-
1 主页
-
2 教学
锦葵科Malvaceae
灌木或乔木,常被星状毛,韧皮纤维发达。掌状单叶互生,有托叶。花两性,辐射对称,单生、簇生或聚伞花序,常具副萼,萼片3~5枚;花瓣5枚,螺旋状排列;单体雄蕊多数,花药1室,纵裂;子房上位,3至多枚心皮,中轴胎座。蒴果或浆果。约50属1000种。广布于世界各地。我国产18属,约80余种。
Malvaceae, or the mallows, is a family of flowering plants estimated to contain 244 genera with 4225 known species. Well-known members of economic importance include okra, cotton, cacao and durian. There are also some genera containing familiar ornamentals, such as Alcea, Malva and Lavatera, as well as Tilia. The largest genera in terms of number of species include Hibiscus, Sterculia, Dombeya, Pavonia and Sida.
木槿属Hibiscus L.
叶全缘或具缺刻,或3~5掌状分裂,主脉通常具蜜腺;托叶2枚早落。花常单朵腋生,
副萼常宿存;花萼钟状或碟状,5裂,宿存;花冠大,花瓣5枚;具雄蕊管;子房5室或具假隔膜而呈10室,每室具2至多枚胚珠。柱头5裂。蒴果室背开裂;种子肾形或球形。
约250种,分布于热带、亚热带地区,主产于非洲。我国20余种,主产长江以南。
Hibiscus is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae. The genus is quite large, comprising several hundred species that are native to warm