-
1 主页
-
2 资料
大戟科——EUPHORBIACEAE
1、乔木、灌木或草本,常有乳状汁液,白色,稀为淡红色。
2、叶互生,少有对生或轮生,单叶,稀为复叶,或叶退化呈鳞片状,边缘全缘或有锯齿,稀为掌状深裂;具羽状脉或掌状脉;叶柄长至极短,基部或顶端有时具有1-2枚腺体;
3、花单性,雌雄同株或异株,单花或组成各式花序,通常为聚伞或总状花序,
4、果为蒴果,常从宿存的中央轴柱分离成分果爿,或为浆果状或核果状;种子常有显著种阜,胚乳丰富、肉质或油质,胚大而直或弯曲,子叶通常扁而宽,稀卷叠式。
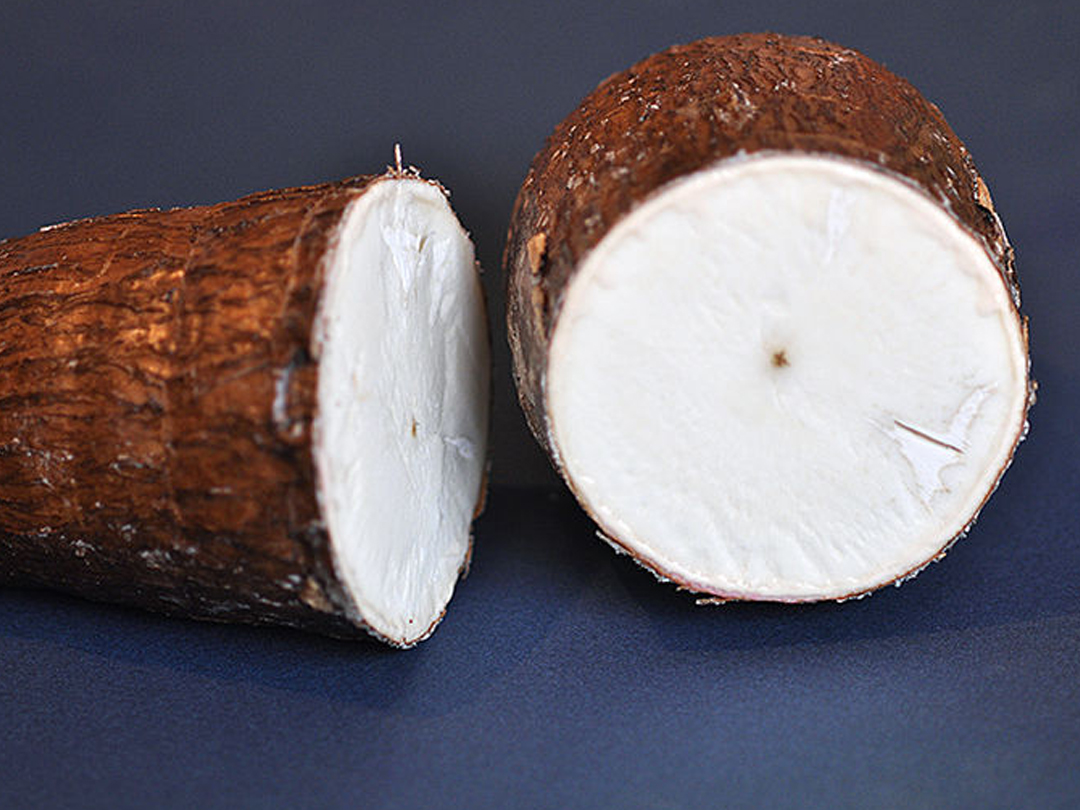
约300属,5000种,广布于全球,但主产于热带和亚热带地区。最大的属是大戟属 Euphorbia Linn.,约2000种。我国连引入栽培共约有70多属,约460种,分布于全国各地,但主产地为西南至台湾。
本科植物起源较早,
大戟科有多种经济植物,最重要的为橡胶树 Hevea brasiliensis(Willd. ex A. Juss.) Muell. Arg.,为主要产橡胶的植物,世界热带地区约有30多个国家和地区引种;我国广东、海南、广西南部和云南南部也较大规模种植。油桐 Vernicia fordii (Hemsl.) Airy Shaw. 和木油桐 V. montana Lour. 产桐油,为最好的干性油。乌桕 Sapium sebiferum (Linn.) Roxb. 产蜡和油,为蜡烛和肥皂的原料。蓖麻 Ricinus communis Linn. 种子产蓖麻油,供药用,其叶可饲养蓖麻蚕。粗糠柴 Mallotus philippinensis (Lam.) Muell. Arg. 的树皮富含单宁,可作染料。巴豆 Croton tiglium Linn. 为著名泻药,又可作杀虫剂,也产单宁。余甘子 Phyllantbus emblica Linn. 的果富含高量维生素C,供食用,干叶可作枕心填料。木薯 Manihot esculenta Crantz 的块根含丰富的淀粉,是人类的重要食物之一;叶可喂蚕。巴豆属和大戟属中有多种植物产树脂。变叶木属 Codiaeum A. Juss. 叶下珠属 Phyllanthus Linn.,麻风树属 Jatropha Linn. 及大戟属等多种植物,广为栽培供观赏。在热带地区,有刺的大戟属植物常栽作绿篱。产于非洲南部的大戟科植物好望角毒漆 Hyaenanche capensis Pers.,是已知有毒植物中含毒性最强的一种。毛果算盘子 Glochidion eriocarpus Champ. ex Benth.,叶下珠 Phyllanthus urinaria Linn.、甘遂 Euphorbia kansui Liou 和香鸡骨 Croton crassifolius Geisel. 等大多数种类均能作中草药,但多数有毒,宜慎用。
一、铁苋菜属Acalypha L.
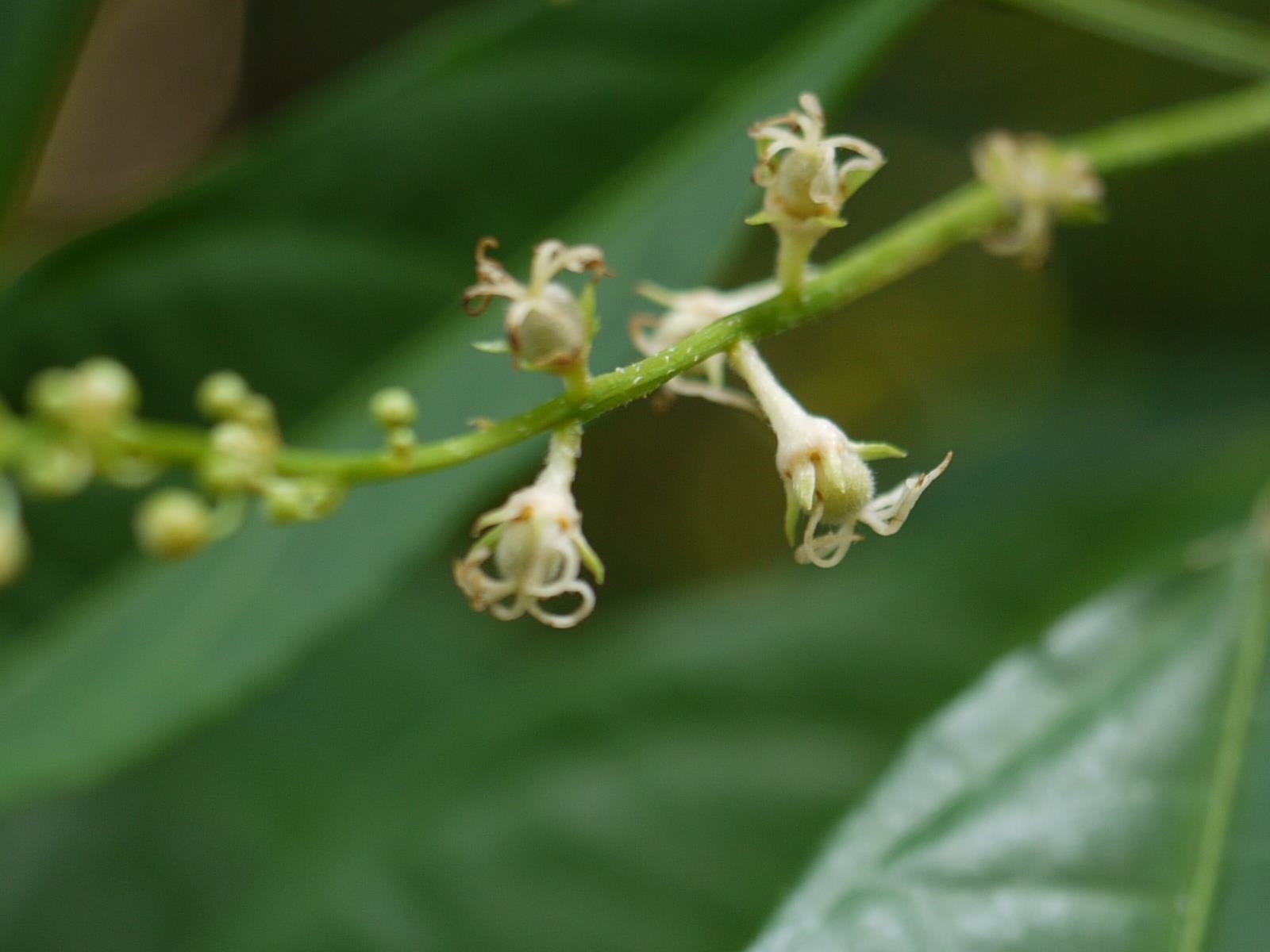
一年生或多年生草本,灌木或小乔木。叶互生,通常膜质或纸质,叶缘具齿或近全缘,具基出脉3-5条或为羽状脉;叶柄长或短;托叶披针形或钻状,有的很小,凋落。雌雄同株,稀异株,花序腋生或顶生,雌雄花同序或异序;雄花序穗状,雄花多朵簇生于苞腋或在苞腋排成团伞花序;雌花序总状或穗状花序,通常每苞腋具雌花1-3朵,雌花的苞片具齿或裂片,花后通常增大;雌花和雄花同序 (两性的) ,花的排列形式多样,通常雄花生于花序的上部,呈穗状,雌花1-3朵,位于花序下部;花无花瓣,无花盘;雄花:花萼花蕾时闭合的,花萼裂片4枚,镊合状排列;雄蕊通常8枚,花丝离生,花药2室,药室叉开或悬垂,细长、扭转,蠕虫状;不育雌蕊缺;雌花:萼片3-5枚,覆瓦状排列,近基部合生;子房3或2室,每室具胚珠1颗,花柱离生或基部合生,撕裂为多条线状的花柱枝。蒴果,小,通常具3个分果爿,果皮具毛或软刺;种子近球形或卵圆形,种皮壳质,有时具明显种脐或种阜,胚乳肉质,子叶阔、扁平。
约450种,广布于世界热带、亚热带地区。我国约17种,其中栽培2种,除西北部外,各省区均有分布。
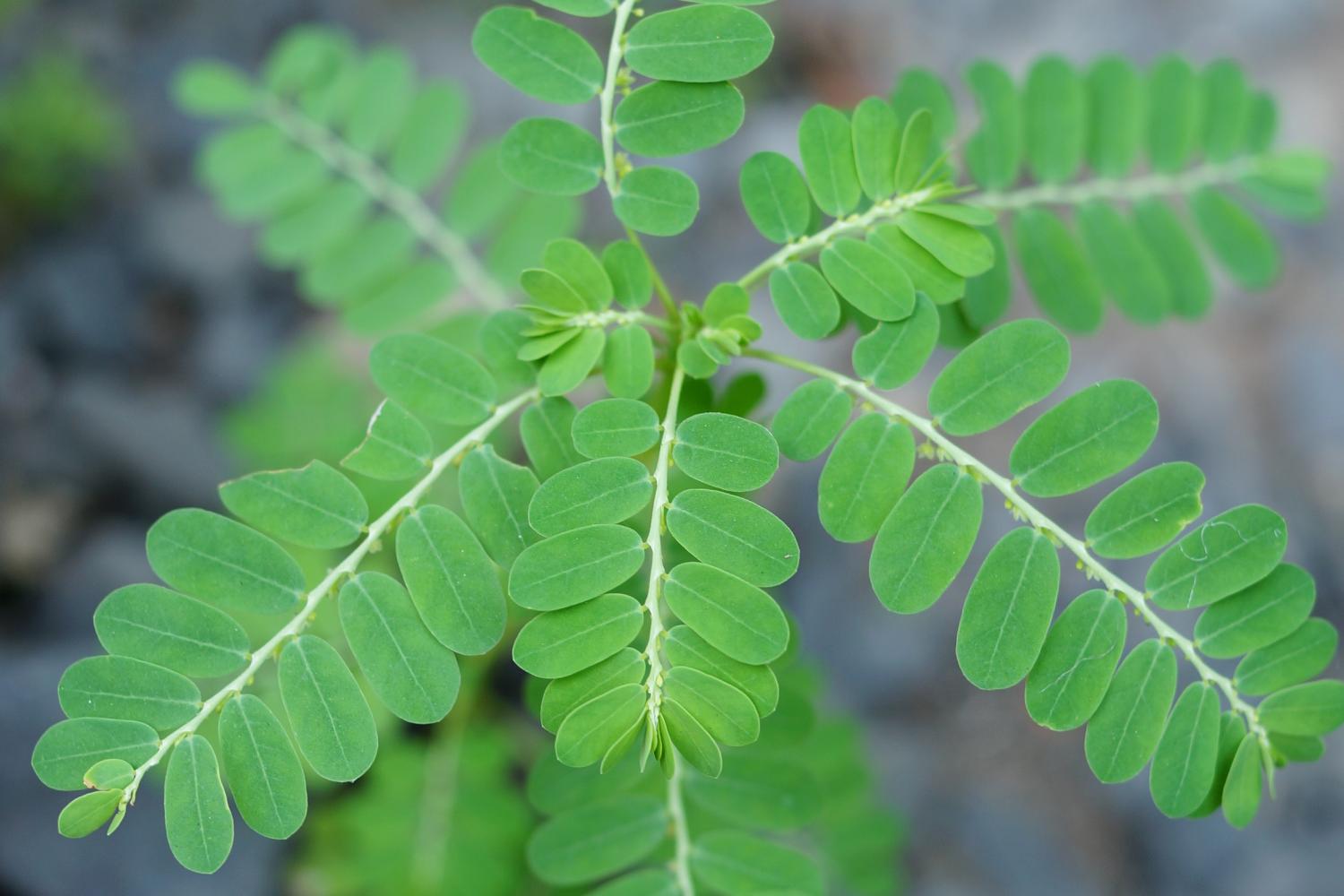
