-
1 主页
-
2 教学
2.69玄参科Scropariaceae
草本、灌木或乔木。单叶对生,无托叶。花两性,不整齐;萼4~5裂宿存;花冠4~5裂,常二唇形;雄蕊常2强;子房上位常2室,胚珠多数,柱头头状或2裂。蒴果稀浆果状。
约200属3000种,广布全球各地。我国约57属600余种,全国各地均有分布。
泡桐属Pau1ownia Sieb.et Zucc.
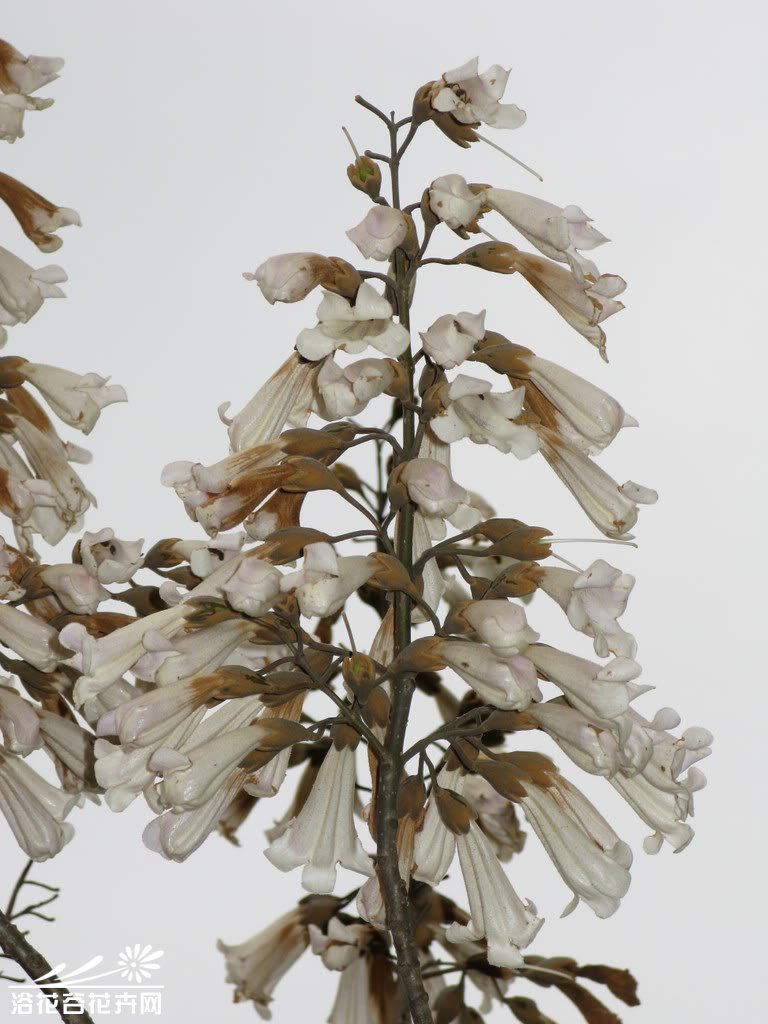
