Ⅰ.Select the correct answer
1. In memory management, the strategy, called ( ) , allows programs to run even when they are only partially in main memory.
A. virtual memory B. swapping
C. paging D. segmentation
2.Which of the following is not the job of the memory manager?
A. allocating memory to processes
B. relocation and protection
C. keeping track of which parts of memory is in use
D. scheduling a process to run
3.Comparing page with segment, which one is correct? ( )
A. Given a system, the page’s size is fixed, but the segment’s size is dynamic;
B. Given a system, the page’s size is dynamic, but the segment’s size is fixed;
C. Given a system, both the page’s size and the segment’s size are dynamic;
D. Given a system, both the page’s size and the segment’s size are fixed.
4. That part of the program where the shared memory is accessed is called the ( ).
A. memory manager B. file system
C. scheduler D. critical region
5. In memory management, the strategy, called ( ) , consists of bringing in each process in its entirety, running it for a while, then putting it back on the disk.
A. virtual memory B. swapping
C. paging D. segmentation
6. ( ) maps the virtual addresses onto the physical memory addresses.
A.TLB B. PCB
C.DMA D. MMU
7. The device that performs the check and mapping virtual address onto physical address is called ( ).
A.scheduler B.MMU
C.device controller D.page table
8. In the following page replacement algorithms, which can cause Belady’s anomaly. ( )
A.FIFO B.LRU
C.NRU D.OPT
9. In memory management, the purpose of adopting swapping technique is ( ).
A.saving main memory space
B.extending main memory capacity in physical way
C.improving CPU efficiency
D.implementing main memory sharing
10. The maximum capacity of virtual memory ( ).
A.is sum of main memory and external memory
B.lies on address structure of computer
C.is discretionary(任意的)
D.lies on address space of jobs
11. The real-time system must respond to the occurring external event in ( ) .
A.response time B.turnaround time
C.a certain time D.scheduling time
12. In memory management, the size of each partition is ( ) by using fixed partition allocation.
A.same
B.changing with job
C.different but fixed beforehand(预先)
D.different but fixed with the length of job
13. The goals of virtual memory implementation is ( ).
A.protecting memory B.program floating(浮动)
C.extending external memory D.extending main memory
14. In memory management with segment, if physical address is expressed with 24 bits and the segment number is expressed with 8 bits, then the maximum length of each segment is ( ).
A.224 B.216
C.28 D.232
15. Why the system could occur the thrashing?
A Improper replacement algorithms
B The large amount of information exchange
C Memory capacity is sufficient
D Demand paging method
Ⅱ. Fill in the blanks.
1.The virtual address space is divided up into units called . The corresponding units in the physical memory are called . Both of them are always the same size.
2.In memory management, the strategy, that allows programs to run even when they are only partially in main memory, is called .
3.In paging relocation algorithm, could make Belady phenomenon .
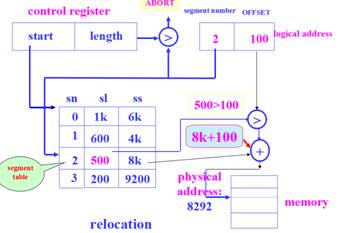
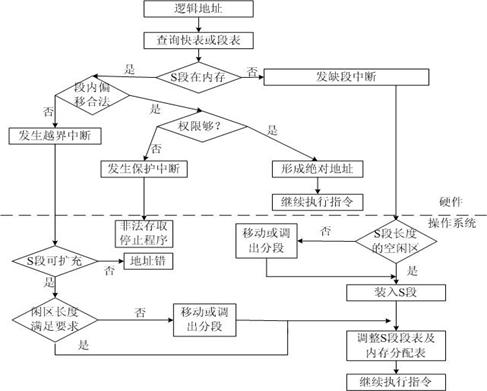
Ⅲ. Using the following page table, supposing the computer has 32-bit addresses and the page size is 4KB, give the physical address corresponding to each of the following virtual addresses:
Page number | Frame number |
0 | 6 |
1 | 5 |
2 | 3 |
3 | 2 |
(a) 5000 (b) 12000
Ⅳ. A virtual memory has 32 pages in its user space, every 1KB, the main memory is 16KB. Suppose the user’s pages 0,1,2,3 are allocated in physical blocks 5, 10, 4, 7 respectively. Please translate virtual addresses 0A5C and 093C and 0000 0000 0010 0001 to physical addresses.