1.铁苋菜(种子植物名称)海蚌含珠(广东),蚌壳草(四川)
Acalypha australis L.
俗名:蛤蜊花、海蚌含珠、蚌壳草
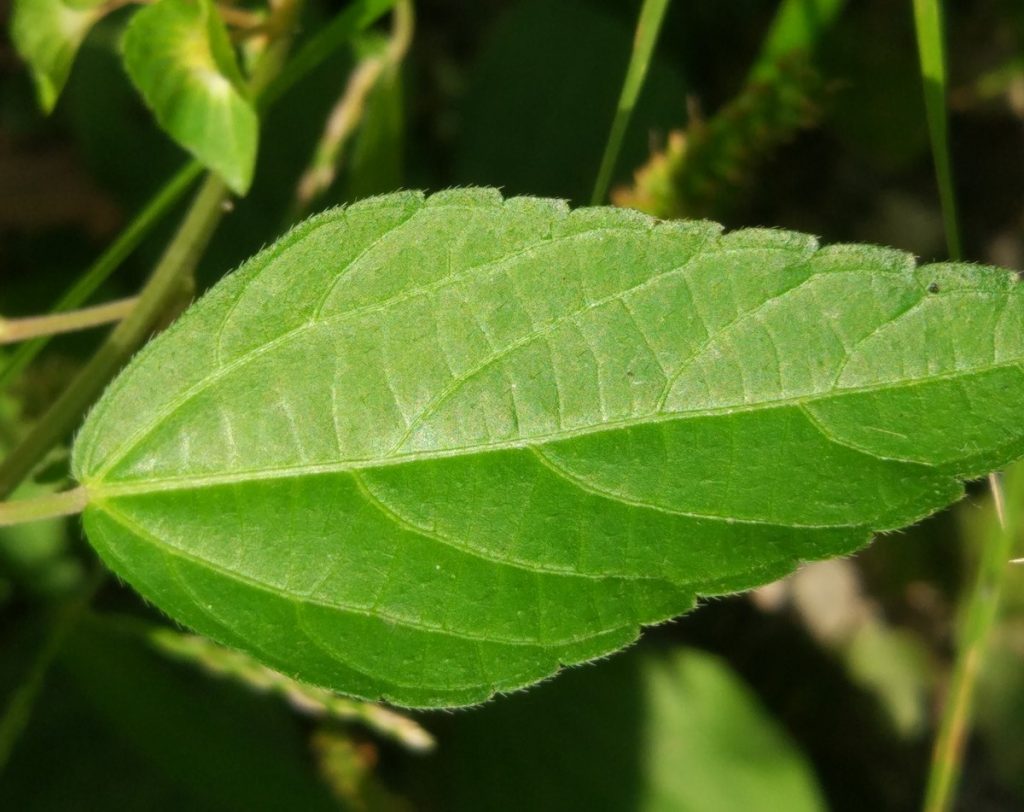
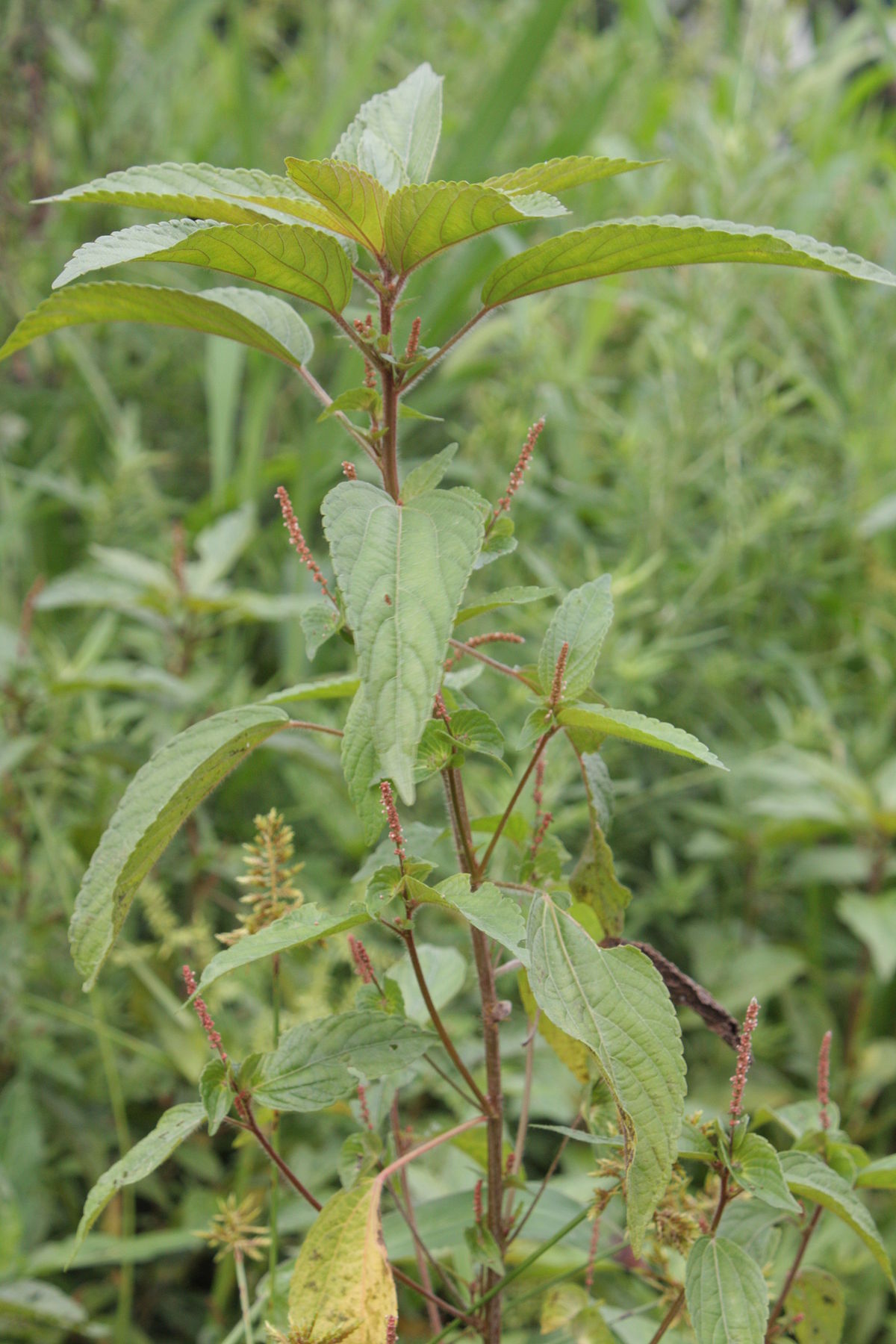
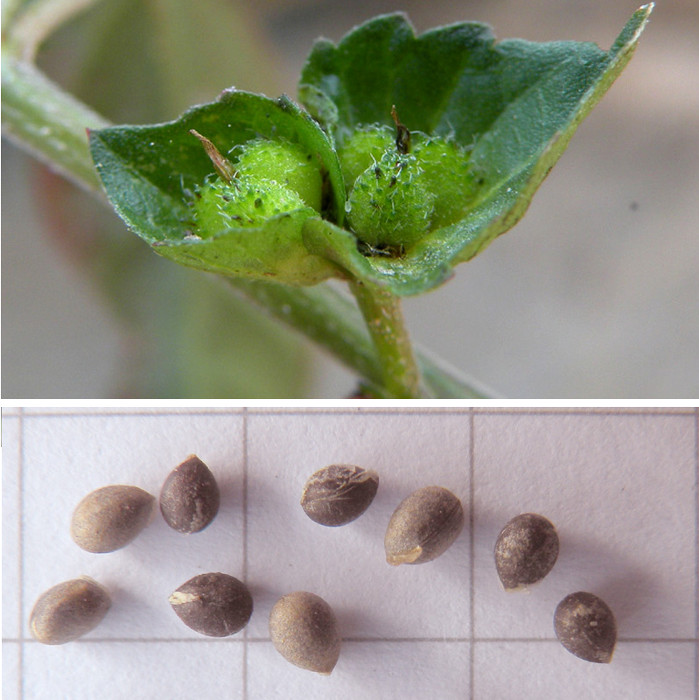
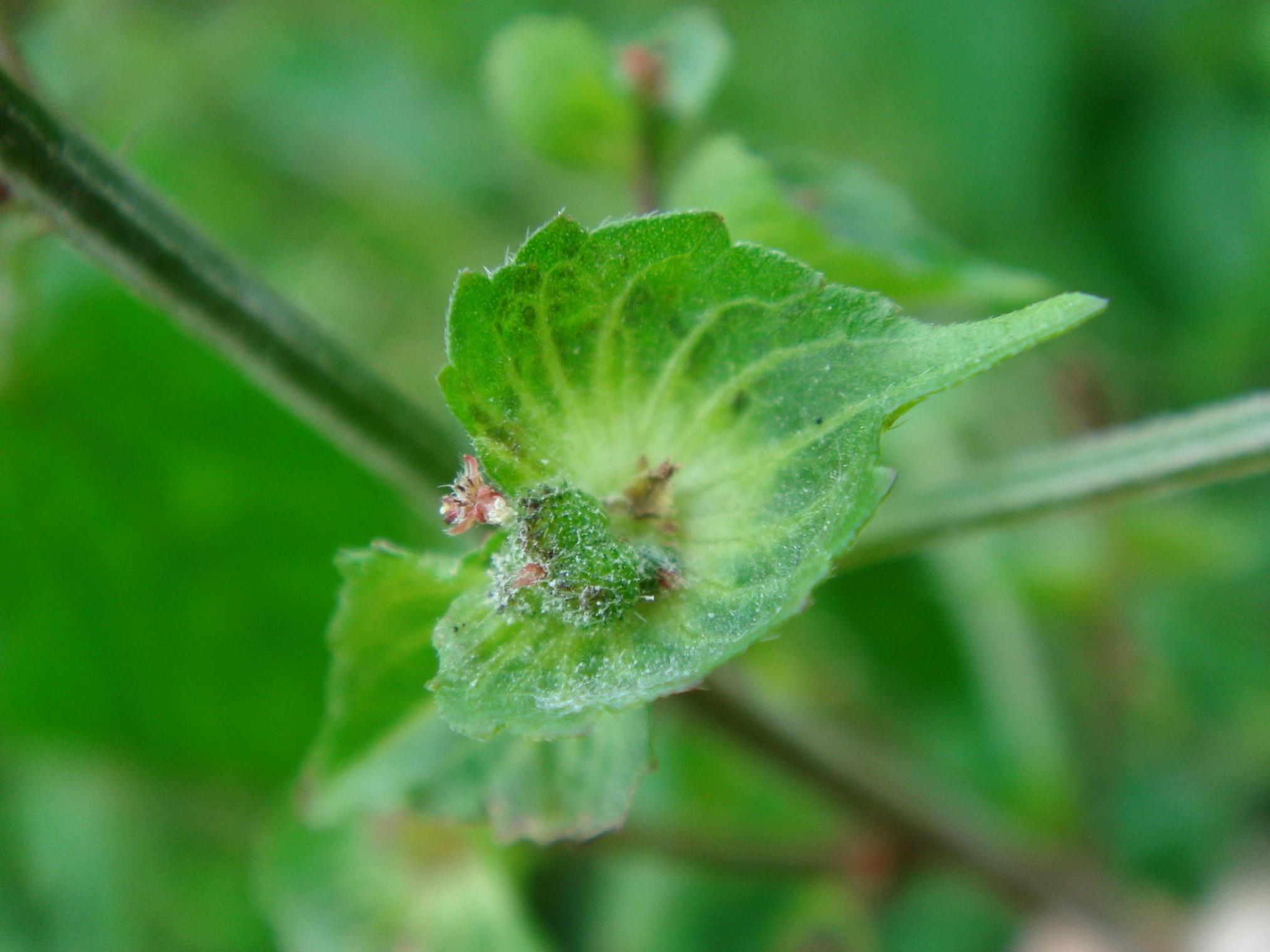
一年生草本,高0.2-0.5米,小枝细长,被贴毛柔毛,毛逐渐稀疏。
叶膜质,长卵形、近菱状卵形或阔披针形,长3-9厘米,宽1-5厘米,顶端短渐尖,基部楔形,稀圆钝,边缘具圆锯,上面无毛,下面沿中脉具柔毛;基出脉3条,侧脉3对;叶柄长2-6厘米,具短柔毛;托叶披针形,长1.5-2毫米,具短柔毛。
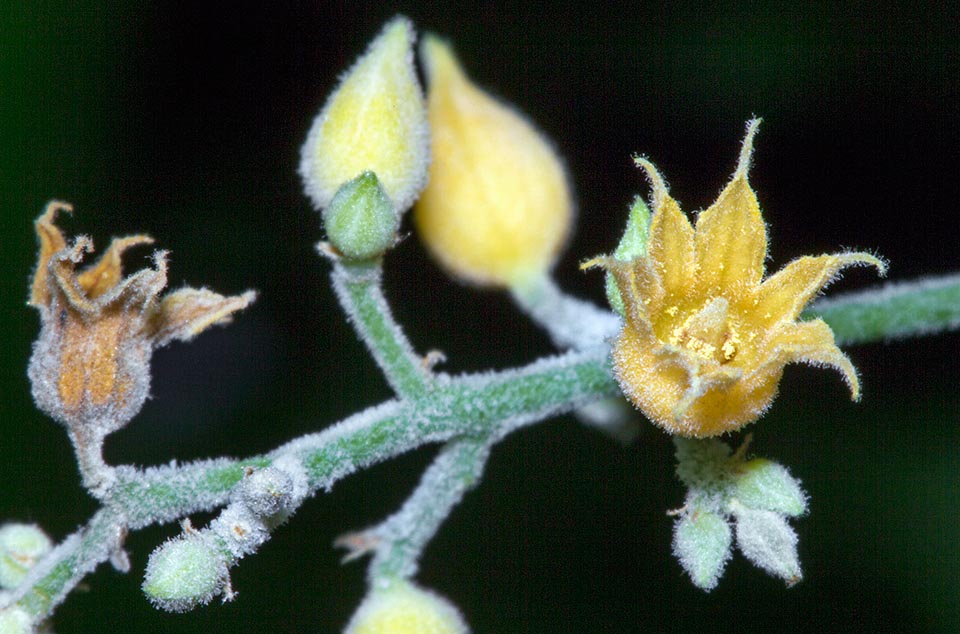
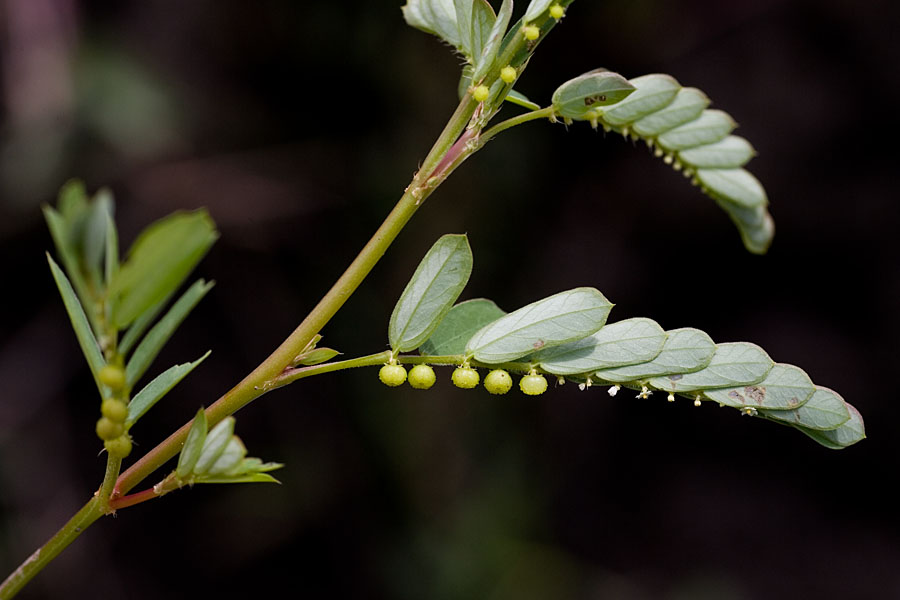
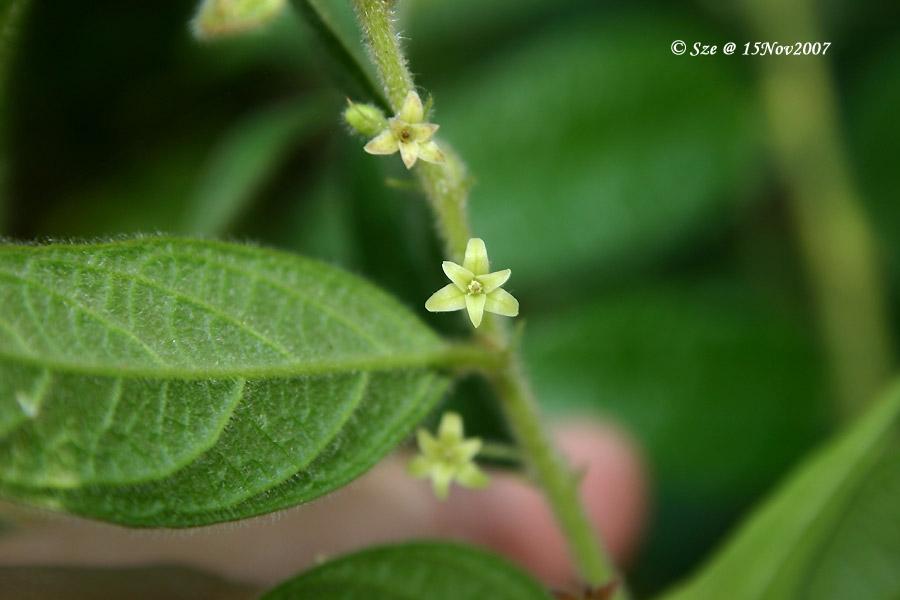
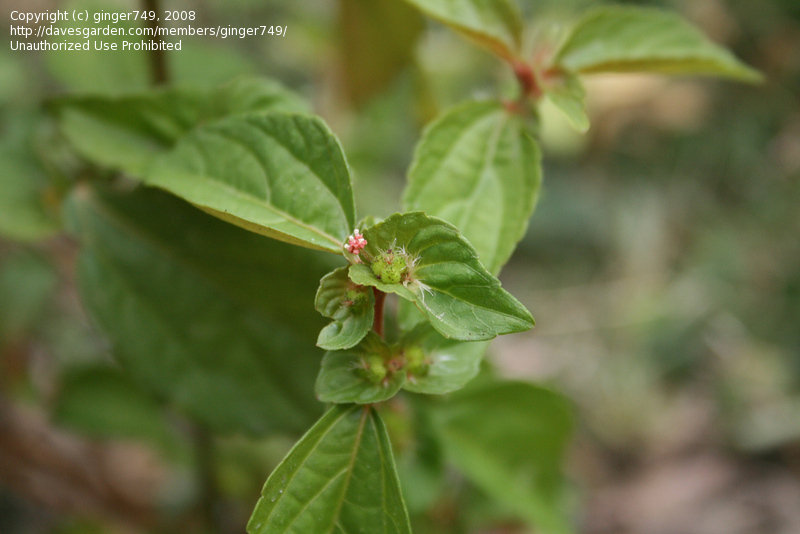
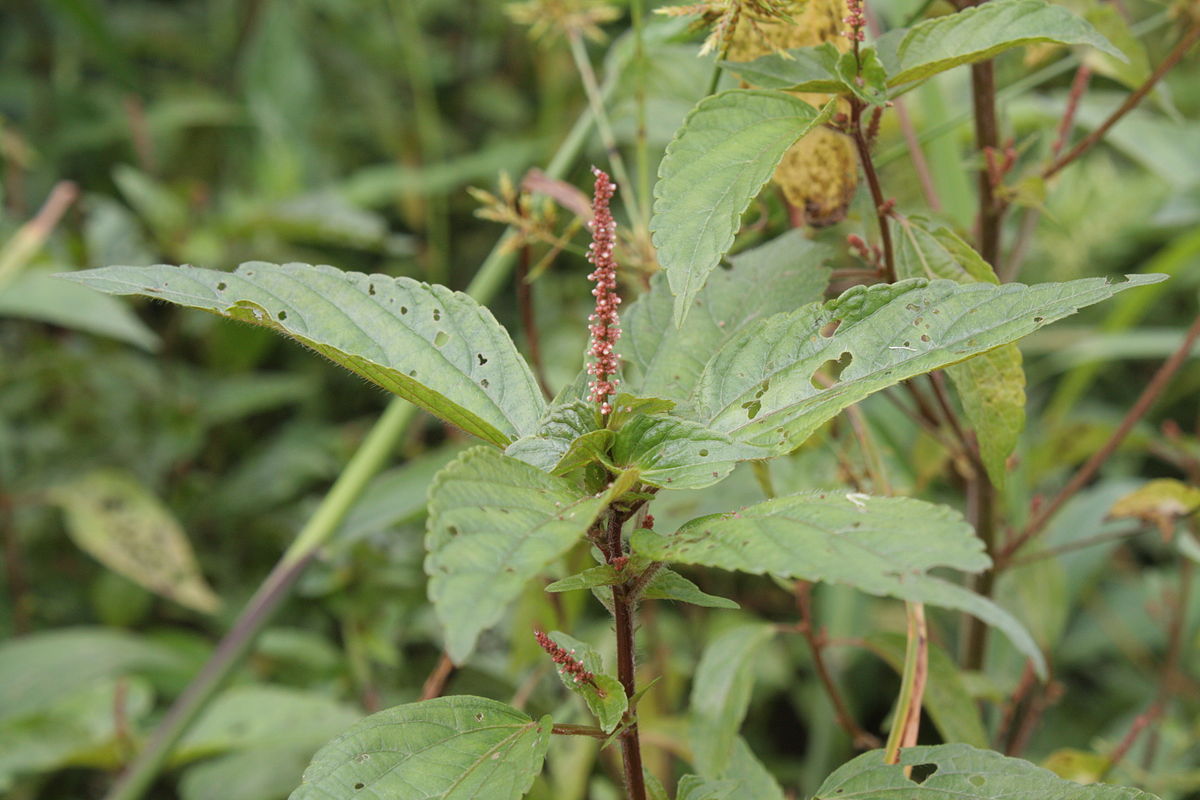
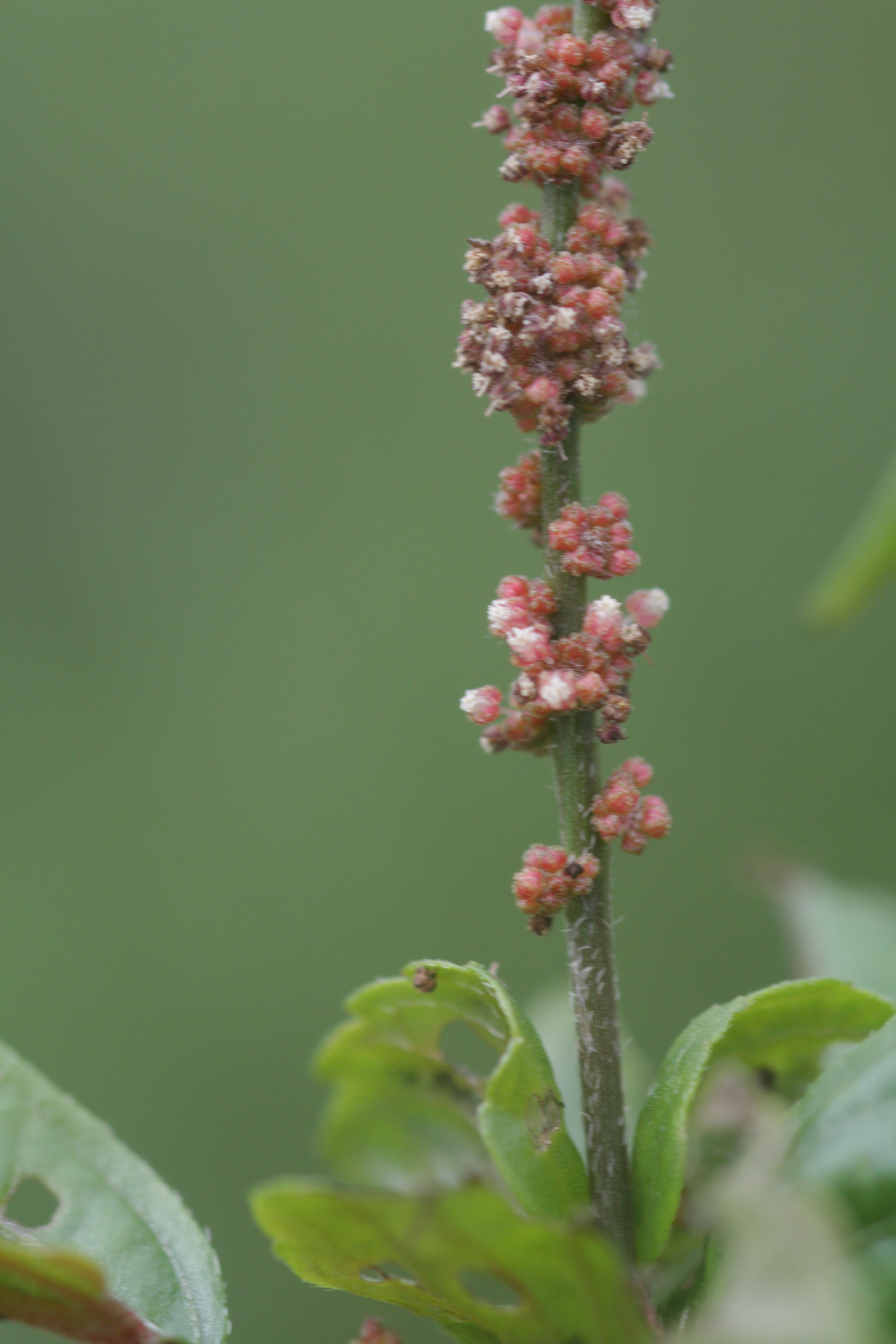
雌雄花同序,花序腋生,稀顶生,长1.5-5厘米,花序梗长0.5-3厘米,花序轴具短毛,雌花苞片1-2(-4)枚,卵状心形,花后增大,长1.4-2.5厘米,宽1-2厘米,边缘具三角形齿,外面沿掌状脉具疏柔毛,苞腋具雌花1-3朵;花梗无;雄花生于花序上部,排列呈穗状或头状,雄花苞片卵形,长约0. 5毫米,苞腋具雄花5-7朵,簇生;花梗长0.5毫米;雄花:花蕾时近球形,无毛,花萼裂片4枚,卵形,长约0.5毫米;雄蕊7-8枚;雌花:萼片3枚,长卵形,长0.5-1毫米,具疏毛;子房具疏毛,花柱3枚,长约2毫米,撕裂5-7条。
蒴果直径4毫米,具3个分果,果皮具疏生毛和毛基变厚的小瘤体;种子近卵状,长1.5-2毫米,种皮平滑,假种阜细长。花果期4-12月。
我国除西部高原或干燥地区外,大部分省区均产。生于海拔20-1 200 (-1 900)米平原或山坡较湿润耕地和空旷草地,有时石灰岩山疏林下。俄罗斯远东地区、朝鲜、日本、菲律宾、越南、老挝也有分布。现逸生于印度和澳大利亚北部
我国的标本,花序顶端有时生1朵雌花,其萼片4枚,子房3室,花柱3枚,无苞片。
广布的杂草,植株高度和叶片形状有较大变化,被毛亦有差别,本志不根据这些区分为变种或变型。据Acalypha minima的原始描述,其叶形和被毛特征为本种的形态变化范围,故予归并。
Acalypha australis, commonly known as Asian copperleaf, is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae native to eastern Asia.
Acalypha australis is an erect, branched, annual herb that can grow from 30 - 60cm tall.
The plant is harvested from the wild for local use as a medicine.
Locally common in open disturbed habitats and gardens; at elevations from sea-level up to 1,500 metres.
The whole plant is used to cure dysentery, diarrhoea, scrofula, dermatitis, nosebleed, haemoptysis, as well as to stop coughs and to cure swollen feet.
The leaves are used in poulticing(做成膏状药) snake bites.









