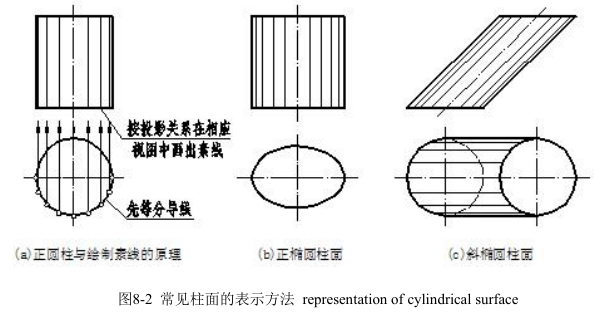
一、柱面 cylindrical face
直母线沿曲导线运动,并始终平行另一直导线所形成的曲面称为柱面。柱面上所有素线相互平行。
1.柱面的分类 Sorts of cylindrical surface cylindrical surfaces
柱面以它正截面(垂直于轴线的截面)的形状和底面与轴线的相对位置分类命名:
柱面的正截面为圆,底面垂直轴线,称为正圆柱面,如图 8-2(a)所示。
柱面的正截面为椭圆,底面垂直轴线,称为正椭圆柱面,如图 8-2(b)所示。
柱面的正截面为椭圆,底面不垂直轴线,称为斜椭圆柱面,如图 8-2(c)所示。
Sorts of cylindrical surface cylindrical surfaces name after the shape and relative position of section perpendicular to the axis. Cylindrical surfaces include right cylindrical surface, right elliptic surface and oblique elliptic surface.
2.素线的画法 Representation of generating lines
制图标准规定,素线用细实线绘制,素线只绘制在曲面可见的投影部分。图 8-2(a)表示了绘制直线面素线的原理。从理论上说,绘制直线面素线可等分其导线(导线为圆时即为等分圆周),过等分点按投影对应关系在相应的视图中画出素线。在实际绘图时,柱面在反映其轴线实长的视图中的素线,可按越靠近轮廓素线越稠密,越靠近轴线越稀疏的规律目测画出。
GB regulates that one should draw generating lines with thin solid line and only draft the visible portion of the projection on the surface. In fact, one can follow the rules to finish projections of generating lines. That is nearer to the contour line of denser, on the contrary, closer to the axis of sparser.
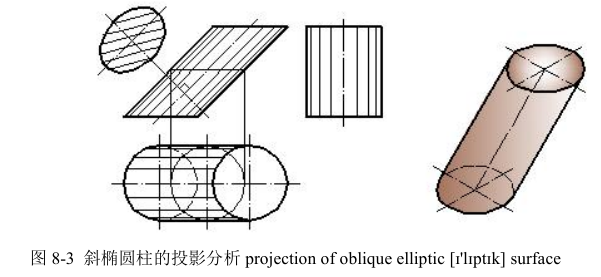
3.斜椭圆柱的画法 Construction of oblique elliptic [ɪ'lɪptɪk] surface
画斜椭圆柱的投影和画正圆柱一样,需要画出上底面、下底面、柱面的轮廓素线及轴线的投影。
由图 8-3 可看出斜椭圆柱的投影有以下特点:
(1)三个投影都没有积聚性,在反映底面实形的投影中两底面的投影不重合。
(2)平行底面的截交线是与底面直径相等的圆。
(3)垂直轴线的截交线为椭圆;所有素线均与轴线平行。
The axis is oblique the H- projection plane. The top view is two circles and they are not coincident.The section perpendicular to the axis is an ellipse and the section parallel the bottom faces is a circle.Generating lines should be drawn in every view and all generating lines parallel the projection of axis( draw generating lines based on the textbook).