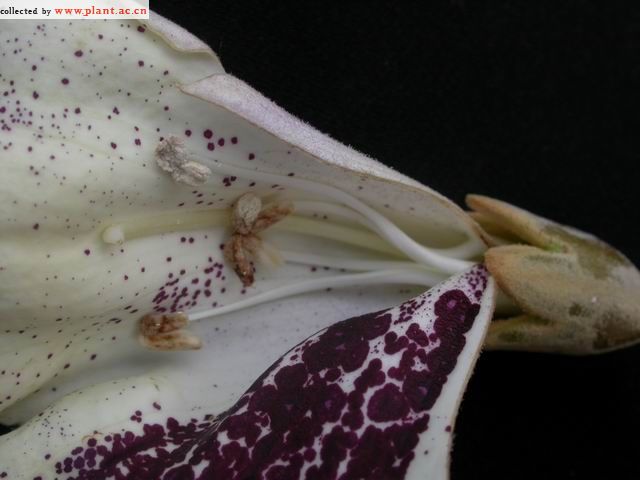
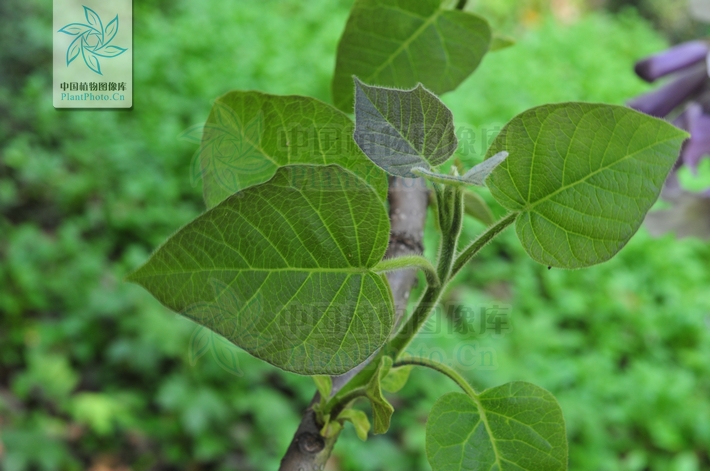
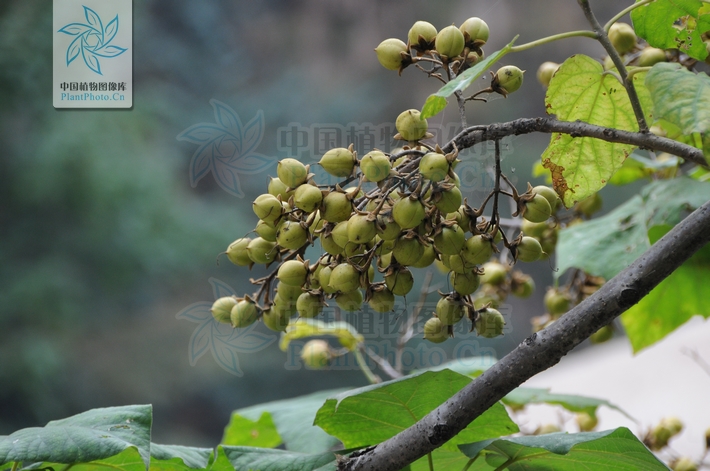
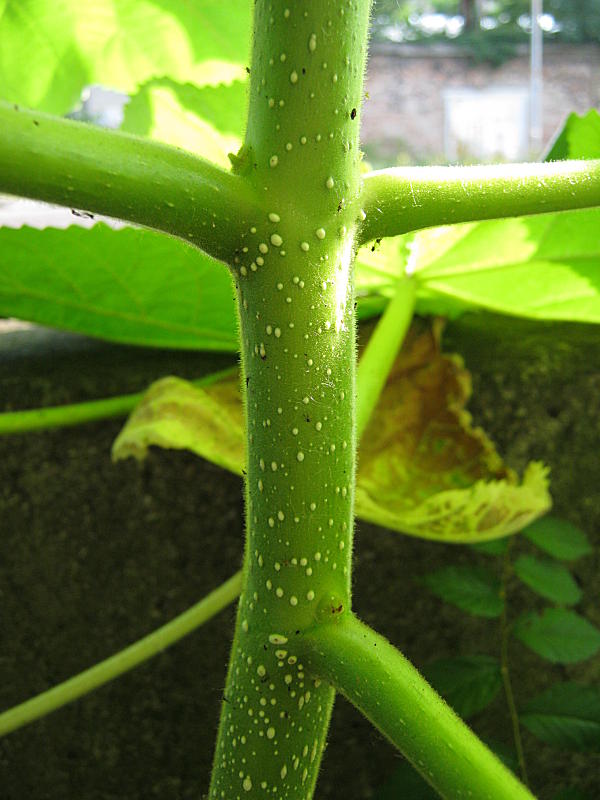
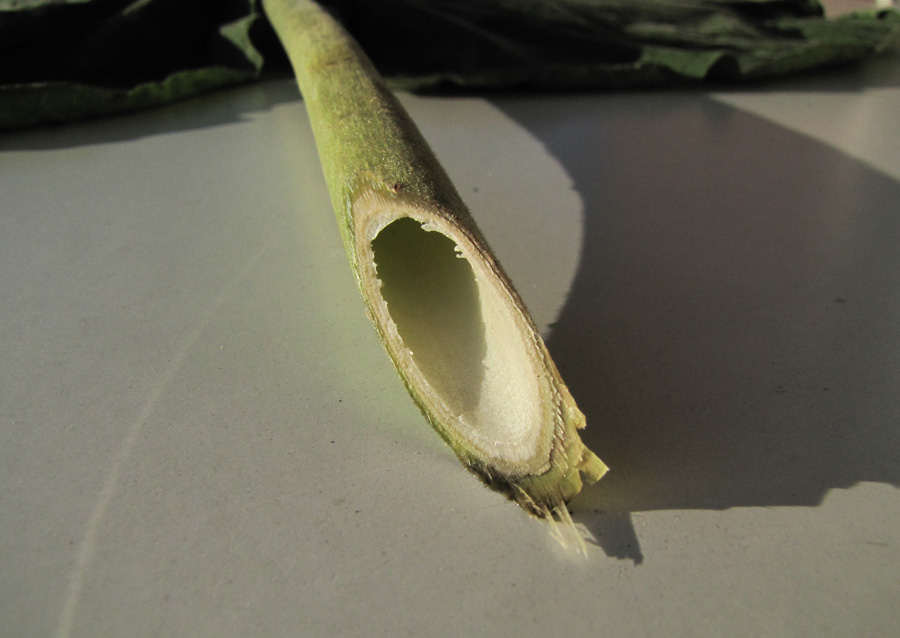