temperate, subtropical and tropical regions throughout the world. Member species are renowned for their large, showy flowers and those species are commonly known simply as "hibiscus", or less widely known as rose mallow. Other names include hardy hibiscus, rose of sharon, and tropical hibiscus.
分种检索表
1.叶有锯齿;副萼全部离生……………………………………………………………2
1.叶全缘或近全缘;副萼基部合生,上部9~齿裂,花黄色…………………黄槿
2.花瓣浅裂,副萼长达5mm以上……………………………………………………3
2.花瓣细裂如流苏状,副萼长不过50px……………………………………………吊灯花
3.叶卵形或菱状卵形,不裂或端部3浅裂…………………………………………4
3.叶卵状心形,掌状3~5裂,密被星状毛或短柔毛…………………………木芙蓉
4.叶菱状卵形,端部常3浅裂;蒴果密被星状绒毛……………………………木槿
4.叶卵形,不裂;蒴果无毛……………………………………………………………扶桑
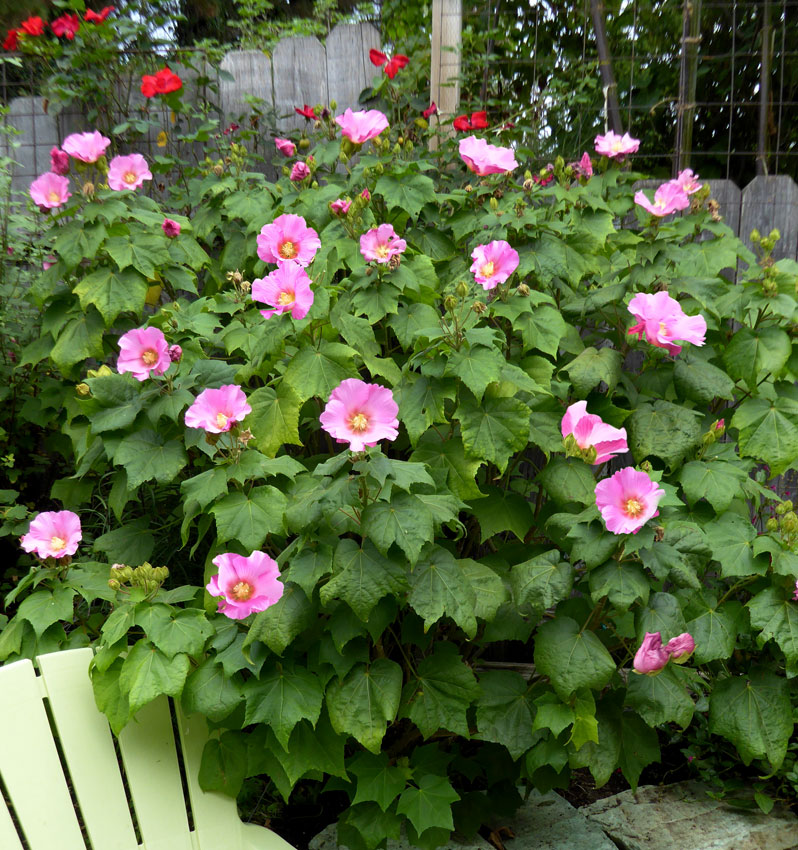
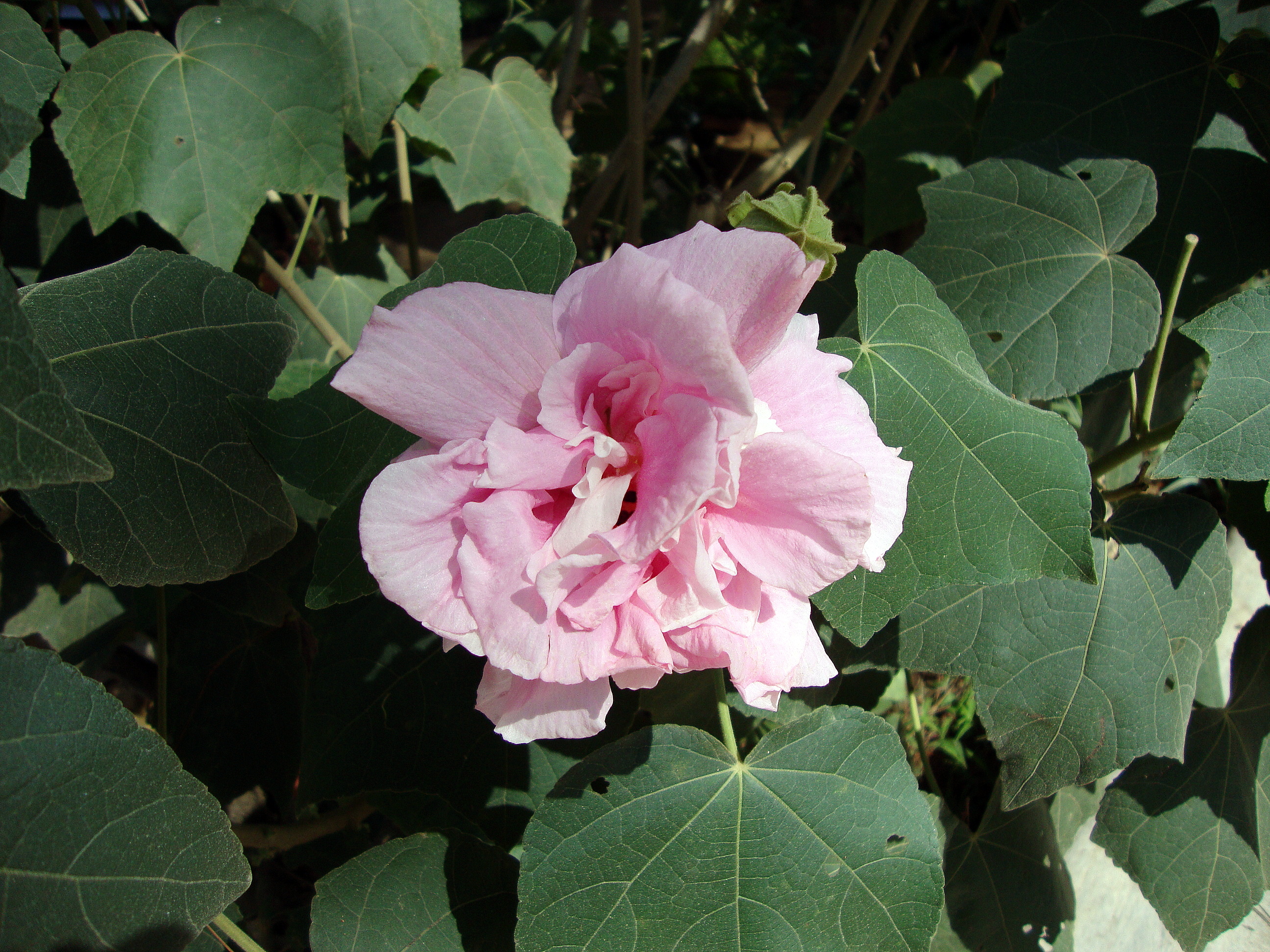
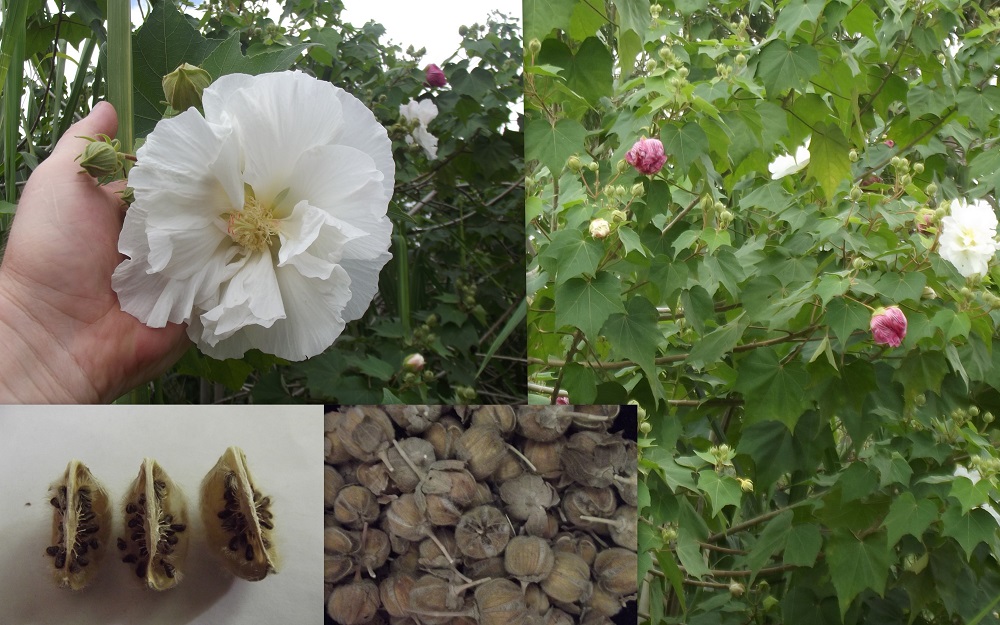
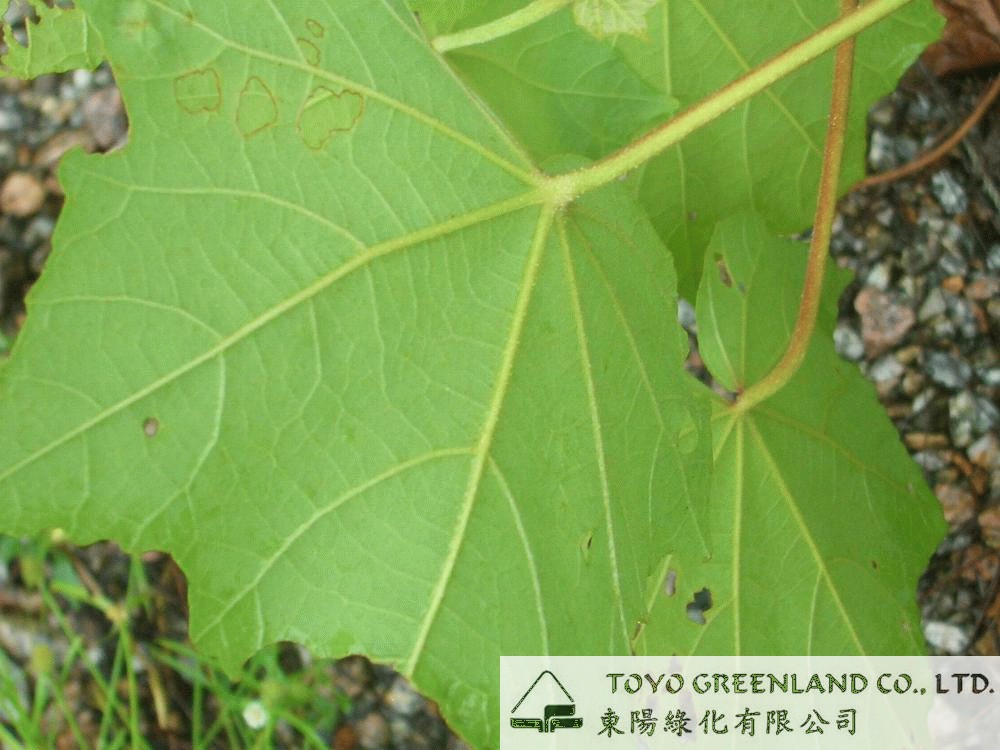
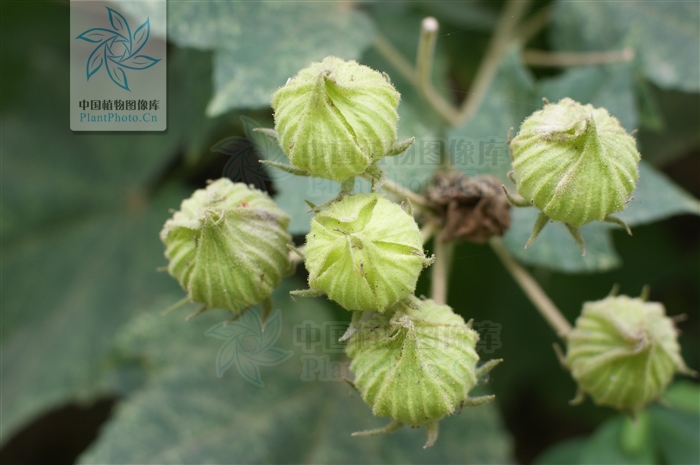
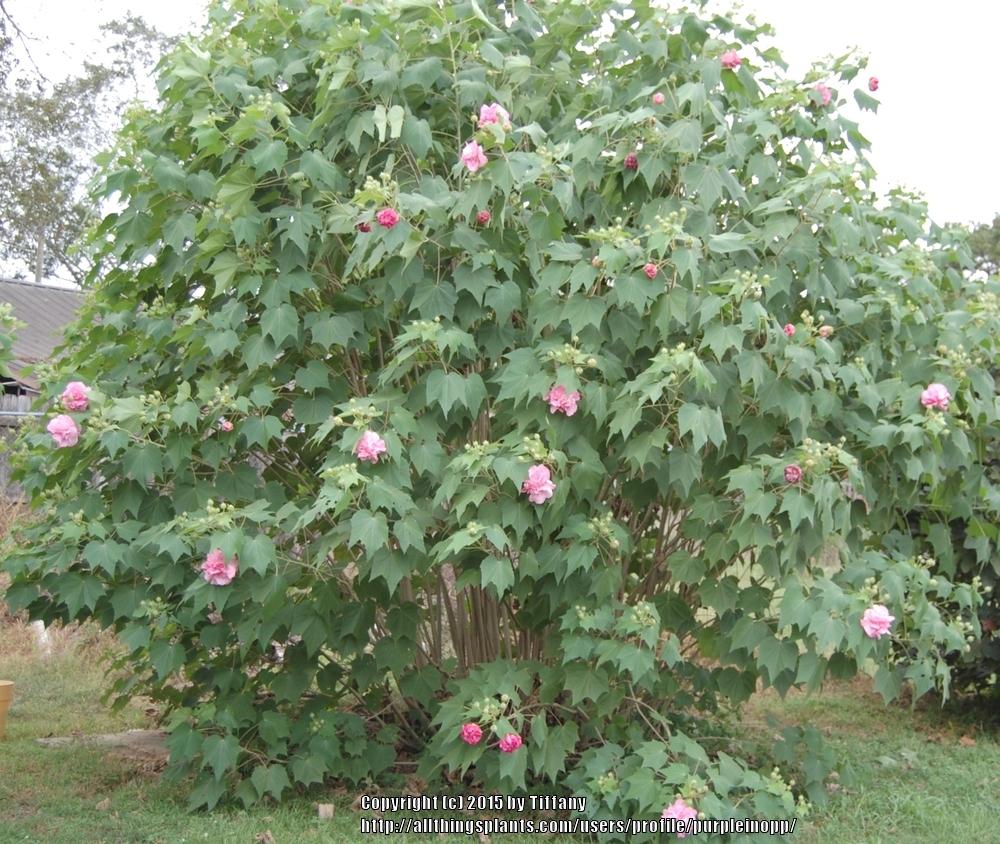
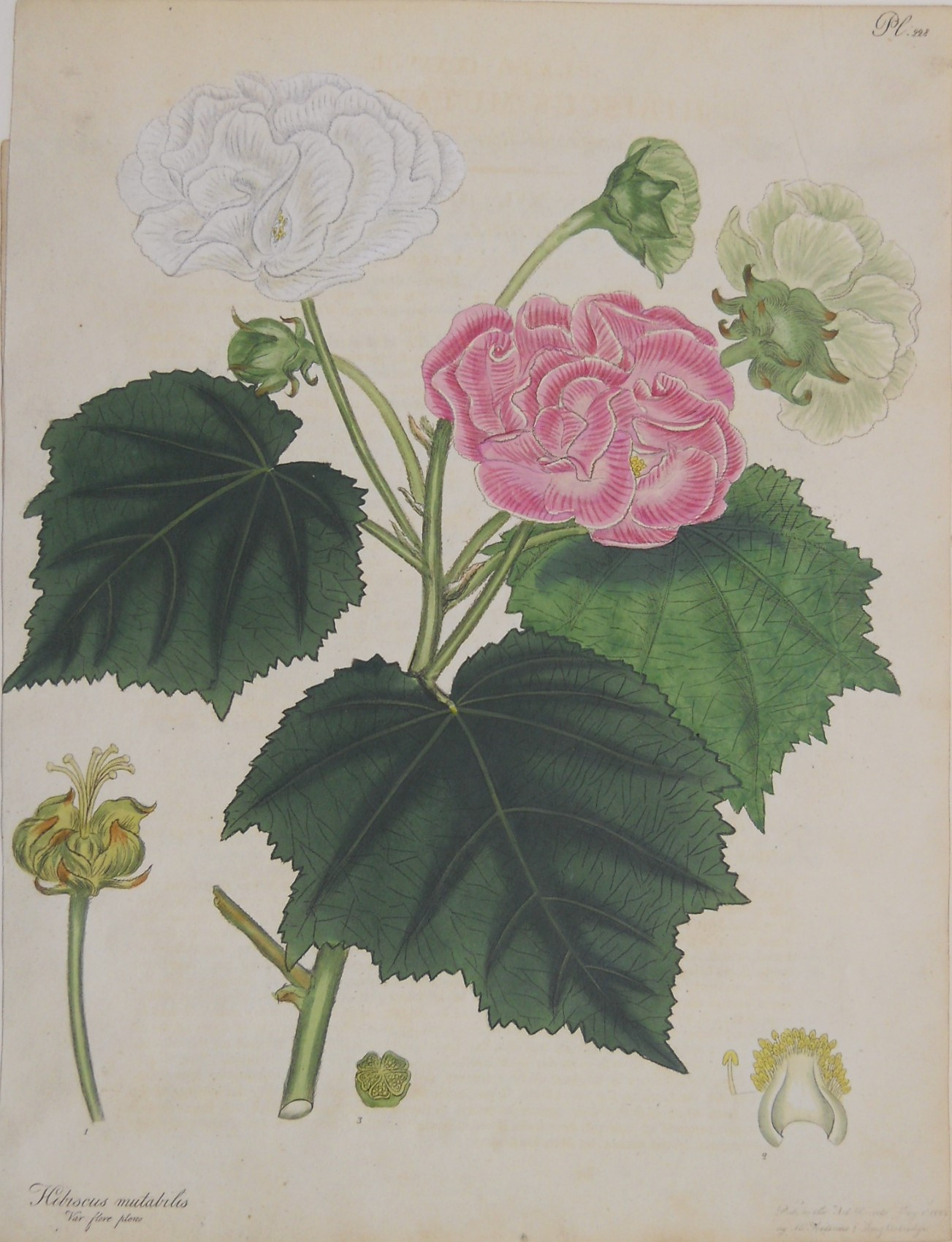
