Democritus and the Greek Philosophers
Around 2,500 years ago, early Greek philosophers believed the entire universe was a single, huge, entity. In other words, "everything was one." They believed that all objects, all matter, and all substances were connected as a single, big, unchangeable "thing." Democritus was one of the first people to propose the term "atoms." As an alternative to the beliefs of the Greek philosophers, he suggested that atomos, or atomon - tiny, indivisible, solid objects - make up all matter in the universe.

Early Greek philosophers tried to understand the nature of the world through reason and logic, not through experiment and observation. As a result, they had some very interesting ideas, but they felt no need to justify their ideas based on life experiences. In many ways, you can think of the Greek philosophers as being "all thought and no action." It's truly amazing how much they achieved using their minds, but because they never performed any experiments, they missed or rejected many discoveries that they could have made otherwise. Greek philosophers dismissed Democritus' theory entirely. Unfortunately, it took over two millennia before the theory of atomos (or "atoms," as they're known today) was fully accepted.
The development of the atomic theory owes much to the work of two men: Antoine Lavoisier, who did not himself think of matter in terms of atoms but whose work laid organization groundwork for thinking about elements, and John Dalton, to whom the atomic theory is attributed. Much of Lavoisier’s work as a chemist was devoted to the study of combustion. He became convinced that when a substance is burned in air, it combines with some component of the air. Eventually he realized that this component was the dephlogisticated air which had been discovered by Joseph Priestly (1733 to 1804) a few years earlier. Lavoisier renamed this substance oxygen. In an important series of experiments he showed that when mercury is heated in oxygen at a moderate temperature, a red substance, calx of mercury, is obtained. (A calx is the ash left when a substance burns in air.) At a higher temperature this calx decomposes into mercury and oxygen. Lavoisier’s careful experiments also revealed that the combined masses of mercury and oxygen were exactly equal to the mass of calx of mercury. That is, there was no change in mass upon formation or decomposition of the calx. Lavoisier hypothesized that this should be true of all chemical changes, and further experiments showed that he was right. This principle is now called the law of conservation of mass.
As Lavoisier continued his experiments with oxygen, he noticed something else. Although oxygen combined with many other substances, it never behaved as though it were itself a combination of other substances. Lavoisier was able to decompose the red calx into mercury and oxygen, but he could find no way to break down oxygen into two or more new substances. Because of this he suggested that oxygen must be an element—an ultimately simple substance which could not be decomposed by chemical changes.
Lavoisier did not originate the idea that certain substances (elements) were fundamental and all others could be derived from them. This had first been proposed in Greece during the fifth century B.C. by Empedocles, who speculated that all matter consisted of combinations of earth, air, fire, and water. These ideas were further developed and taught by Aristotle and remained influential for 2000 years.
Lavoisier did produce the first table of the elements which contained a large number of substances that modern chemists would agree should be classifies as elements. He published it with the knowledge that further research might succeed decomposing some of the substances listed, thus showing them not to be elements. One of his objectives was to prod his contemporaries into just that kind of research. Sure enough the “earth substances” listed at the bottom were eventually shown to be combinations of certain metals with oxygen. It is also interesting to note that not even Lavoisier could entirely escape from Aristotle’s influence. The second element in his list is Aristotle’s “fire,” which Lavoisier called “caloric,” and which we now call “heat.” Both heat and light, the first two items in the table, are now regarded as forms of energy rather than of matter.
Although his table of elements was incomplete, and even incorrect in some instances, Lavoisier’s work represented a major step forward. By classifying certain substances as elements, he stimulated much additional chemical research and brought order and structure to the subject where none had existed before. His contemporaries accepted his ideas very readily, and he became known as the father of chemistry.
John Dalton (1766 to 1844) was a generation younger than Lavoisier and different from him in almost every respect. Dalton came from a working class family and only attended elementary school. Apart from this, he was entirely self-taught. Even after he became famous, he never aspired beyond a modest bachelor’s existence in which he supported himself by teaching mathematics to private pupils. Dalton made many contributions to science, and he seems not to have realized that his atomic theory was the most important of them. In his “New System of Chemical Philosophy” published in 1808, only the last seven pages out of a total of 168 are devoted to it!