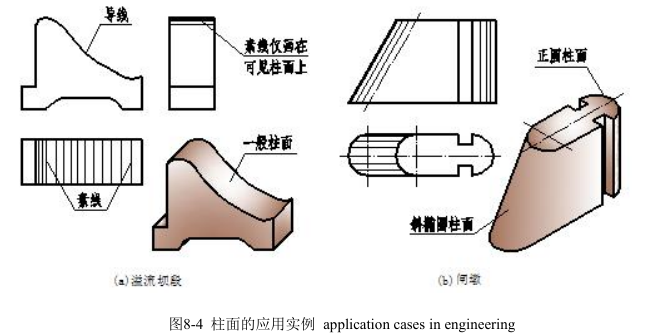
4.柱面的应用 application of cylindrical surfaces
图 8-4 所示是柱面在工程中的应用实例。
Application of cylindrical surfaces in engineering is as shown in fig 8-4.
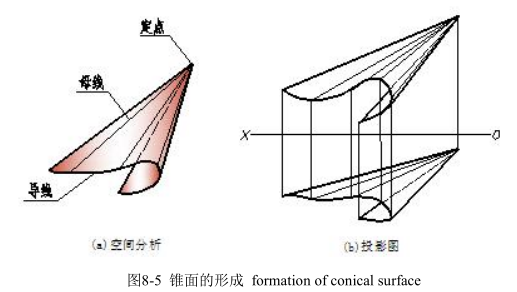
二、锥面 conical surfaces
直母线沿着曲导线移动,并始终通过一定点所形成的曲面称为锥面,如图 8-5 所示。
Straight generating line moves along a curved line, and always through a certain point will produce a conical surface as shown in fig 8-5.
1.锥面的分类 classification of conical surfaces
锥面也是以它正截面(垂直于轴线的截面)的形状和底面与轴线的相对位置分类命名:
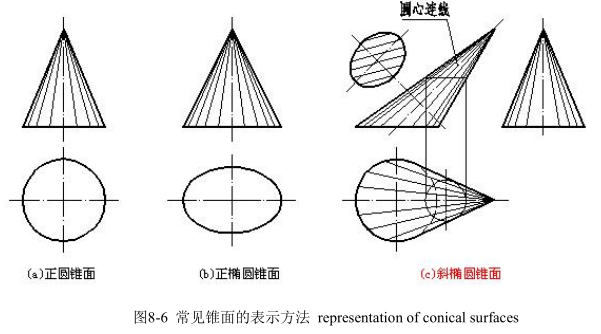
锥面的正截面为圆,底面垂直轴线,称为正圆锥面,如图 8-6(a)所示。
锥面的正截面为椭圆,底面垂直轴线,称为正椭圆锥面,如图 8-6(b)所示。
锥面的正截面为椭圆,底面不垂直轴线,称为斜椭圆锥面,如图 8-6(c)所示。
锥面素线的画法原理与柱面相同。
Conical surfaces are named the shape of cross section and the relative position between bottom face and axis. If the cross section is a circle and the bottom face is perpendicular to the axis, the face is called circular conical surface. If the cross section is an ellipse and the bottom face is perpendicular to the axis, the face is called elliptic conical surface. If the cross section is an ellipse and the bottom face is not perpendicular to the axis, the face is called oblique elliptic conical surface. The construction of generating lines is same as the cylindrical surfaces.
2.斜橢圆锥的画法 construction of oblique elliptic conical surface
画斜橢圆锥的投影和画正圆锥基本一样,需要画出底面、锥尖、锥面的轮廓素线和圆连心线的投影,如图 8-6(c)所示。由图 8-6(c)可看出斜椭圆锥面的投影有以下特点:
(1)平行底面的截交线为直径不相等的圆。
(2)垂直轴线的截交线为一系列大小不等的椭圆。
(3)所有素线都通过锥尖。
The methods are almost same as the circular conical surface.one needs to show the bottom face, conical vertex, contour lines and projection of joint center line shown in fig 8-6(c). Characteristics of oblique elliptic conical surfaces.
(1)The intersections of parallel bottom are different circle.
(2)The intersections of perpendicular to the axis are different ellipses.
