第二节 平面体轴测图的画法 SECTION TWO AXONOMETRIC DRAWING OF PLANNAR SOLIDS
一、平面体正等测的画法 isometric drawing of planner solids
如图 7-2(a)所示,正等测的轴间角∠XOY=∠YOZ=∠ZOX=120°。OZ 轴成垂直位置,OX 轴和 OY 轴可用 30°三角板配合丁字尺绘出。轴间角的大小说明轴测图中长、宽、高方向的画法。
The isometric angles among axis are ∠XOY=∠YOZ=∠ZOX=120°and the OZ axis is in the vertical position, the OX and OY axis can be drawn with 30 °squares. As shown in Figure 3-2 (a)
正等测的轴向伸缩系数 p=q=r=0.82,为了画图简便,常采用简化轴向伸缩系数p=q=r=1作图,因而正等测图比实际物体的轴测图放大了1/0.82倍,即1.22倍,如图7-2(b)所示。轴向伸缩系数说明了量取长、宽、高尺寸时所采用的比例。
The isometric deformation coefficients are p=q=r=0.82. The coefficient is often simplified with 1 in order to make it easy for construction. That is to say the isometric drawing is larger than the true object.as shown in 7-2(b).
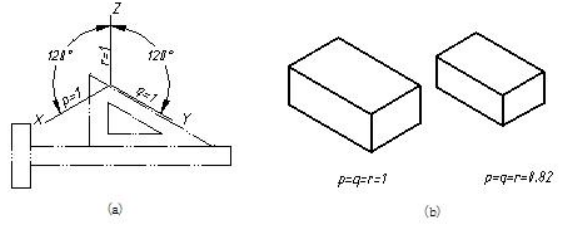
图7-2 正等测的轴间角和轴向伸缩系数 parameters of isometric projection
画轴测图常用的方法有:特征面法、叠加法、切割法。画轴测图时,轴测图上不必画出轴测轴,可画出参照轴测轴,然后以测量尺寸方便为原则选定起画点,依据“平行性”、“可量性”画出。
Now we introduce several commonly used methods in drawing axonometric projection. Such as feature surface, superposition, and cutting methods. One doesn’t need to draw axonometric axis ,however, One can draft reference axis to make it convenient and must follow the construction principles during making axonometric drawings.
1.特征面法 feature surface
特征面法用于画基本体轴测图。特征面法画轴测图的思路是:对柱类形体,先画出反映柱体形状特征的可见底面,再画出可见的侧棱,然后画出另一底面的可见轮廓线,如图 7-3 所示;对台(或锥)类形体,先画出两底面(或底面和锥尖),再画出可见的侧棱,如图 7-4 所示。
Characteristic surface method is useful for drawing axonometric projection of basic solids. Then we follows these steps. Firstly, finish axonometric drawing of the visible feature base of object. Then draw visible side edges, finally produce the projection of the other base. As shown in fig7-3 and fig 7-4.
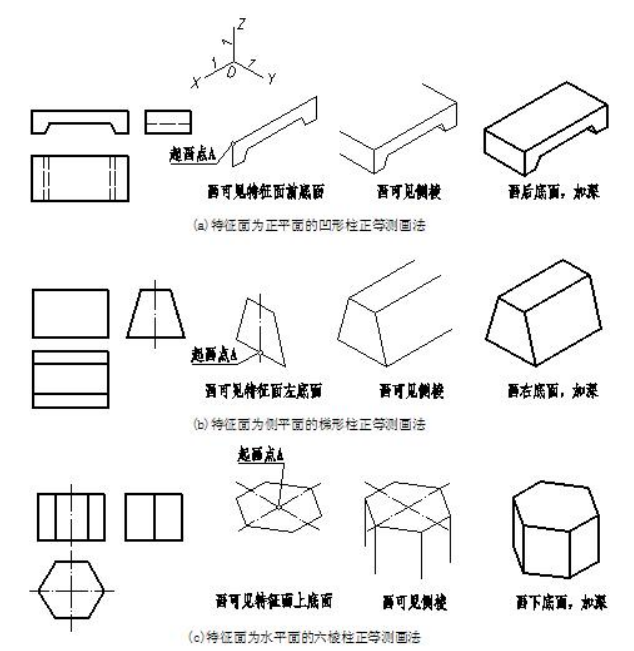
图7-3 用特征面法画柱类形体正等测的示例samples of feature base
2.叠加法 superposition method
叠加法用于画叠加体轴测图。叠加法画轴测图的思路是:从主到次逐个画出各基本体的轴测图,擦去被遮挡的图线。叠加时一定要注意基本体之间的定位。
Superposition method does work in making superposition type solids. The idea is to construct axonometric drawing of every basic solid from primary to secondary solids and ignore invisible outlines. Please pay attention to the relative position among basic solids.