Dalton studied the weights of various elements and compounds. He noticed that matter always combined in fixed ratios based on weight, or volume in the case of gases. Chemical compounds always contain the same proportion of elements by mass, regardless of amount, which provided further support for Proust's law of definite proportions. Dalton also observed that there could be more than one combination of two elements.
From his experiments and observations, as well as the work from peers of his time, Dalton proposed a new theory of the atom (1803). This later became known as Dalton's atomic theory. The published (1808) tenets of this theory were as follows:
All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms.
Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties.
Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed.
Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds.
In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged.
The postulates of the atomic theory are given below. The first is no advance on the ancient Greek philosopher Democritus who had theorized almost 2000 years earlier that matter consists of very small particles.
THE POSTULATES OF DALTON'S ATOMIC THEORY
All matter is composed of a very large number of very small particles called atoms.
For a given element, all atoms are identical in all respects. In particular all atoms of the same element have the same constant mass, while atoms of different elements have different masses.
The atoms are the units of chemical changes. Chemical reactions involve the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms, but atoms are neither created, destroyed, divided into parts, or converted into atoms of any other kind.
Atoms combine to form molecules in fixed ratios of small whole numbers.
The second postulate, however, shows the mark of an original genius; here Dalton links the idea of atom to the idea of element. Lavoisier’s criterion for an element had been essentially a macroscopic, experimental one. If a substance could not be decomposed chemically, then it was probably an element. By contrast, Dalton defines an element in theoretical, sub-microscopic terms. An element is an element because all its atoms are the same. Different elements have different atoms. There are just as many different kinds of elements as there are different kinds of atoms.
Now look back a moment to the physical states of mercury, where sub-microscopic pictures of solid, liquid, and gaseous mercury were given. Applying Dalton’s second postulate to this figure, you can immediately conclude that mercury is an element, because only one kind of atom appears. Although mercury atoms are drawn as spheres in the figure, it would be more common today to represent them using chemical symbols. The chemical symbol for an element (or an atom of that element) is a one- or two-letter abbreviation of its name. Usually, but not always, the first two letters are used. To complicate matters further, chemical symbols are sometimes derived from a language other than English. For example the symbol for Hg for mercury comes from the first and seventh letters of the element’s Latin name, hydrargyrum.
| Name | Symbol | Atomic Number | Atomic Weight | Name | Symbol | Atomic Number | Atomic Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinium2 | Ac | 89 | (227) | Molybdenum | Mo | 42 | 95.96(2) |
| Aluminum | Al | 13 | 26.981 5386(8) | Neodymium | Nd | 60 | 144.242(3) |
| Americium2 | Am | 95 | (243) | Neon | Ne | 10 | 20.1797(6) |
| Antimony | Sb | 51 | 121.760(1) | Neptunium2 | Np | 93 | (237) |
| Argon | Ar | 18 | 39.948(1) | Nickel | Ni | 28 | 58.6934(4) |
| Arsenic | As | 33 | 74.92160(2) | Niobium | Nb | 41 | 92.90638(2) |
| Astatine2 | At | 85 | (210) | Nitrogen | N | 7 | 14.0067(2) |
| Barium | Ba | 56 | 137.327(7) | Nobelium2 | No | 102 | (259) |
| Berkelium2 | Bk | 97 | (247) | Osmium | Os | 76 | 190.23(3) |