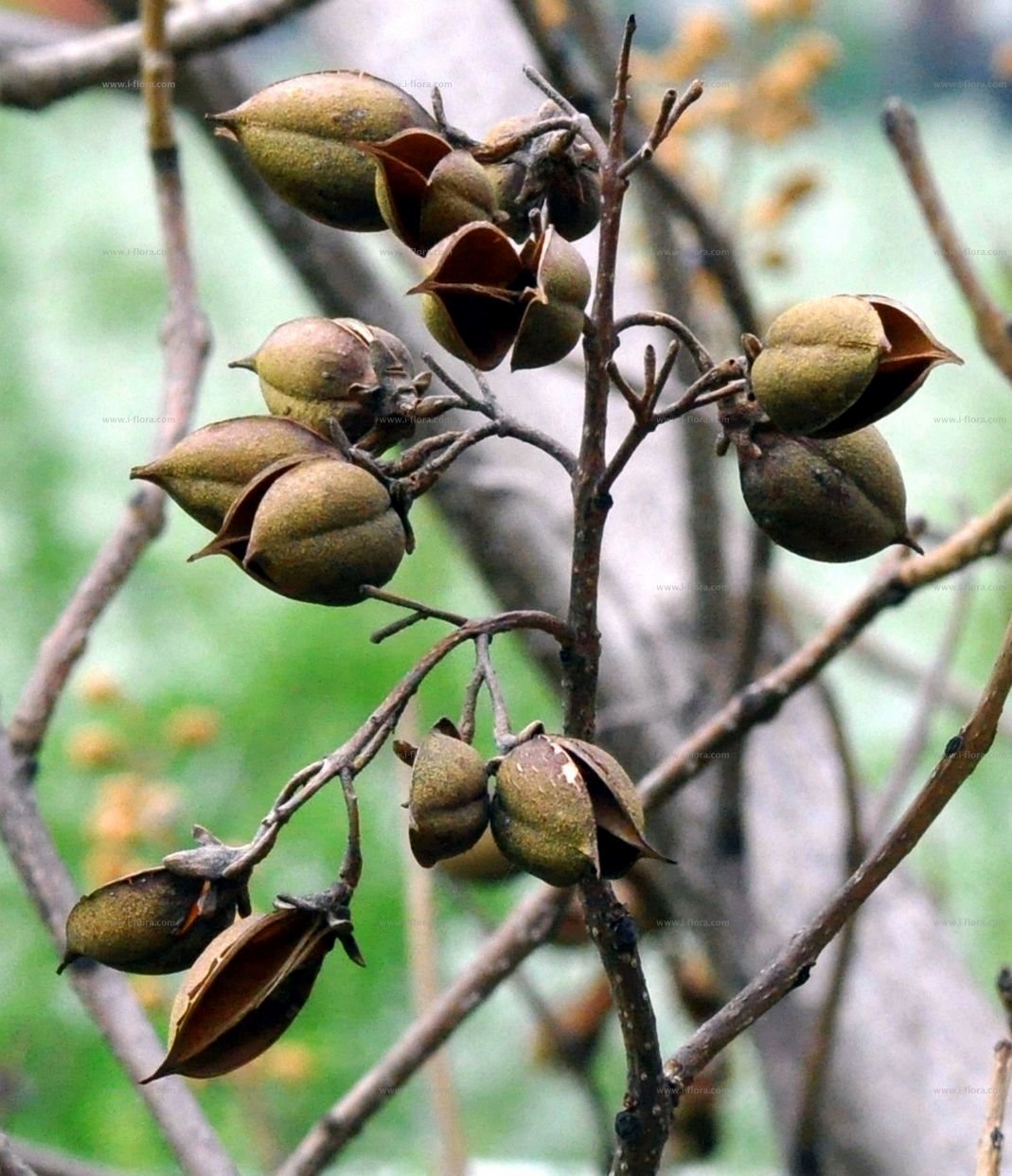
落叶乔木。小枝粗壮,髓腔大;常无顶芽,侧芽常叠生。单叶对生,有时3枚轮生,全缘、波状或3~5浅裂;叶柄长。聚伞圆锥花序,以蕾越冬,花蕾大,密被毛;萼钟状,5裂;花冠二唇形,紫或白色,内常有深紫色斑点;2强雄蕊;柱头2裂。蒴果。
1o余种,分布于东亚,主产我国,几乎遍布全国。
分种检索表
1.花冠紫色或紫蓝色,花萼裂至中部或过中部;叶两面均被毛……………………紫花泡桐