图 7-5 所示是用叠加法画挡土墙正等测的作图步骤。挡土墙可看成由一个直十棱柱和两个三棱柱组合而成。应先画主体直十棱柱,再按三棱柱的位置逐一将两个三棱柱画出,完成作图。
The retaining wall can be regarded as three prisms. The construction steps are as follows.
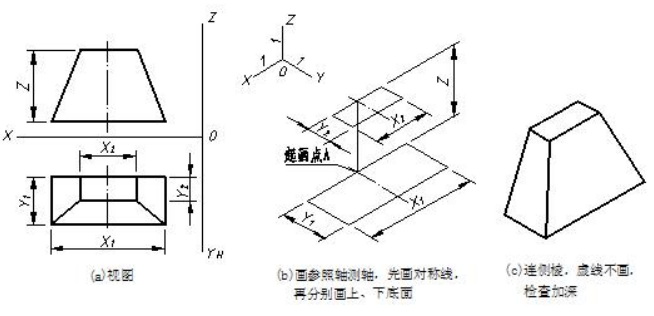
图7-4 用特征面法画台类形体正等测的示例sample of feature base
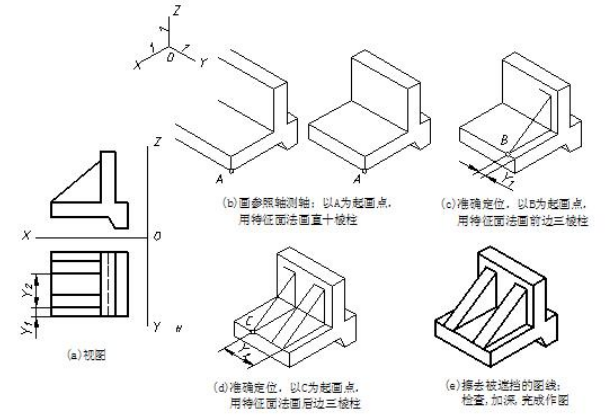
图7-5 用叠加法画物体正等测的示例 samples of superposition method
3.切割法 cutting method
切割法用于画切割体轴测图。切割法画轴测图的思路是:先画出原体,然后通过“移线”,的方法依次画出切割处。切割时一定要注意切割位置的确定。
The cutting method applies to make axonometric drawing of cutting solids. The idea is to draw the original solid, and then cut the solid based on given views. One should determine the cutting position during cutting solid away from the original solid.
图 7-6 所示是用切割法画轻型桥台上部正等测的作图步骤。该物体的原体可看成是直六棱柱,在前面居中上下切出一个倒置的半四棱台孔。应先画出原体直六棱柱,再按孔的位置通过移线画出孔,完成作图。
The solid in the example can be regarded as a prism and cut a frustum of rectangular pyramid away the prism. The steps described are as follows.
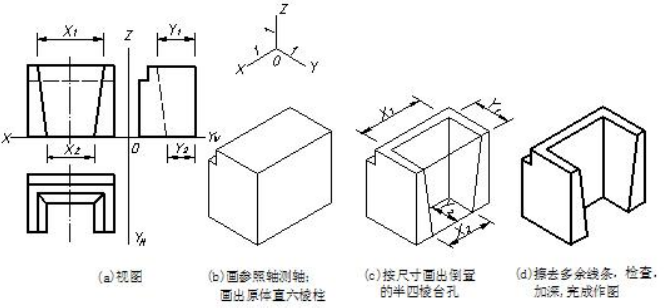
图7-6 用切割法画物体正等测的示例 sample of cutting method
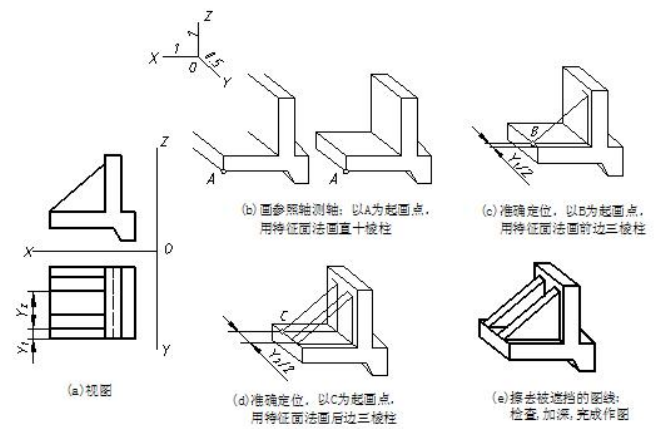
图7-7 用叠加法画物体斜二测的示例 sample of superposition method