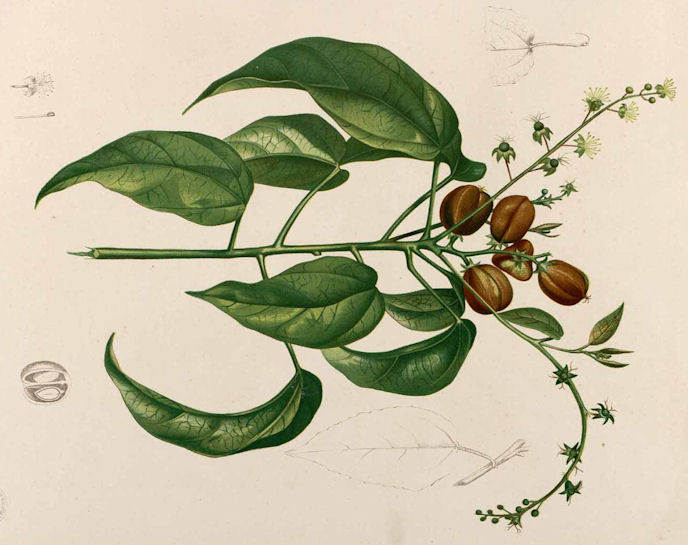
二、乌桕属Sapium P. Br.
乔木或灌木。叶互生,罕有近对生,全缘或有锯齿,具羽状脉;叶柄顶端有2腺体或罕有不存在;托叶小。花单性,雌雄同株或有时异株,若为雌雄同序则雌花生于花序轴下部,雄花生于花序轴上部,密集成顶生的穗状花序,穗状圆锥花序或总状花序,稀生于上部叶腋内,无花瓣和花盘;苞片基部具2腺体。雄花小,黄色,或淡黄色,数朵聚生于苞腋内,无退化雌蕊;花萼膜质,杯状,2-3浅裂或具2-3小齿;雄蕊2-3枚,花丝离生,常短,花药2室,纵裂。雌花比雄花大,每一苞腋内仅1朵雌花;花萼杯状,3深裂或管状而具3齿,稀为2-3萼片;子房2-3室,每室具1胚珠,花柱通常3枚,分离或下部合生,柱头外卷。蒴果球形、梨形或为3个分果爿,稀浆果状,通常3室,室背弹裂、不整齐开裂或有时不裂;种子近球形,常附于三角柱状、宿存的中轴上,迟落,外面被蜡质的假种皮或否,外种皮坚硬;胚乳肉质,子叶宽而平坦。
约120种,广布于全球,但主产热带地区,尤以南美洲为最多。我国有9种,多分布于东南至西南部丘陵地区。
1.乌桕(唐本草)腊子树(浙江温州)、桕子树(四川)、木子树(湖北兴山、江西武宁)
Sapium sebiferum (Linn.)
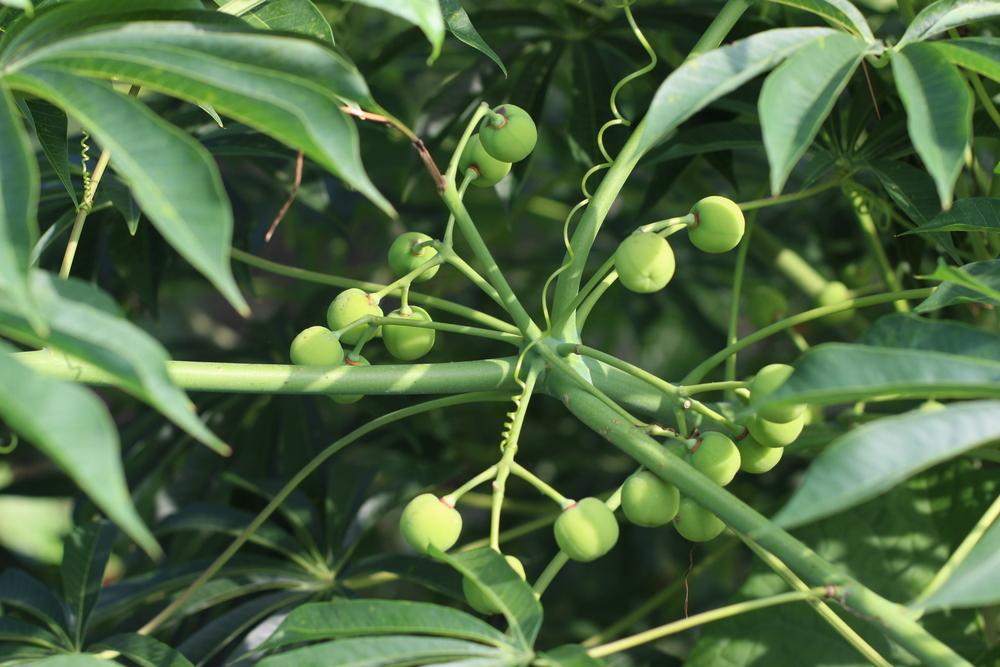
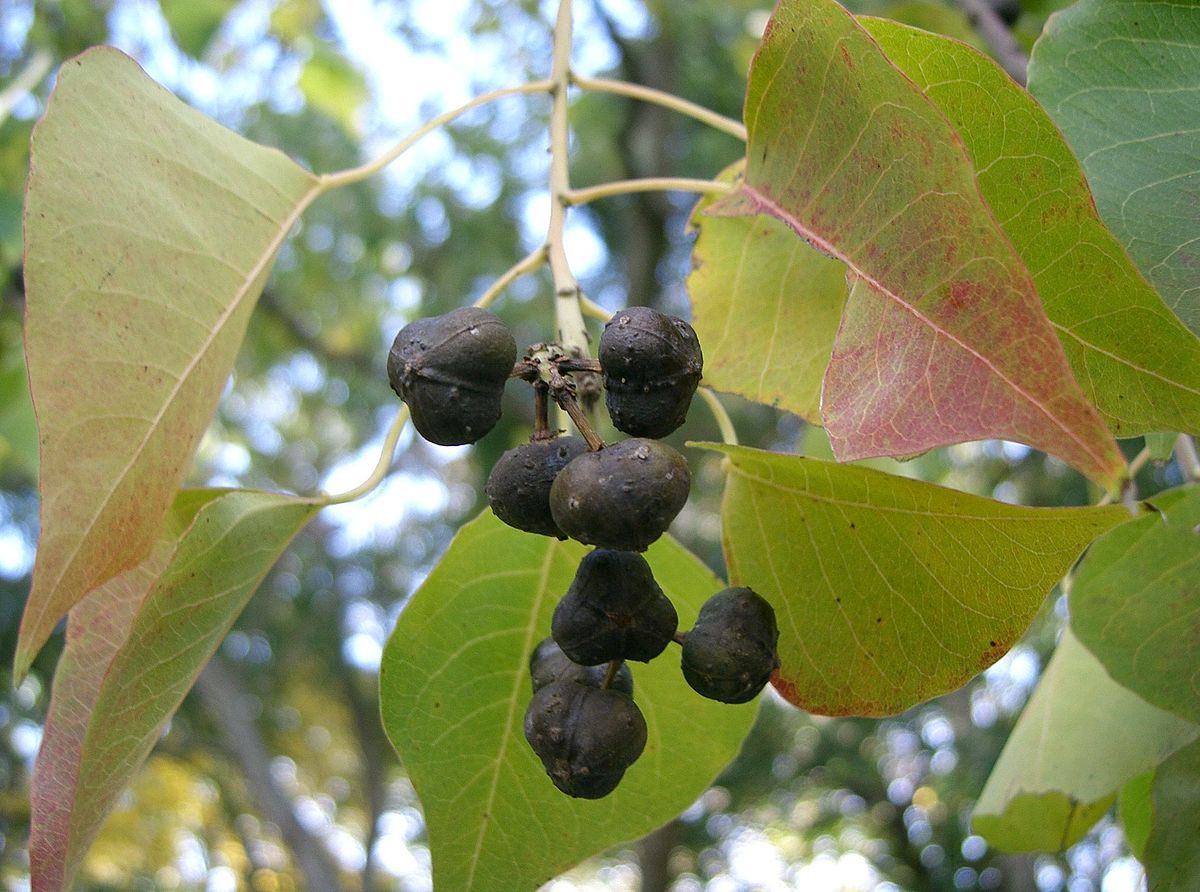
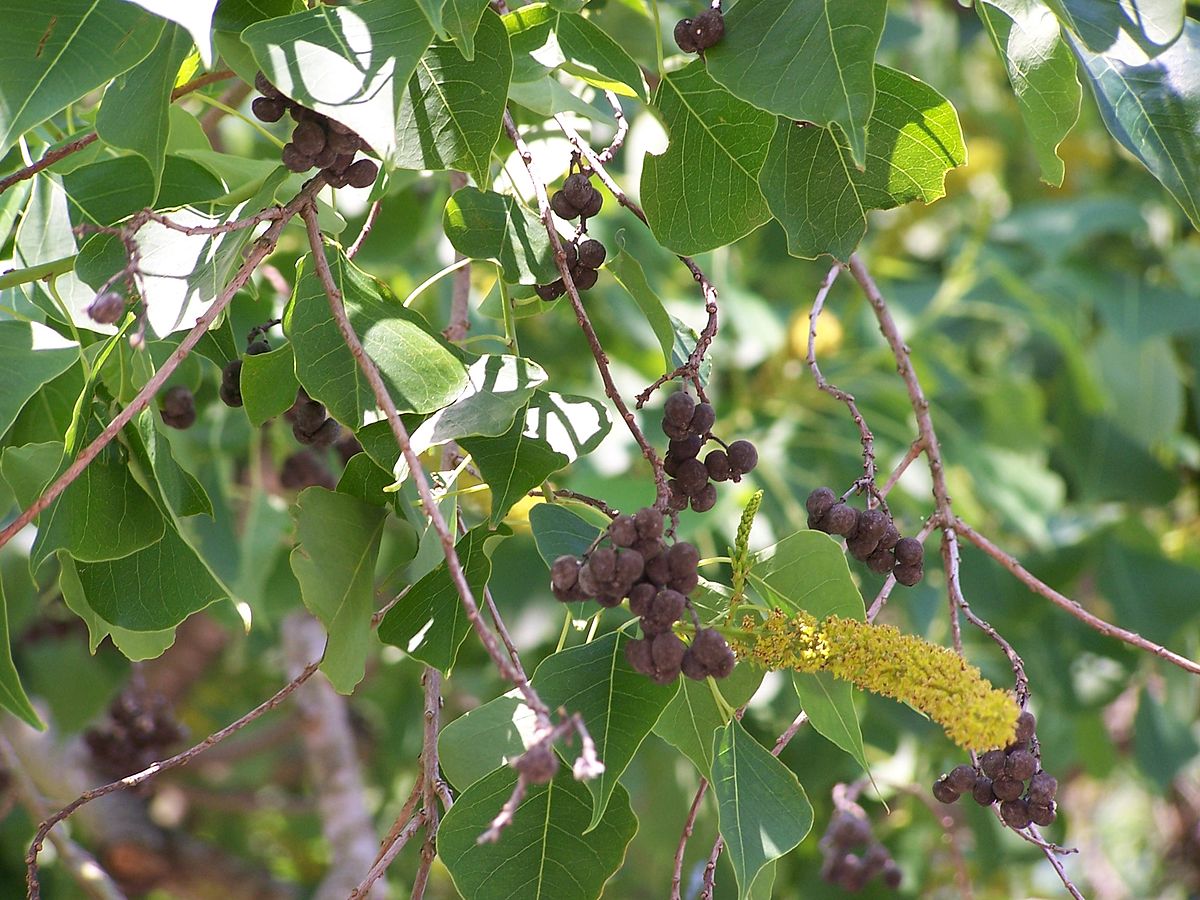
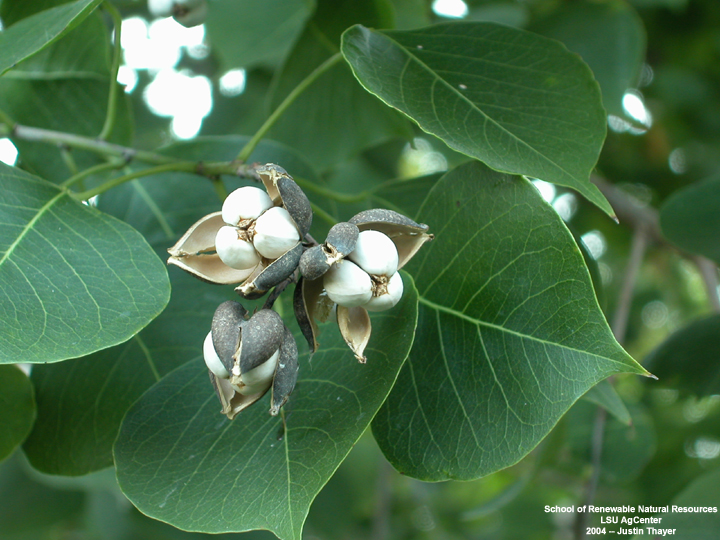
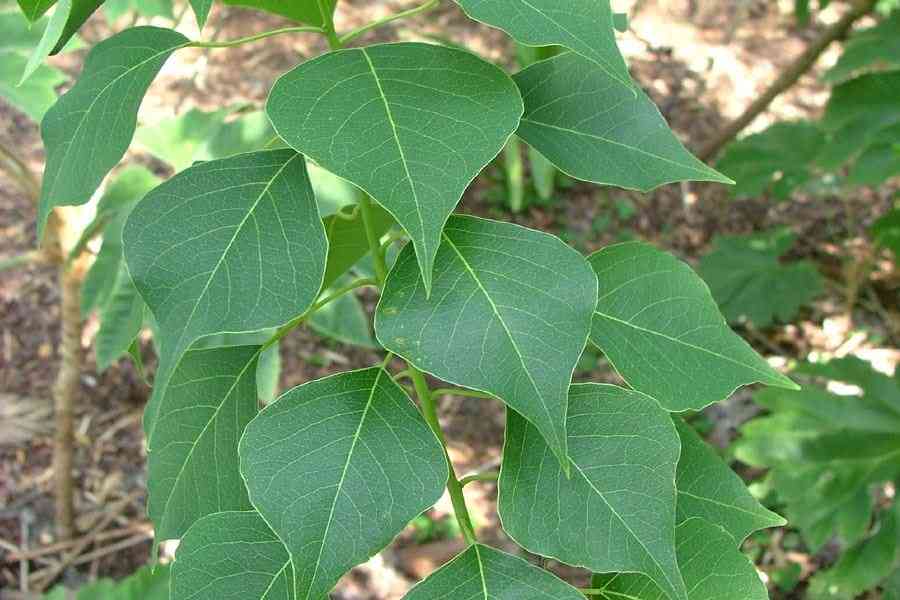
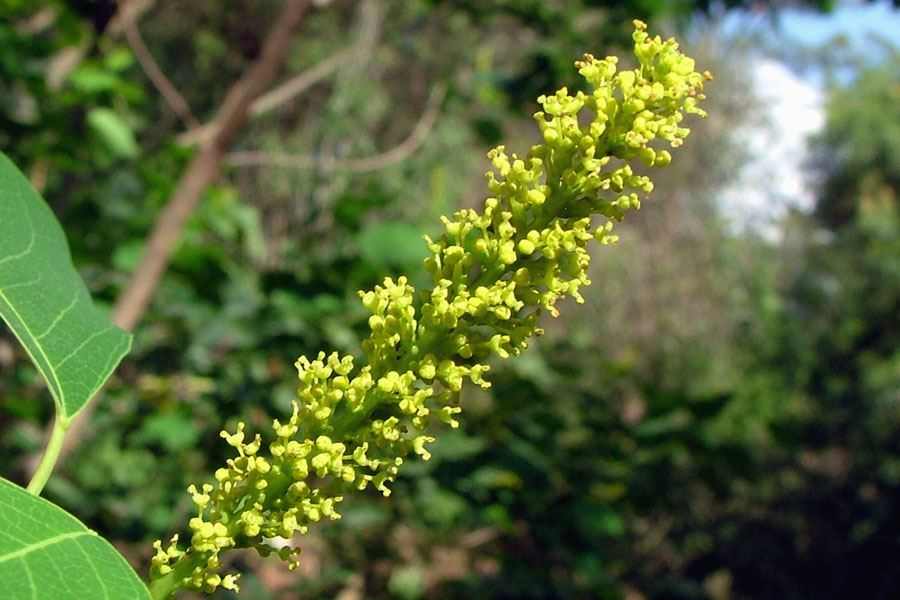
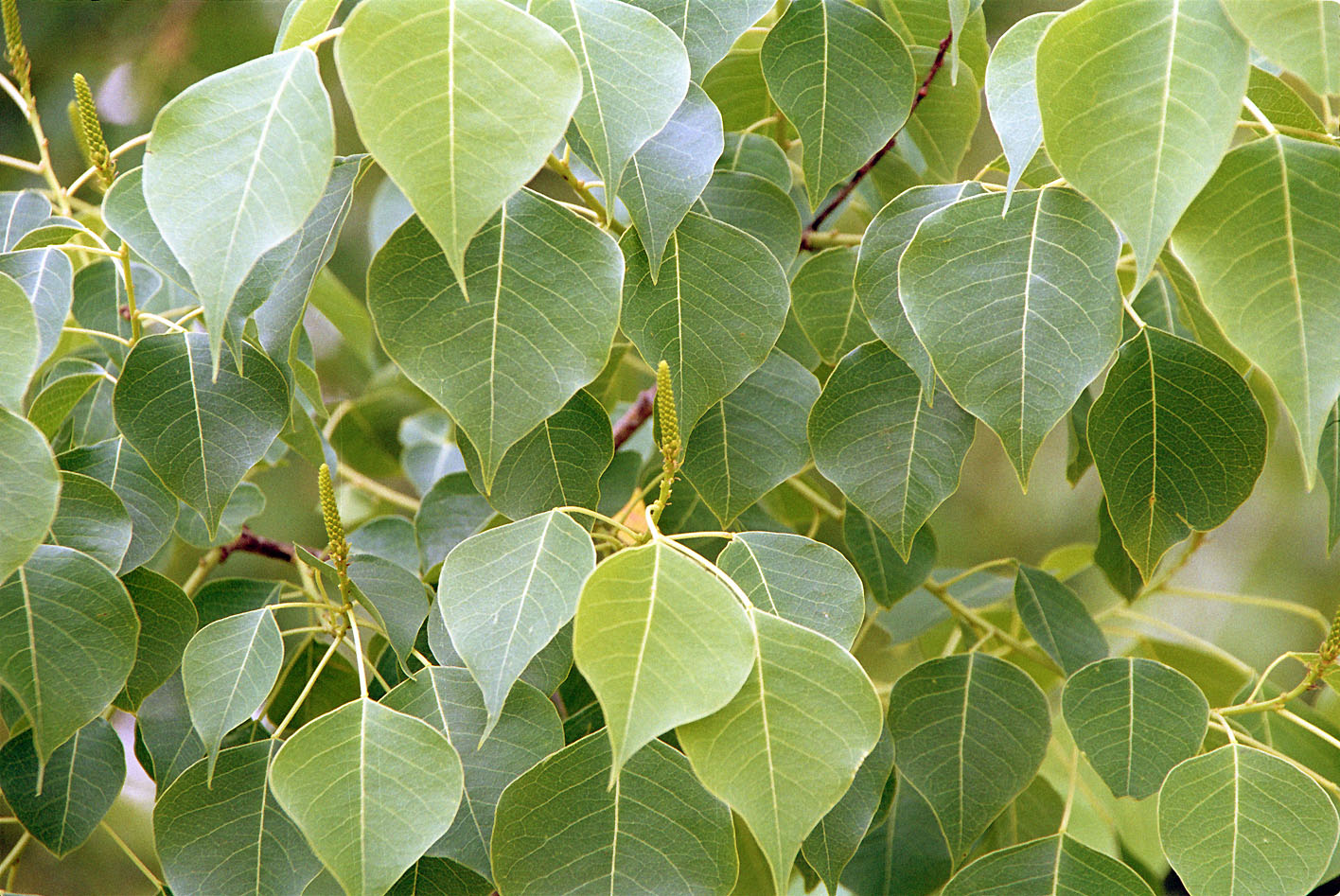
乔木,高可达15米许,各部均无毛而具乳状汁液;树皮暗灰色,有纵裂纹;枝广展,具皮孔。叶互生,纸质,叶片菱形、菱状卵形或稀有菱状倒卵形,长3-8厘米,宽3-9厘米,顶端骤然紧缩具长短不等的尖头,基部阔楔形或钝,全缘;中脉两面微凸起,侧脉6-10对,纤细,斜上升,离缘2-5毫米弯拱网结,网状脉明显;叶柄纤细,长2.5-6厘米,顶端具2腺体;托叶顶端钝,长约1毫米。花单性,雌雄同株,聚集成顶生、长6-12厘米的总状花序,雌花通常生于花序轴最下部或罕有在雌花下部亦有少数雄花着生,雄花生于花序轴上部或有时整个花序全为雄花。雄花:花梗纤细,长1-3毫米,向上渐粗;苞片阔卵形,长和宽近相等约2毫米,顶端略尖,基部两侧各具一近肾形的腺体,每一苞片内具10-15朵花;小苞片3,不等大,边缘撕裂状;花萼杯状,3浅裂,裂片钝,具不规则的细齿;雄蕊2枚,罕有3枚,伸出于花萼之外,花丝分离,与球状花药近等长。雌花;花梗粗壮,长3-3.5毫米;苞片深3裂,裂片渐尖,基部两侧的腺体与雄花的相同,每一苞片内仅1朵雌花,间有1雌花和数雄花同聚生于苞腋内;花萼3深裂,裂片卵形至卵头披针形,顶端短尖至渐尖;子房卵球形,平滑,3室,花柱3,基部合生,柱头外卷。蒴果梨状球形,成熟时黑色,直径1-1.5厘米。具3种子,分果爿脱落后而中轴宿存;种子扁球形,黑色,长约8毫米,宽6-7毫米,外被白色、蜡质的假种皮。花期4-8月。
在我国主要分布于黄河以南各省区,北达陕西、甘肃。生于旷野、塘边或疏林中。日本、越南、印度也有;此外,欧洲、美洲和非洲亦有栽培。模式标本采自广州近郊。
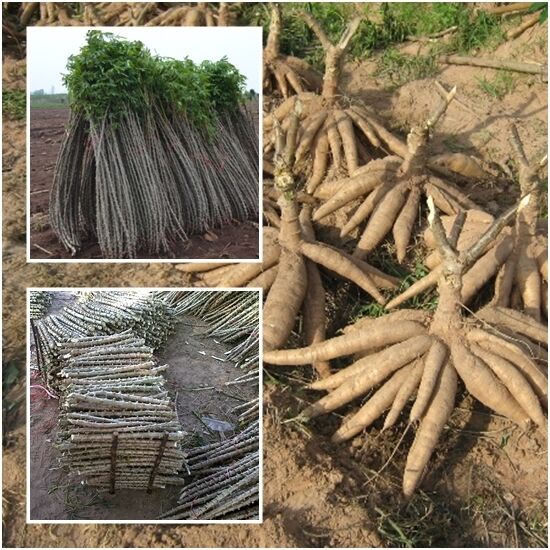
木材白色,坚硬,纹理细致,用途广。叶为黑色染料,可染衣物。根皮治毒蛇咬伤。白色之蜡质层(假种皮)溶解后可制肥皂、蜡烛;种子油适于涂料,可涂油纸、油伞等。
Triadica sebifera is a tree native to eastern China and Taiwan. It is commonly called Chinese tallow(牛脂,动物脂), Chinese tallowtree, Florida aspen(山杨), chicken tree, gray popcorn(爆米花) tree, or candleberry tree. The seeds are the sources of stillingia(乌桕) oil, a drying oil used in paints and varnishes(涂漆). The fatty coat of the seeds, used for candle and soap making, is known as stillingia tallow; hence its common name. It is relevant to biodiesel生物柴油 production because it is the third most productive vegetable oil producing crop in the world, after algae(澡类) and oil palm. The leaves are used as herbal medicine to treat boils. The plant sap and leaves are reputed to be toxic, and decaying leaves from the plant are toxic to other species of plants. The species is classified as a noxious invader in the southern U.S.
