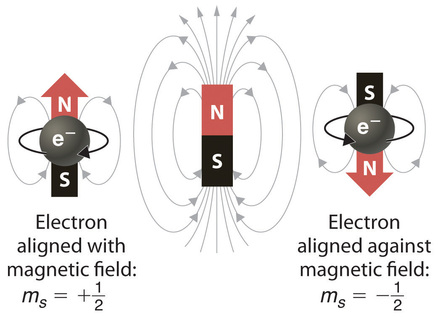
In an external magnetic field, the electron has two possible orientations (Figure Figure 2). These are described by a fourth quantum number (ms), which for any electron can have only two possible values, designated +½ (up) and −½ (down) to indicate that the two orientations are opposites; the subscript s is for spin. An electron behaves like a magnet that has one of two possible orientations, aligned either with the magnetic field or against it.
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
The implications of electron spin for chemistry were recognized almost immediately by an Austrian physicist, Wolfgang Pauli (1900–1958; Nobel Prize in Physics, 1945), who determined that each orbital can contain no more than two electrons. He developed the Pauli exclusion principle: No two electrons in an atom can have the same values of all four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms).
By giving the values of n, l, and ml, we also specify a particular orbital (e.g., 1s with n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0). Because ms has only two possible values (+½ or −½), two electrons, and only two electrons, can occupy any given orbital, one with spin up and one with spin down. With this information, we can proceed to construct the entire periodic table, which was originally based on the physical and chemical properties of the known elements.
Summary
The arrangement of atoms in the periodic table arises from the lowest energy arrangement of electrons in the valence shell. In addition to the three quantum numbers (n, l, ml) dictated by quantum mechanics, a fourth quantum number is required to explain certain properties of atoms. This is the electron spinquantum number (ms), which can have values of +½ or −½ for any electron, corresponding to the two possible orientations of an electron in a magnetic field. The concept of electron spin has important consequences for chemistry because the Pauli exclusion principle implies that no orbital can contain more than two electrons (with opposite spin).