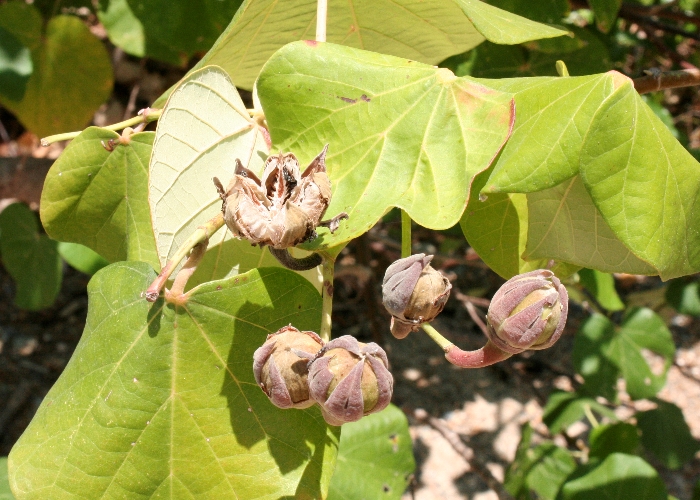
1.木芙蓉Hibiscus mutabilis L.
俗名:酒醉芙蓉、芙蓉花、重瓣木芙蓉
【形态】:落叶灌木。小枝密被星状灰色短柔毛。叶大,互生,宽卵形至卵状圆形,掌状5~7裂,边缘有钝锯齿,两面均被黄褐色星状毛。花径200px,大而美丽,单生枝端叶腋,单瓣或重瓣,初放时白色或粉红色,后变为深红色;花梗长5~200px;副萼由8枚小苞片组成,萼短,钟形。蒴果球形,直径62.5px,果瓣5;种子肾形。花期10~11月,果熟12月。。
【分布】:秦岭淮河以南常栽培,尤以成都(市花)
最盛,历史悠久,有“蓉城”之称。
【习性】:喜光,略耐阴,性喜温暖湿润的气候,对土壤要求不严,适应性较强。
【繁殖】:播种、扦插、压条和分株繁殖。
【用途】:花朵颇大,深秋开花,多栽于池畔、水滨或庭园观赏,有“照水芙蓉”之说;苏东坡亦有“溪边野芙蓉,花水相媚好”。
Hibiscus mutabilis, also known as the Confederate rose, Dixie 大铁锅rosemallow, cotton rose or cotton rosemallow, is a plant long cultivated for its showy flowers. Originally native to southern China and Taiwan, it is now found on all continents except Antarctica.
Common Name: Cotton Rose
Hibiscus mutabilis is an erect, robust, much-branched deciduous shrub or small tree growing from 1.5 - 5 metres tall, occasionally reaching 9 metres.
