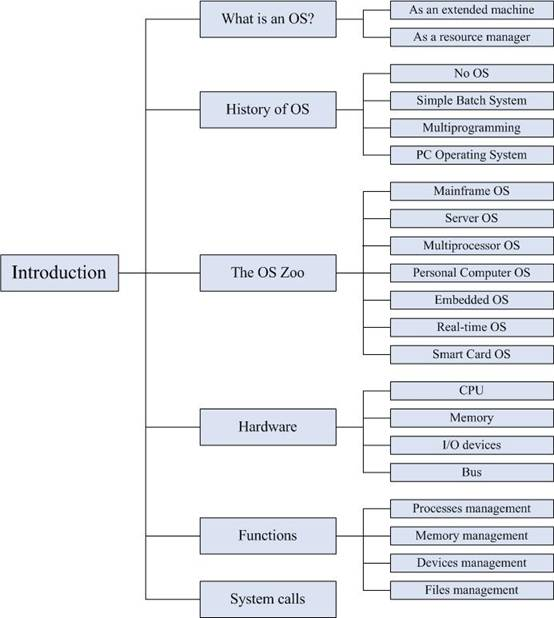
操作系统概述主要介绍了操作系统的定义、操作系统的发展历史、操作系统的分类、计算机硬件相关概念、操作系统的功能、系统调用等内容。通过该模块的学习,从宏观上对操作系统有个整体认识,为后续模块的学习打下基础。
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
(1) Master(掌握): What is an operating system; Batch Systems; Multiprogramming; CPU mode; Systems Call; Trap.
(2) Understand(理解): Off-Line; Spooling; Time-sharing; Real-time operating systems; computer hardware.
(3) Know(了解): PC operating systems; Mainframe operating systems; Embedded operating systems; Server operating systems; Win32 API.
Basic(知识点)
1. What is an operating system
2. History of operating systems
3. The operating system zoo
4. The functions of operating systems
5. Computer hardware review
6. System calls
Emphasis(重点)
1. What is an operating system
2. Multiprogramming
3. CPU mode: kernel mode and user mode
4. System calls
Difficulty(难点)
1. The difference between trap and interrupt
2. The implementing of system calls
3. The difference between kernel mode and user mode
1. What is an Operating System?
(1) From the user’s view
① The Operating systems provide the interfaces between the users and the computer
② The Operating System as an Extended Machine
(2) From the system’s view
① The Operating System as a Resource Manager
② The Operating System as an program’s scheduler
2. History of Operating Systems
(1) The First Generation (1945-1955) :Vacuum Tubes and Plug-boards——no OS
(2) The Second Generation (1955-1965): Transistors and Simple Batch Systems
· Batch systems: collecting a tray full of jobs and reading them onto a magnetic tape and then letting those jobs to running in turn continuously.
· Off line: the input and output of data and programs are not controlled by main machine but peripheral machine.
(3) The Third Generation (1965-1980) :ICs and Multiprogramming
· Multiprogramming: partitioning memory into several pieces, with a different job in each partition. While one ob was waiting for I/O to complete, another job could be using the CPU.
· Spooling (Simultaneous Peripheral Operations On Line)
· Timesharing: each user has an online terminal, the CPU can be allocated in turn to the jobs that want service.