1.花冠乳白色至微带紫色,花萼浅裂至1/4~1/3;叶表无毛,背面被毛………白花泡桐
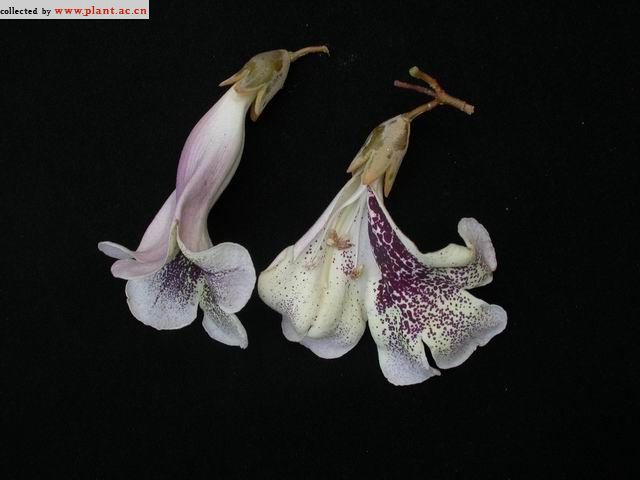
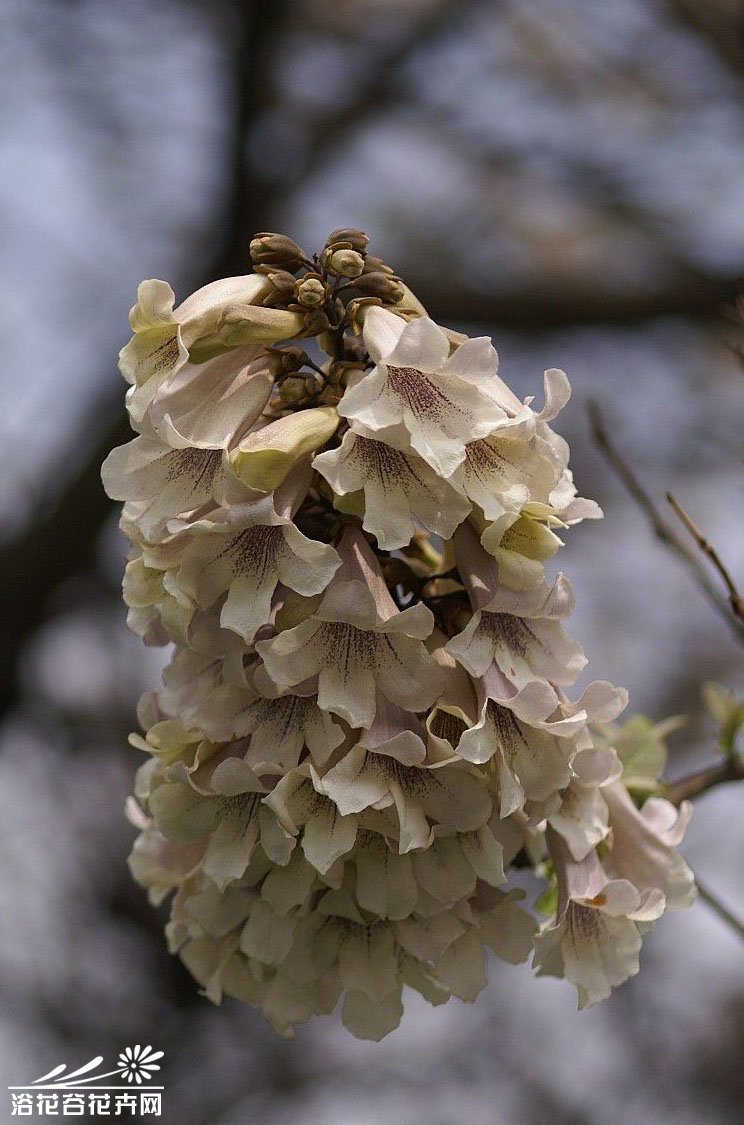
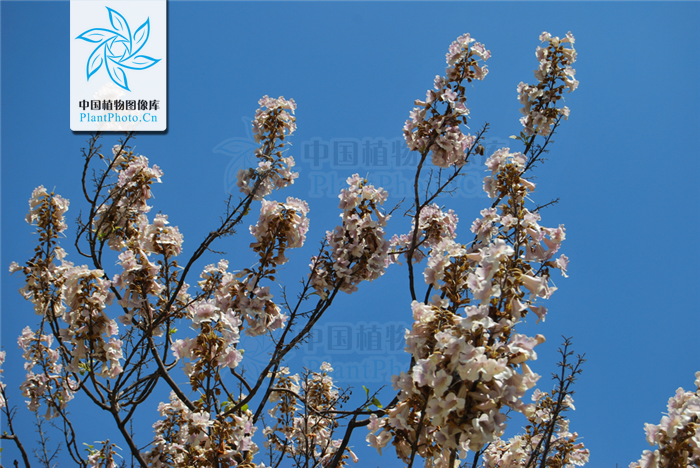
1.紫花泡桐(毛泡桐)Paulownia tomentosa(Thunb.)Steud.