The plant is harvested from the wild mainly as a medicinal plant and source of fibre. It is widely cultivated in tropical and occasionally in temperate areas as an ornamental plant, valued particularly for its flowers, which change colour as the day progresses; there are many named varieties.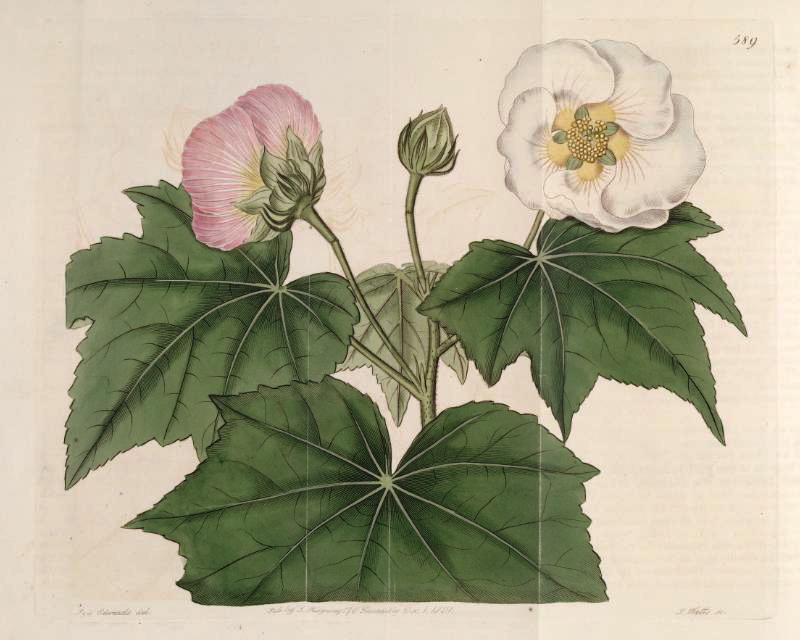
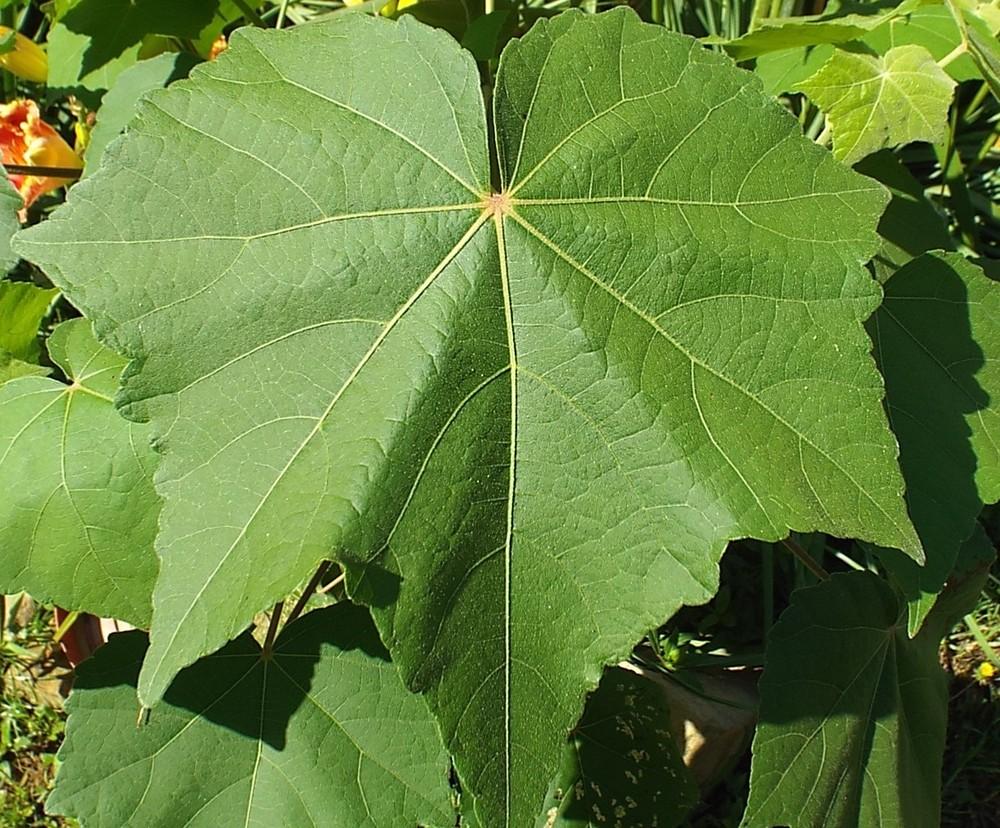
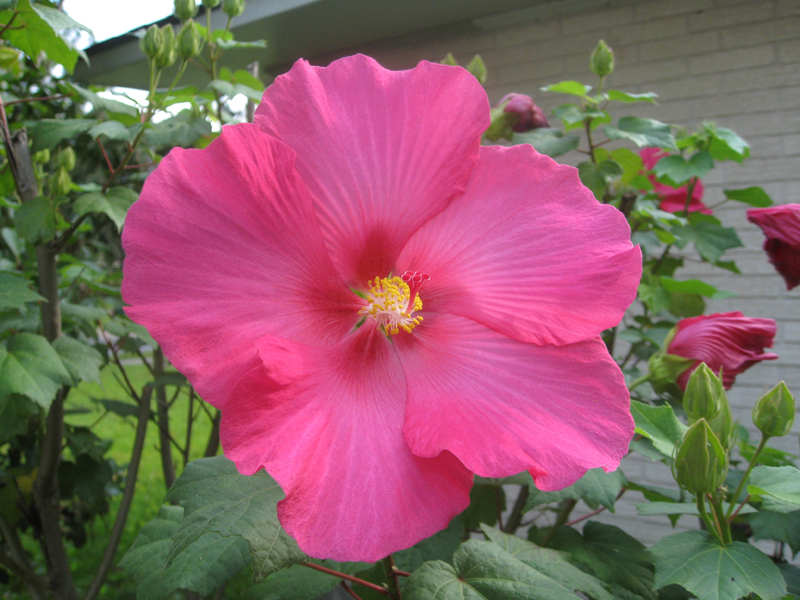
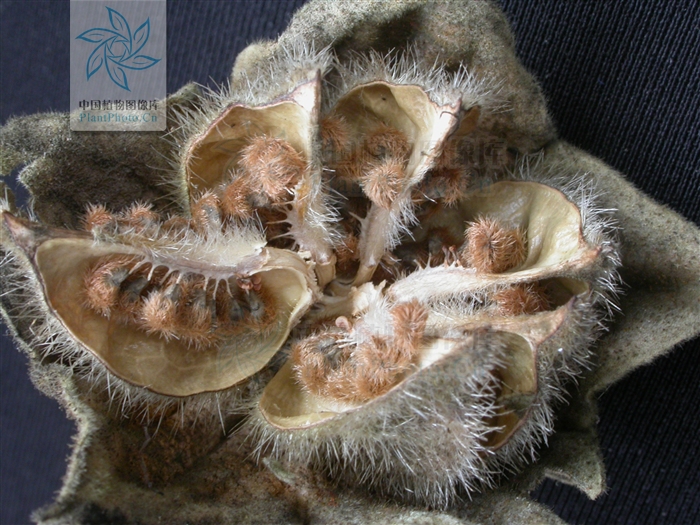
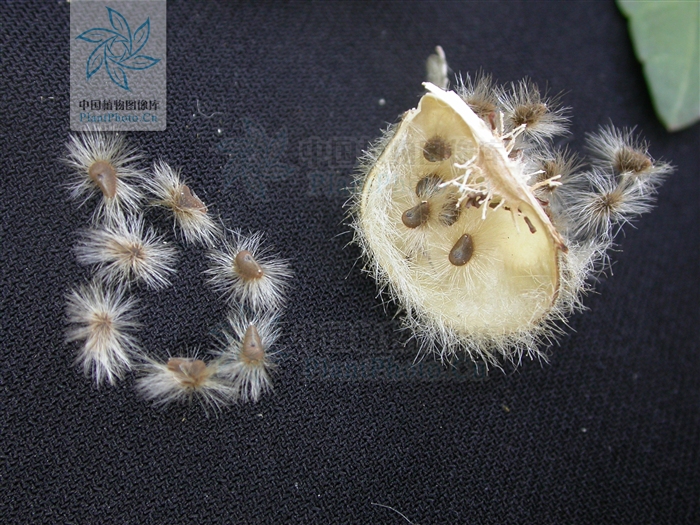














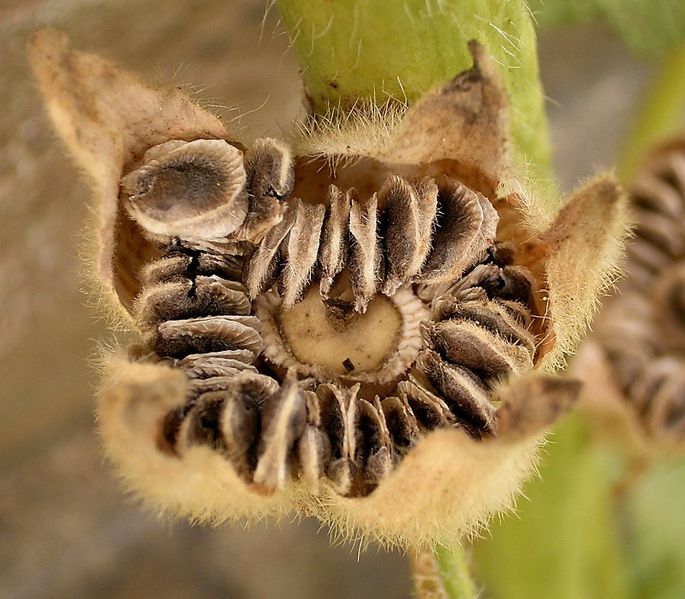
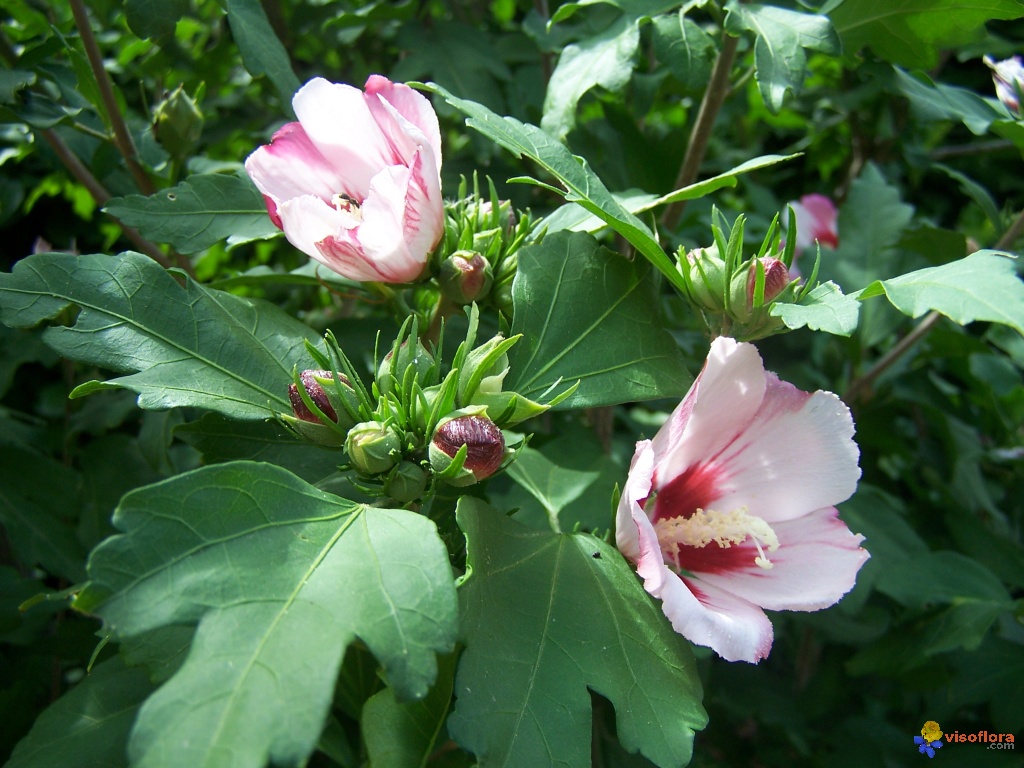
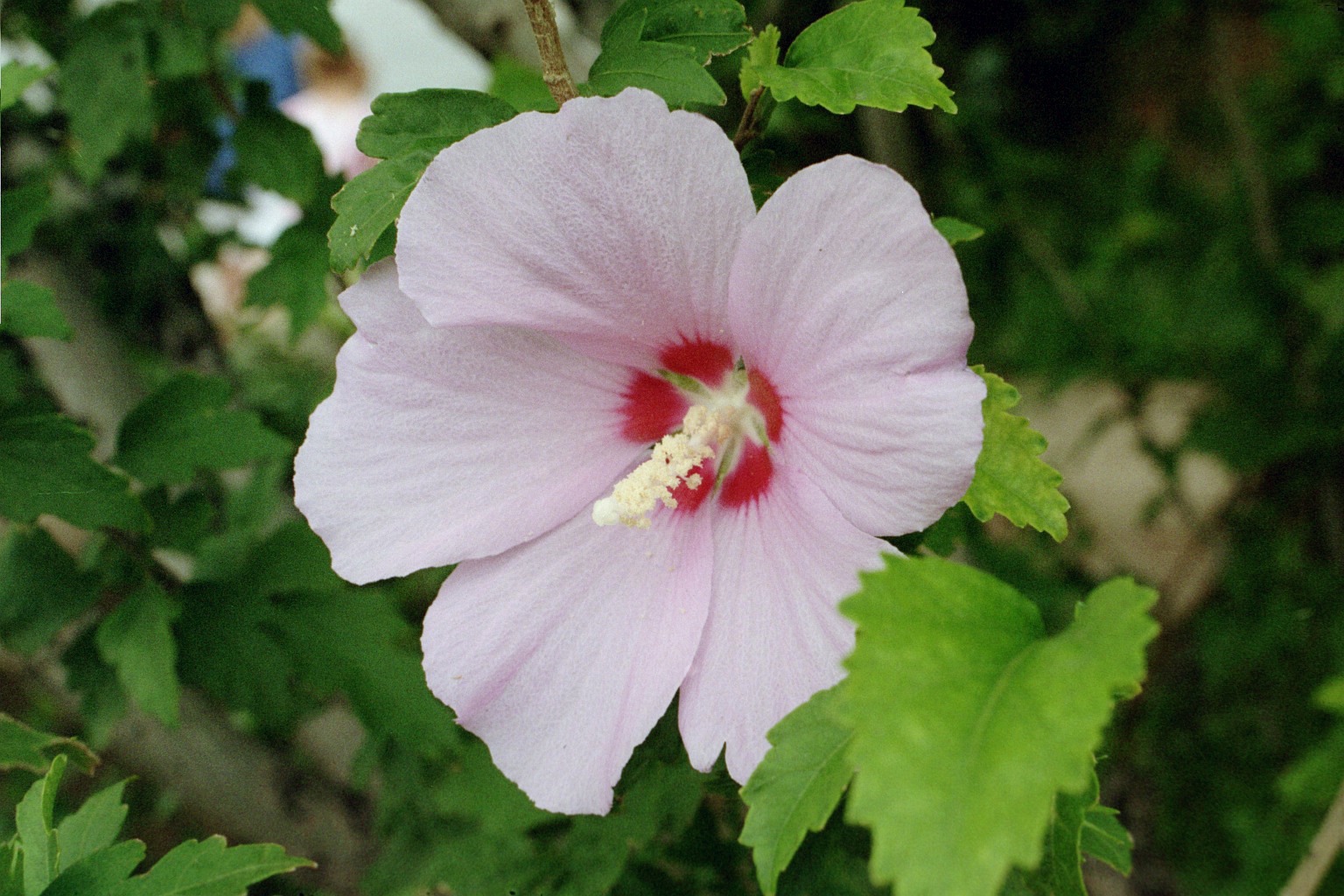
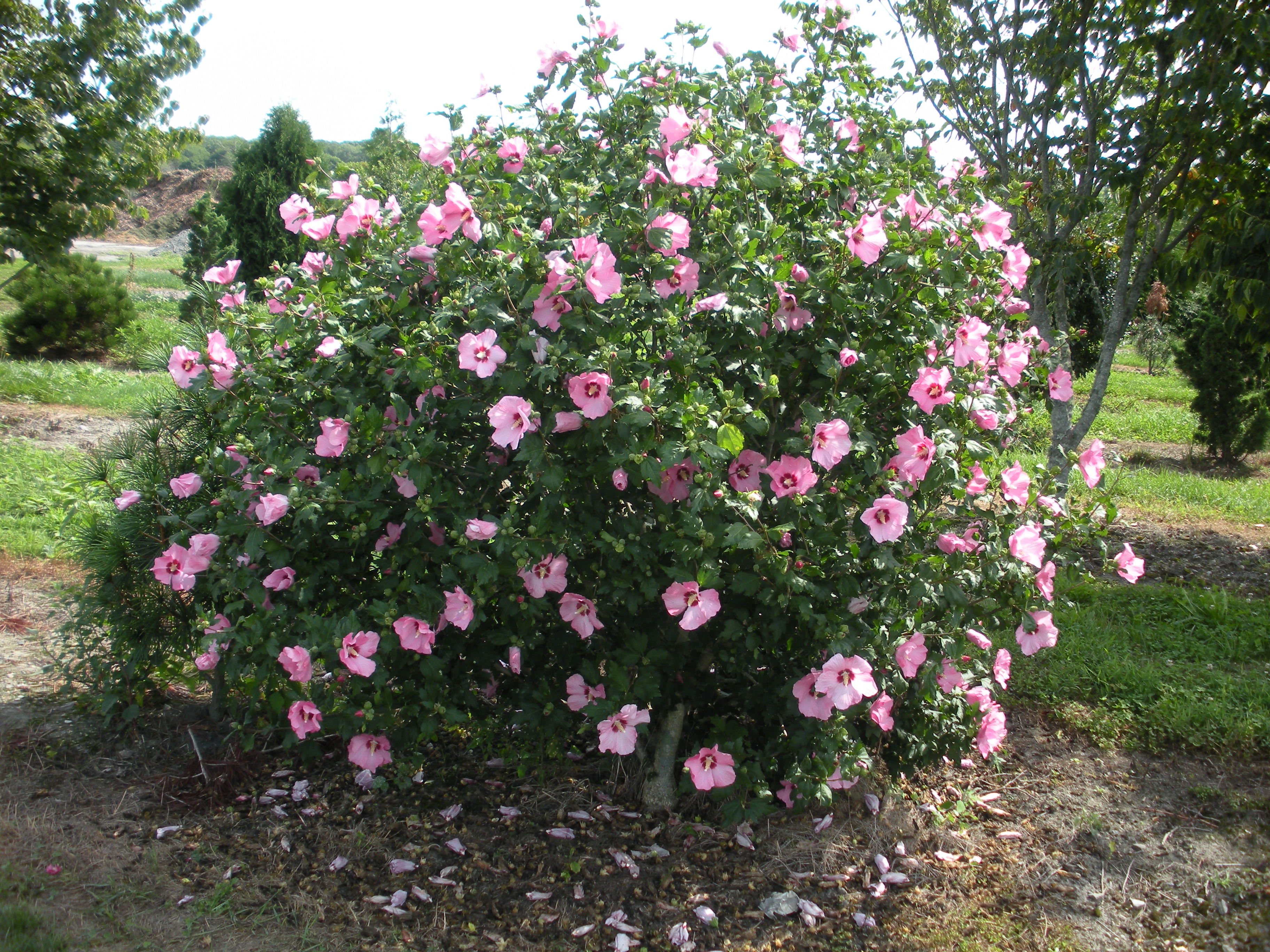
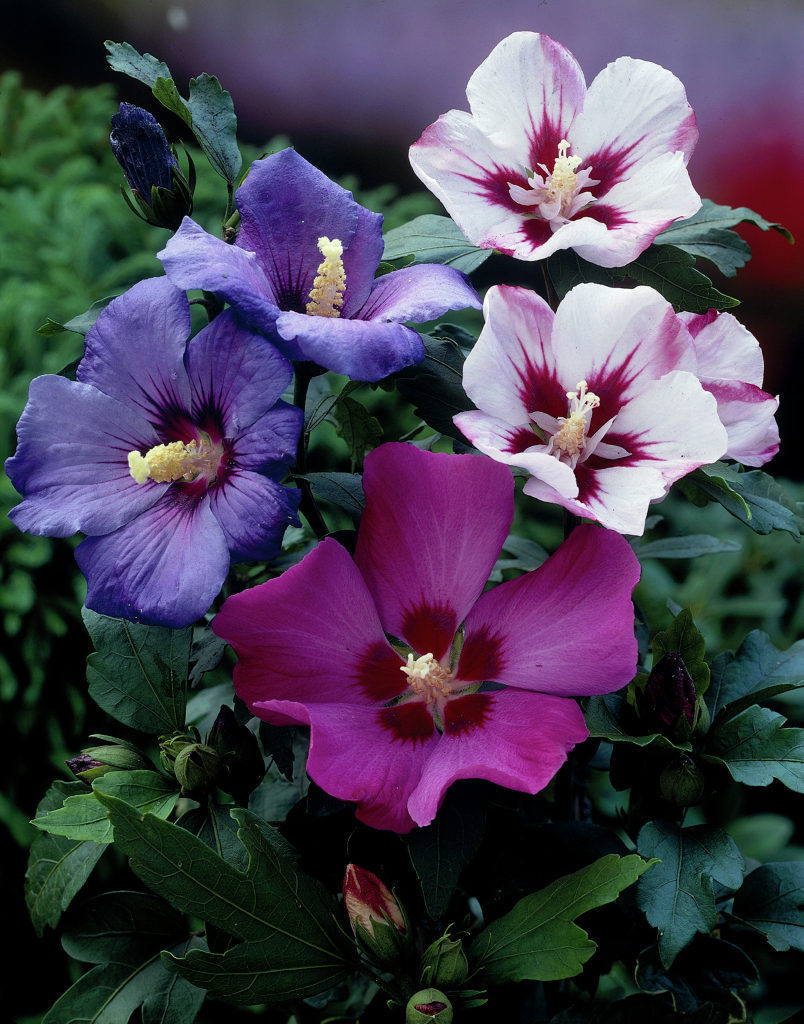
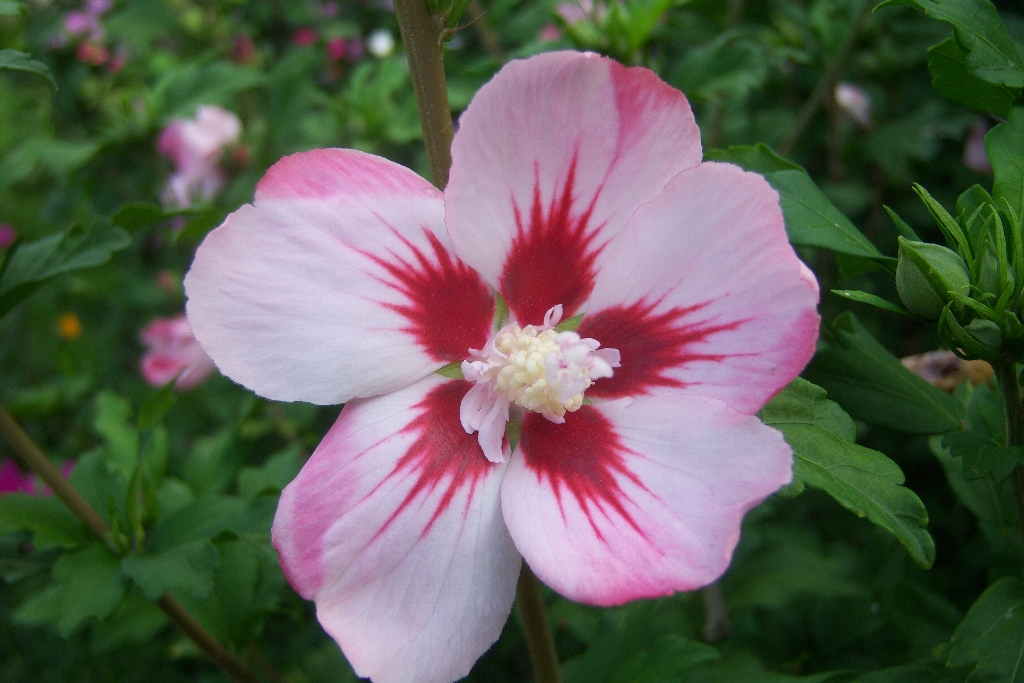
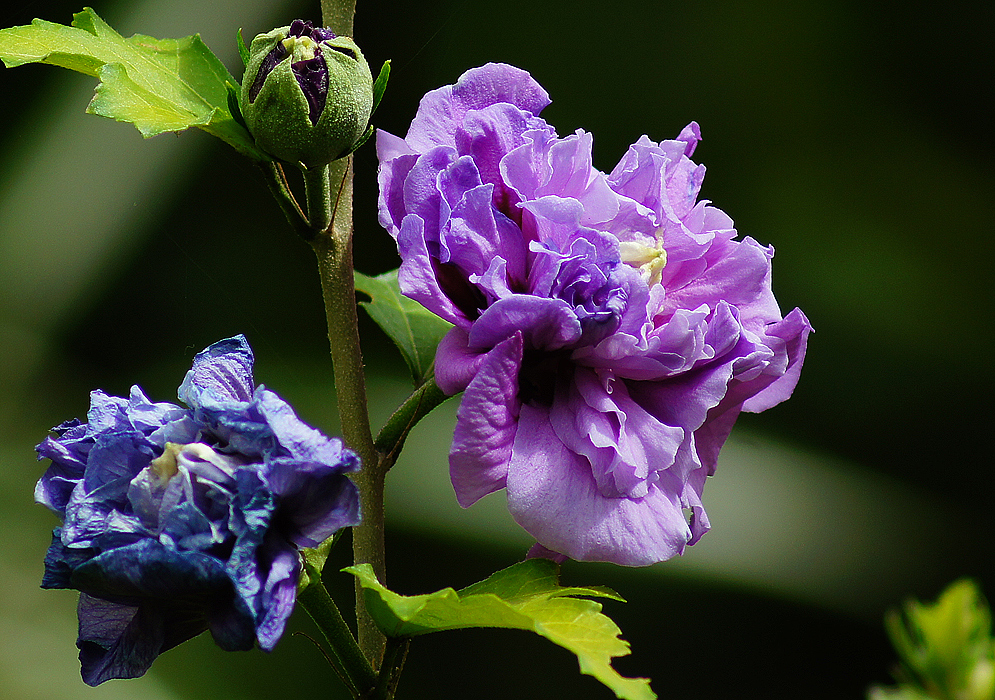
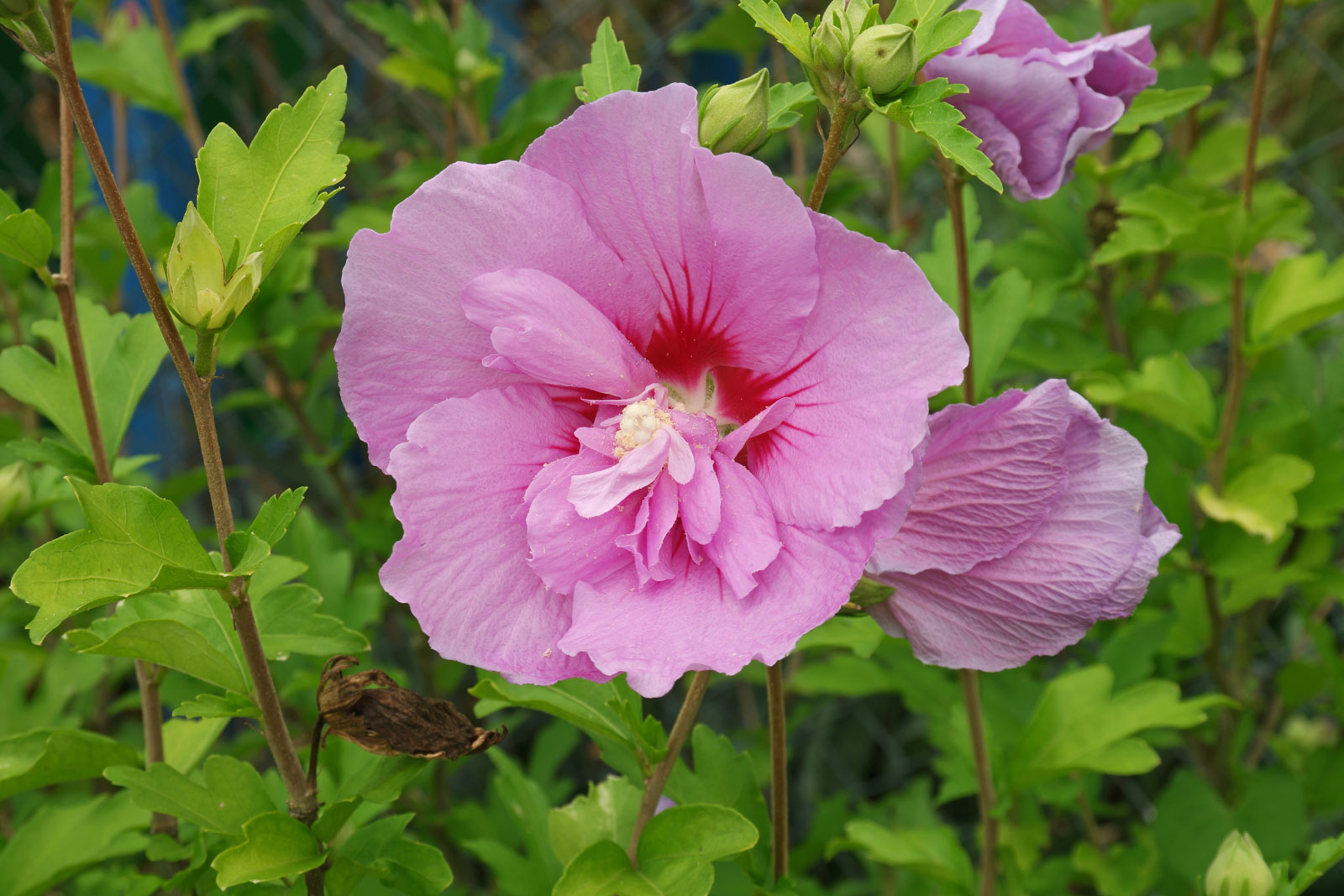
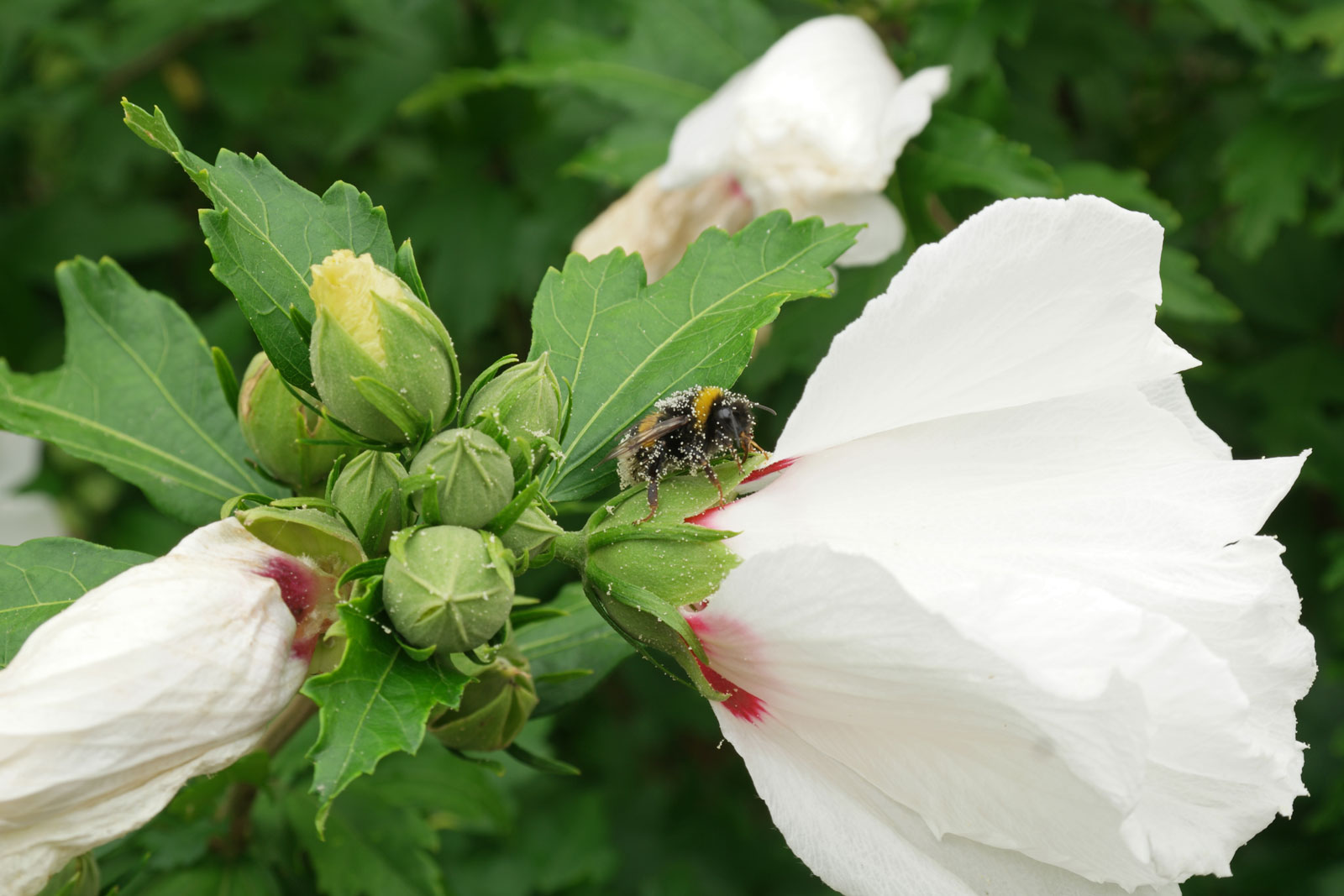
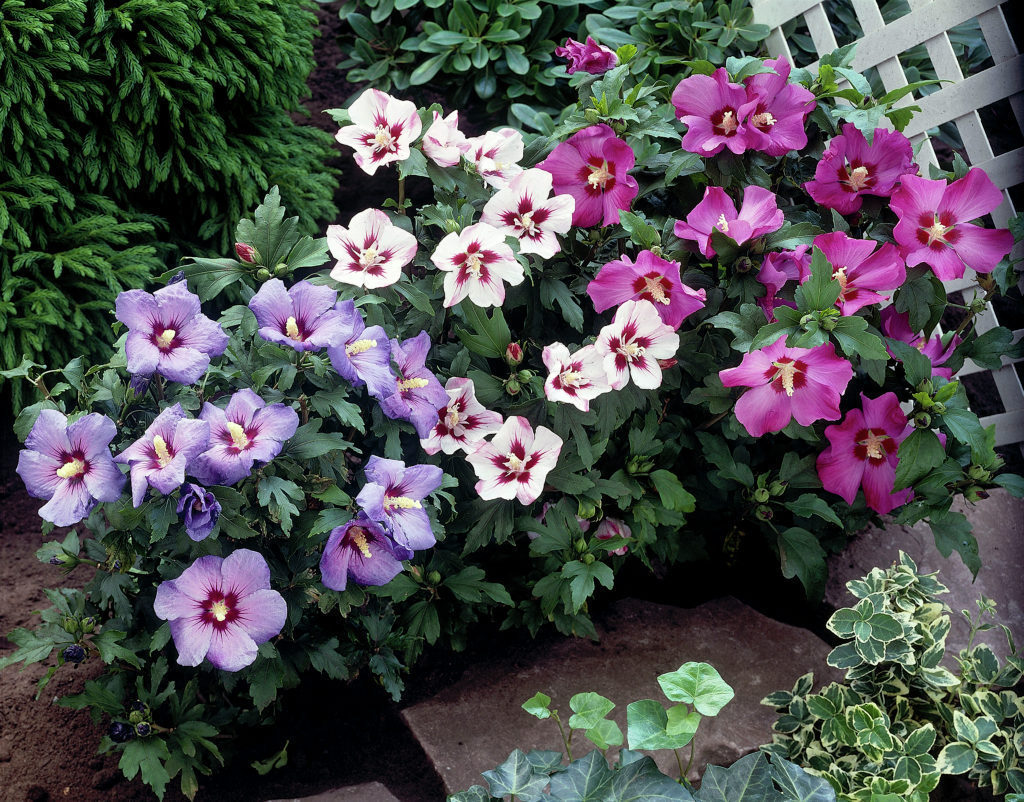
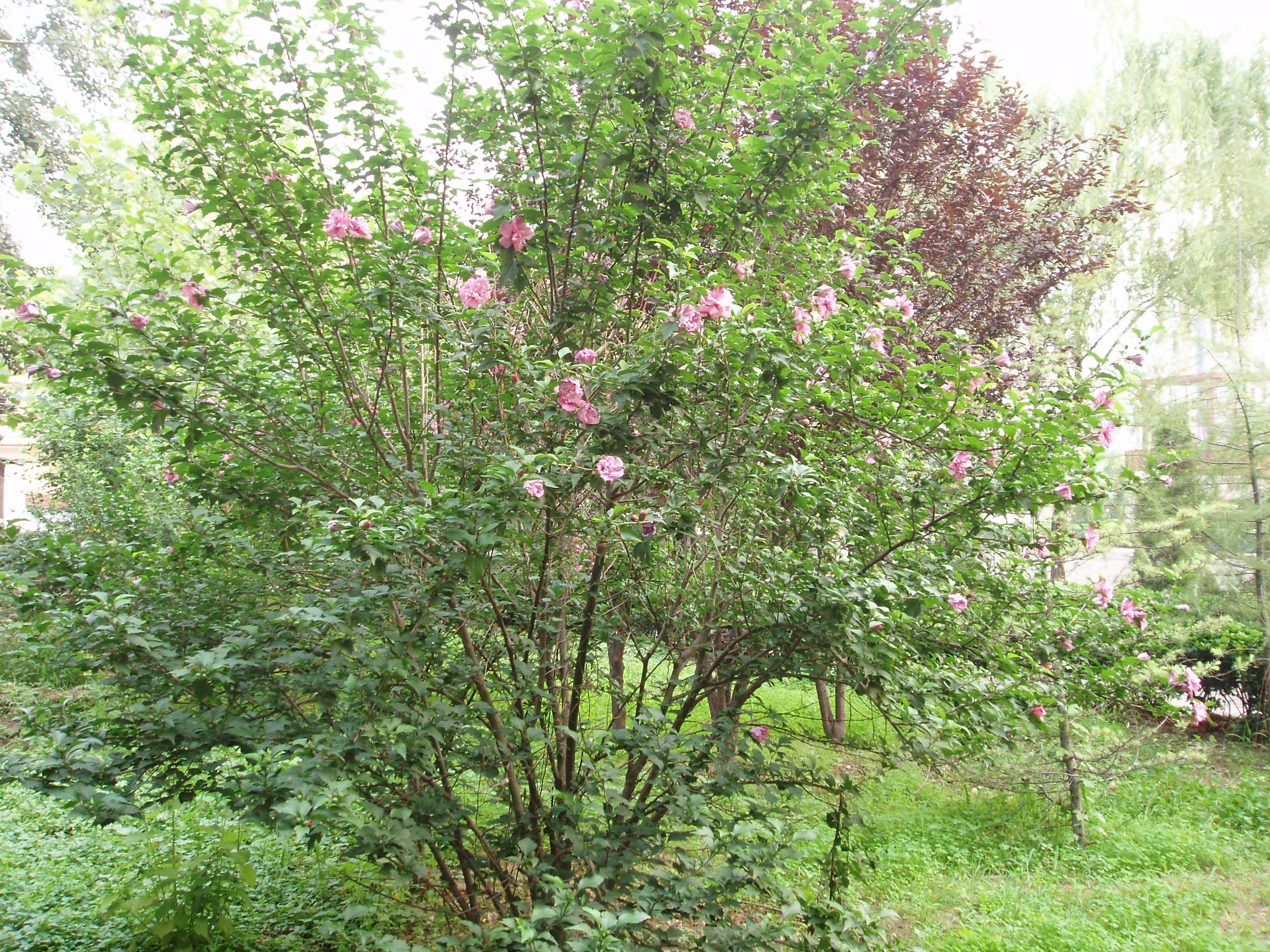
2.木槿HibiscussyriacusL.