| Beryllium | Be | 4 | 9.012182(3) | Oxygen | O | 8 | 15.9994(3) |
| Bismuth | Bi | 83 | 208.98040(1) | Palladium | Pd | 46 | 106.42(1) |
| Bohrium2 | Bh | 107 | (272) | Phosphorus | P | 15 | 30.973762(2) |
| Boron | B | 5 | 10.811(7) | Platinum | Pt | 78 | 195.084(9) |
| Bromine | Br | 35 | 79.904(1) | Plutonium2 | Pu | 94 | (244) |
| Cadmium | Cd | 48 | 112.411(8) | Polonium2 | Po | 84 | (209) |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 | 40.078(4) | Potassium | K | 19 | 39.0983(1) |
| Californium2 | Cf | 98 | (251) | Praseodymium | Pr | 59 | 140.90765(2) |
| Carbon | C | 6 | 12.0107(8) | Promethium2 | Pm | 61 | (145) |
| Cerium | Ce | 58 | 140.116(1) | Protactinium2 | Pa | 91 | 231.03588(2) |
| Cesium | Cs | 55 | 132.9054519(2) | Radium2 | Ra | 88 | (226) |
| Chlorine | Cl | 17 | 35.453(2) | Radon2 | Rn | 86 | (222) |
| Chromium | Cr | 24 | 51.9961(6) | Rhenium | Re | 75 | 186.207(1) |
| Cobalt | Co | 27 | 58.933195(5) | Rhodium | Rh | 45 | 102.90550(2) |
| Copper | Cu | 29 | 63.546(3) | Roentgenium2 | Rg | 111 | (280) |
| Curium2 | Cm | 96 | (247) | Rubidium | Rb | 37 | 85.4678(3) |
| Darmstadtium2 | Ds | 110 | (281) | Ruthenium | Ru | 44 | 101.07(2) |
| Dubnium2 | Db | 105 | (268) | Rutherfordium2 | Rf | 104 | (267) |
| Dysprosium | Dy | 66 | 162.500(1) | Samarium | Sm | 62 | 150.36(2) |
| Einsteinium2 | Es | 99 | (252) | Scandium | Sc | 21 | 44.955912(6) |
| Erbium | Er | 68 | 167.259(3) | Seaborgium2 | Sg | 106 | (271) |
| Europium | Eu | 63 | 151.964(1) | Selenium | Se | 34 | 78.96(3) |
| Fermium2 | Fm | 100 | (257) | Silicon | Si | 14 | 28.0855(3) |
| Fluorine | F | 9 | 18.9984032(5) | Silver | Ag | 47 | 107.8682(2) |
| Francium2 | Fr | 87 | (223) | Sodium | Na | 11 | 22.98976928(2) |
| Gadolinium | Gd | 64 | 157.25(3) | Strontium | Sr | 38 | 87.62(1) |
| Gallium | Ga | 31 | 69.723(1) | Sulfur | S | 16 | 32.065(5) |
| Germanium | Ge | 32 | 72.64(1) | Tantalum | Ta | 73 | 180.94788(2) |
| Gold | Au | 79 | 196.966569(4) | Technetium2 | Tc | 43 | (98) |
| Hafnium | Hf | 72 | 178.49(2) | Tellurium | Te | 52 | 127.60(3) |
| Hassium2 | Hs | 108 | (277) | Terbium | Tb | 65 | 158.92535(2) |
| Helium | He | 2 | 4.002602(2) | Thallium | Tl | 81 | 204.3833(2) |
| Holmium | Ho | 67 | 164.93032(2) | Thorium2 | Th | 90 | 232.03806(2) |
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1.00794(7) | Thulium | Tm | 69 | 168.93421(2) |
| Indium | In | 49 | 114.818(3) | Tin | Sn | 50 | 118.710(7) |
| Iodine | I | 53 | 126.90447(3) | Titanium | Ti | 22 | 47.867(1) |
| Iridium | Ir | 49 | 192.217(3) | Tungsten | W | 74 | 183.84(1) |
| Iron | Fe | 26 | 55.845(2) | Uranium2 | U | 92 | 238.02891(3) |
| Krypton | Kr | 36 | 83.798(2) | Vanadium | V | 23 | 50.9415(1) |
| Lanthanum | La | 57 | 138.90547(7) | Xenon | Xe | 54 | 131.293(6) |
| Lawrencium2 | Lr | 103 | (262) | Ytterbium | Yb | 70 | 173.054(5) |
| Lead | Pb | 82 | 207.2(1) | Yttrium | Y | 39 | 88.90585(2) |
| Lithium | Li | 3 | [6.941(2)]1 | Zinc | Zn | 30 | 65.38(2) |
| Lutetium | Lu | 71 | 174.9668(1) | Zirconium | Zr | 40 | 91.224(2) |
| Magnesium | Mg | 12 | 24.3050(6) | -2,3,4 | 112 | (285) | |
| Manganese | Mn | 25 | 54.938045(5) | -2,3 | 113 | (284) | |
| Meitnerium2 | Mt | 109 | (276) | - 2,3 | 114 | (287) | |
| Mendelevium2 | Md | 101 | (258) | -2,3 | 115 | (288) | |
| Mercury | Hg | 80 | 200.59(2) | -2,3 | 116 | (293) | |
| -2,3 | 118 | (294) |
The chemical symbols for all the currently known elements are listed above in the table, which also includes atomic weights. These symbols are the basic vocabulary of chemistry because the atoms they represent make up all matter. You will see symbols for the more important elements over and over again, and the sooner you know what element they stand for, the easier it will be for you to learn chemistry. These more important element have been indicated in the above table by colored shading around their names.