Triadica sebifera :
Common Name(s): Chinese tallow treePopcorn Tree
Previously known as: Sapium sebiferum
This plant has medium severity poison characteristics.
This plant is an invasive species in North Carolina
Description
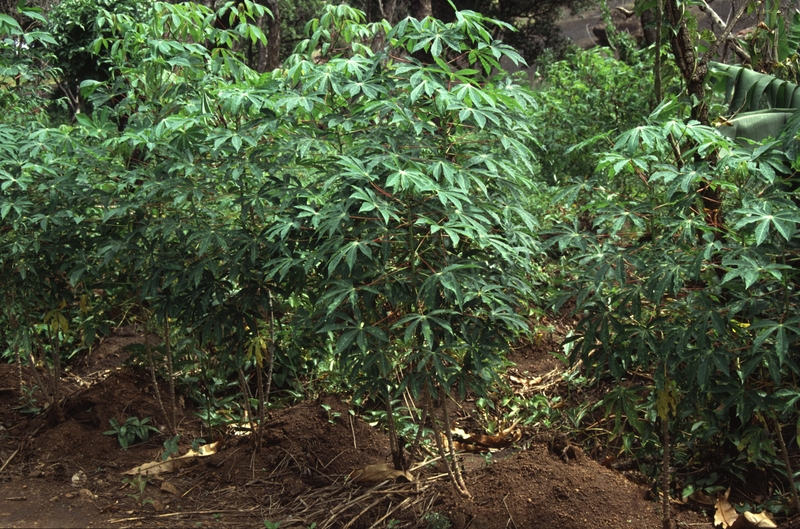
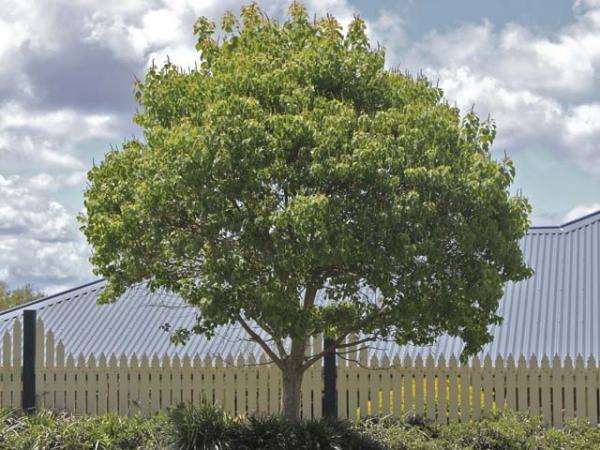
Chinese tallow is a drought-tolerant shade tree in the Euphorbiaceae family. Native to China and Japan, it was introduced in South Carolina in the 1700's. It was first introduced as an ornamental tree as well as for making soap from the seed oils. It wasn't until the early 1900's that its use as an ornamental tree spread. It can be found from eastern North Carolina southward to Florida. From Florida, it spread in a westerly direction, through Louisiana, Arkansas into Texas.
It can reach heights and widths of 40 feet, with a 3-foot diameter, excellent for creating shade. Its deep taproot allows the tree to hydrate in drought conditions. It will reach taller heights when located in an area, such as a lawn, that received more moisture. In dryer locations it tends to become more broad and does not grow to its potential height.
Its branches grow low to the ground. They are long and appear in a drooping fashion. Twigs are waxy and quite slender.
This tree invades wet areas such as ditches and stream banks as well as some upland dry areas. In undisturbed forests, it can prohibit native vegetation, and alter soil conditions due to the tannins (organic substance) in leaf litter. The ability to grow in crowded locations, as well as any lighting conditions, allows the establishment of additional trees. In Florida, it is present in over half of the counties, and has been placed on the State of Florida Noxious Weed List as well as on FLEPPC's (Florida's Exotic Pest Plant Council) List of Invasive species. The seeds are spread by birds, only complicating the spread. In order to eradicate this plant, total removal of the plant and seeds is required.
Insects, Diseases, and Other Plant Problems: No serious pest issues. The leaves and fruit are toxic to humans and cattle. This tree is invasive in North Carolina as well as other locations.









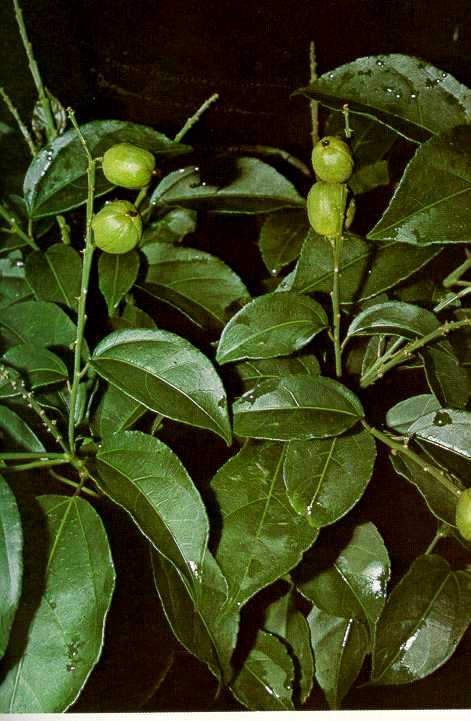
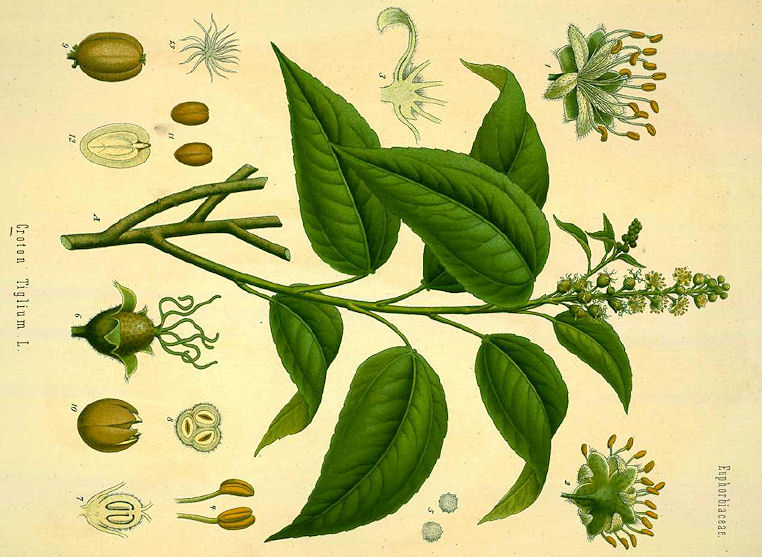
三、蓖麻属Ricinus L.
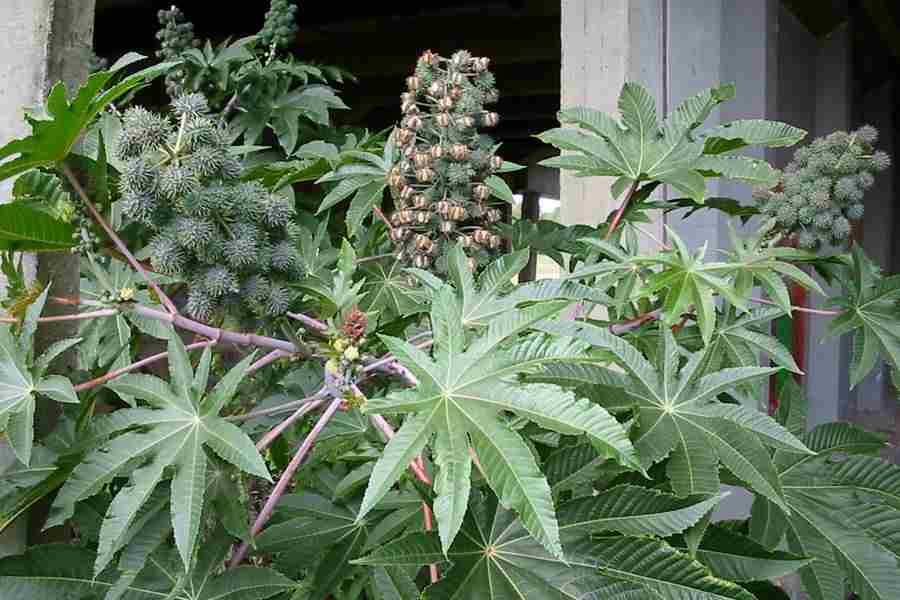
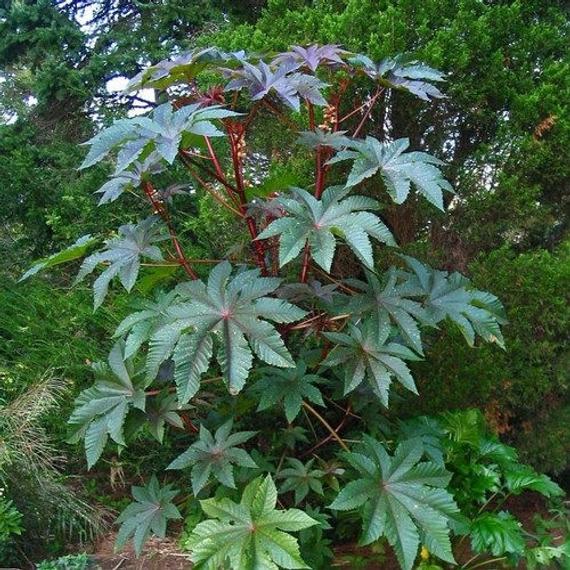
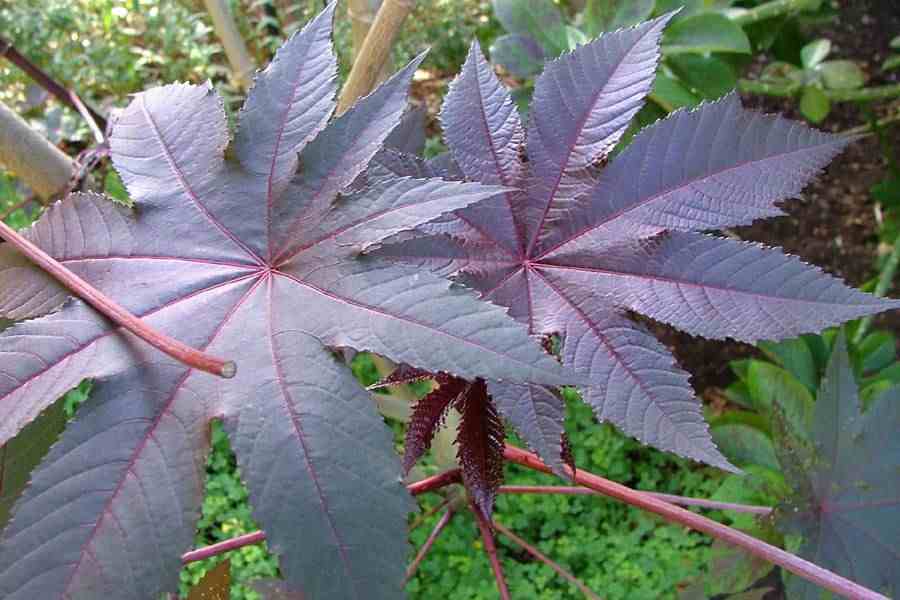
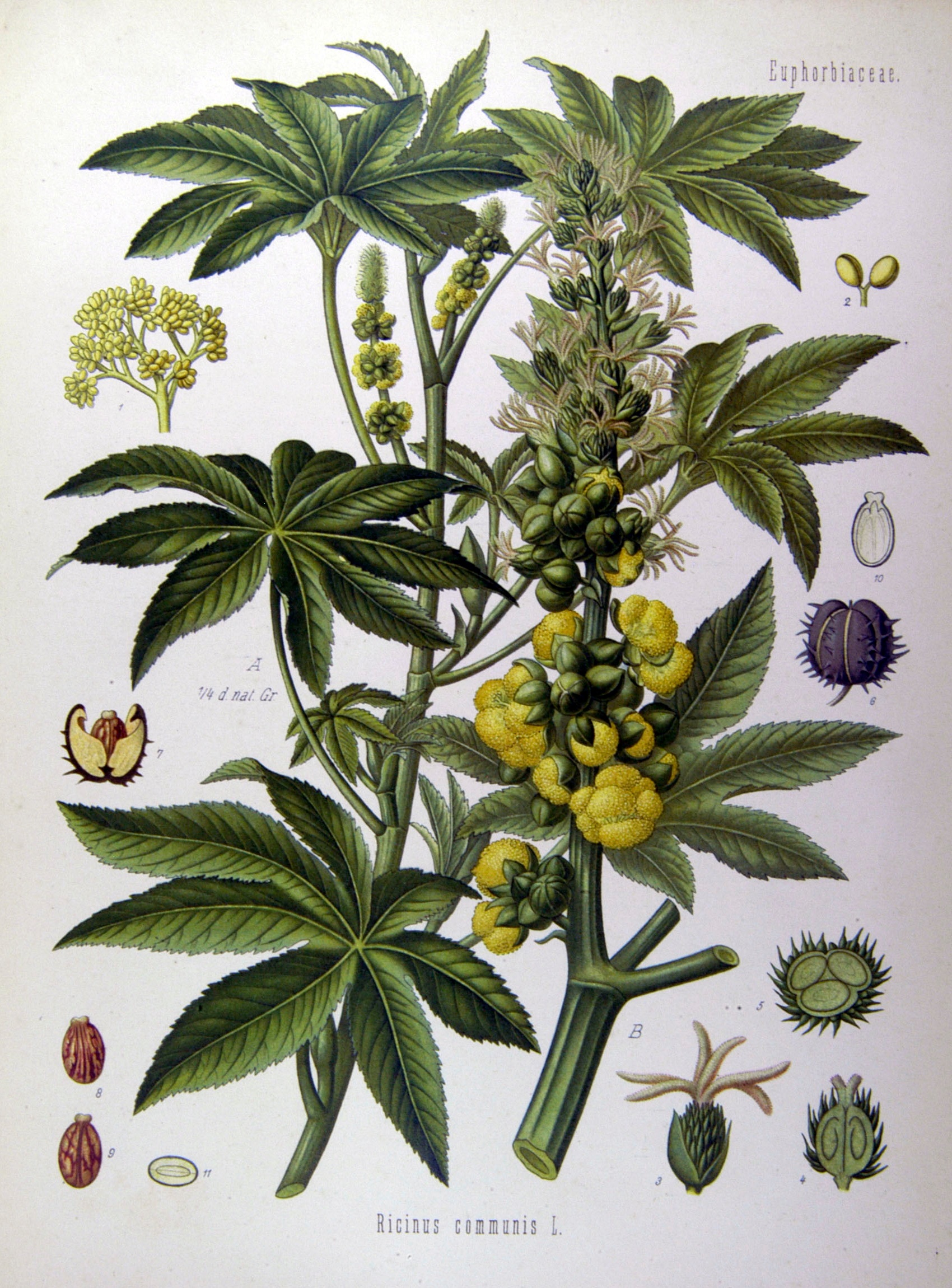
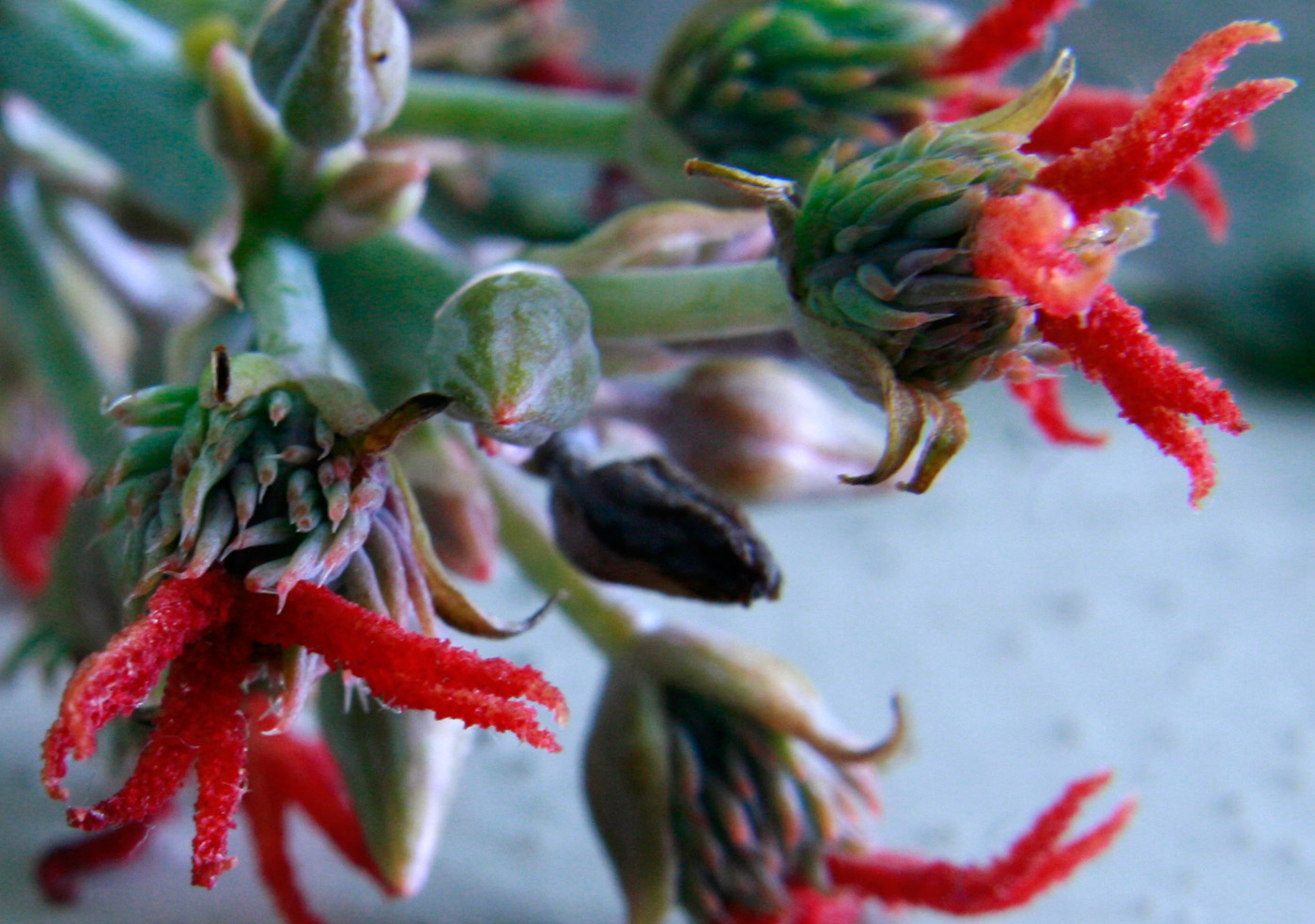
一年生草本或草质灌木;茎常被白霜。叶互生,纸质,掌状分裂,盾状着生,叶缘具锯齿;叶柄的基部和顶端均具腺体;托叶合生,凋落。花雌雄同株,无花瓣,花盘缺;圆锥花序,顶生,后变为与叶对生,雄花生于花序下部,雌花生于花序上部,均多朵簇生于苞腋;花梗细长;雄花:花萼花蕾时近球形,萼裂片3-5枚,镊合状排列;雄蕊极多,可达1000枚,花丝合生成数目众多的雄蕊束,花药2室,药室近球形,彼此分离,纵裂;无不育雌蕊;雌花:萼片5枚,镊合状排列,花后凋落,子房具软刺或无刺,3室,每室具胚珠1颗,花柱3枚,基部稍合生,顶部各2裂,密生乳头状突起。蒴果,具3个分果爿,具软刺或平滑;种子椭圆状,微扁平,种皮硬壳质,平滑,具斑纹,胚乳肉质,子叶阔、扁平;种阜大。
单种属。广泛栽培于世界热带地区。我国大部分省区均有栽培。
1.蓖麻〔唐本草〕
Ricinus communis L.