俗名:喇叭花、朝天暮落花、荆条、木棉、朝开暮落花、白花木槿、鸡肉花、白饭花、篱障花、大红花
【形态】:落叶灌木。茎直立,嫩枝密被绒毛,小枝灰褐色。叶多为菱状卵形,长3~150px,先端有时3浅裂,基部楔形,边缘有缺刻。花单生叶腋,钟状,直径5~200px,单瓣或重瓣,有白、粉、红、紫等色,雄蕊多数,心皮多数,螺旋状排列于延长花托上。蒴果卵圆形,直径50px,有短缘,密被星状绒毛;种子熟时黑褐色。花期6~9月,果10~11月成熟。。
【分布】:我国特有树种,分布于我国长江流域各省区,各地广为栽培。
【习性】:喜光,喜温暖湿润气候和深厚、富于腐殖质的酸性土壤,稍耐阴和低温,适应
性强,不耐水湿。萌蘖力强,耐修剪。抗烟尘和有害气体能力强。
【繁殖】:常用扦插繁殖,播种、压条亦可。
【用途】:枝繁叶茂,夏、秋开花,满树花朵,花大有香气,花期长,为良好园林观赏树种。韩国国花。
Hibiscus syriacus is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family, Malvaceae. It is native to south-central and southeast China, but widely introduced elsewhere, including much of Asia. It was given the epithet syriacus because it had been collected from gardens in Syria. Common names include the rose of Sharon, Syrian ketmia, shrub althea, and rose mallow. It is the national flower of South Korea and is mentioned in the South Korean national anthem.、
Hibiscus syriacus
Common Name(s): Hibiscus、Rose of China、Rose of Sharon、Rose of-SharonShrub、 Althea
Description
Drought, wet soil, and air pollution tolerant; late to leaf out in spring; prefers hot weather; spring pruning will increase flower size; flowers on new growth; moderate to rapid growth rate. This plant is moderately salt tolerant. Despite it's name, Rose of Sharon is not related to roses at all.
Sun to partial shade; prefers moist, well-drained soil but tolerates wet soil.
Insects, Diseases, and Other Plant Problems: Rose of Sharon has been reported to be invasive in some states, including Virginia and Kentucky