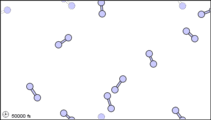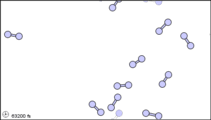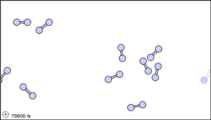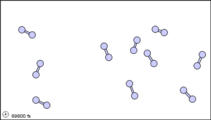
Dalton’s fourth postulate states that atoms may combine to form molecules. An example of this is provided by bromine, the only element other than mercury which is a liquid at ordinary room temperature (20°C). Macroscopically, bromine consists of dark-colored crystals below –7.2°C and a reddish brown gas above 58.8°C. The liquid is dark red-brown and has a pungent odor similar to the chlorine used in swimming pools. It can cause severe burns on human skin and should not be handled without the protection of rubber gloves.
 |  |  |
| (a) in the gaseous state | (b) as a liquid | (c) in solid form |
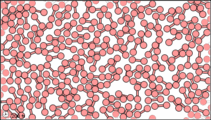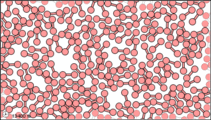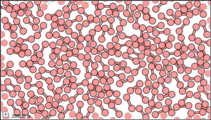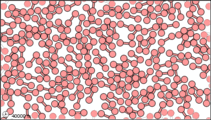
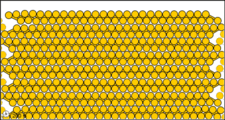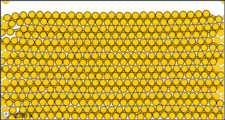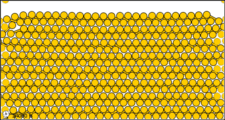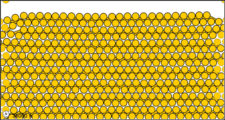
Figure 3: Sub-microscopic view of the diatomic molecules of the element bromine (a) in the gaseous state (above 58°C); (b) in liquid form (between -7.2 and 58.8°C); and (c) in solid form (below -7.2°C).
The sub-microscopic view of bromine in the following figure is in agreement with its designation as an element—only one kind of atom is present. Except at very high temperatures, though, bromine atoms always double up. Whether in solid, liquid, or gas, they go around in pairs. Such a tightly held combination of two or more atoms is called a molecule.