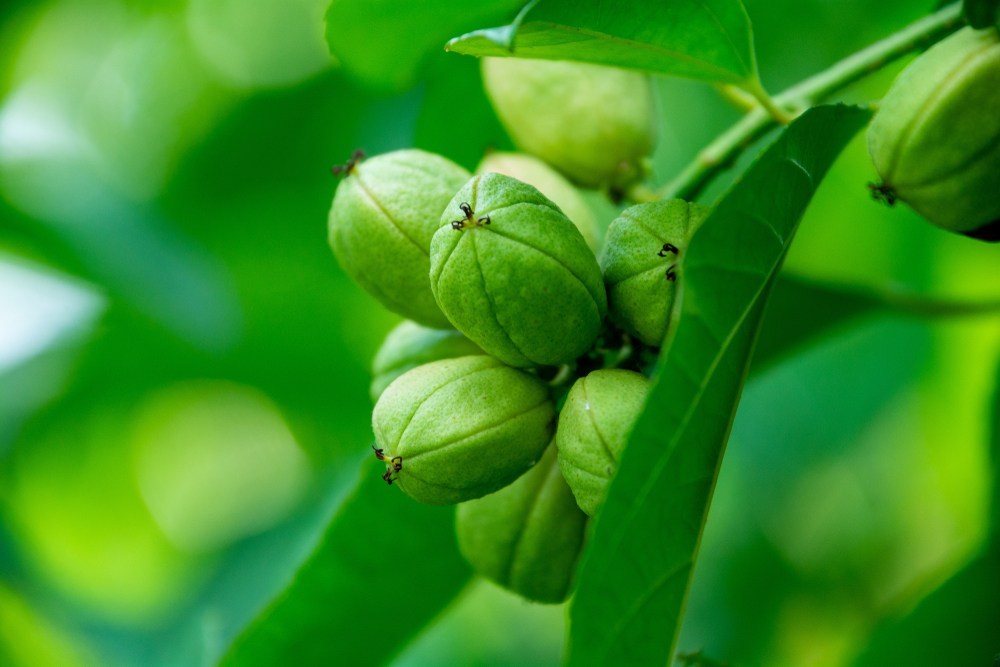
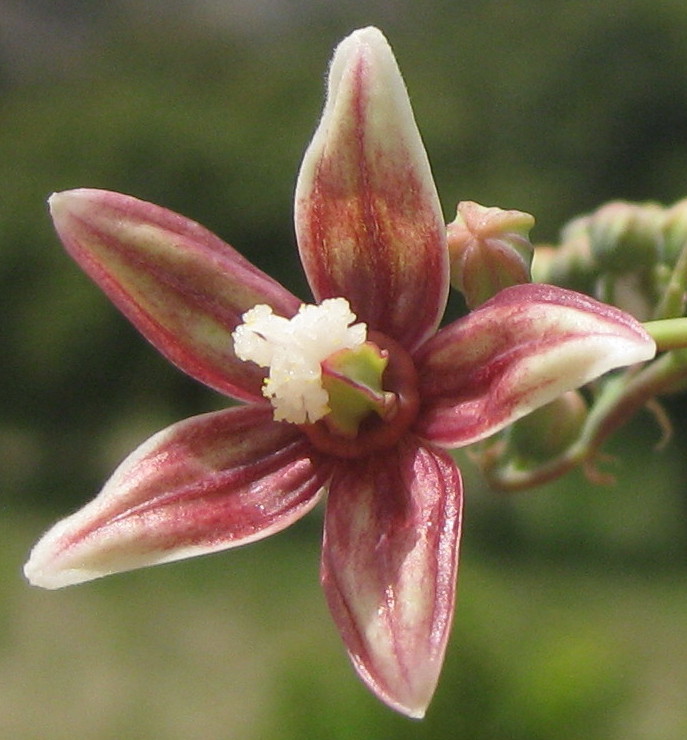
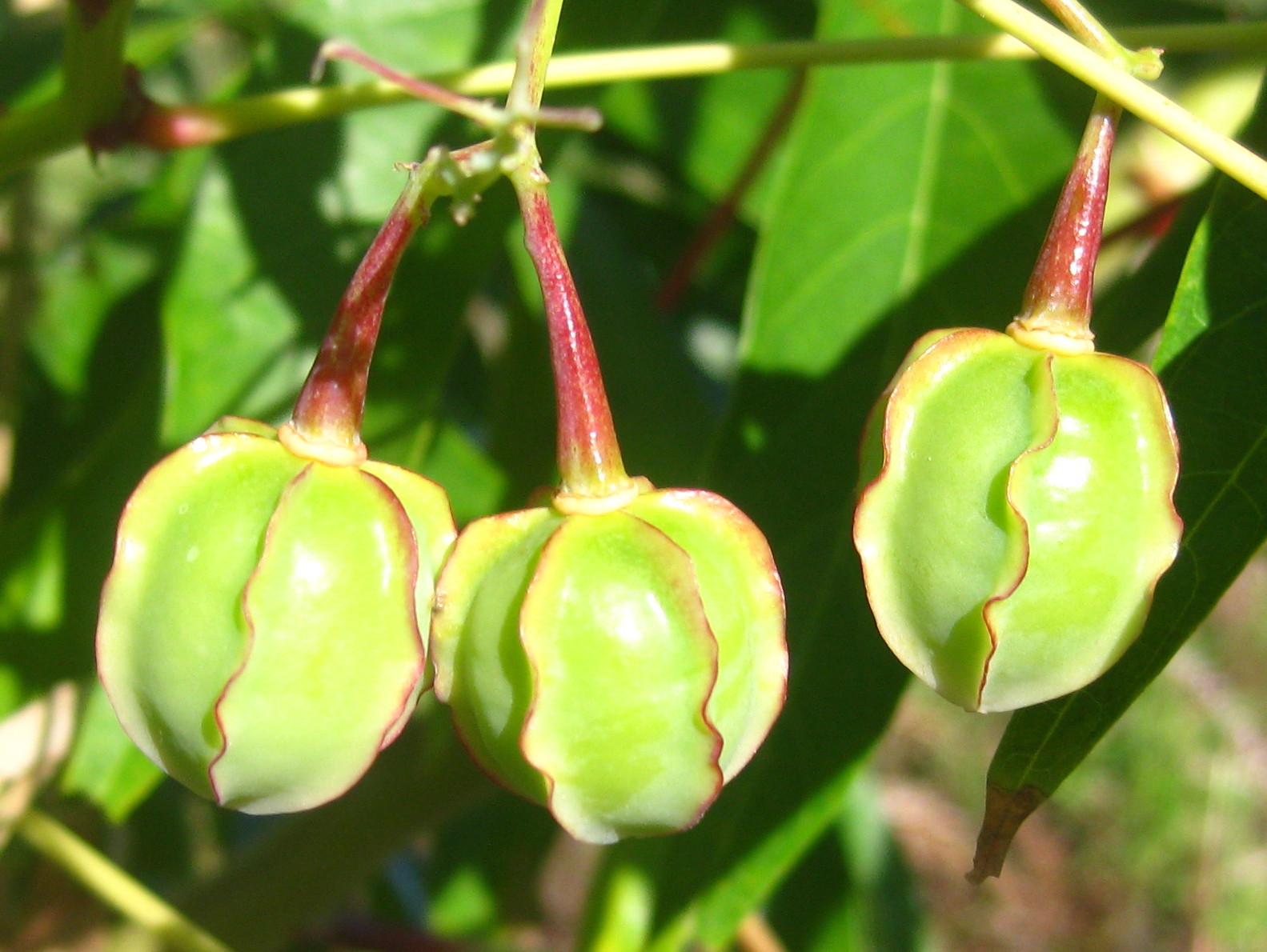
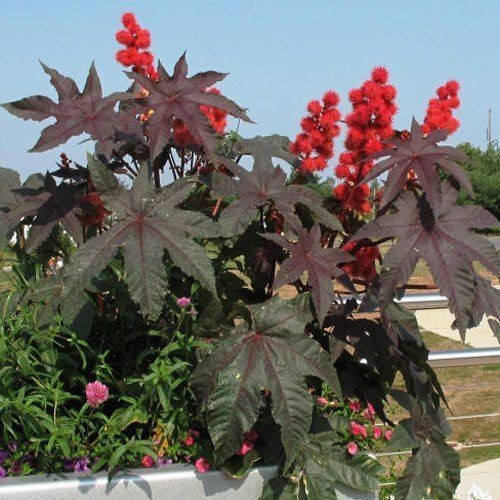
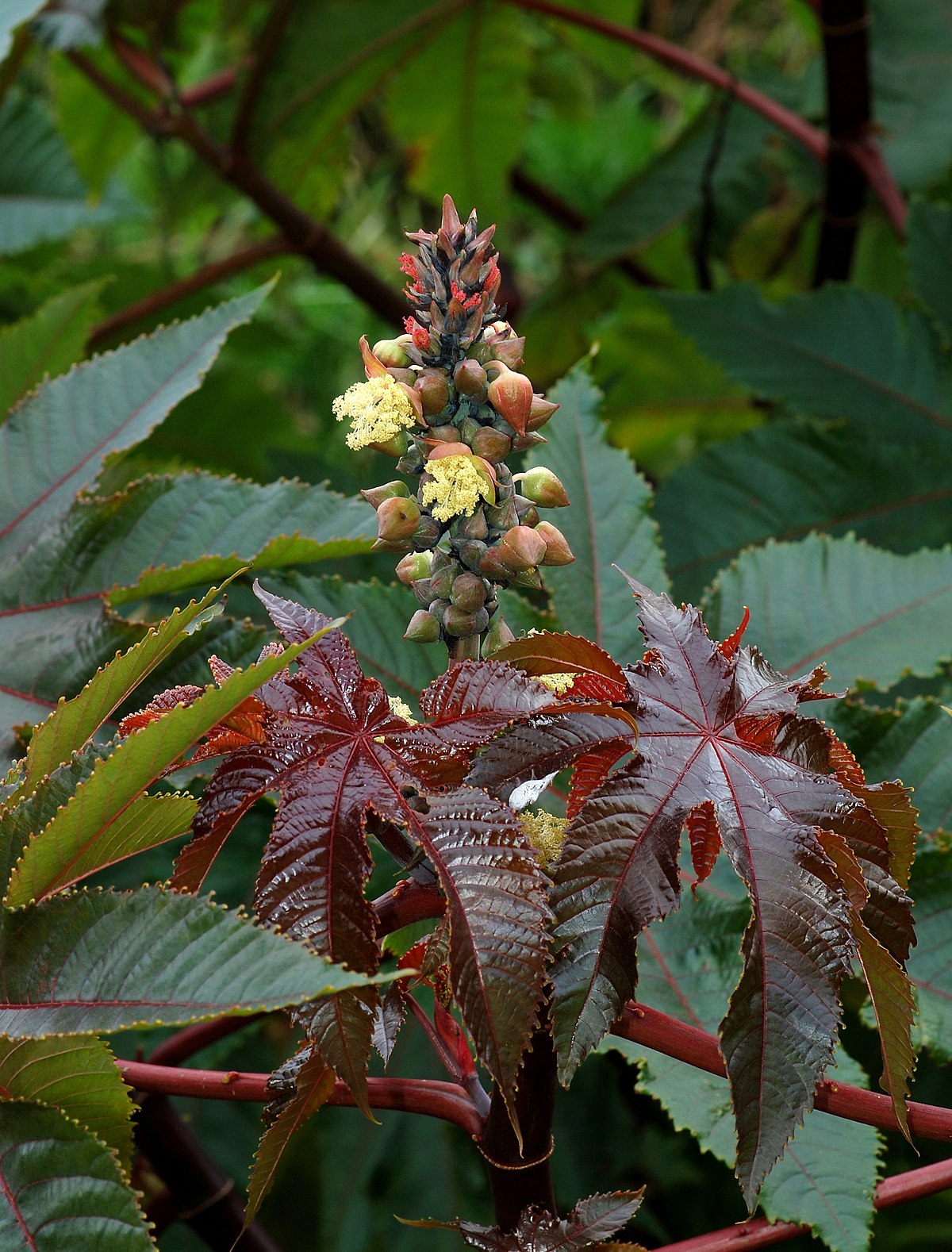
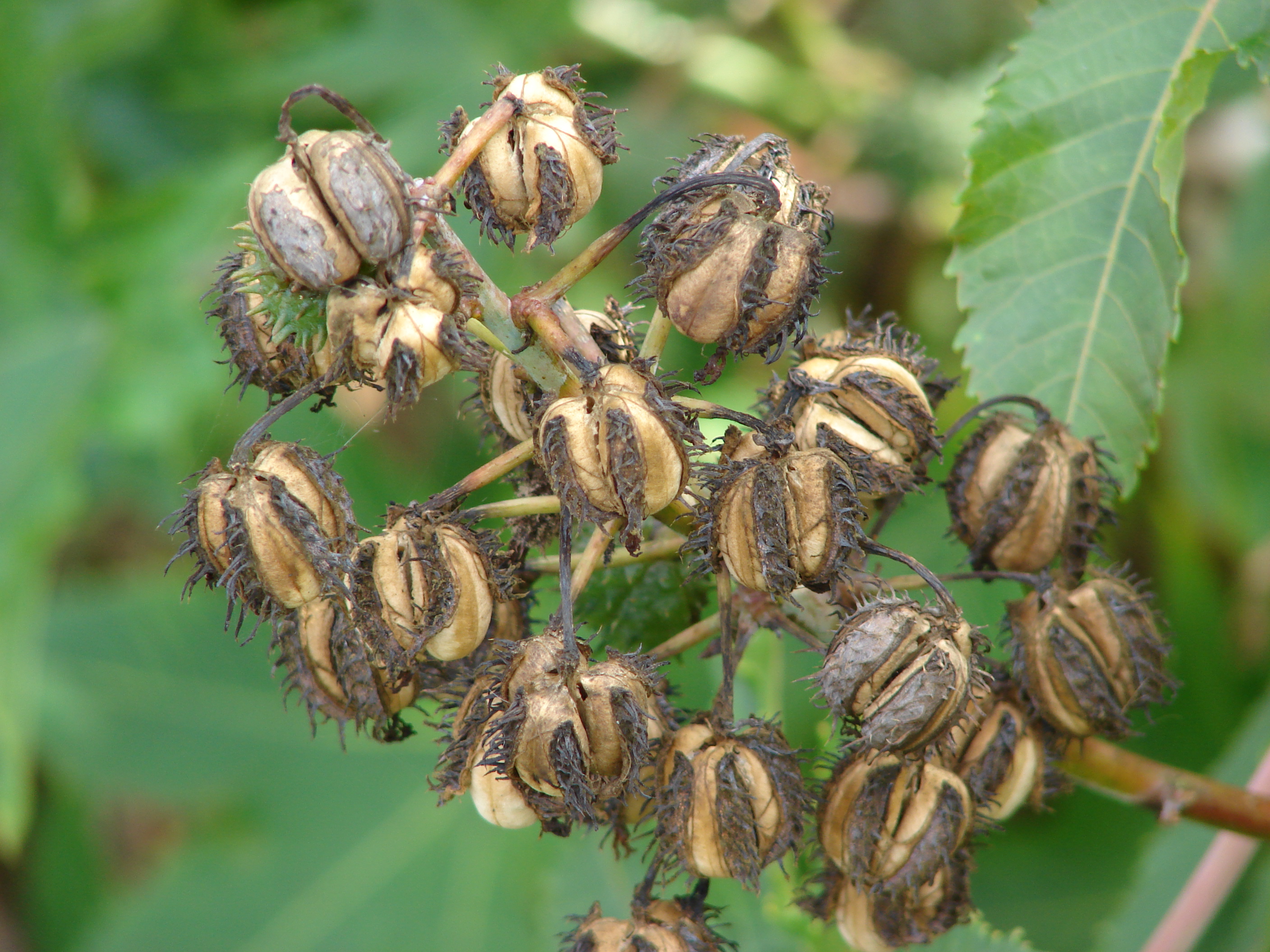
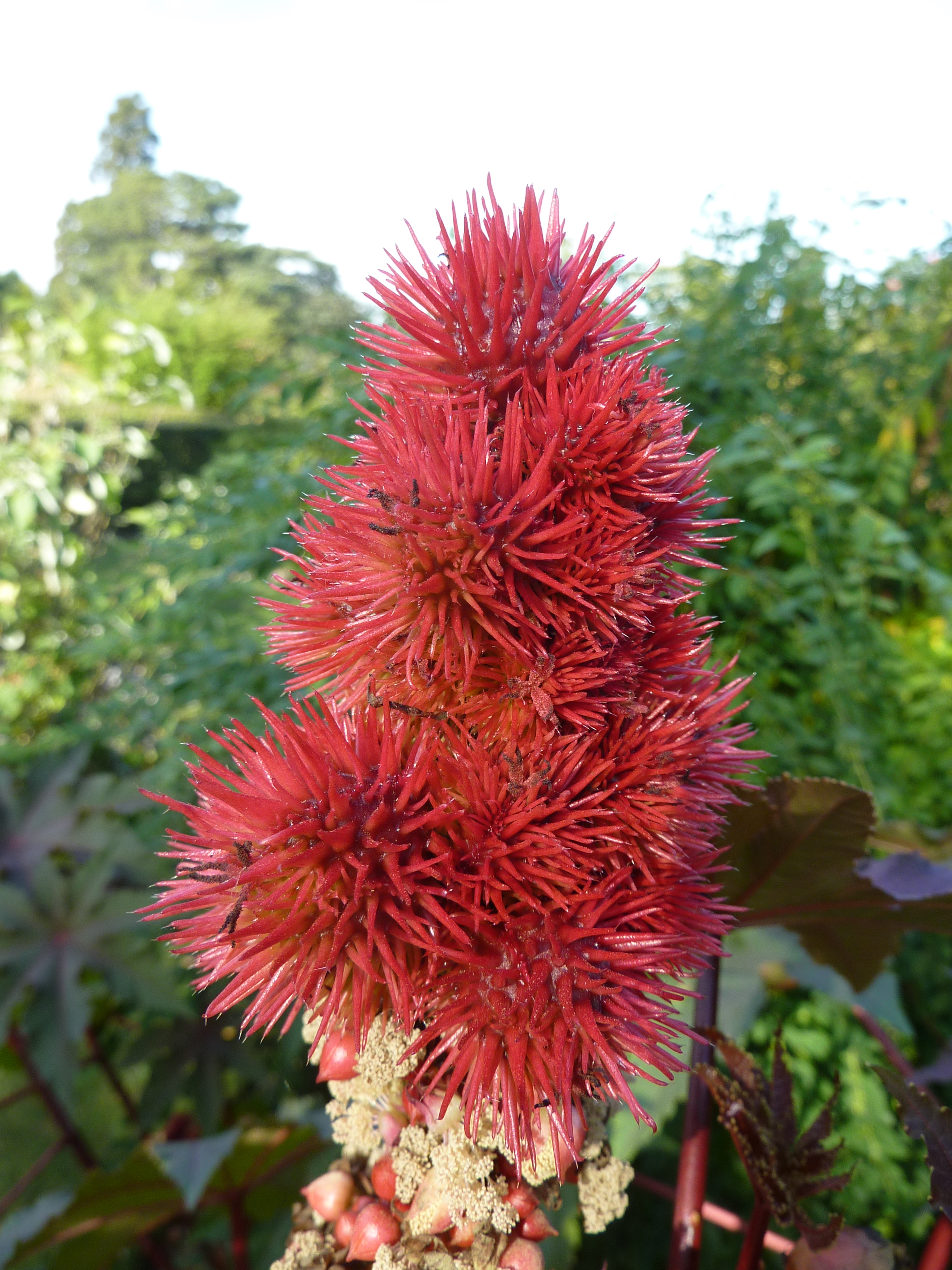
一年生粗壮草本或草质灌木,高达5米;小枝、叶和花序通常被白霜,茎多液汁。叶轮廓近圆形,长和宽达40厘米或更大,掌状7-11裂,裂缺几达中部,裂片卵状长圆形或披针形,顶端急尖或渐尖,边缘具锯齿;掌状脉7-11条。网脉明显;叶柄粗壮,中空,长可达40厘米,顶端具2枚盘状腺体,基部具盘状腺体;托叶长三角形,长2-3厘米,早落。总状花序或圆锥花序,长15-30厘米或更长;苞片阔三角形,膜质,早落;雄花:花萼裂片卵状三角形,长7-10毫米;雄蕊束众多;雌花:萼片卵状披针形,长5-8毫米,凋落;子房卵状,直径约5毫米,密生软刺或无刺,花柱红色,长约4毫米,顶部2裂,密生乳头状突起。蒴果卵球形或近球形,长1.5-2.5厘米,果皮具软刺或平滑;种子椭圆形,微扁平,长8-18毫米,平滑,斑纹淡褐色或灰白色;种阜大。花期几全年或6-9月(栽培)。
原产地可能在非洲东北部的肯尼亚或索马里;现广布于全世界热带地区或栽培于热带至温暖带各国。我国作油脂作物栽培的为一年生草本;华南和西南地区,海拔20-500米(云南海拔2 300米)村旁疏林或河流两岸冲积地常有逸为野生,呈多年生灌木。本种的栽培品种多,依茎、叶呈红色或绿色,果具软刺或无,种子的大小和斑纹颜色等区分。
蓖麻油在工业上用途广,在医药上作缓泻剂;种子含蓖麻毒蛋白(ricin)及蓖麻碱(ricinine),若误食种子过量(小孩2-7粒,成人约20粒)后,将导致中毒死亡。
Ricinus communis, the castor bean or castor万向轮 oil plant, is a species of perennial flowering plant in the spurge(大㦸科植物) family, Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species in the monotypic单一型的 genus, Ricinus, and subtribe, Ricininae. The evolution of castor and its relation to other species are currently being studied using modern genetic tools. It reproduces with a mixed pollination system which favors selfing by geitonogamy(同株授粉) but at the same time can be an out-crosser by anemophily(风媒传粉) or entomophily(虫媒授粉).