Quick ID Hints:
1、large, tropical looking, 5-petaled flowers
2、erect, spreading habit with upright branches
3、3-lobed leaves are 2-4 inches long
4、simple, alternate, coarsely toothed leaves
5、5-valved, dehiscent capsule persists thru winter












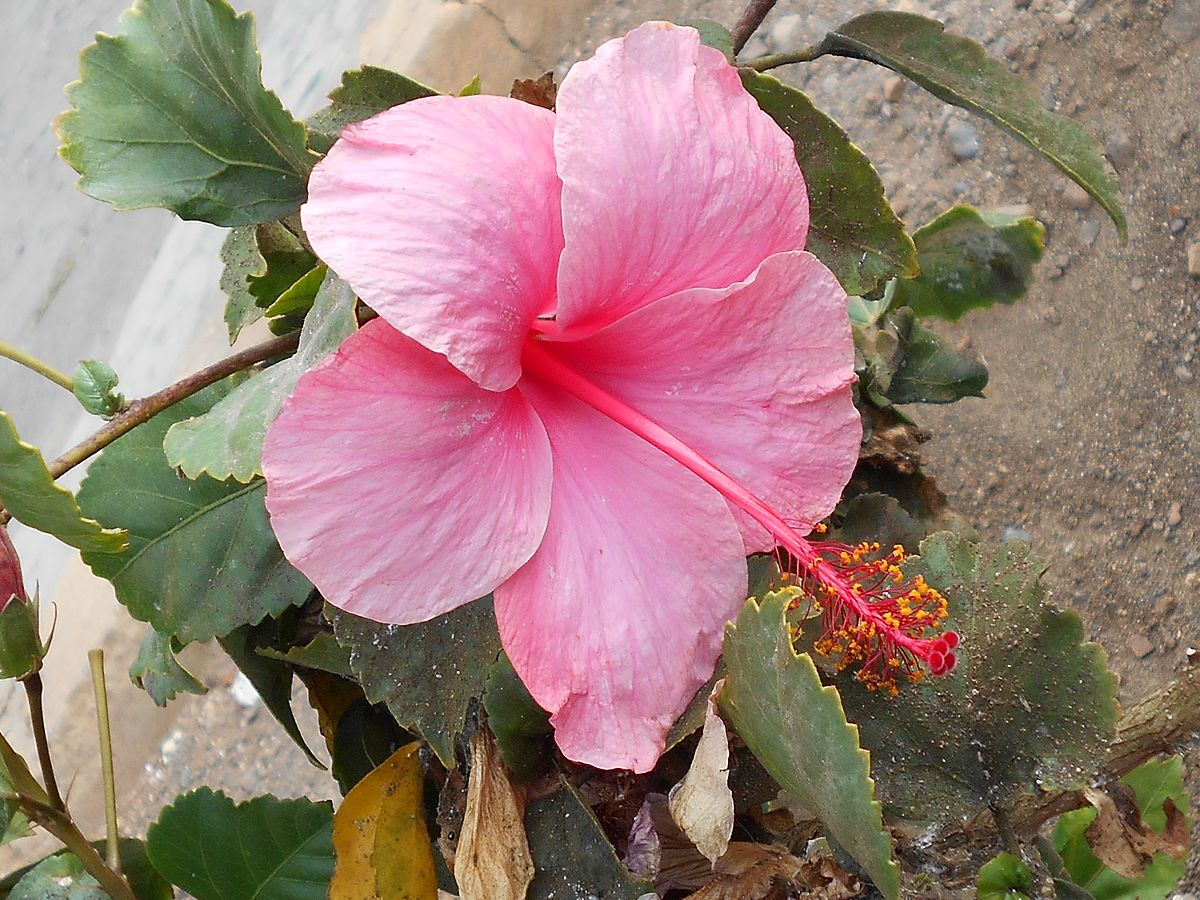
3.朱槿 (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.)
俗名:状元红、桑槿、大红花、佛桑、扶桑、花叶朱槿
【形态】:常绿灌木,直立多分枝,树冠椭圆形。叶互生,长卵形,长4~225px,边缘有粗齿,基部全缘,3出脉,上面有光泽。腋生花大,副萼6~7枚,线状分离;萼绿色,长约50px,裂片卵形或披针形;花冠直径cm,花瓣倒卵形,通常玫红、淡红、淡黄、白色等,有时重瓣;雄蕊柱超出花冠外,花梗长而有关节。蒴果卵形,有喙。花期5~11月。
【分布】:分布于我国南部,现各地栽培。
【习性】:喜光,喜温暖湿润气候。不耐阴、不耐寒、不耐旱,耐修剪。
【繁殖】:多以扦插繁殖,也可进行嫁接。
【用途】:扶桑花大色艳,花期长,是著名的观赏花卉。北方多盆栽观赏。马来西亚国花。
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis
Common Name(s): Chinese Hibiscus
Description:
This is a tropical evergreen plant known for its bold flowers that can be up to 6 inches across with a showy central tube. When grown outdoors it may rise to 10 feet. It has a spread of up to 8 feet, glossy green leaves, and declines when temperatures drop below 60F. This plant is often grown in containers and pruning helps to keep it compact.
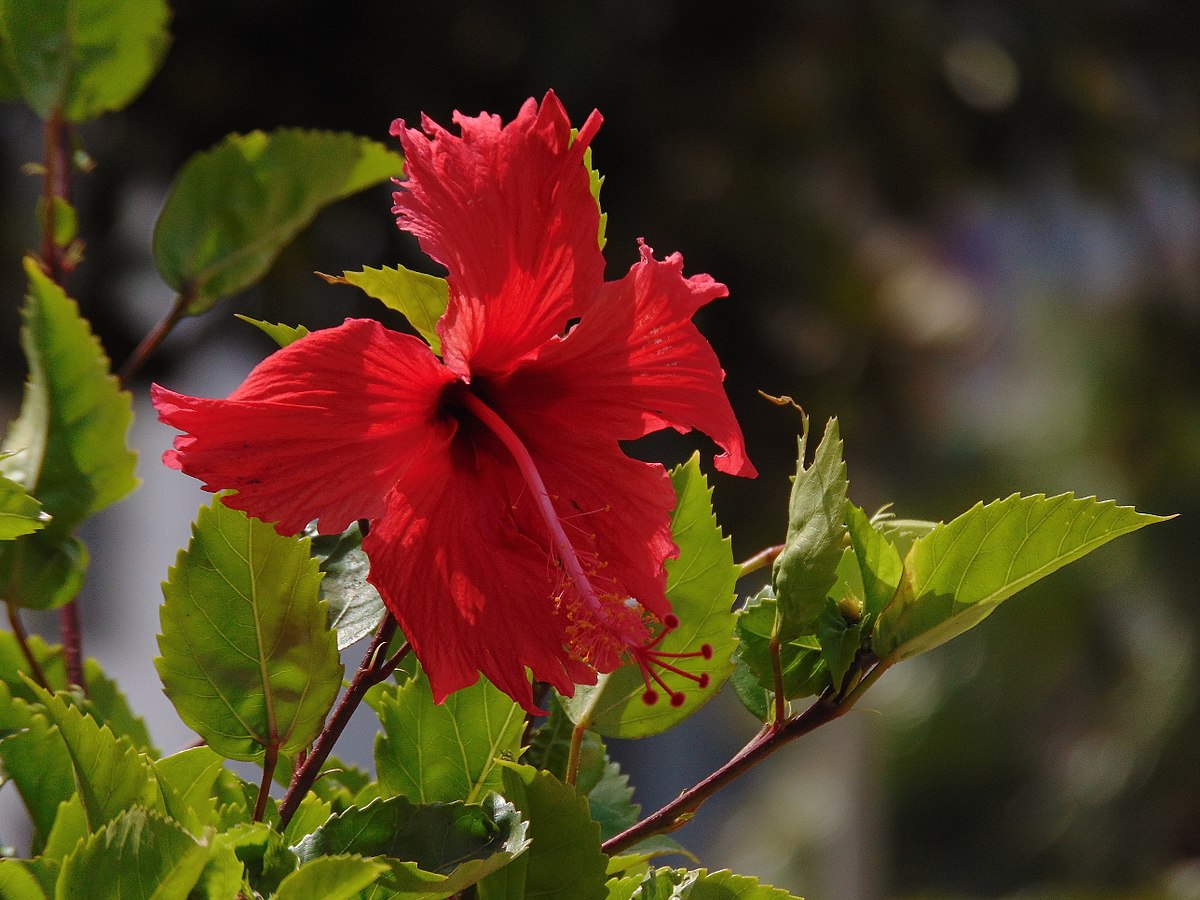
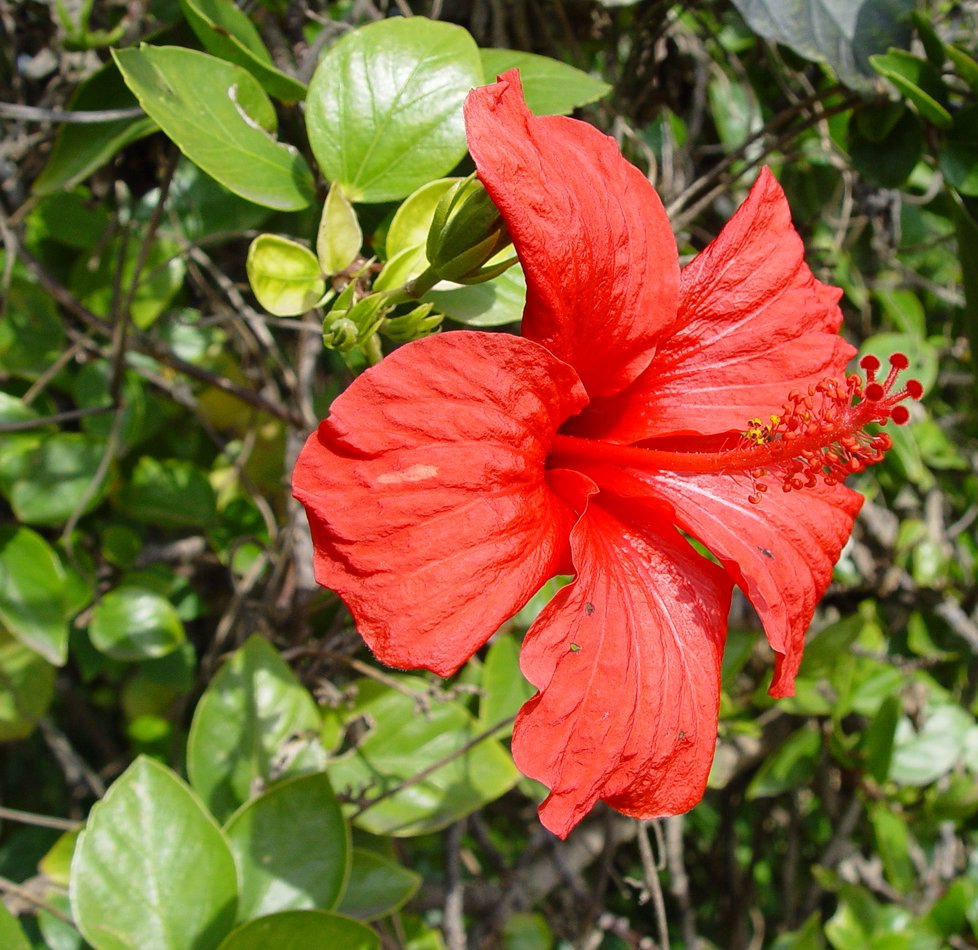
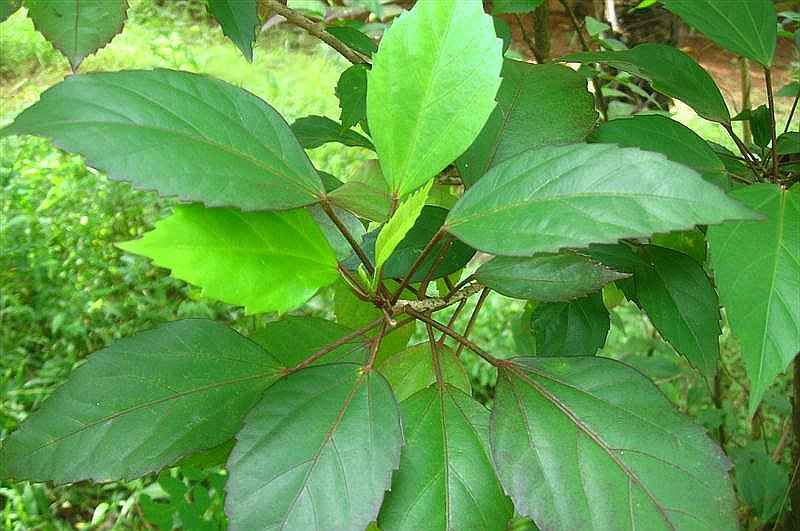
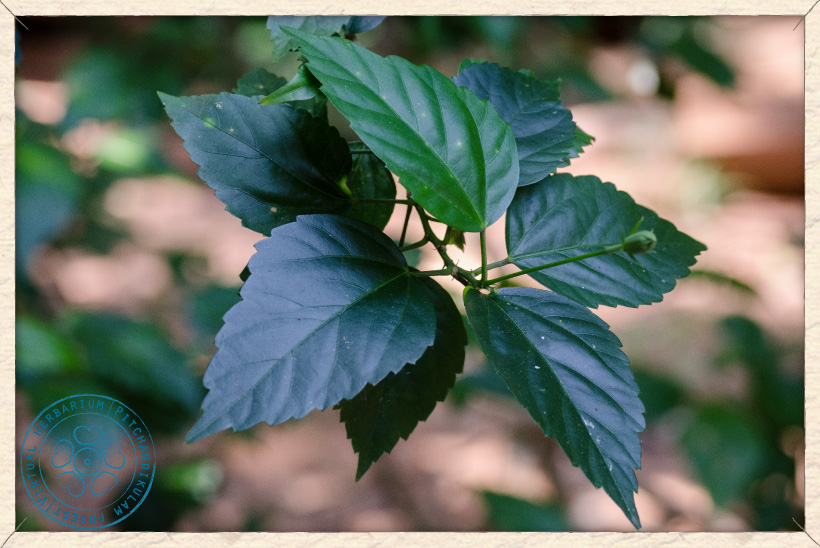
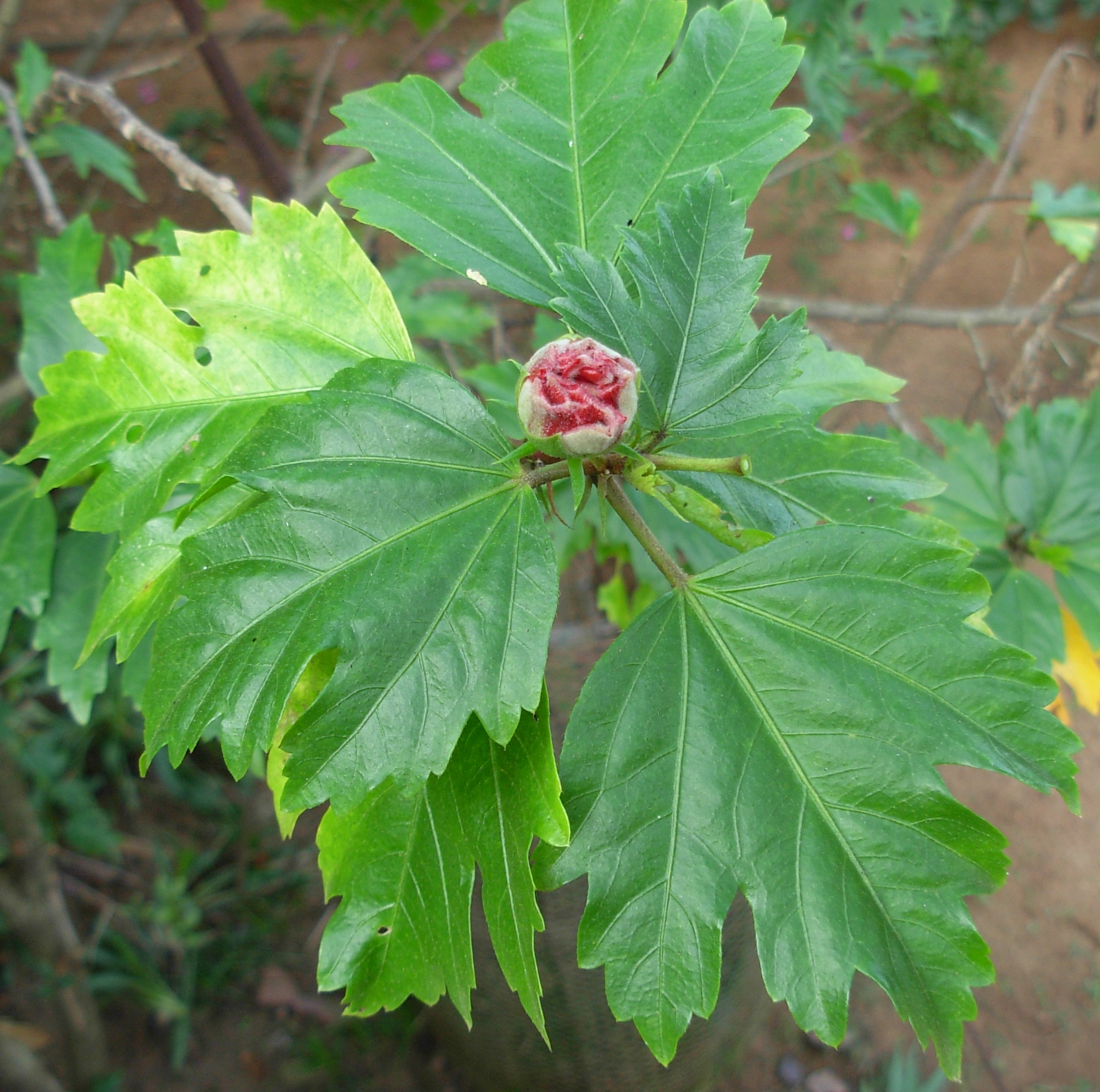
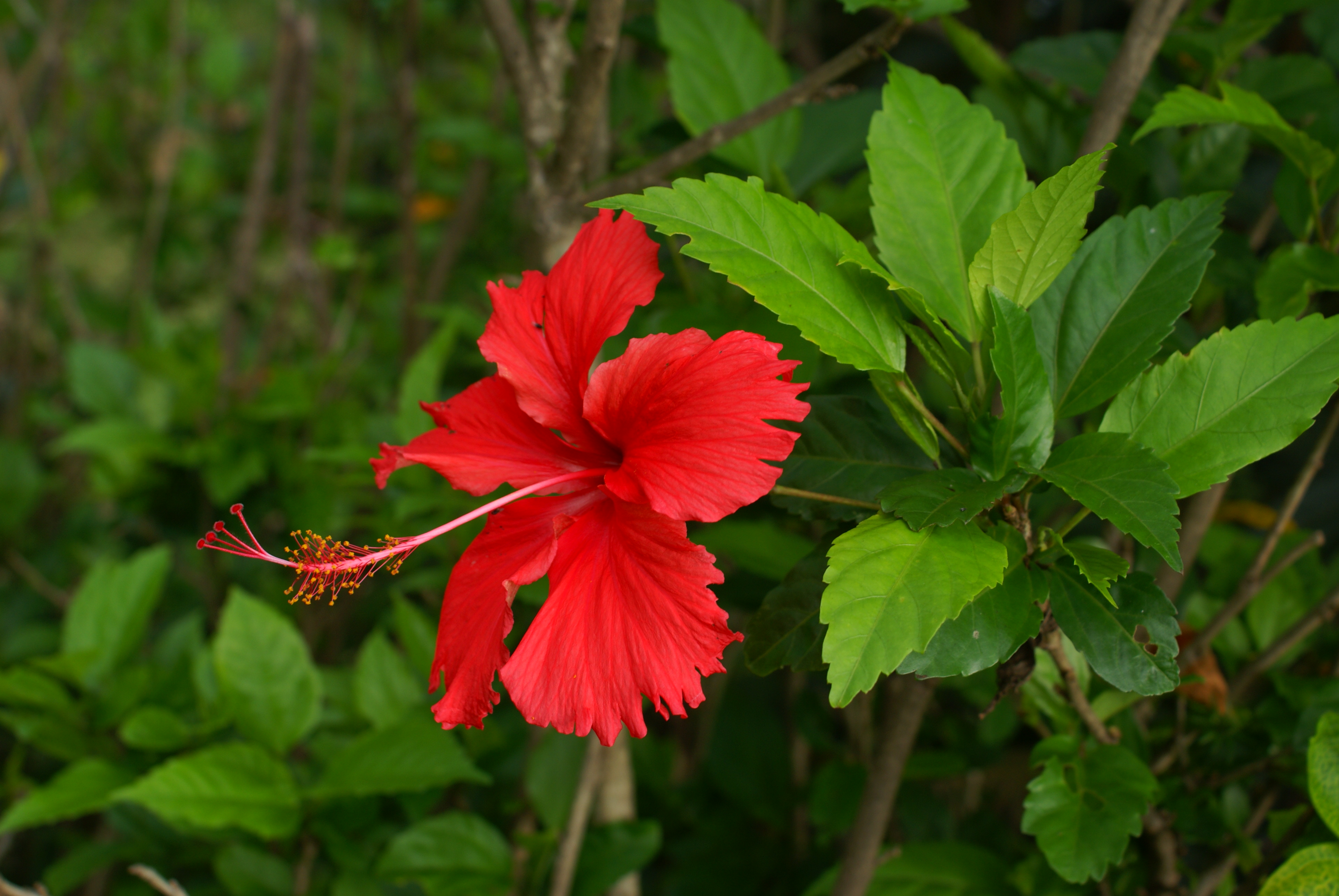





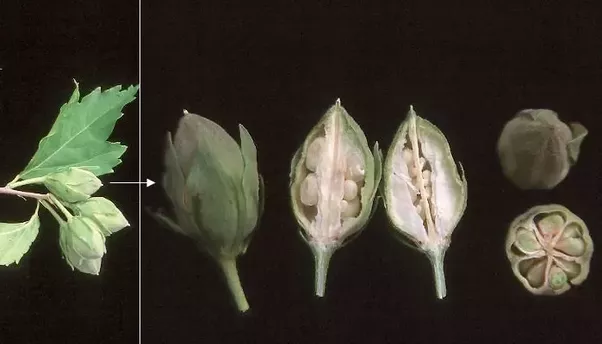


4.吊灯花(拱手花篮)HibiscusschizopetalusHook.f.