(3)All the generating lines are through the vertex of cone.
3.方圆渐变面 Square gradient
图 8-7 中所示的方圆渐变面是斜椭圆锥面在工程上的应用实例。在工程中,引水洞洞身通常设计成圆形断面,而在进、出口处为了安装闸门需要,往往设计成矩形断面,在矩形断面和圆形断面之间,常用一个由矩形逐渐变化成圆形的过渡段来连接,这个过渡段的迎水表面称为方圆渐变面。
Construction of a gradual surface from a circle to a square Representation: three views and some necessary sectional view. Method: end faces Analysis: finish its left view firstly. It is a circle and a square and then, draws its top view and front view in every case based on projection rules. Remember to draw generating lines on curved surfaces. Notices: one should know how to draw its axonometric drawing. One also needs to learn how to draw generating lines in the views. One can be able to provide the sectional views of it.
图 8-8(a)为方圆渐变面的立体图。方圆渐变面是由四个三角形平面和四个部分斜椭圆锥面组成。矩形的四个角就是四个部分斜椭圆锥的锥顶,圆周的四段圆弧就是四个部分斜椭圆锥面的底圆,四个三角形平面与四个部分斜椭圆锥面平滑相切。方圆渐变面一般用三视图和必要的断面图来表示。
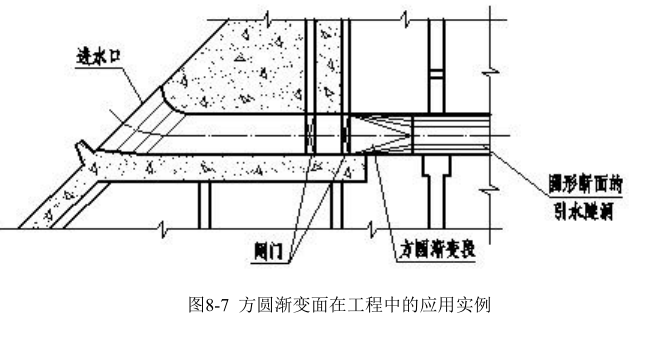
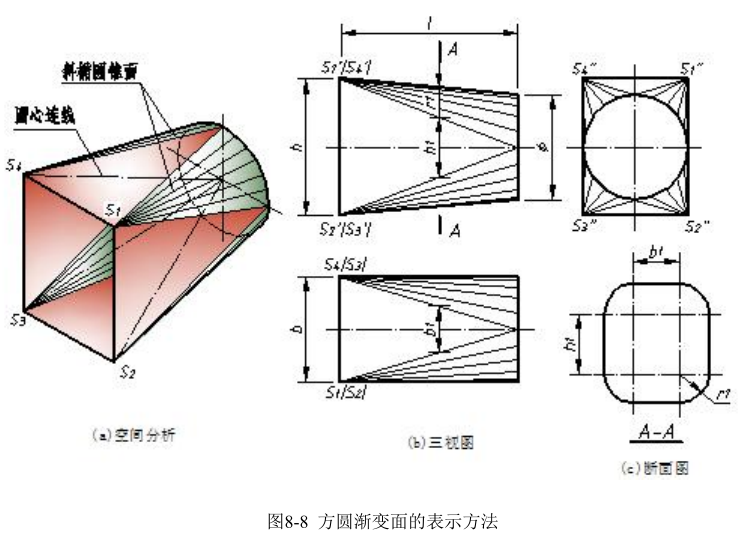
图 8-8(b)所示是方圆渐变面的三视图,与圆锥曲面一样,方圆渐变面中的锥面上要画出素线。图 8-8(c)所示是方圆渐变面的断面图,方圆渐变面的横断面是带四个圆角的矩形,其中圆角半径 r1 和直线段长度 b1、h1 都随剖切位置的不同而变化。画方圆渐变面的断面图时,应在剖切位置上准确的量取决定断面大小的尺寸 b1、h1 和 r1。