Ⅴ.Using the following page table, supposing the computer is 16-bit, the page size is 2K, give the physical address corresponding to each of the following virtual addresses:
Page number | Frame number |
0 | 4 |
1 | 7 |
2 | 1 |
(a) 100 (b) 144cH
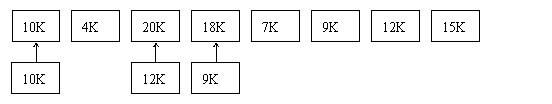
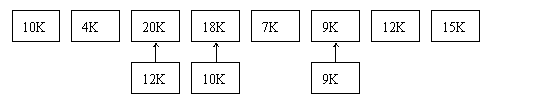
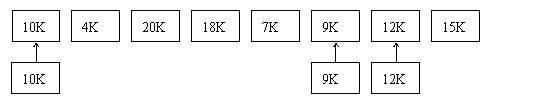
Ⅵ. Consider a swapping system in which memory consists of the following hole sizes in memory order: 10KB, 4KB, 20KB, 18KB, 7KB, 9KB, 12KB, and 15KB.Which hole is taken for successive segment requests of
1) 12KB
2) 10KB
3) 9KB
for first fit, best fit, worst fit, and next fit?
Ⅶ. Question about page replacement.
If the LRU,OPT and FIFO page replacement algorithm are used with three page frames, compute the page fault rate with the reference string 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 1, 2, 3 ,4, 5, if the three frames are initially empty? Write out calculating procedure.
Answer
Ⅰ.Select the correct answer
ADADB DBAAB CCDBA
Ⅱ. Fill in the blanks.
Pages, page frames
Virtual memory
FIFO
Ⅲ.Answer:
page number = int [5000/ 4096] = 1
Offset=5000%4096=904
Then physical address is 5 * 4096 + 904 = 21384
page number = int [12000/ 4096] = 2
Offset = 12000%4096= 3808
Then physical address is 3*4096+3808= 16096
Ⅳ. Answer:
The virtual memory has 32 pages, 2^5=32
So, the page number occupied 5 bits
1KB=2^10
So, the offset occupied 10 bits
So, the page number occupied 6 bits
0----0000
1----0001
2----0010
3----0011
4----0100
5----0101
6----0110
7----0111
8----1000
9----1001
A----1010
B----1011
C----1100
D----1101
E----1110
F----1111
0A5C=0000 1010 0101 1100
Page number=000010=2, offset=10 0101 1100=2^2+2^3+2^4+2^6+2^9=604
2----4
Starting address in physical memory=4*1024=4096
Physical address=4096+604=4700
And so on…...
Ⅴ.Answer:
page number = int [100/2048] = 0
Offset = 100%2048 = 100
So its frame number is 4
Then physical address is 4*2048+100 = 8292
(b) 144cH
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0
Page number offset
Or 144cH----5196; int [5196/2048] = 2; 5196%2048 = 1100
So page number is 2;
Offset is 1100 Corresponding frame number is 1
Physical address:1*2048+1100 = 3148
Ⅵ.
first fit: 20KB 10KB 18KB
best fit: 12KB 10KB 9KB
worst fit: 20KB 18KB 15KB
next fit: 20KB 18KB 9KB
Ⅶ.
LRU:
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|
| 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
|
| 1 | 4 | 4 |
|
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
|
| 2 | 2 | 5 |
Page fault rate is 10/12*100% = 83.3%
OPT:
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
|
| 1 |
|
| 3 | 3 |
|
| 2 | 2 | 2 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 2 | 4 |
|
|
| 3 | 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 5 | 5 |
|
Page fault rate is 7/12*100% = 58.3%
FIFO:
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
|
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
Page fault rate is 9/12*100% = 75%