Ricinus communis
Common Name(s): African Wonder Tree、Castor Bean、Castor Bean Plant、Castor Oil Plant、Castor-oil Plant、Mole Bean Plant
This plant has high severity poison characteristics.
Description
Castor Bean is a cultivated, annual herbaceous ornamental in the Euphorbiaceae (spruge) family native to Africa.
Plant in full sun in rich moist soils. Fertilize regularly for the best growth. Pruning may be necessary to shape the plant. Plants will have low drought tolerance until well established.
Insects, Diseases, and Other Plant Problems: Spider mites occasionally attack plants that are drought-stressed. If broken seeds are ingested, it is likely to cause death in humans. It may also be fatal to livestock and pets, but it is not often available to them.
Poison Severity:
High
Poison Symptoms:
Immediate or delayed nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, weakness, colic, depression, loss of appetite, trembling, sweating, loss of coordination, difficulty breathing, sweating, progressive central nervous system depression and fever, convulsions, coma; may be fatal; severe allergic reaction in certain individuals following skin contact with broken seeds. May also be fatal to livestock and pets.
Poison Toxic Principle:
Ricin, a phytotoxalbumin, plus ricinine, an alkaloid
Causes Contact Dermatitis:No
Poison Part:Leaves、Seeds
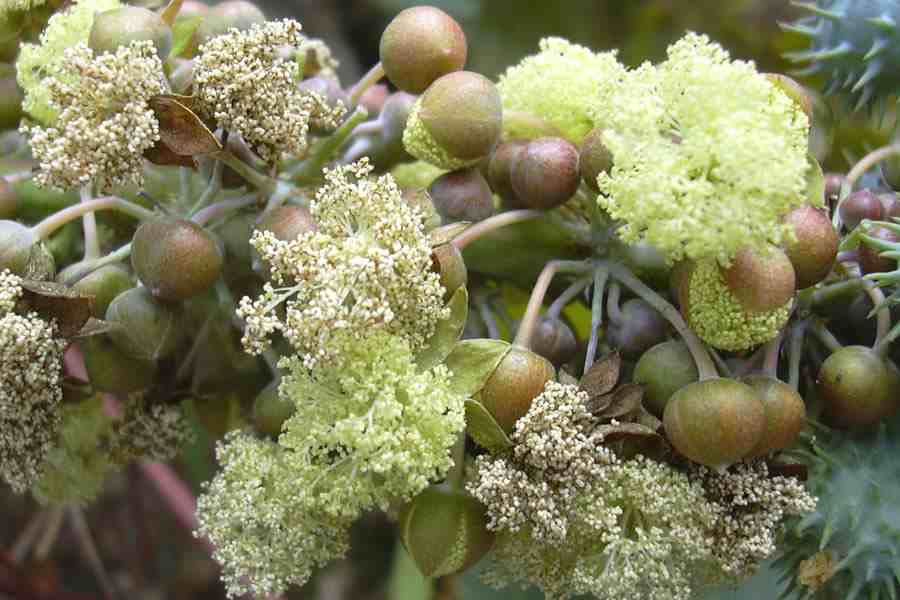
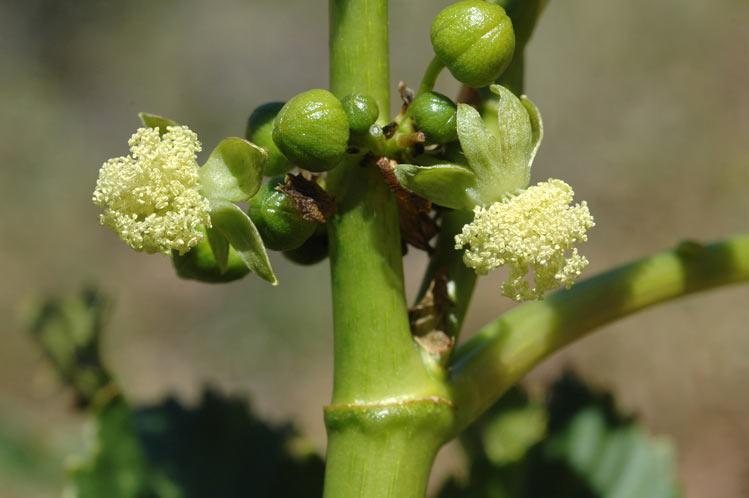













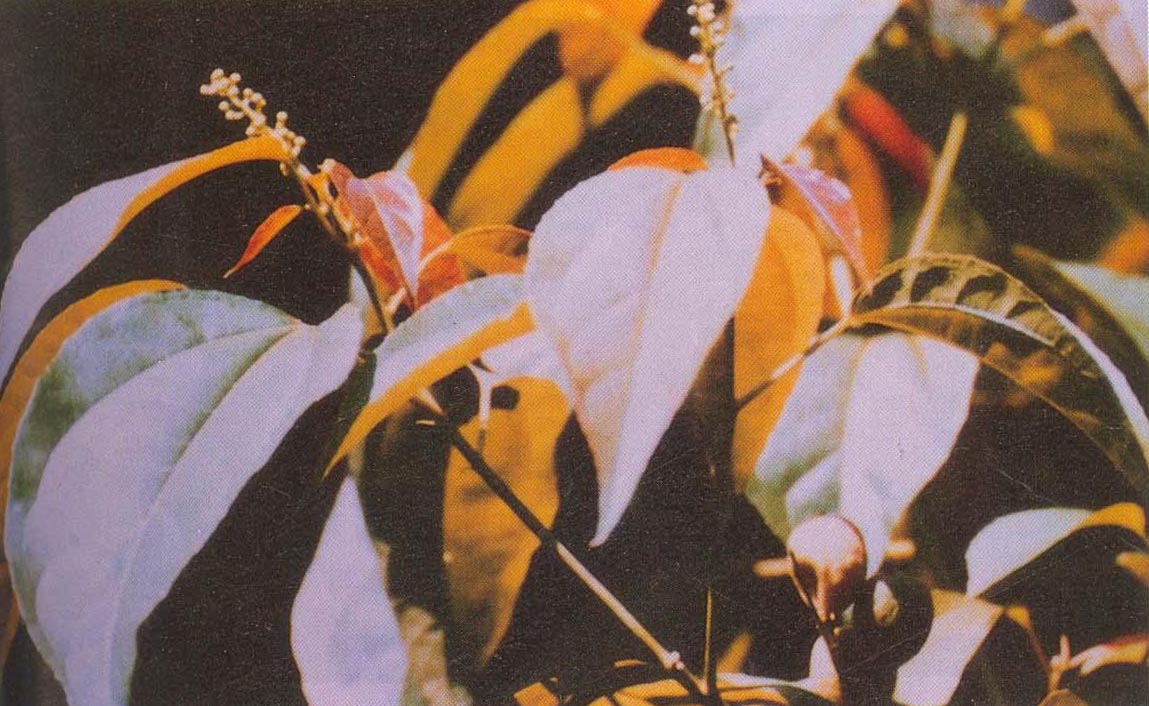
四、油桐属Vernicia Lour.
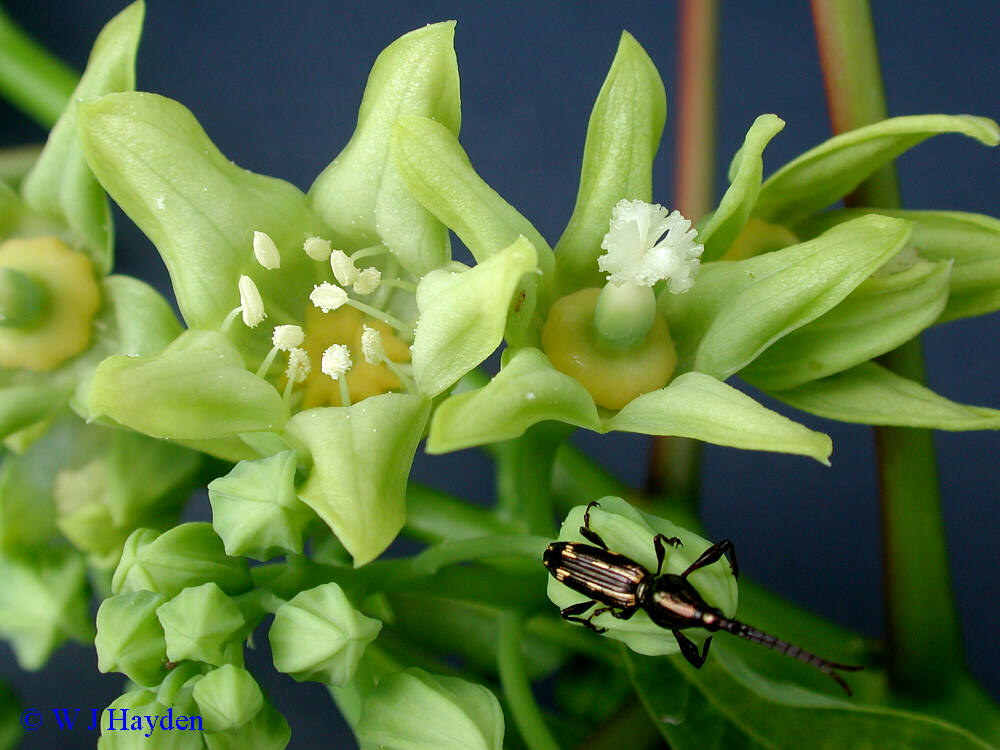
落叶乔木,嫩枝被短柔毛。叶互生,全缘或1-4裂;叶柄顶端有2枚腺体。花雌雄同株或异株,由聚伞花序再组成伞房状圆锥花序;雄花花萼花蕾时卵状或近圆球状,开花时多少佛焰苞状,整齐或不整齐2-3裂;花瓣5枚,基部爪状;腺体5枚;雄蕊8-12枚,2轮,外轮花丝离生,内轮花丝较长且基部合生;雌花:萼片、花瓣与雄花同;花盘不明显或缺;子房密被柔毛,3(-8)室,每室有1颗胚珠,花柱3-4枚,各2裂。果大,核果状,近球形,顶端有喙尖,不开裂或基部具裂缝,果皮壳质,有种子3(-8)颗;种子无种阜,种皮木质。
3种;分布于亚洲东部地区。我国有2种;分布于秦岭以南各省区。
本属植物均为经济植物,其种子的油称桐油。为干性油,用于木器、竹器、舟揖等涂料,也为油漆等原料。
1. 油桐(种子植物名称) 桐油树,桐子树,罂子桐(本草拾遗),荏桐(本草衍义)
Vernicia fordii (Hemsl.)
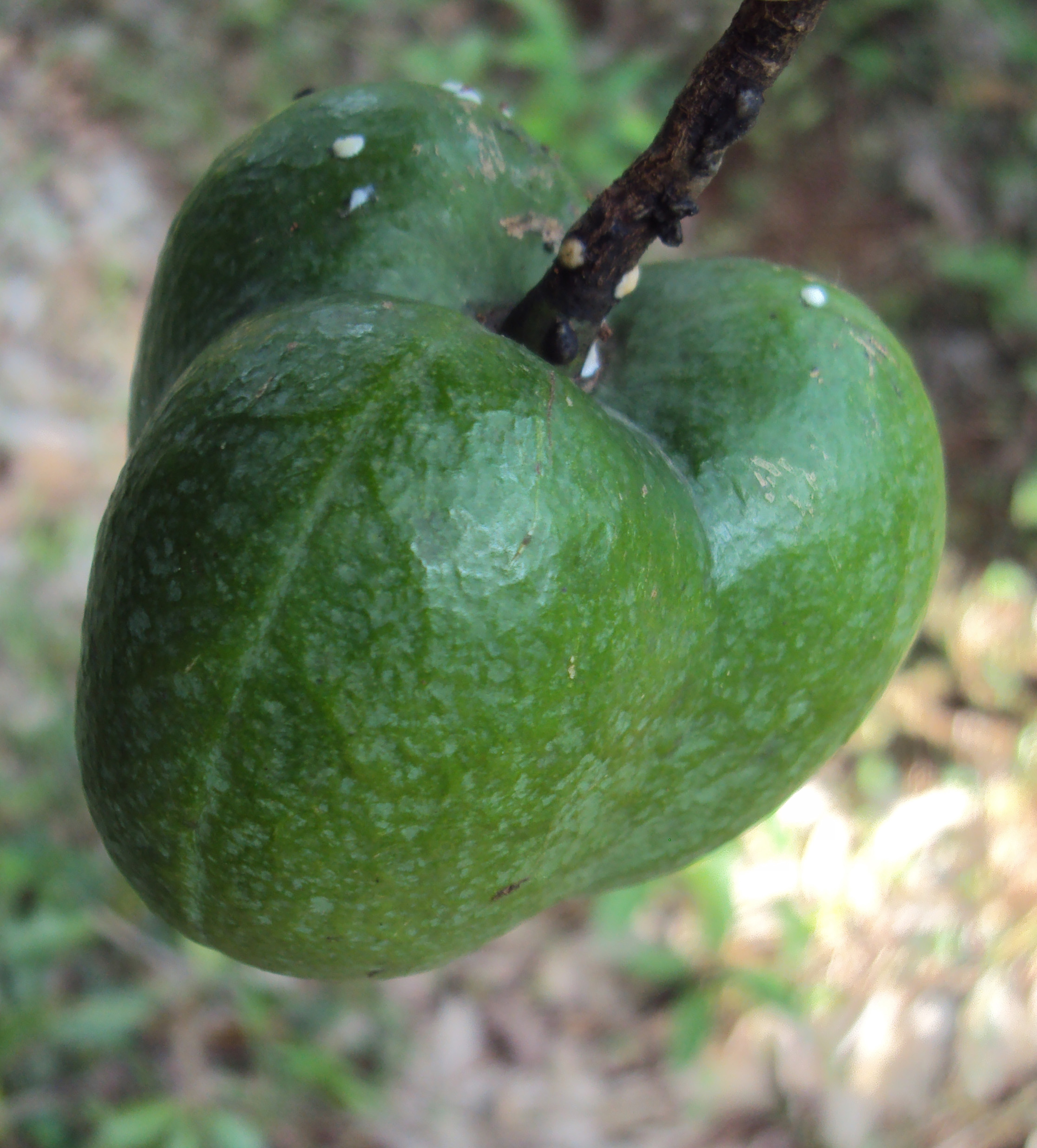
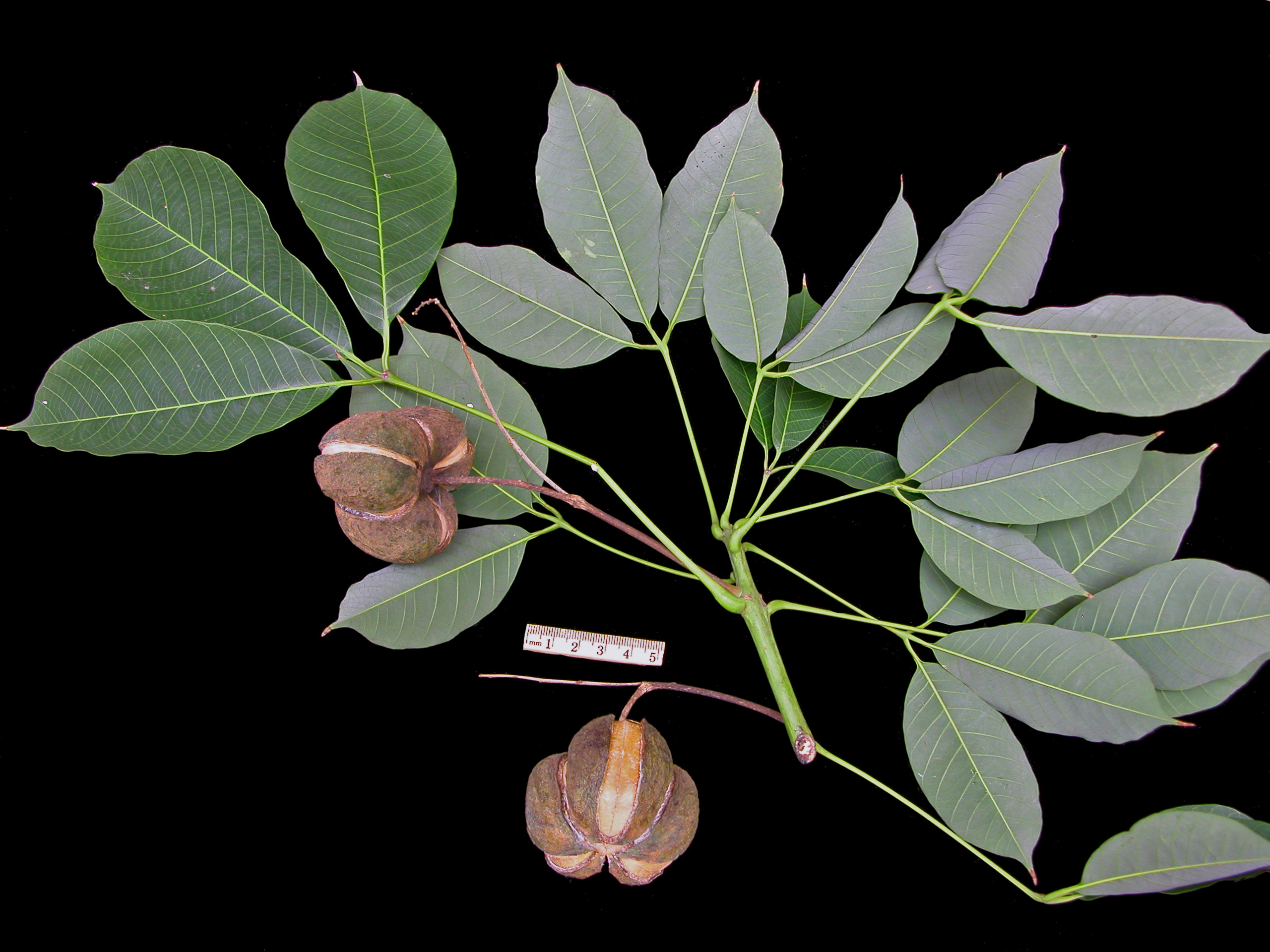
落叶乔木,高达10米;树皮灰色,近光滑;枝条粗壮,无毛,具明显皮孔。叶卵圆形,长8-18厘米,宽6-15厘米,顶端短尖,基部截平至浅心形,全缘,稀1-3浅裂,嫩叶上面被很快脱落微柔毛,下面被渐脱落棕褐色微柔毛,成长叶上面深绿色,无毛,下面灰绿色,被贴伏微柔毛;掌状脉5(-7)条;叶柄与叶片近等长,几无毛,顶端有2枚扁平、无柄腺体。花雌雄同株,先叶或与叶同时开放;花萼长约1厘米,2(-3)裂,外面密被棕褐色微柔毛;花瓣白色,有淡红色脉纹,倒卵形,长2-3厘米,宽1-1.5厘米,顶端圆形,基部爪状;雄花:雄蕊8-12枚,2轮;外轮离生,内轮花丝中部以下合生;雌花:子房密被柔毛,3-5(-8)室,每室有1颗胚珠,花柱与子房室同数,2裂。核果近球状,直径4-6(-8)厘米,果皮光滑;种子3-4(-8)颗,种皮木质。花期3-4月,果期8-9月。
产于陕西、河南、江苏、安徽、浙江、江西、福建、湖南、湖北、广东、海南、广西、四川、贵州、云南等省区。通常栽培于海拔1 000米以下丘陵山地。越南也有分布。模式标本采自湖北宜昌。
本种是我国重要的工业油料植物;桐油是我国的外贸商品;此外,其果皮可制活性炭或提取碳酸钾。
Vernicia fordii, usually known as the tung tree is a species of Vernicia in the spurge family native to southern China, Burma, and northern Vietnam. It is a small to medium-sized deciduous tree growing to 20 m tall, with a spreading crown. The bark is smooth and thin, and bleeds latex if cut. The leaves are alternate, simple, 4.5–25 cm long and 3.5–22 cm broad, heart-shaped or with three shallow, maple枫树-like lobes, green above and below, red conspicuous glands at the base of the leaf, and with a 5.5–26 cm long petiole. The flowers are 2.5–3.5 cm diameter, with five pale pink to purple petals with streaks of darker red or purple in the throat; it is monoecious with individual flowers either male or female, but produced together in the inflorescences. The flowers appear before or with the leaves in loose, terminal clusters. The fruit is a hard, woody pear-shaped berry 4–6 cm long and 3–5 cm diameter, containing four or five large, oily seeds; it is green initially, becoming dull brown when ripe in autumn.
TOXIC PLANT
one seed can be fatal to humans, however all parts of the tung tree are poisonous even though it has been used to treat skin conditions and constipation(便秘). Symptoms may include severe stomach pain, vomiting(吐), diarrhea(腹泻), weakness, slowed breathing, and poor reflexes. The leaves give some people a poison-ivy-like rash(皮疹).
Tung oil trees are cultivated primarily for their seeds, but also used as ornamental trees in the landscape. The seeds produce oils that are used in the manufacture of lacquers(漆), varnishes(罩光漆), paints, linoleum(油毡), oilcloth, resins(树脂、松香), artificial leather, felt-base floor coverings, and greases(油脂), brake-linings(衬里) and in clearing and polishing compounds. In its native range, the seedlings have been planted for thousands of years. During World War II, the Chinese used tung oil for motor fuel.
