二、曲面体表面取点 getting points on the curved solids
在曲面体表面上取点和在平面上取点的基本方法相同,即当曲面体表面的一个投影
具有积聚性时,可利用积聚性投影直接求得点的投影;当各投影都没有积聚性时,则需
要用辅助线法来求。
Accumulation and auxiliary line methods are still applied to solve the problem of getting
points on the surface of curved solids.
应指出的是:曲面无论有没有积聚性,轮廓素线上的点均可以直接求得。
It should be pointed out: points in the contour line can be obtained directly whether the curved
surface is collection or not.
【例 4-9】如图 4-10(a)所示,已知圆柱面上 K 和 A 两点的正面投影 k′、a′,求作 K和 A 点的水平投影和侧面投影。
【Eg.4-9】Known the vertical projections of point A and K on a cylinder, please work out the other two projections of them as shown in fig 4-10(a).
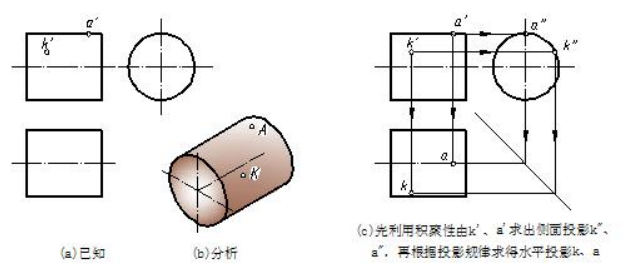
图4-10 圆柱体表面取点 get points on the surface of a cylinder
分析 analysis
圆柱面的侧面投影积聚为一圆线,因此 K、A 两点的侧面投影 k″、a″必在该圆周上,可直接求。由于 k′、a′可见,所以 K 点位于圆柱的前半圆柱面上,A 点位于正向轮廓素线上,如图 4-10(b)所示。
The side vertical projection of the cylinder is collecting a circle, so it is easy to work out k″and a″.because k″and a″are visible , point K is on the front-half cylindrical surface and pointA is located is the vertical contour line as shown in 4-10(b).
【例 4-10】如图 4-11(a)所示,已知圆锥面上 A 点的正面投影 a′,求 A 点的水平投影和侧面投影。
【Eg.4-10】as shown in fig4-11(a). Please complete the projections of point A based on its vertical projection.
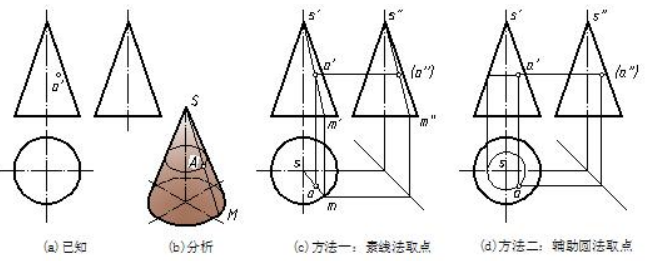
图4-11 圆锥体表面取点 get point on the surface of a cone
分析 analysis
如图 4-11(b)所示,A 点在圆锥面上,圆锥面无积聚性,应用辅助线法求。圆锥面是直线面,可利用素线作辅助线,称素线法。圆锥面又是轴线为铅垂线的回转面,该面上可作出一系列水平圆,所以又可利用水平圆作辅助线,称辅助圆法。
As we know, the point is on the conical surface and the surface is a general plane , so auxiliary method is the good choice. The conical face is made up of a line and makes generating line to be regarded as auxiliary line. At the same time, the axis of the cone is perpendicular to horizontal projection plane; one makes a series of horizontal parallel concentric circles instead of auxiliary line.
作图 construction
方法一:用素线法求 a 及 a″。如图 4-11(c)所示,连接 s′a′并延长交圆周于 m′,s′m′即为过点 A 的素线。M 点在底面上,根据投影规律由 m′可直接求出 m 和 m″,再连接 sm 和 s″m″,即得辅助线的水平投影和侧面投影。根据直线上点的从属性和点的投影规律可求画出 a 及 a″,a″不可见。
Method one: using generating line to work out horizontal and side vertical projections. As shown in fig 4-25(c). Connect s′ and a′. The extension line of s′a′ intersects m′ with the circle .the line of s′m′ is the generating line through point A. Point M is on the bottom surface and work out m and m″following projection rules. And then , join sm and s″m″in every case, obtain the horizontal and side vertical projections of the generating line. According to the subordination and projection rules of point, it is very convenient to figure out the desired projections of point A. the side vertical projection is invisible because it is located on the right and half conical surface.
方法二:用辅助圆法求 a 及 a″。如图 4-11(d)所示,过 A 点在圆锥面上作一辅助圆,辅助圆的水平投影是与底面同心的圆,正面投影和侧面投影均为水平直线。过 a′作一水平线交两侧轮廓素线,长度即为辅助圆的直径,以水平投影中心 S 为圆心,上述长度之半为半径画圆得辅助圆的水平投影,根据投影规律可求出辅助圆的侧面投影。同理,由直线上点的从属性和点的投影规律可求出 a 及 a″,a″不可见。
Method two: using auxiliary circle to obtain the horizontal and side vertical projections of point A. As shown in fig 4-25(d). Firstly, make an auxiliary circle through point A, the horizontal projection of it is a concentric circle with the bottom face. The other two projections of the auxiliary circle are both horizontal parallel lines. Secondly , draw a horizontal parallel line through a′and intersects the left and the right contour lines. The length from the two intersections is the diameter of the auxiliary circle. Thirdly, draft the auxiliary circle with the center point. Follow projection rules to figure out side vertical projection of the circle. In the same way as method one, one can give the projections of point A and determine the visibility of the projections.
如果点位于圆锥的底面或素线上,可以直接求。如果在锥曲面上,可以通过做辅助直线或辅助素线求点的投影。
If a point is the base or generators, one can work it out directly. If it is on cone surface, one must draw some auxiliary generating line or auxiliary circle to do it.
作图步骤:
判断点的位置;绘制辅助素线或辅助圆;完成辅助素线或辅助圆的投影;求点的投影;判别点投影的可见性。
Step1. Determine where the point is.
Step2. Draw auxiliary line or circle.
Step3. Finish the projections of auxiliary line or circle.
Step4. Complete the projections of points on the auxiliary line or circle.
Step4. Distinguish whether the point is visible or not.
小结 Make a conclusion
完成点的投影后,要判别其可见性;读图能力以及理解视图含义非常重要;点、线和面的投影特性;投影规律,将这些应用到解题中。
Remember to offer the visibility of point after one finishes the projections of point on the surface of solid. The ability of reading and understanding views, plays an important role in getting points on the surface of solid. One should have good understanding of projection characteristics of points, lines and planes.In other words, one should put the principle and the knowledge into practice.