通用名:毛泡桐
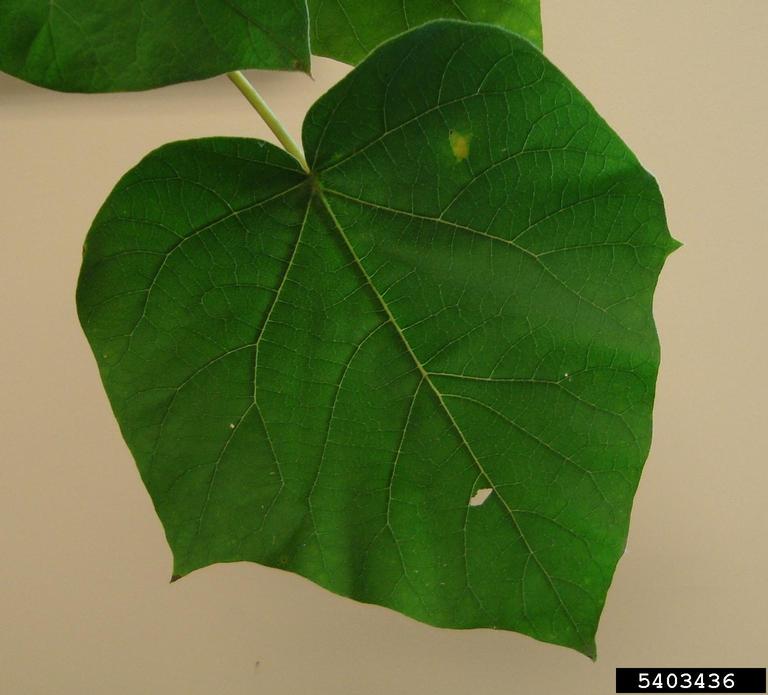
【形态】:树干耸直。树皮褐灰色。幼枝常具黏质短腺毛。叶宽卵形或卵形,长20~725px,宽15~700px,全缘或3~5裂,表面被长柔毛、腺毛及分枝毛,背面密被具长柄的白色树枝状毛。花蕾近圆形,密被黄色毛;花萼盘状钟形,深裂至1/2或更深,外被绒毛;花冠紫色或蓝紫色。蒴果卵圆形,长3~100px,果皮薄而脆,宿萼反卷。花期4~5月,果期9~10月。
【分布】:主要分布于长江以北,西部有野生,各地栽培。
【习性】:喜光,不耐阴;较耐寒,-25。C时易受冻;较耐干旱,不耐积水,不耐盐碱;喜深厚、肥沃、湿润、疏松土壤。根系发达,生长快,寿命短,萌芽、萌蘖性强。对二氧化硫、氯气、氟化氢等气体抗性较强。
【繁殖】:埋根繁殖为主,也可播种、埋干、留根繁殖。
【用途】:树冠宽阔,树干端直,叶大荫浓,花大艳丽。可作庭荫树、行道树、独赏树及“四旁”绿化树种。是重要的速生用材树种。也是良好的饲料和肥料树种。
Paulownia tomentosa, common names princess tree, empress tree, or foxglove-tree, is a deciduous hardwood tree in the family Paulowniaceae, native to central and western China. It is an extremely fast-growing tree with seeds that disperse readily, and is a persistent exotic异国情调的; 奇异的; invasive species in North America, where it has undergone naturalisation in large areas of the Eastern US. P. tomentosa has also been introduced to Western and Central Europe, and is establishing itself as a naturalised species there as well.
Paulownia tomentosa
Common Name(s): Empress Tree、Princess Tree、Royal Empress Tree、Royal Paulownia
This plant is an invasive species in North Carolina
Description