Species Characteristics
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Habit: trees are deciduous and can grow up to 40 feet tall having smooth bark and soft wood
Leaves: heart-shaped, sometimes lobed, alternate leaves are dark green and up to 6 inches wide. A distinguishing characteristic of tung oil tree are the presence of two red glands at the apices of the petiole.
Flowers: white with a rose colored center and are borne in clusters arising from terminal buds of shoots from the previous season. Tung oil tree flowers before it produces its leaves.
Fruit: spherical or pear-shaped, green to purple at maturity
Seeds: 4 to 5 seeds, hard outer shell and a kernel from which the oil is obtained
Distribution in Florida: central and north
Impacts
Tung oil tree invades forest edges, right-of-ways, and urban green spaces. Spread is accomplished mainly through seed production. Fruit production begins when trees are 2 to 4 years old. Vegetative reproduction occurs by way of suckers from underground stems. Tung oil tree is able to grow in a wide array of environmental conditions, making it a successful, but slow invasive.
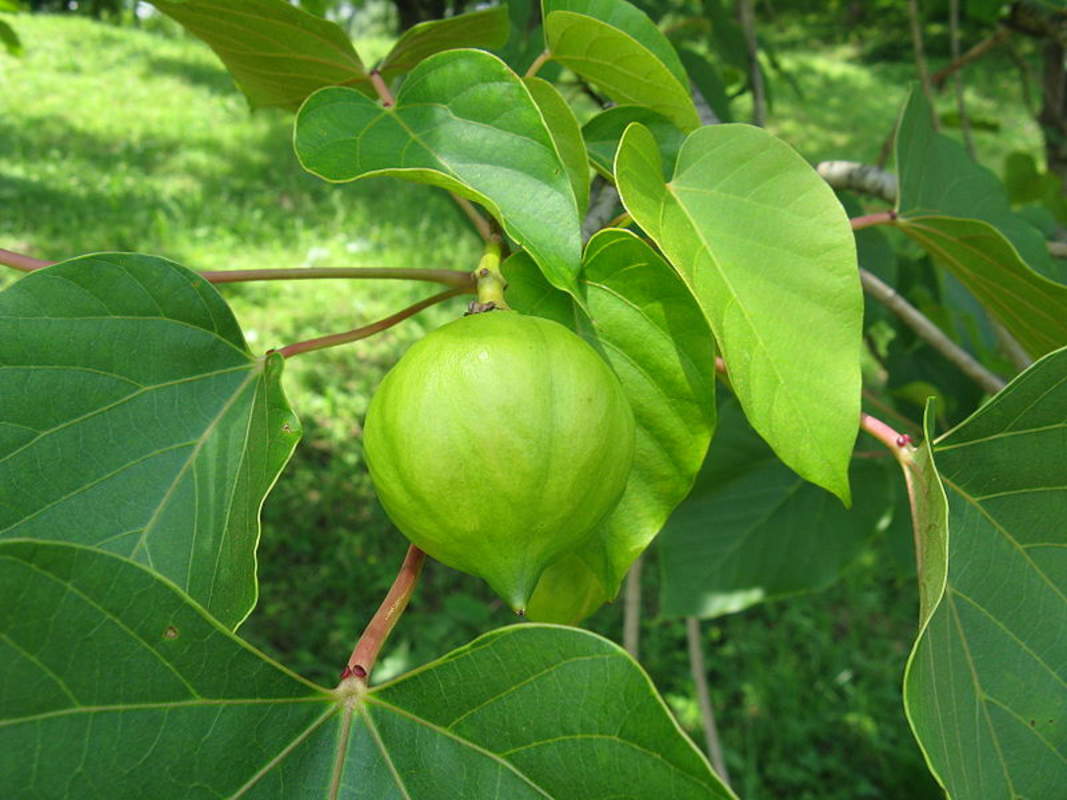
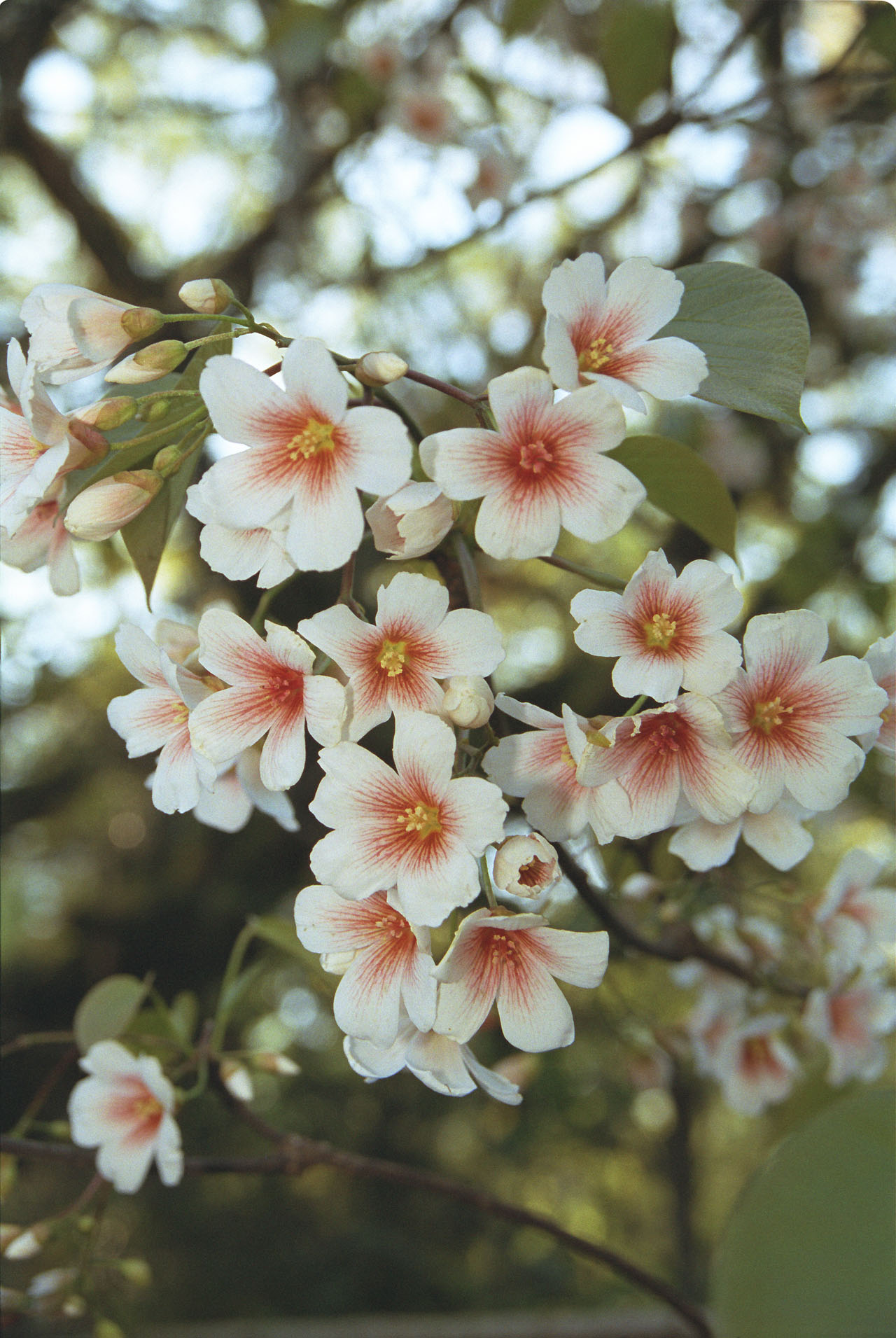
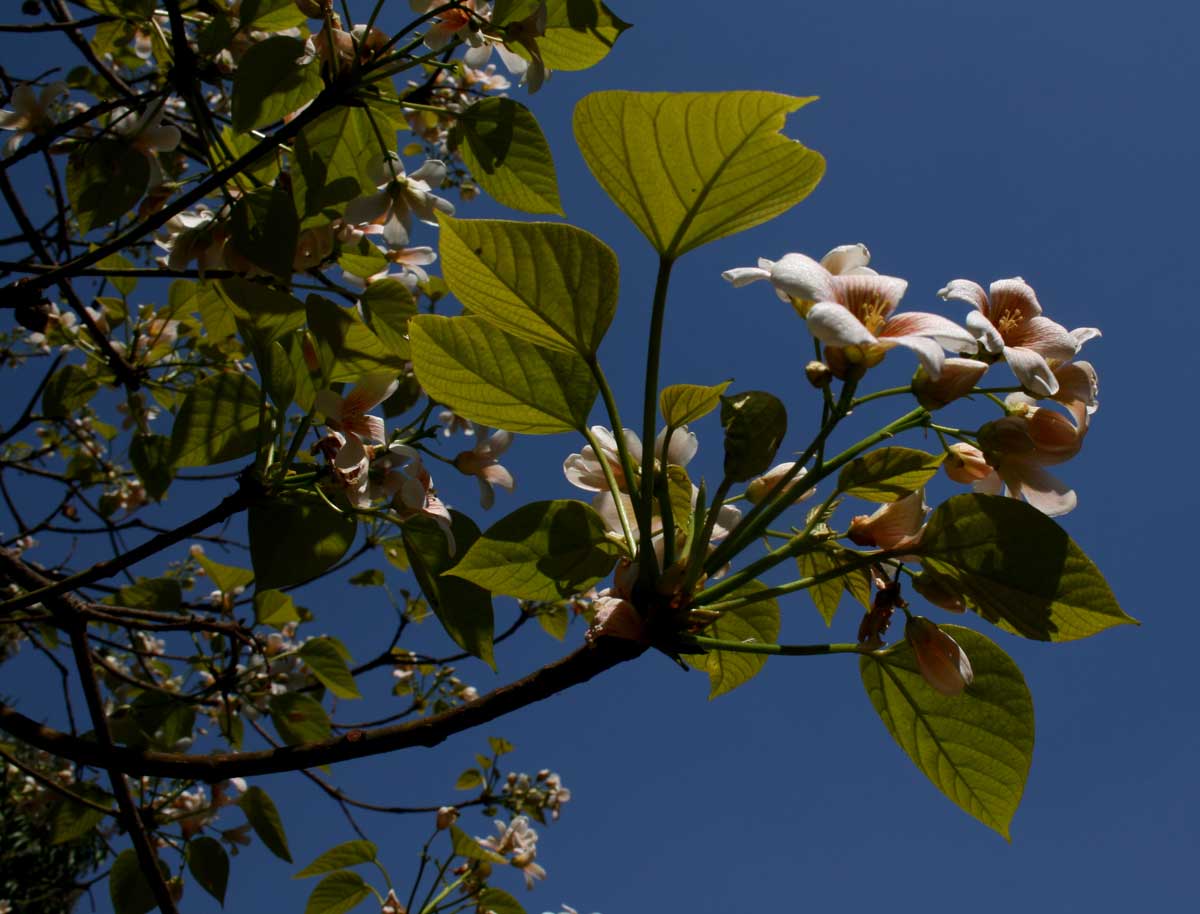
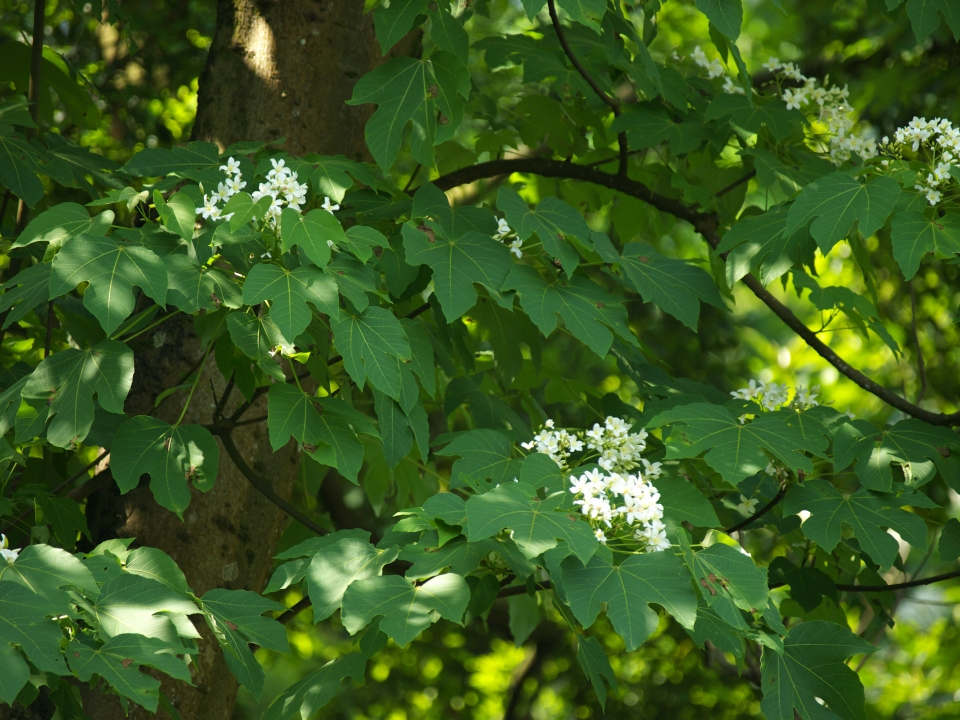
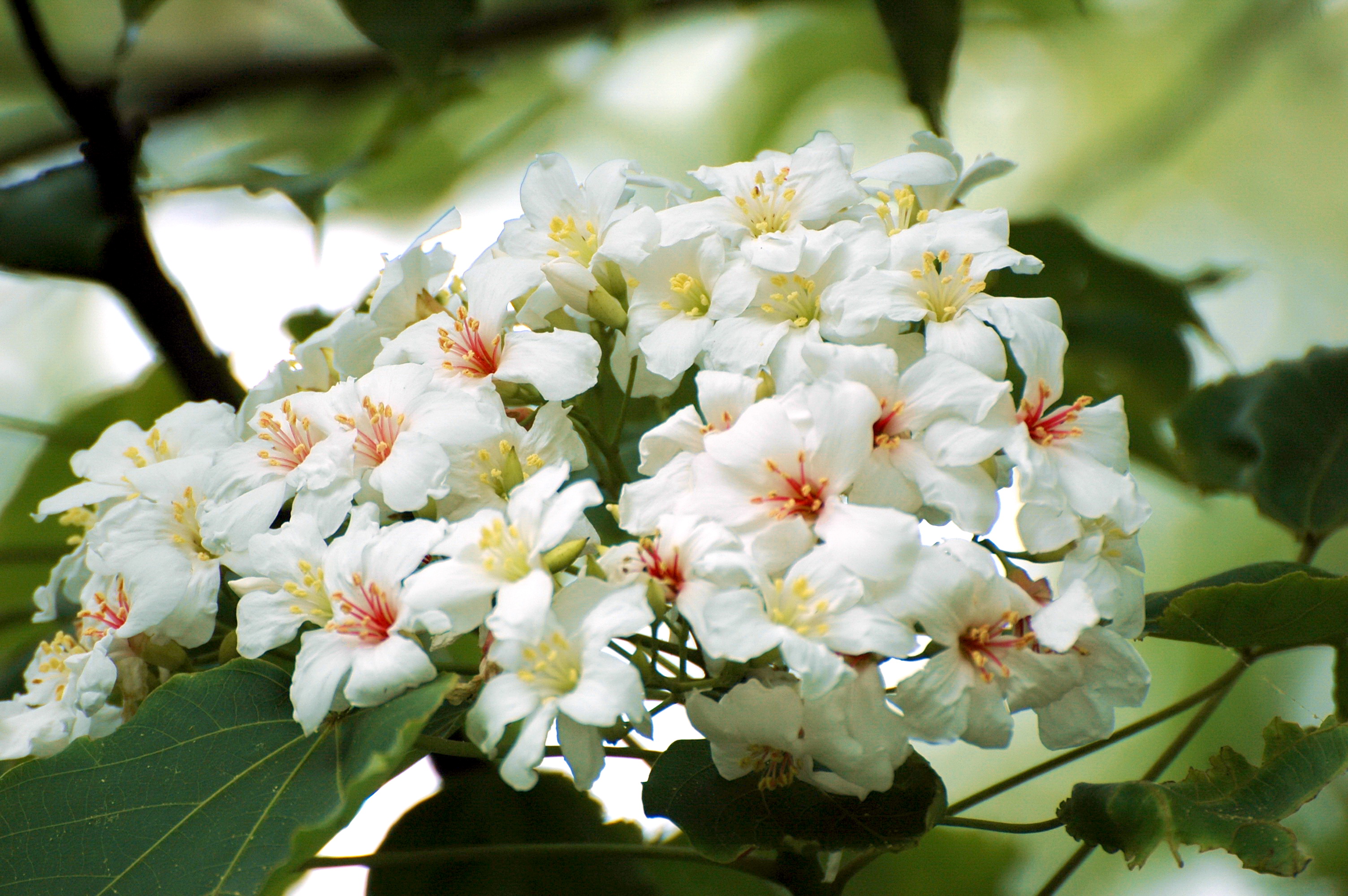
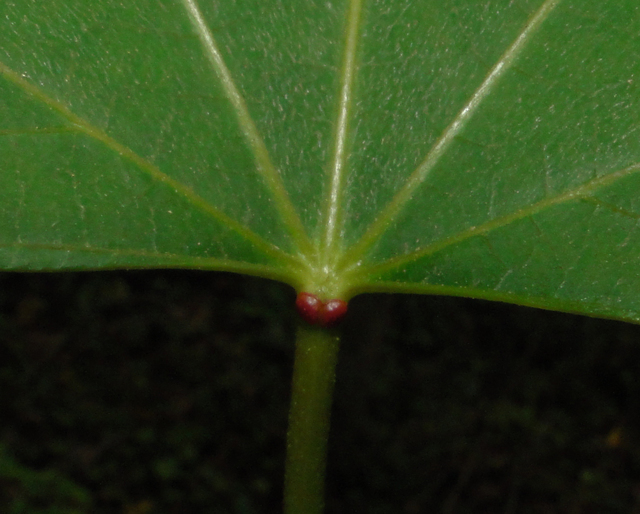
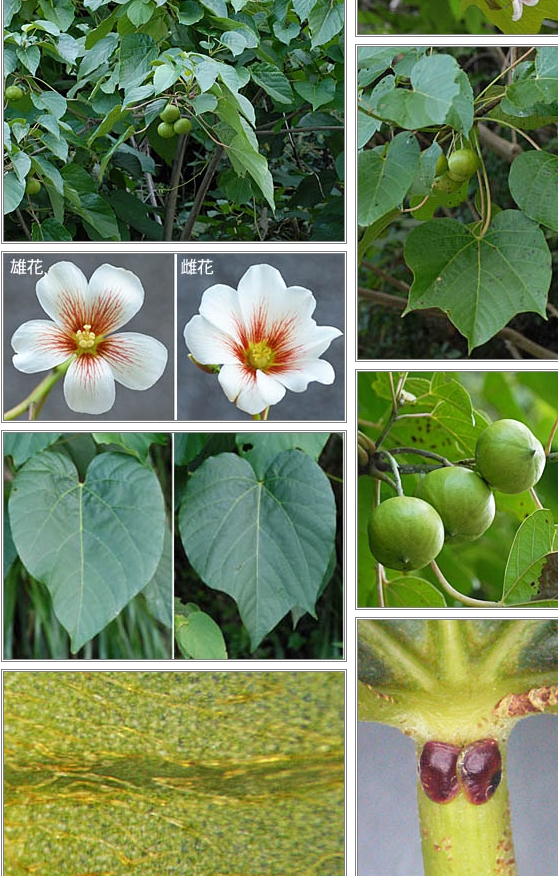











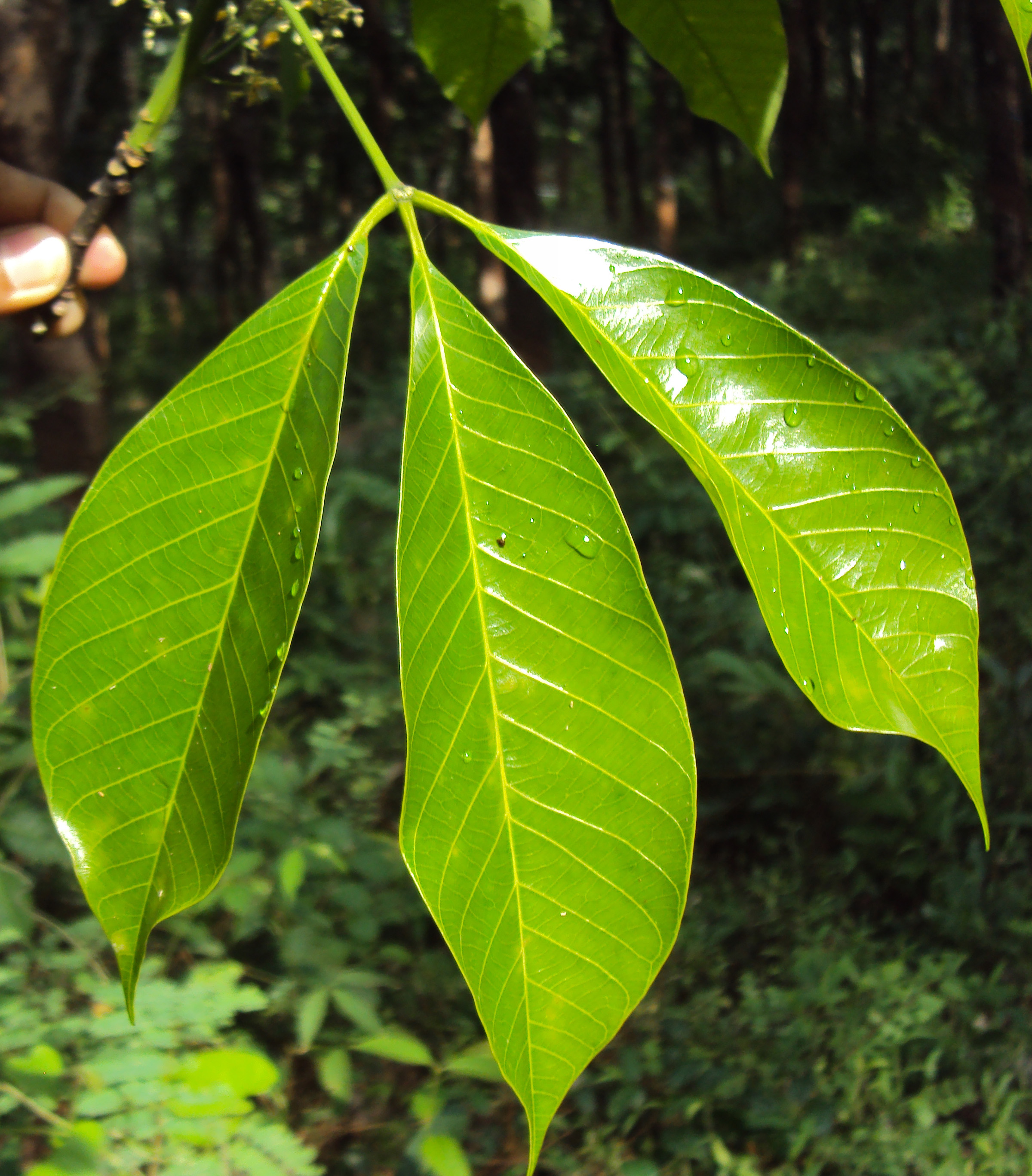
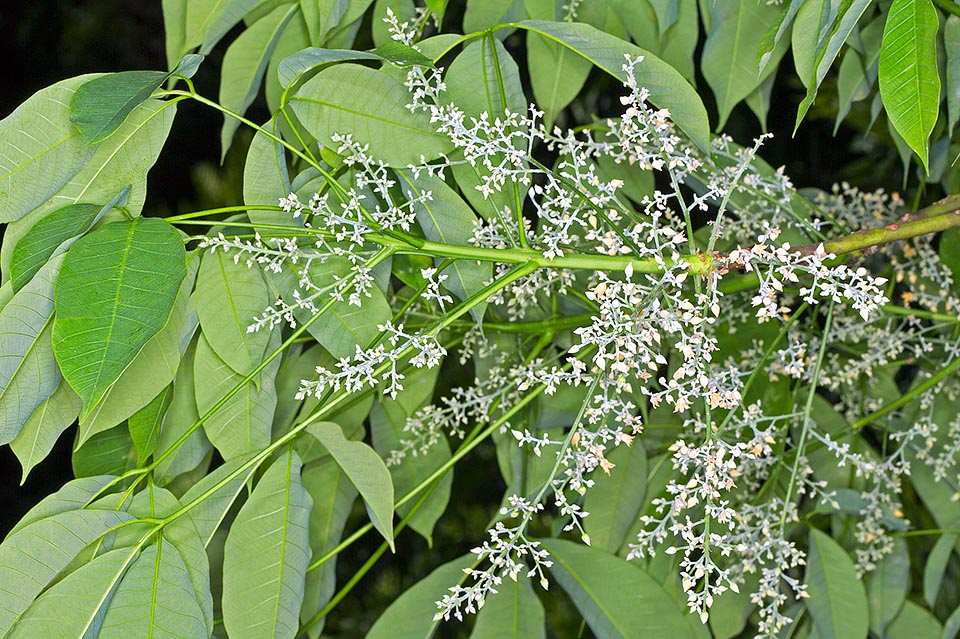
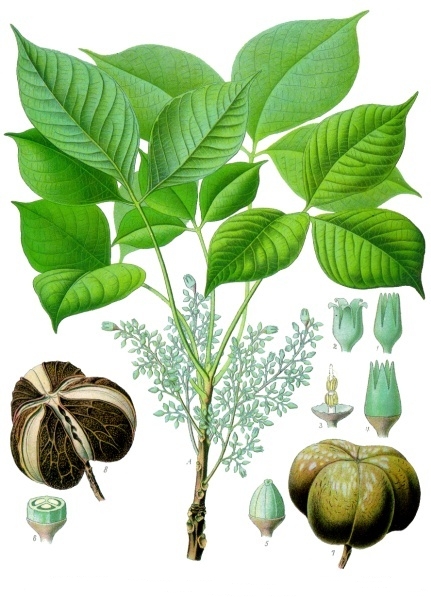
五、橡胶树属Hevea Aubl.
