两曲面立体相交 Two curved surfaces intersect in three dimensions
两曲面立体表面的相贯线一般是闭合的空间曲线,特殊情况下可能是平面曲线或直线。
The intersecting line of two curved solid surfaces is usually a closed space curve, in special cases it may be a plane curve or a straight line.
曲面体表面光滑,不象平面体那样有棱线,因此求两曲面体的相贯线时,一般是先求出相贯线上一系列点,然后依次连成光滑曲线,并根据其可见性画成实线或虚线。求相贯线上的点时,通常先求控制点 (两立体外轮廓线上的点、距投影面最远及最近的点等能控制相贯线投影的范围、走向及可见性的点) ,再根据需要求若干个中间点。
The surface of a curved body is smooth, unlike a plane body with edges and corners. Therefore, when calculating the intersecting line of two curved bodies, it is generally a series of points on the intersecting line, and then successively connect them into smooth curves, and draw solid or dotted lines according to their visibility.For the point on the intersecting line, the control point (the point on the external contour line of the two sides, the point furthest from the projection plane and the point closest to it, etc., which can control the projection scope, direction and visibility of the intersecting line) is usually first sought, and then several intermediate points are required according to the needs.
求相贯线的常用方法为面上取点法、辅助平面法和辅助球面法。
The common methods to find the intersecting line are surface method, auxiliary plane method and auxiliary sphere method.
一、 面上取点法 Take the point method on the surface
因为相贯线是相交两立体表面的共有线,所以,当相交两立体中一个立体表面的投影有积聚性时,相贯线的这个投影已知,其余投影可以用面上取点的方法求出。
Because the intersecting line is the common line of intersecting two stereoscopic surfaces, when the projection of one stereoscopic surface of intersecting two stereoscopic surfaces is cumulative, the projection of the intersecting line is known, and the rest of the projection can be calculated by taking points on the surface.
两圆柱正交内外表面相贯线的形状、投影和求法与两外表面相贯线相同。
The shape projection and method of intersecting line of inner and outer surface of two cylinders are the same as that of intersecting line of outer surface.
1. 两圆柱孔的内表面相贯The inner surfaces of the two cylindrical holes are related
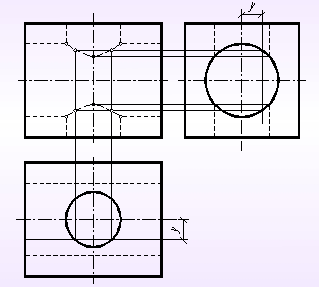
2. 圆杆外表面与圆柱孔表面产生相贯线The outer surface of the circular rod intersects the surface of the cylindrical hole