This plant is problematic and alternatives should be considered. Please see the suggestions in the left-hand column.
Native to Eastern Asia the princess tree is a deciduous fast growing tree in the Paulowniaceae family. The tree is named in honor of Russian Princess Anna Paulowna (1795-1865)安娜·帕夫诺夫娜, while the species name tomentosa means hairy in Latin. This shade tree grows rapidly adding 15 feet each year to reach a mature height of 50 feet and width of 30 feet in just 10 years. It is considered one of the fastest growing trees in the world.
The leaves of this plant are large and velvety soft looking very much like those on a catalpa梓 tree. Flowers appear on second year wood are light purple pink, showy, and smell like vanilla香子兰,香草; . Woody brown seed capsules follow and in the fall they break open to reveal winged seeds.
It tolerates a range of soils including low fertility and high acidity but prefers moist, deep, sandy-loam well-drained soil. While it can withstand some light shade it prefers full sun. Air pollution and coastal conditions do not bother this tree in the slightest and it self seeds very easily in the landscape. The canopy produces dense shade making it difficult to grow plants underneath and it competes with native plants for nutrients and water. This tree is not recommended for landscape planting.
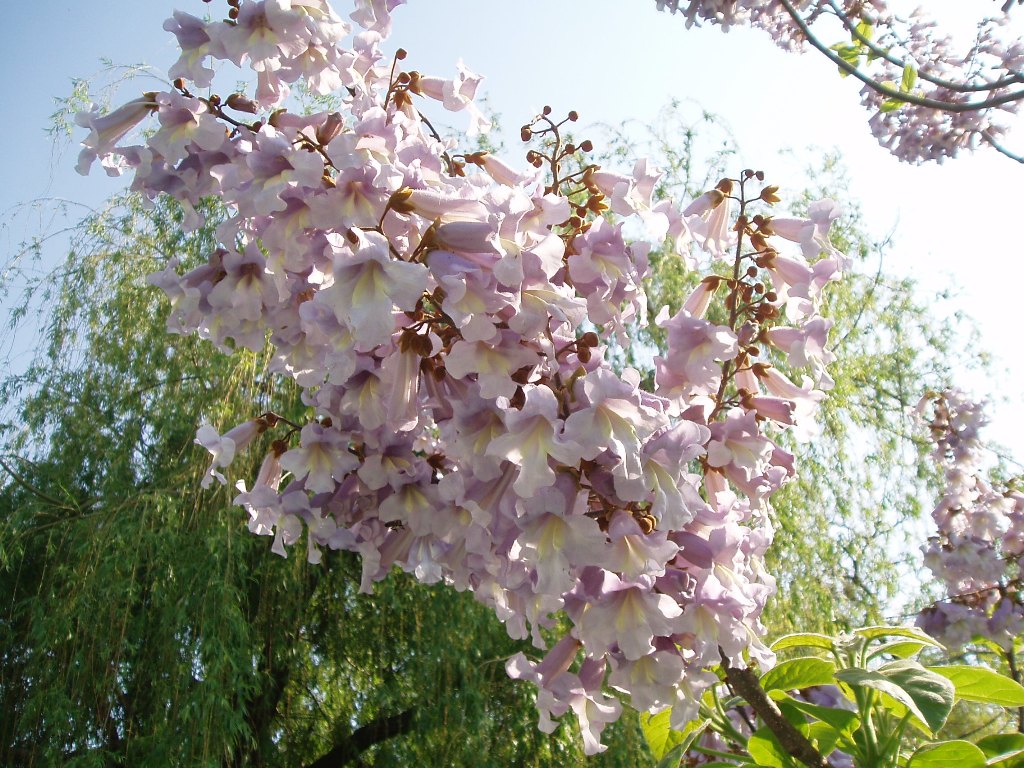
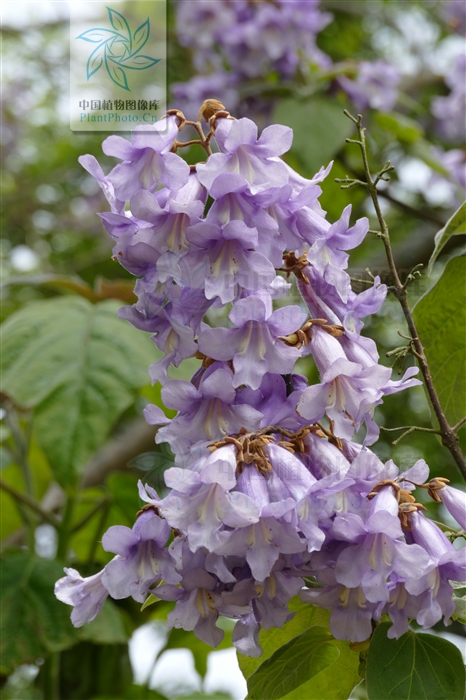
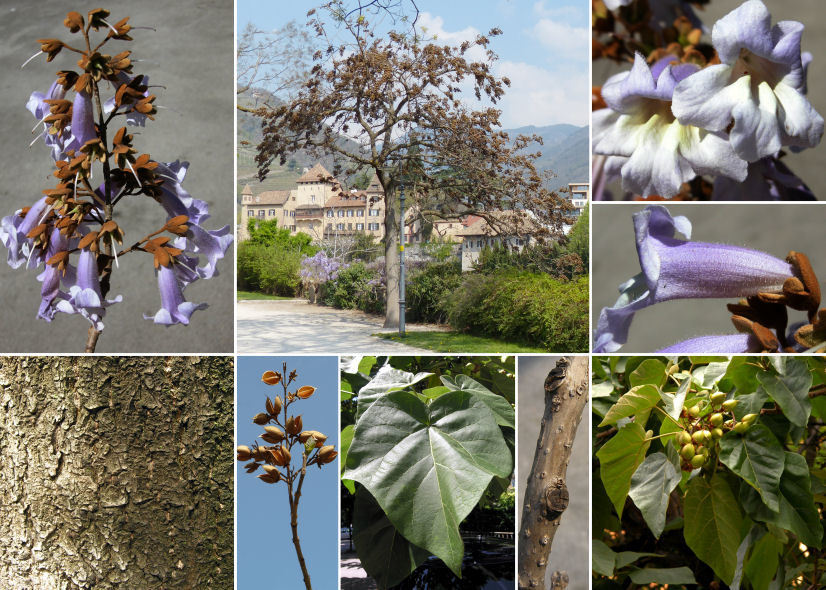
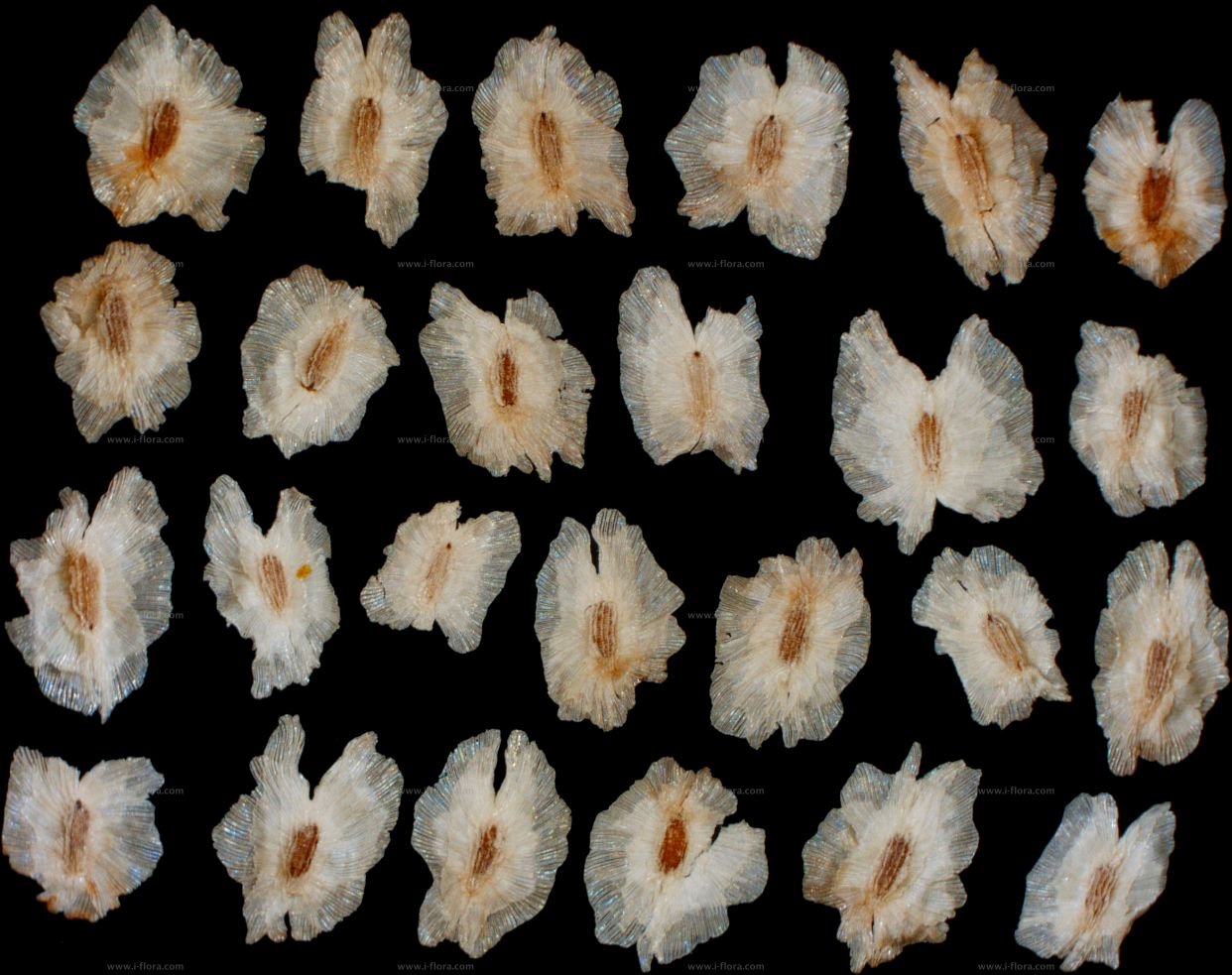







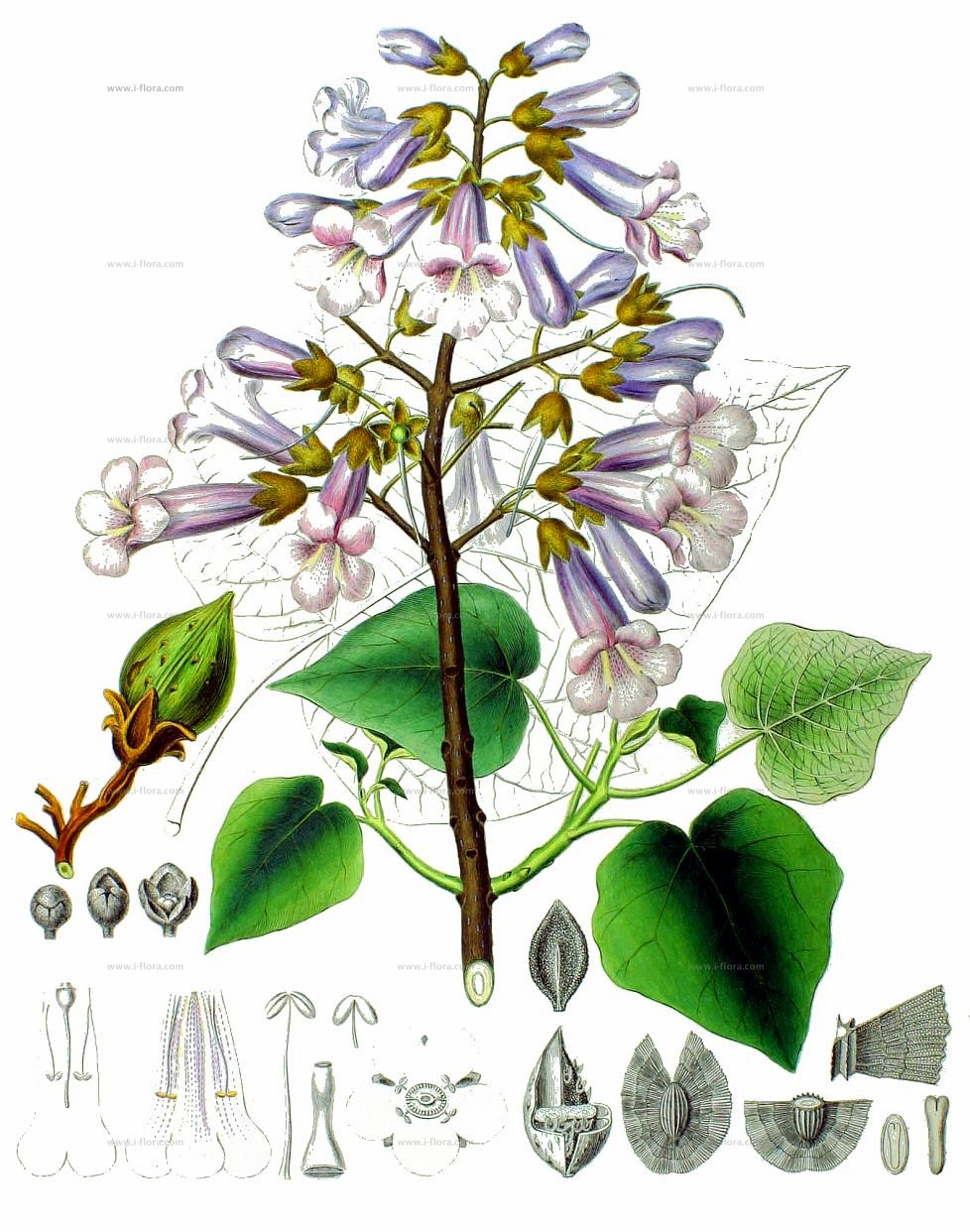

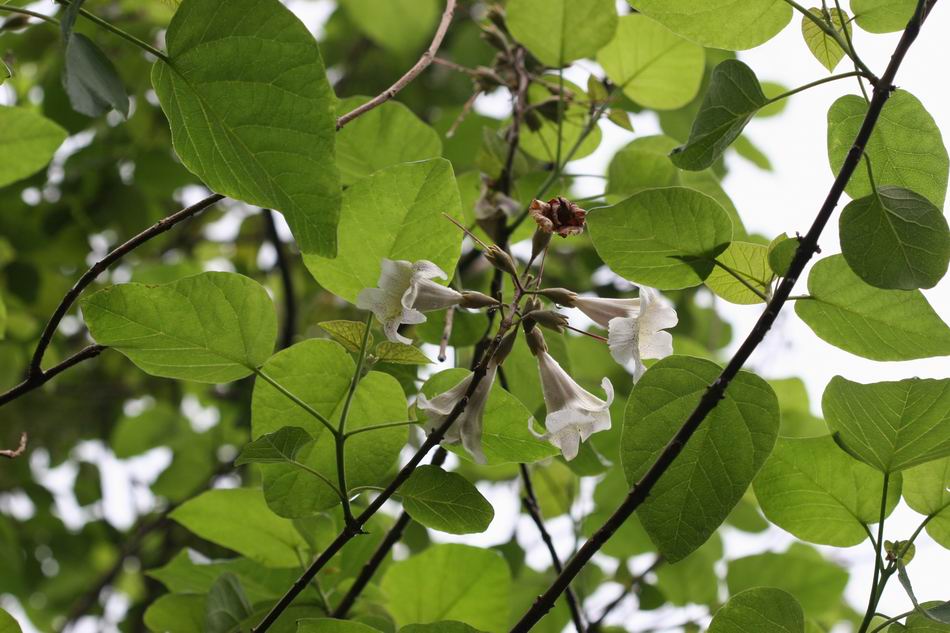
2.白花泡桐(泡桐)Paulownia fortunei(Seem.)Hemsl.
俗名:通心条、饭桐子、笛螺木、沙桐彭、火筒木、华桐、大果泡桐、泡桐、白花桐、哇哈哈
【形态】:高达20m,树冠宽卵形或圆形。树皮灰褐色。小枝幼时有毛。叶长卵形,长10~625px,宽6~375px,先端渐尖,基部心形,全缘,稀浅裂,背面被白色星状毛。花蕾倒卵状椭圆形;花萼倒圆锥状钟形,浅裂至1/4~1/3,无毛;花冠乳白色至微带紫色,内具紫色斑点及黄色条纹。蒴果椭圆形,长6~275px。花期3~4月,果期9~10月。
【分布】:主产长江流域以南各省,现辽宁以南广泛栽培。
【习性】:喜光稍耐阴,耐寒性稍差。深根性,生长快,萌蘖性强。
【繁殖】:埋根繁殖为主,也可播种、埋干、留根繁殖。
【用途】:早春繁花似锦,夏日绿树成荫,甚为美观,可作庭荫树、行道树、独赏树及“四旁”绿化树种。是重要的速生用材树种。也是良好的饲料和肥料树种。花、果均可人药。
Paulownia fortunei commonly called the dragontree, dragon tree or Fortune's empress tree, is a deciduous tree in the family Paulowniaceae, native to southeastern China, Laos and Vietnam. It is an extremely fast-growing tree, due to its use of C₄ carbon fixation, and is planted for timber harvesting. It appears to be nowhere near as dangerously invasive as Paulownia tomentosa.
Paulownia fortunei
Common Name(s): Dragontree、Dragon Tree、Empress Tree、Fortune's Empress Tree、Princess Tree
Description:
Dragontree is a fast-growing deciduous flowering tree native to China and Taiwan and has naturalized in parts of the USA including all areas of NC. It can grow up to 20 feet a year when young maturing at 50-75 feet tall. In spring it blooms with many clusters of large tubular flowers before leaf-out. The heart-shaped leaves are large up to 9 inches long.
This tree is used as an ornamental tree and also grown for timber. In Asia, it has been used to help remove heavy metals in contaminated soils, to decrease air pollution and for reforestization.
Dragon Tree is adaptable to soil types as long as they are well-drained and prefers full sun. It is susceptible to root rot in wet soils. It can be used as a shade tree in yards and parks or as a street tree. See the recommended native trees on the left side of the screen.
The University of Florida states it has a high potential for invasiveness and does not recommend planting.