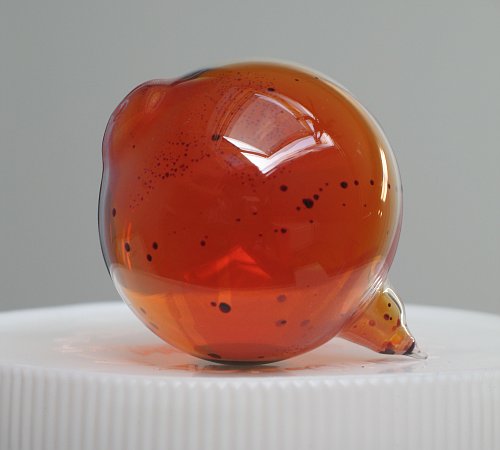
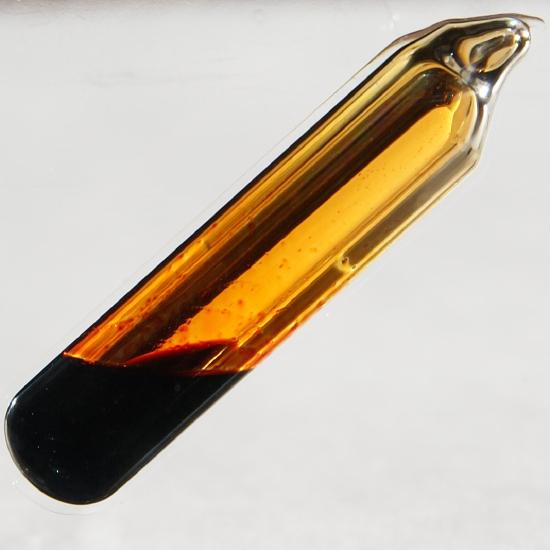


The composition of a molecule is indicated by a chemical formula. A subscript to the right of the symbol for each element tells how many atoms of that element are in the molecule. For example, the atomic weights table gives the chemical symbol Br for bromine, but each molecule contains two bromine atoms, and so the chemical formula is Br2. According to Dalton’s fourth postulate, atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers, and so the subscripts in a formula should be small whole numbers.
DALTON'S EYES
As a scientist, John Dalton was also interested in colorblindness. Both he and his brother suffered from red/green colorblindness. At this time (1794), no other scientist had explored this medical issue. He devised theories (although not correct) as to why he could not differentiate between red and green. In addition, he named this medical condition "Daltonism." Upon his death (1844), he donated his eyes to a medical research facility in Manchester, England. Today, his eyes are still on display at the Museum of Science and Industry in Manchester, England.
DALTON WAS NOT COMPLETELY CORRECT
Dalton's atomic theory has been largely accepted by the scientific community, with the exception of three changes. We know now that:
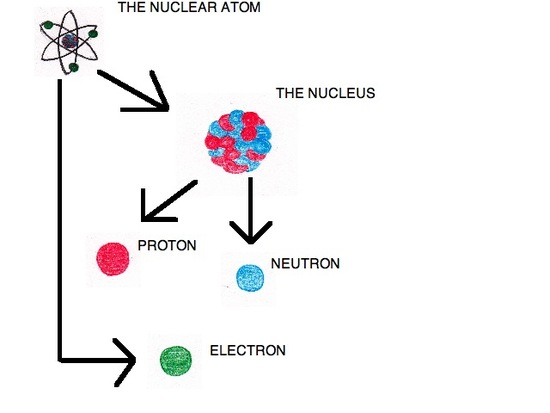
An atom is composed of smaller particles (electrons, protons, and neutrons).
All atoms of an element are not identical. The existence of isotopes illustrates this phenomena.
Through the use of nuclear reactions, atoms of one element can be changed into atoms of another element.
The first two will be be discussed later in this chapter, while the last requires introducing "nuclear chemistry" and will be discussed in a different chapter.