【形态】:灌木。枝叶均无毛。叶卵形或椭圆形,长4~175px,叶缘具锯齿;托叶线形。
花单生叶腋,长10~350px;花梗下垂,中部具关节;小苞片7~8枚,线形;花萼筒状,长约1.Scm,2~3浅裂;花冠红色,花瓣长5~175px,先端流苏状,外卷;雄蕊及花柱伸出花冠之外,长9~275px,花丝上半部分离;花柱5枚,柱头头状。蒴果圆柱状。花期3~11月。。
【分布】:原产于非洲东部。我国华南一带可露地栽培,北方温室栽培。
【习性】:喜高温、不耐寒,需在高温温室越冬。不耐阴。
【繁殖】:扦插繁殖。
【用途】:花形奇特、美丽,几乎全年开花。
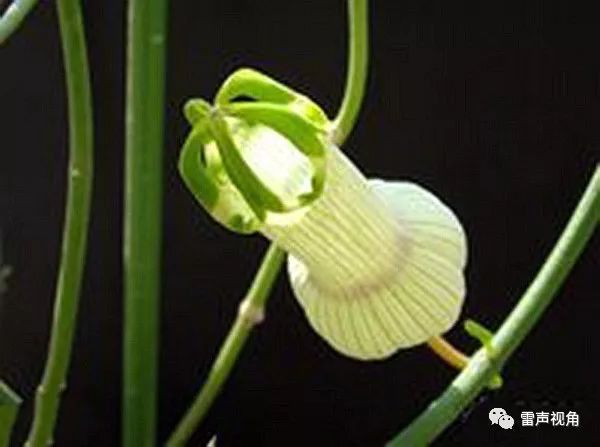
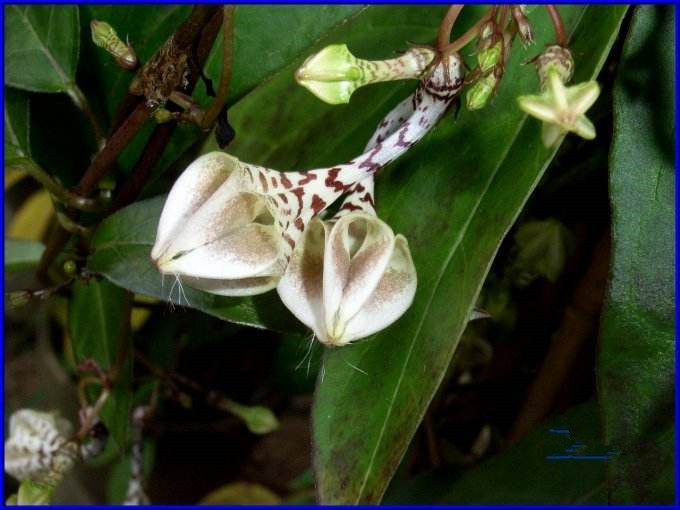
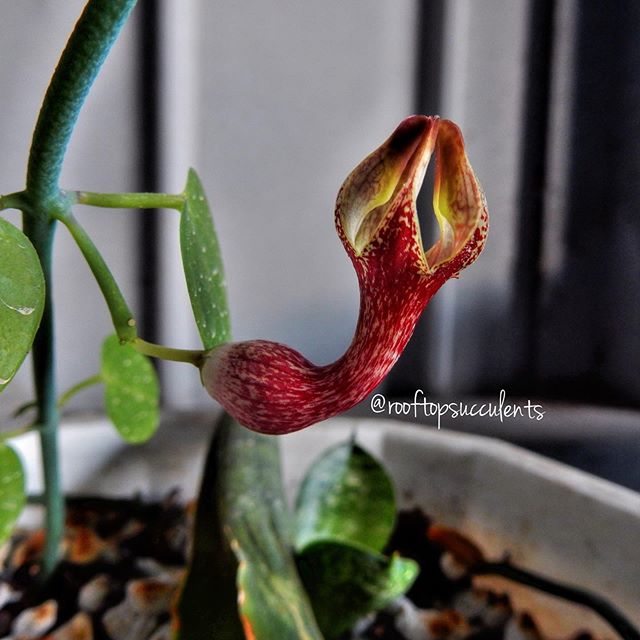
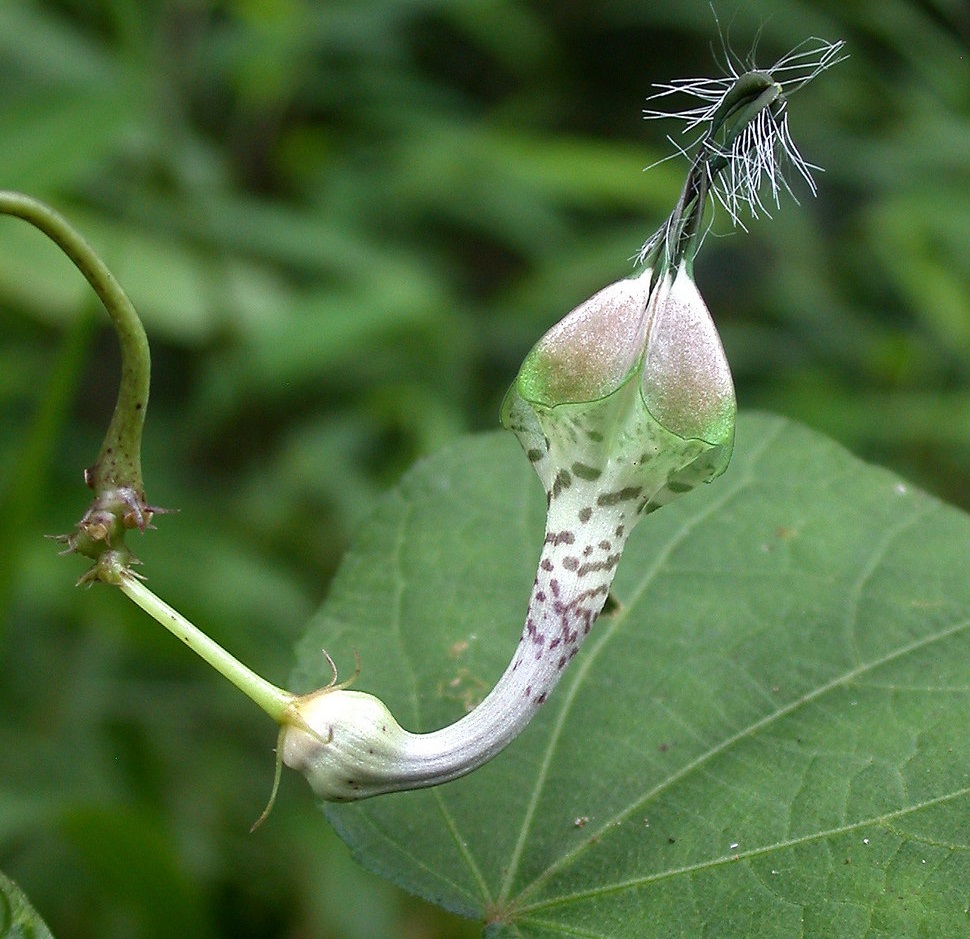
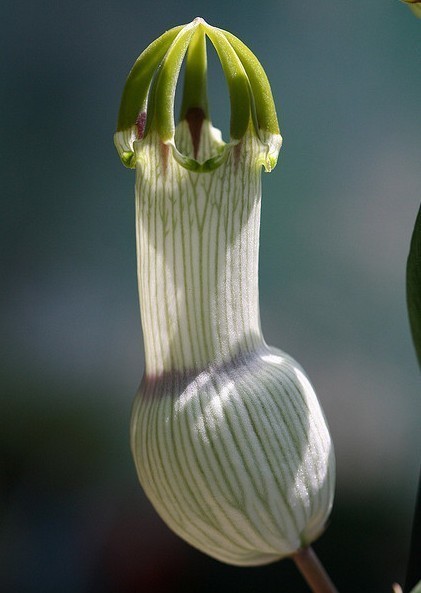





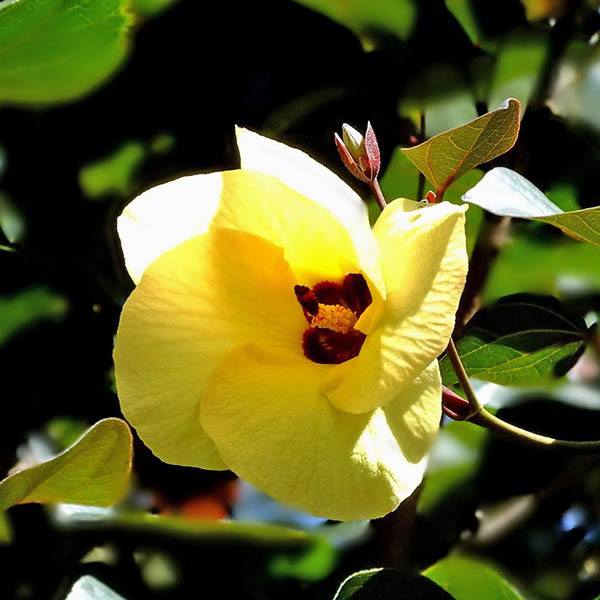
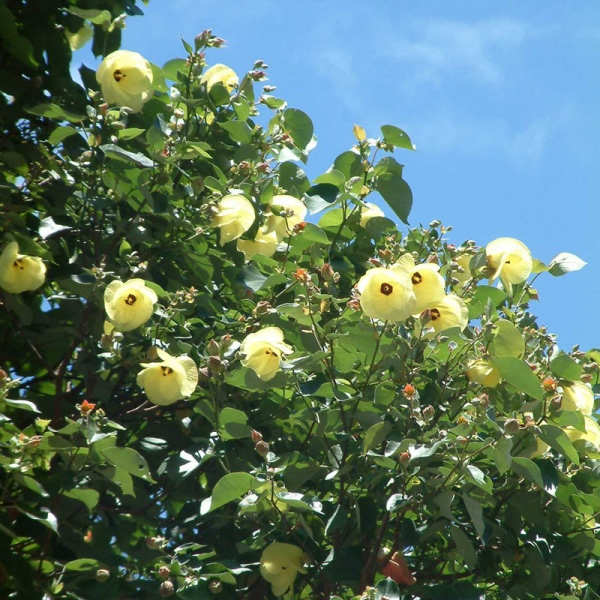
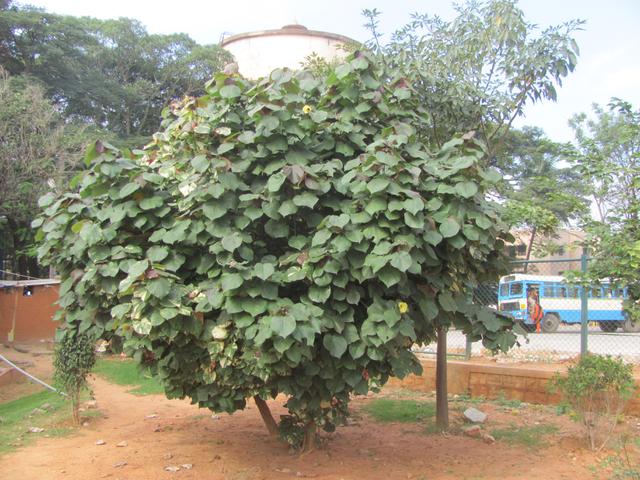
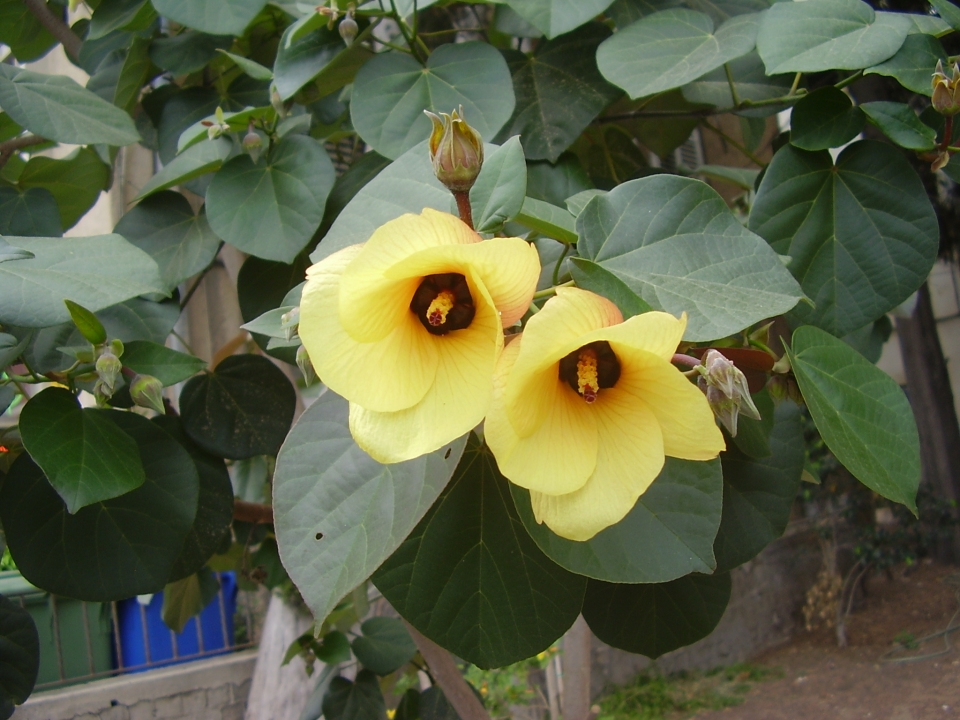
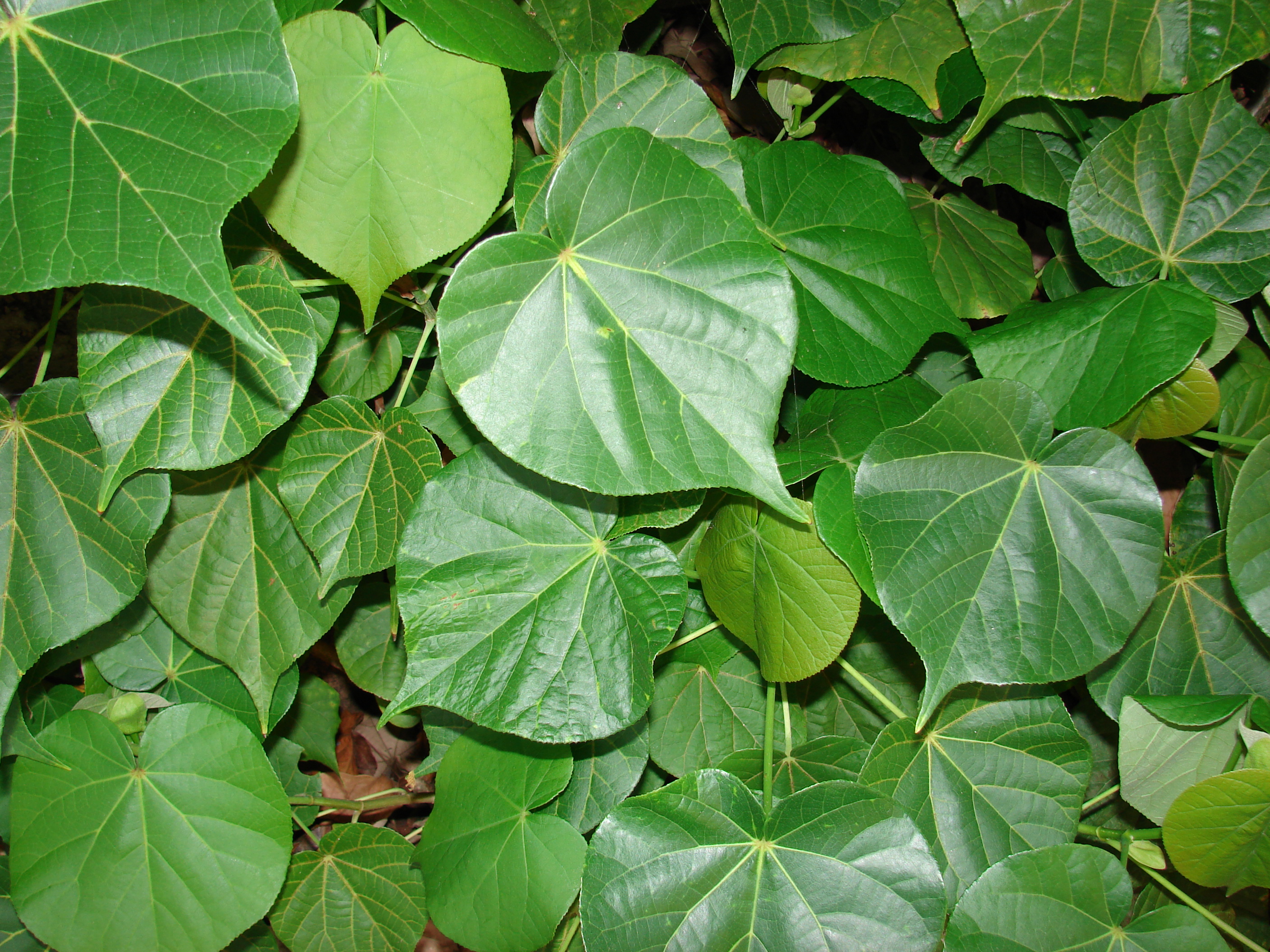
5.黄槿Hibiscus tiliaceus L.
黄槿(李文饶文集)右纳(中山传信录),桐花、海麻(海南),万年春(广东),盐水面头果(台湾)
【形态】:常绿小乔木。树皮灰白色,小枝近无毛。广卵形叶革质,背面灰白色,密生星状绒毛;叶柄长8~200px;托叶早落。花顶生或腋生,常数朵排成聚伞花序;小苞片7~10,线状披针形,中部以下连合成杯状;萼长1~75px,基部合生,裂片5,披针形;花冠黄色,直径1600px。蒴果卵圆,长约50px,5瓣裂,果瓣木质;种子多数。花期6~8月。
【分布】:分布于我国台湾、广东;日本、印度、马来西亚和大洋洲也有。
【习性】:对土壤要求不严,耐瘠薄和干旱。深根性,耐水湿。
【繁殖】:播种或扦插法。
【用途】:树冠球形,整齐,赏,可作为海岸防护树种。枝叶浓密。黄槿生活力极强,宜作庭荫树、行道树及盆栽观
Hibiscus tiliaceus is a species of flowering tree in the mallow family, Malvaceae, that is native to the Old World tropics. Common names include sea hibiscus, beach hibiscus, coastal hibiscus, coastal cottonwood, green cottonwood.The specific epithet, "tiliaceus", refers to its resemblance of the leaves to those of the related Tilia species.