(4) The Fourth Generation (1980-present): Personal Computers
· GUI (Graphical User Interface)
· user friendly
· Network Operating System
· Distributed Operating System
3. The operating system zoo
(1) Mainframe Operating Systems
(2) Server Operating Systems
(3) Multiprocessor Operating Systems
(4) Personal Computer Operating Systems
(5) Embedded Operating Systems
(6) Real-time Operating Systems
(7) Smart Card Operating Systems
4. Computer Hardware Review
(1) Processors (CPU)
· registers
· CPU mod-- usually a bit in the PSW controls the two CPU models: kernel mode; user mode
kernel mode: CPU can access to the complete hardware
user mode: CPU can’t access to the complete hardware
(2) Memory
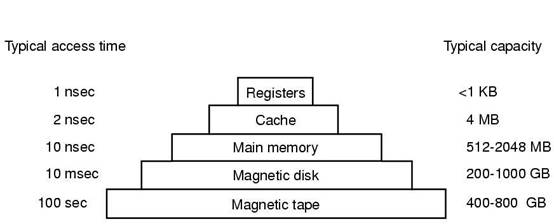
(3) I/O Devices
· Device controllers
(4) Buses
5. The functions of operating systems
(1) Processes management
(2) Memory management
(3) Devices management
(4) File management
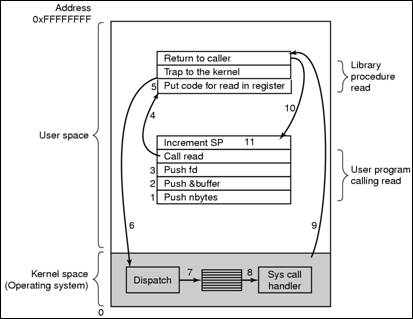
6. System Calls
(1) The interface between operating system and the users.
(2) Trap and Interrupt:
· Trap: the interrupt source comes from the internal of the CPU.
· Interrupt: the interrupt source comes from the external of the CPU.
I.Select the correct answer
1. ( ) operating system allows user to submit many jobs to the computer.
A.Single user B.Distributed
C.Batch D.Monitor(监督)
Answer: C
2. The OS is software that managing ( a ). The functions of operating system are processor management, ( b ) management, devices management and files management. But from the user opinions, the operating system ( c ).
a、A.software B.hardware
C.resources of computer D.application program
b、A.data B.memory
C.hardware D.software
c、A.provides interfaces between user and computer
B.is software that control and manage the resources of computer
C.is software that organize flow(流程)of computer
D.is organism(有机体)of some levels of programs that organized in a certain structure
Answer: C, B, A
3. Multiprogramming technology in OS improves ( ) of CPU and I/O devices.
A.utilization B.reliability
C.stability(稳定性) D.compatibility
Answer: A
4. In ( ) operating system, the computer can process the data coming from procedure feedback(反馈) system and give response in good time.
A.real-time B.timesharing
C. distributed D.single user
Answer: A
5. ( ) are the interfaces that the OS provides to the programmer.
A.Processes B.System calls
C.Library functions D.both B and C
Answer: B
6. The main shortcoming of batch system is ( ).
A.unable executing concurrently B.low utilization of CPU
C.lacking interaction D.non of above
Answer: B
7. ( ) operating system allows more than one terminals connect to one host, and each user has an online terminal and use the computer simultaneously(同时地).
A.Network B.Distributed
C.Timesharing D.Real-time
Answer: C
8. ( ) means that it was intended for users who not only knew nothing about computers but furthermore had absolutely no intention whatsoever of learning.
A.User friendly B.GUI
C.Windows NT D.Interface
Answer: A
Ⅱ. Fill in the blanks.
For , the interrupt source comes from the internal of the CPU.
For , the interrupt source comes from the external of the CPU.
Answer: trap, interrupt
1.What are the two main functions of an operating system?
Answer:
The two main functions of an operating system are managing system resources and providing application programs with a set of primitives that provide higher-level services.
2.Which of the following instructions should be allowed only in kernel mode?
(a) Disable all interrupts
(b) Set the time-of-day clock
(c) read the time-of-day clock
(d) Change the memory map
Answer: (a, b,d)
3. What is the key difference between a trap and an interrupt?
Answer:
1. What is the same point and key difference between a trap and an interrupt?
Answer:
The same: they are all taken from a distant location and the return addresses are all saved on the stack for use later.
The difference: ①Trap is an instruction from the internal of CPU, it switches into kernel mode. Interrupt is an instruction from the external of CPU, it does not change the mode. ②If giving a relative or absolute address where the procedure is located, the Interrupt instruction can jump to an arbitrary address, while Trap cannot.