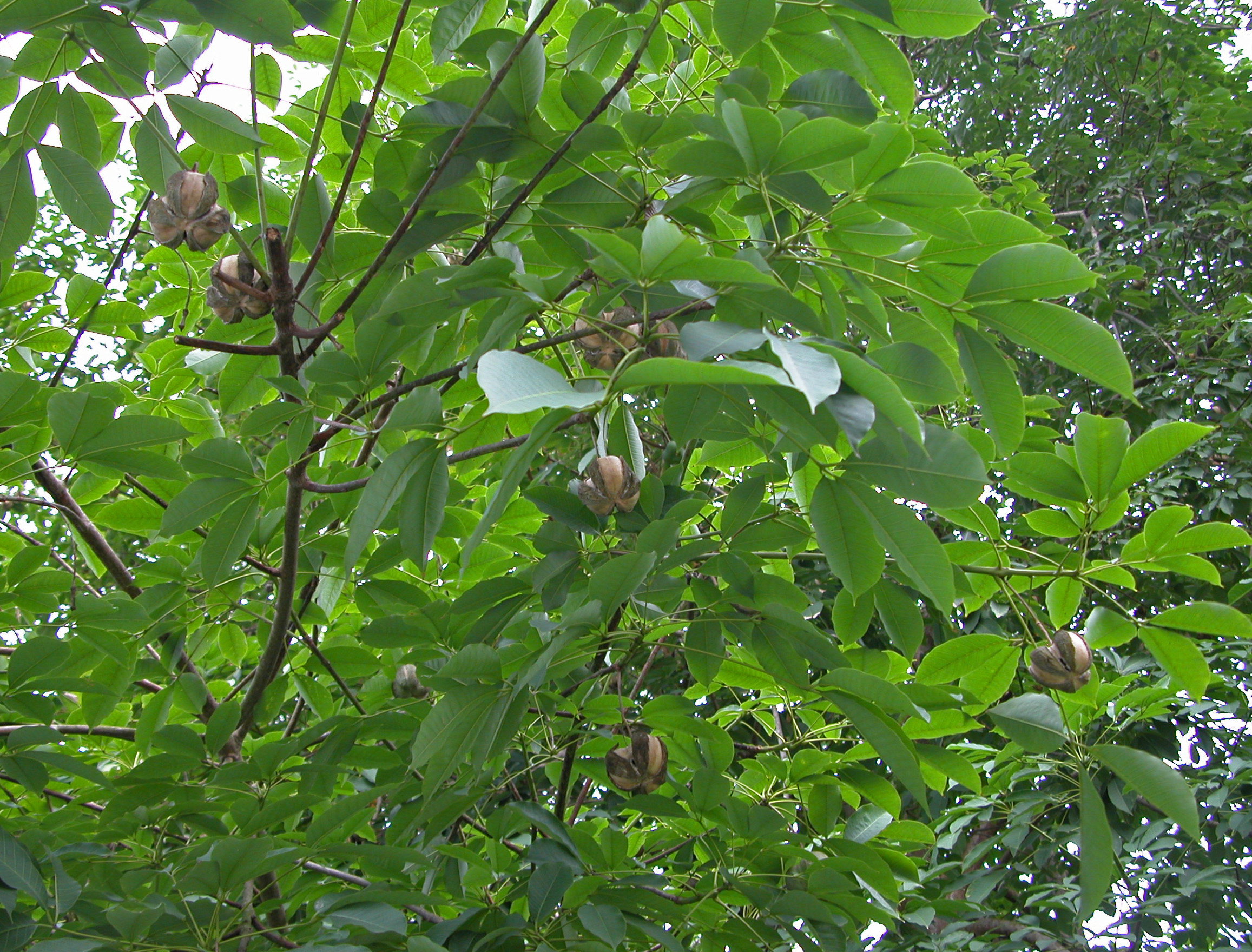
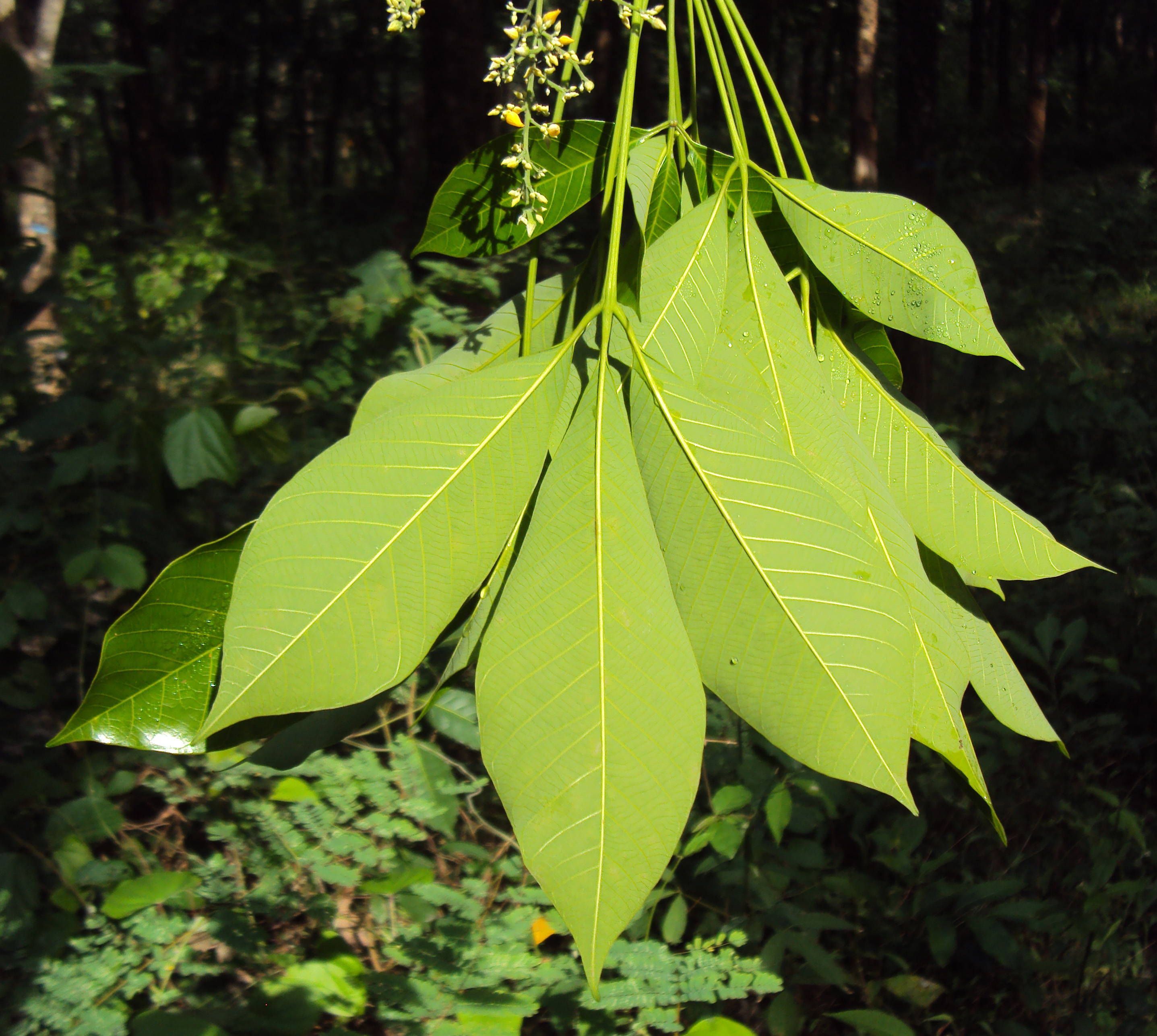
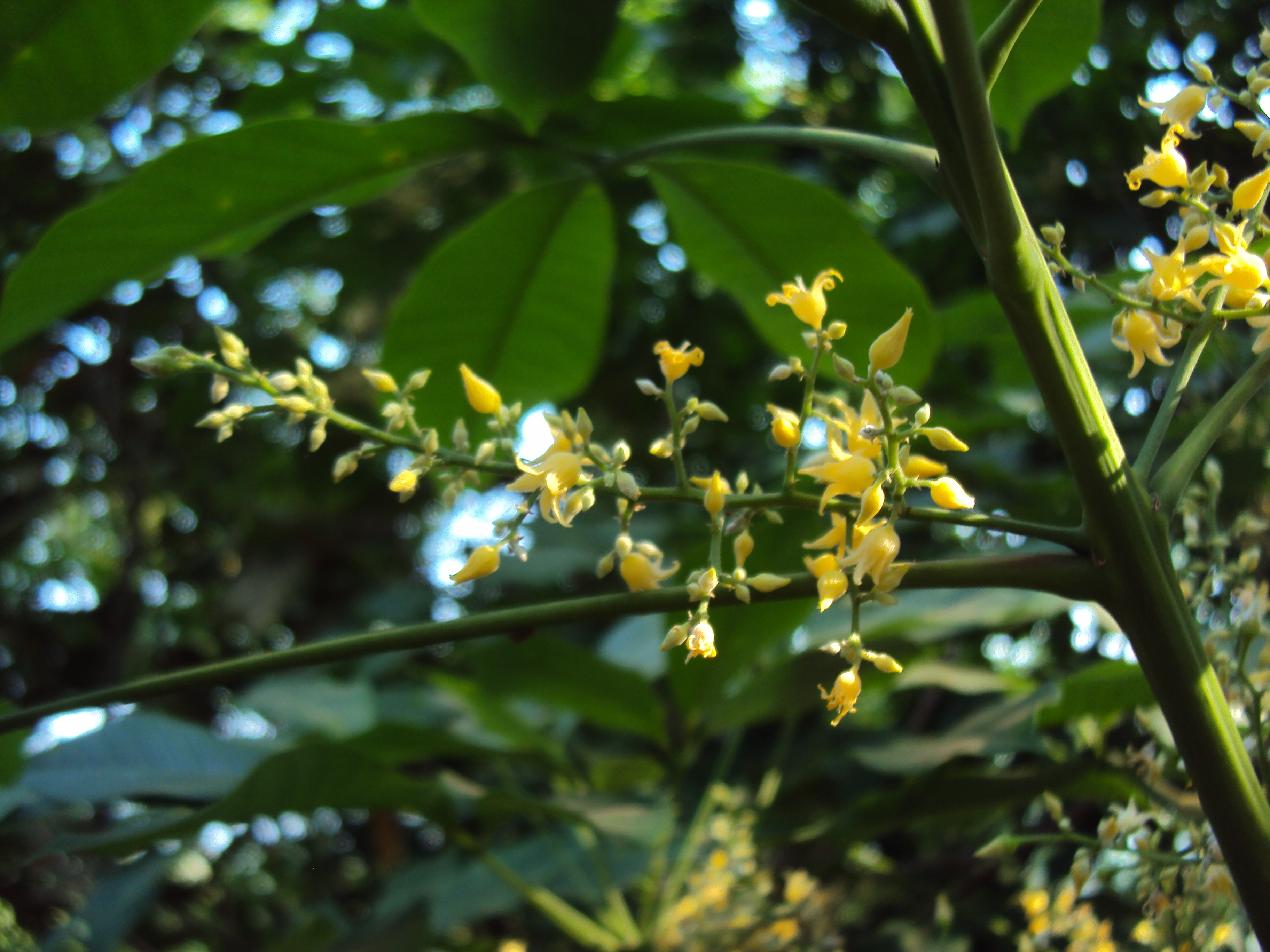
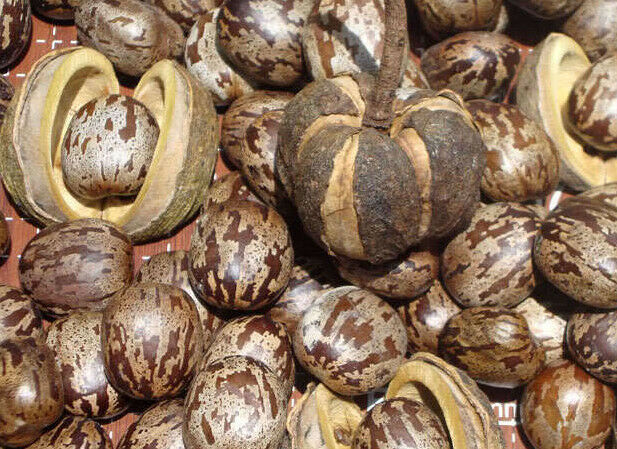
乔木;有丰富乳汁。叶互生或生于枝条顶部的近对生,具长叶柄,叶柄顶端有腺体,具小叶3 (-5)片,全缘,有小叶柄。花雌雄同株,同序,无花瓣,由多个聚伞花序组成圆锥花序,雌花生于聚伞花序的中央,其余为雄花,雄花花蕾时近球形或卵球形,花萼5齿裂或5深裂;花盘分裂为5枚腺体或浅裂或不裂;雄蕊5-10枚,花丝合生成一超出花药的柱状物,花药排成整齐或不整齐的1-2轮;雌花的花萼与雄花同;子房3室,稀较少或较多,每室有1颗胚珠,通常无花柱,柱头粗壮。蒴果大,通常具3个分果爿,外果皮近肉质,内果皮木质;种子长圆状椭圆形,具斑纹,无种阜,子叶宽扁
约12种;分布于美洲热带地区。其中橡胶树,现我国南部栽培
1.橡胶树(广州植物志)巴西橡胶,橡皮树,三叶橡胶 图版32: 1-6
Hevea brasiliensis (Willd. ex A. Juss.) Muell.
大乔木,高可达30米,有丰富乳汁。指状复叶具小叶3片;叶柄长达15厘米,顶端有2 (3-4)枚腺体;小叶椭圆形,长10-25厘米,宽4-10厘米,顶端短尖至渐尖,基部楔形,全缘,两面无毛;侧脉10-16对,网脉明显;小叶柄长1-2厘米。花序腋生,圆锥状,长达16厘米,被灰白色短柔毛;雄花:花萼裂片卵状披针形,长约2毫米;雄蕊10枚,排成2轮,花药2室,纵裂;雌花:花萼与雄花同,但较大;子房(2-) 3(-6)室,花柱短,柱头3枚。蒴果椭圆状,直径5-6厘米,有3纵沟,顶端有喙尖,基部略凹,外果皮薄,干后有网状脉纹,内果皮厚、木质;种子椭圆状,淡灰褐色,有斑纹。花期5-6月。
原产巴西;现广泛栽培于亚洲热带地区;我国台湾、福建南部、广东、广西、海南和云南南部均有栽培,以海南和云南种植较多。本种是最主要的天然橡胶植物。
Hevea brasiliensis, the Pará rubber tree, sharinga tree, seringueira, or most commonly, rubber tree or rubber plant, is a flowering plant belonging to the spurge family Euphorbiaceae. It is the most economically important member of the genus Hevea because the milky latex extracted from the tree is the primary source of natural rubber.
BOTANY
In the wild, the rubber tree will grow to heights of 100 to 130 feet, and can live up to 100 years. Its most famous feature is the milky white sap, known as latex(胶乳), which flows freely from the tree when a sliver of bark is removed. A rubber tree, also referred to as rubberwood, can be tapped for latex once it reaches approximately six years of age. In order to reproduce, the fruit of the rubberwood burst open when ripe, scattering its many seeds in an area spanning up to 100 feet from the tree.
HABITAT
Hevea brasiliensis is a species of rubberwood that is native to rainforests in the Amazon region of South America, including Brazil, Venezuela, Ecuador, Colombia, Peru, and Bolivia. These trees are generally found in low-altitude moist forests, wetlands, riparian(河边的) zones, forest gaps, and disturbed areas. It is a quick growing tree, often the first to establish itself when a gap in the canopy is produced but may be shaded out as more trees fill in the canopy opening. Today, commercially-produced rubber can also be found throughout much of Southeast Asia and Western Africa.
SIGNIFICANCE
First discovered by the ancient Olmec, Maya, and Aztec, the latex sap from the rubber tree was once used to make rubber balls, to waterproof clothes, and even to form homemade shoes. Today, the latex sap from the rubber tree is still used in the modern processing of rubber and is often a substantial source of income for indigenous(土生土长的) populations.
DID YOU KNOW
Historically, cattle ranchers and rubber tappers have disagreed over the rights to clear forest land. Cutting down the forest is not only detrimental to the species that depend on that land, but also damaging to the people that earn a living by sustainably harvesting what the forest provides. Many indigenous people depend on these sources of income to provide for their families and communities.
Chico Mendes, a Brazilian rubber tapper, became famous when he organized the National Council of Rubber Tappers in Brazil to help protest against the clear cutting of land for cattle grazing. Thanks to his efforts, the union gained the support of the Brazilian government and was able to set aside crucial “extractive reserves” within Brazil. These reserves allow for the sustainable harvest of goods, such as rubber or nuts, and protect against the clear cutting of trees. In 1988, Chico Mendes was murdered for his work to create extractive reserves and protect the rainforest. His efforts have been carried on by his coworkers and supporters across the world.