Hibiscus tiliaceus is a tree native to the shores of the Pacific and Indian oceans, today cultivated or naturalised throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the world, particularly in coastal areas. It is grown mainly as an ornamental tree for landscaping, although its wood, bark and flowers have been used for various purposes. It is known by several common names, including 'Cotton-tree' or 'Cottonwood' (Australia), 'Purau' (Tahiti), 'Vau' (Fiji), 'Hau' (Hawaii) and 'Mahoe' (US, mainland?). The Latin species epithed was chosen by Linnaeus because the leaves of H. tiliaceus are similar in shape to those of the linden tree, whose Latin name is Tilia. A group of 22 closely related species in the genus Hibiscus, including H. tiliaceus, has been recently reclassified by Malvaceae taxonomist Paul A. Fryxell into the new genus Talipariti(黄槿属). This article still uses the old name, but this species may eventually be widely known as Talipariti tiliaceum instead.
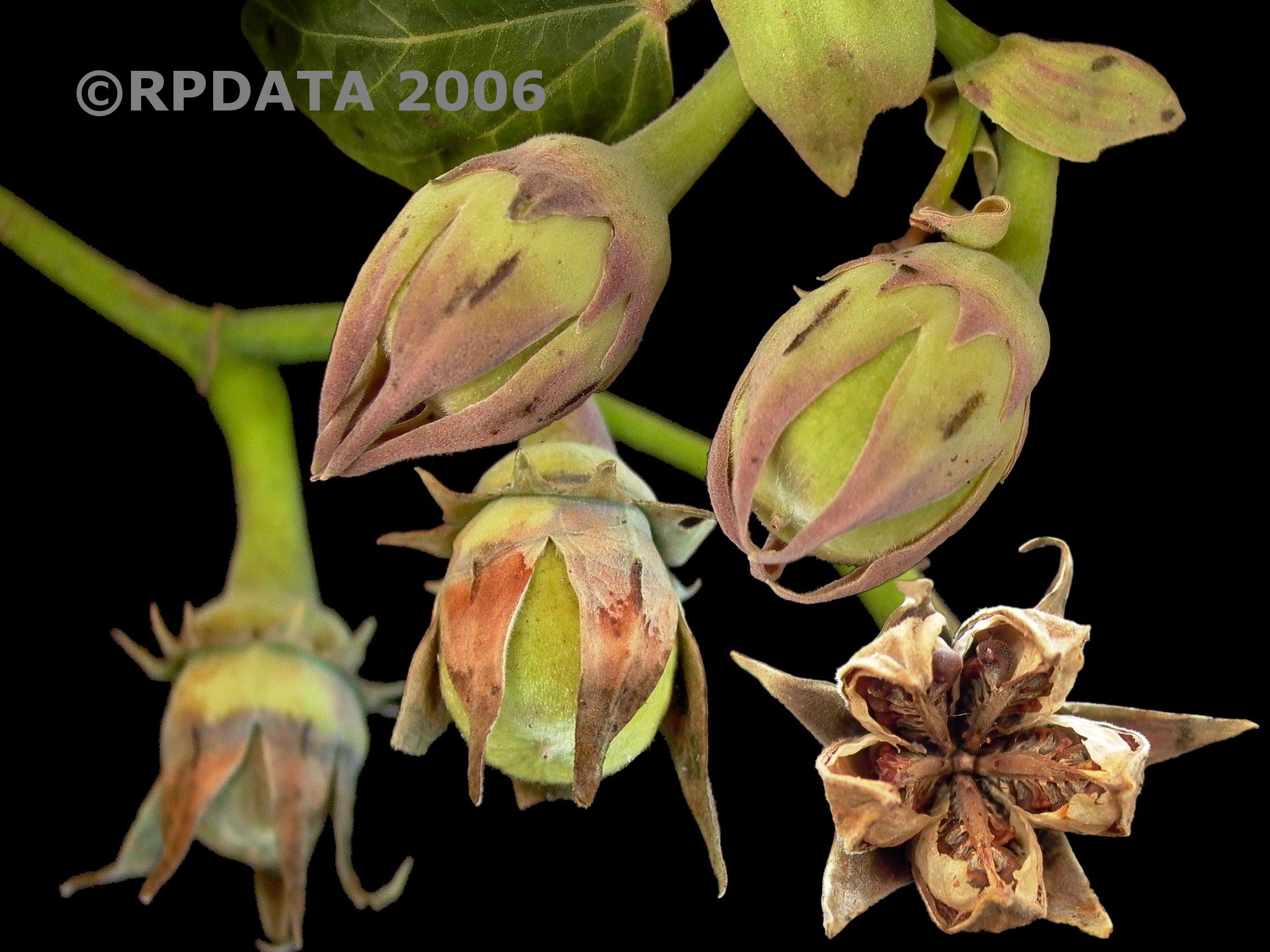










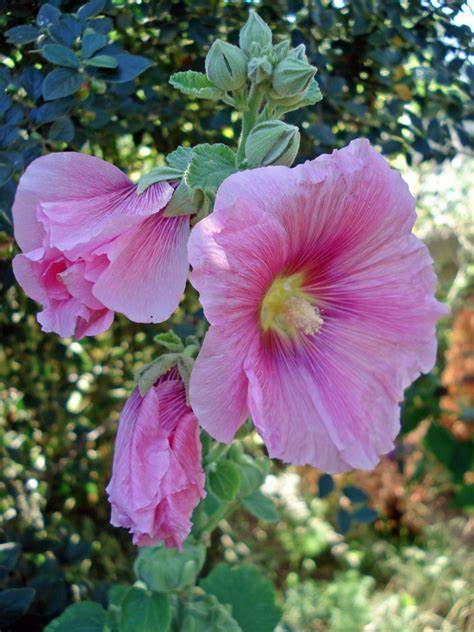
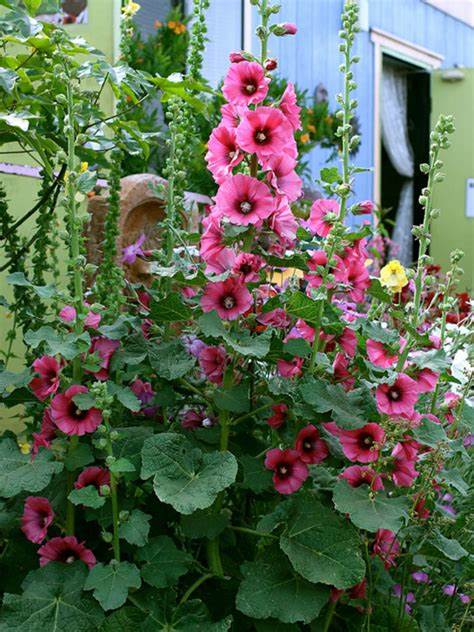
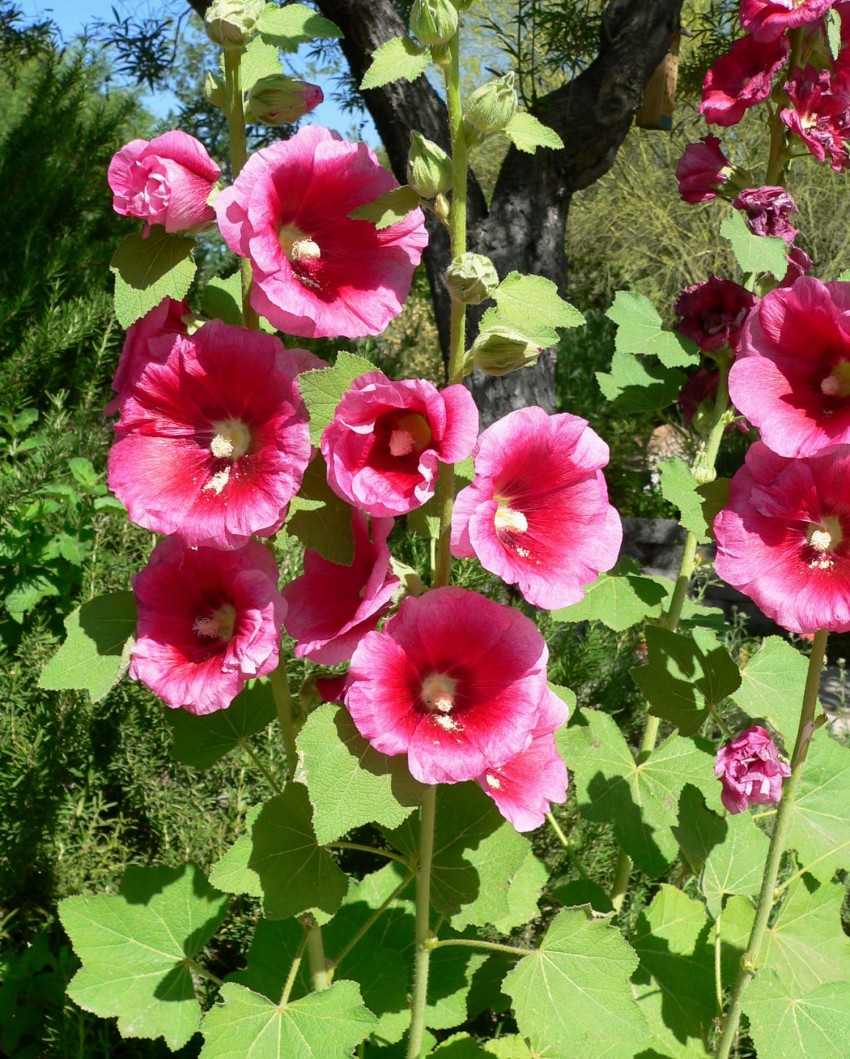
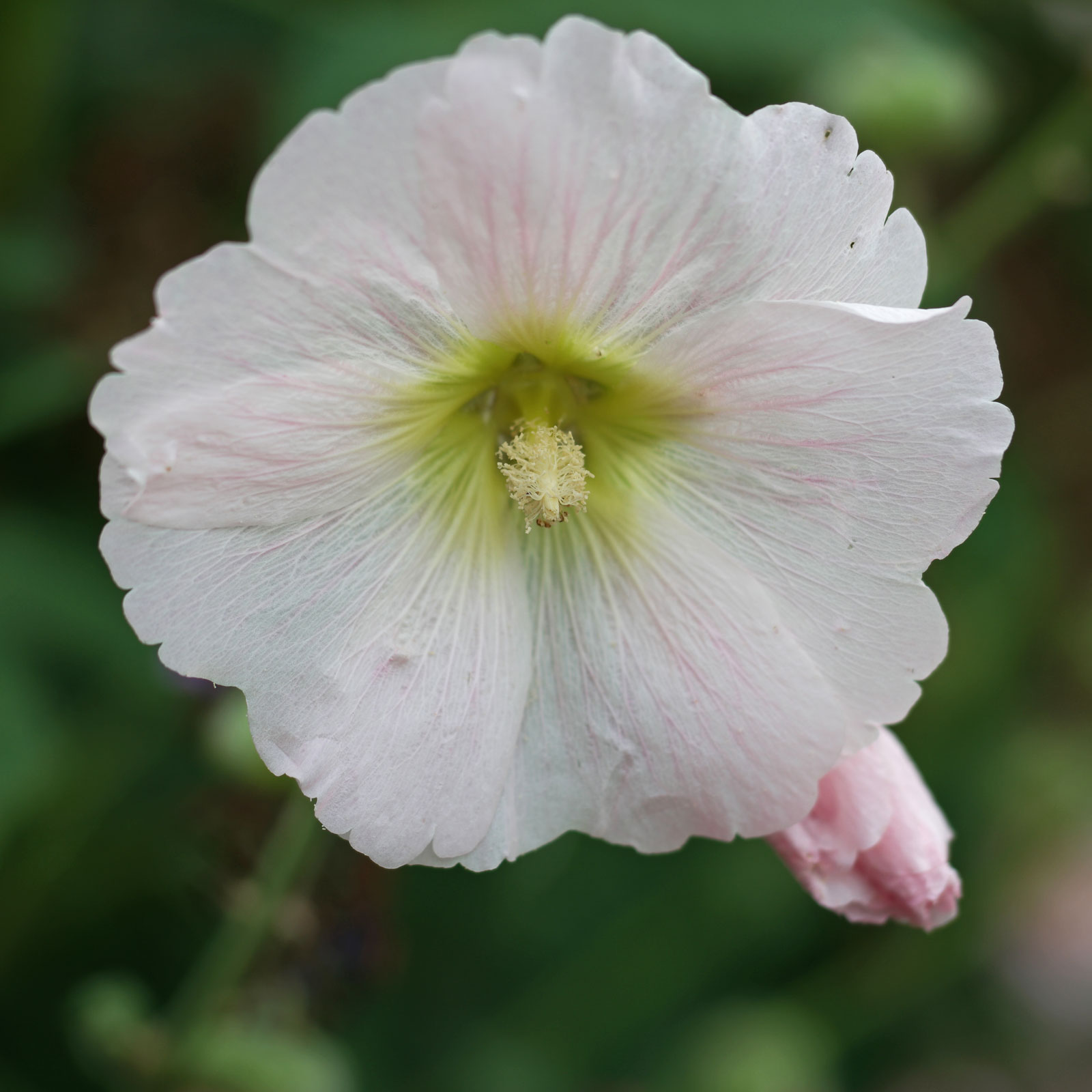
蜀葵(尔雅、嘉祐本草、图考) (Alcea rosea Linnaeus)
俗 名:淑气(蜀季、舌其、暑气、蜀芪、树茄)花(通称),一丈红(陕西、贵州),麻杆花(河南),棋盘花(四川、贵州),栽秧花(贵州),斗蓬花(陕西),“阿克来依里”(新疆维语)
形态特征
因在6月麦子熟时开花,故有名大麦熟;
生活型: 二年生直立草本;
株: 高达2米,茎枝密被刺毛;
茎: 茎枝密被星状毛和刚毛;
叶: 叶近圆心形,直径6-16厘米,掌状5-7浅裂或波状棱角,上疏被星状柔毛、粗糙,下被星状长硬毛或绒毛;叶柄长5-15厘米,被星状长硬毛;托叶卵形,长约8毫米,先端具3尖;
花: 花呈总状花序顶生单瓣或重瓣,有紫、粉、红、白等色;花期6-8月,蒴果,种子扁圆,肾形;喜阳光,耐半阴,忌涝;
果: 果盘状,直径约2厘米,被短柔毛,具纵槽;
种子: 种子肾形;
生态习性
国内产地: 在中国分布很广,华东、华中、华北均有种植;
国外分布: 原产四川,故名曰蜀葵;
物候期: 花期2-8月;
Alcea rosea, the common hollyhock, is an ornamental dicot flowering plant in the family Malvaceae. It was imported into Europe from southwestern China during, or possibly before, the 15th century. William Turner, a herbalist of the time, gave it the name "holyoke" from which the English name derives.
Alcea rosea
Common Name(s): HollyhockHollyhocks
Description
Alcea rosea, or Hollyhocks, are herbaceous flowering plants that reseed themselves and can produce colonies of plants that return in the garden year after year. They are typically found in cultivated areas and rarely in "the wild". Their original habitat is unknown, but the plant is probably a cultigen that started out in Turkey. Note that it is sometimes listed in nursery catalogs under Althaea.
The plant prefers full to partial sun, a heavy, rich, organic soil and seeds, sown in late summer or early fall, will flower the following summer. The plant tolerates a wide range of soil conditions and some light shade, but will not tolerate wet winter soils. Considered a biennial or short-lived perennial. It is a very ornamental plant and the flowers come in a number of various colors, from lavender(淡紫色) to red to yellow, and resemble Papaver somniferum (poppies罂粟). The flowers grow on rigid, towering spikes of 5 to 8 feet tall and usually do not require staking. The plant has a long bloom period of June to August.











