立体投影基础 CHAPTER TWO FOUNDERMENTAL PROJECTION OF SOLIDS
学习目标 TARGET OF LEARNING
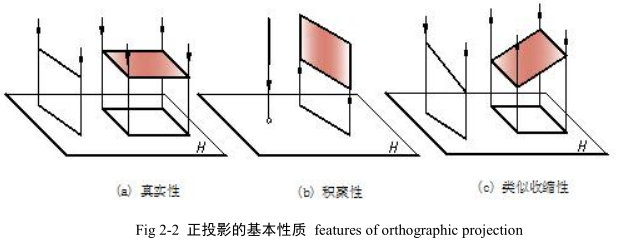
1.了解投影法,理解并熟记正投影的三个基本性质。
2.理解三视图与空间物体的对应关系,理解并熟记三视图间“长对正、高平齐、宽相等”的投影规律。
3.掌握各类基本体三视图的画法,熟记基本体三视图的图形特征。能由基本体的三视图,迅速地想象出它们的立体形状。
4.掌握组合柱、叠加式和切割式简单体三视图的画法要点。能由简单体的三视图,正确地想象出它们的立体形状。
Understand the concept of projection method and remember three basic features of orthographic projection.
Understand the relation between three views and solid and master the projection rules.
Master the construction of three views and keep in mind the features of basic solids. One can imagine solid based on three views of solid.
Master the key points of drawing three views about composite solid, one can be able to imagine the spatial solid based on three views of simple solids.
绘制工程图样依据的是正投影原理,工程形体都可以看成是由一些形状规则且简单的形体组成。了解投影法,掌握基本体、简单体三视图的画法与识读是工程形体投影的基础。
第一节 投影法与正投影的基本性质 SECTION ONE BASIC FEATURES OF PROJECTION AND ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION
一、投影法的概念 CONCEPT OF PROJECTION
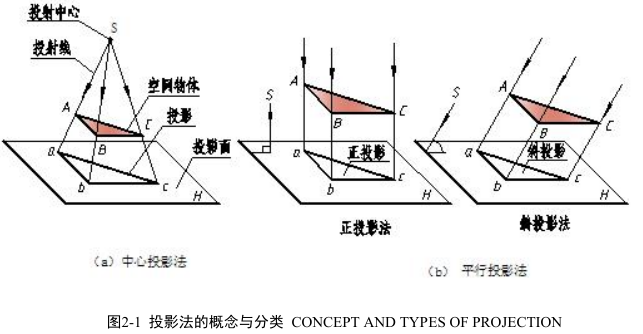
投影法就是投射线通过物体,向选定的平面投射,并在该平面上获得图形的方法。图 2-1(a)中光源 S 点称为投射中心;SAa、SBb、SCc 称为投射线;平面 H 称为投影面;通过物体上各顶点的投射线与投影面的交点 a、b、c 称为物体上各顶点 A、B、C 在 H投影面上的投影;Δabc 图形即为空间物体 ABC 在 H 投影面上的投影。
In daily life, when the sunshine or lamplight irradiates an object, there will be a shadow on the ground or the wall. Scientists abstract the natural phenomena to describe an object with projection. The source of light is called the center of projection. Light ray is called projector. The pre-established plane is called projection plane. The graphics on the plane is called projection. In other word, rojection is when the projection line passes through the object, there will produce projection on the projection plane.
二、投影法的分类 TYPES OF PROJECTION
(1)中心投影法。投射线汇交于一点的投影法称为中心投影法,如图 2-1(a)所示。
Central projection: all the projectors meet a point, as shown in fig2-1(a)
(2)平行投影法。投射线相互平行的投影法称为平行投影法。
Parallel projection: projectors parallel each other, as shown in fig2-1(b).
在平行投影法中,根据投射线与投影面的角度不同,又分为两种:正投影法――投射线与投影面相垂直的平行投影法,如图 2-1(b)所示。斜投影法――投射线与投影面相倾斜的平行投影法,如图 2-1(b)所示。
According to the different angle between projectors and projection plane, parallel projection can be classified orthographic projection and oblique projection. Orthographic projection: if the projectors are perpendicular to the projection plane, the projection is called orthographic projection, as shown in fig2-1(b). Oblique projection: if the projectors are oblique to the projection plane, the projection is called oblique projection, as shown in fig2-1(b).
正投影能真实地表达物体的形状和大小,并且度量性好、作图简便,在工程上应用最广泛。本书主要介绍正投影图。以后各章节中,除特殊说明外,所称投影均指正投影。
Orthographic projection can show the actual size of object and it is convenient to draw and measure, so it is widely used in engineering drawings. This book introduces the projection drawing. In later chapters, orthographic projection is called projection for short.
应当指出:投影不同于一般的影子,影子是一片漆黑,只反映物体的外轮廓,而物 体的投影是将围成这个物体的各面、各棱线进行投影。
It should be pointed out: the projection is different from general shadow, the shadow is a dark, reflect only the outer contour of the object, however, projection can show every plane and line of object.