Discovering Electrons
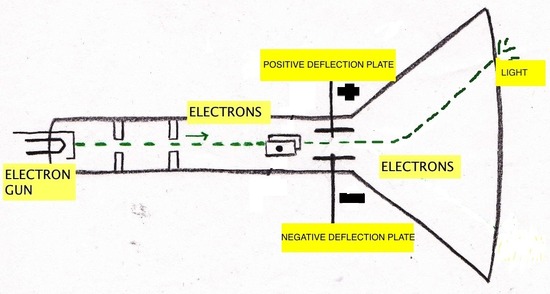
The first cathode-ray tube (CRT) was invented by Michael Faraday (1791-1867). Cathode rays are a type of radiation emitted by the negative terminal, the cathode, and were discovered by passing electricity through nearly-evacuated glass tubes. The radiation crosses the evacuated tube to the positive terminal, the anode. Cathode rays produced by the CRT are invisible and can only be detected by light emitted by the materials that they strike, called phosphors, painted at the end of the CRT to reveal the path of the cathode rays. These phosphors showed that cathode rays travel in straight lines and have properties independent of the cathode material (whether it is gold, silver, etc.). Another significant property of cathode rays is that they are deflected by magnetic and electric fields in a manner that is identical to negatively charged material. Due to these observations, J.J. Thompson (1856-1940) concluded that cathode rays are negatively charged particles that are located in all atoms. It was George Stoney who first gave the term electrons to the cathode rays. The below figures depict the way that the cathode ray is effected by magnetics. The cathode ray is always attracted by the positive magnet and deflected by the negative magnets.
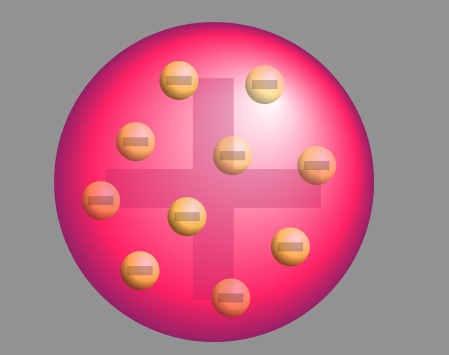
The Plum Pudding Model
After Thompson discovered the electron, he proposed the plum pudding model of an atom, which states that the electrons float in positively-charged material. This model was named after the plum-pudding dessert.
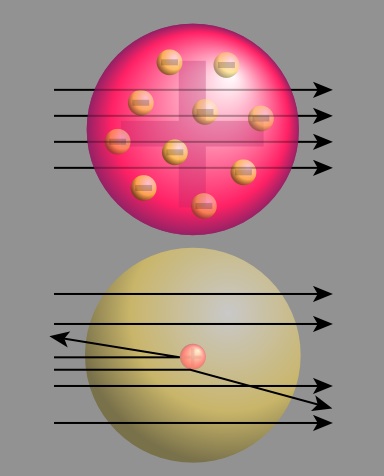
Discovery of the Proton
In 1909, Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) performed a series of experiments studying the inner structure of atoms using alpha particles. Rutherford knew that alpha particles are significantly more massive than electrons and positively charged. Using the plum-pudding model for reference, Rutherford predicted that particles in an alpha beam would largely pass through matter unaffected, with a small number of particles slightly deflected. The particles would only be deflected if they happened to come into contact with electrons. According to the plum pudding model, this occurrence would be very unlikely. In order to test his hypothesis, Rutherford shot a beam of alpha particles at a thin piece of gold foil. Around the gold foil Rutherford placed sheets of zinc sulfide. These sheets produced a flash of light when struck by an alpha particle. However, this experiment produced results that contradicted Rutherford's hypothesis. Rutherford observed that the majority of the alpha particles went through the foil; however, some particles were slightly deflected, a small number were greatly deflected, and another small number were thrown back in nearly the direction from which they had come. Figure 10 shows Rutherford's prediction based off of the plum-pudding model (pink) and the observed large deflections of the alpha particles (gold).
To account for these observations, Rutherford devised a model called the nuclear atom. In this model, the positive charge is held in an extremely small area called the nucleus, located in the middle of the atom. Outside of the nucleus the atom is largely composed of empty space. This model states that there were positive particles within the nucleus, but failed to define what these particles are. Rutherford discovered these particles in 1919, when he conducted an experiment that scattered alpha particles against nitrogen atoms. When the alpha particles and nitrogen atoms collided protons were released.
The Discovery of the Neutron
In 1933, James Chadwick (1891-1974) discovered a new type of radiation that consisted of neutral particles. It was discovered that these neutral atoms come from the nucleus of the atom. This last discovery completed the atomic model.