SYN 注:学名已修订,接受名为Asteraceae。
菊科——COMPOSITAE
草本、亚灌木或灌木,稀为乔木。有时有乳汁管或树脂道。叶通常互生,稀对生或轮生,全缘或具齿或分裂,无托叶,或有时叶柄基部扩大成托叶状;花两性或单性,极少有单性异株,整齐或左右对称,五基数,少数或多数密集成头状花序或为短穗状花序,为1层或多层总苞片组成的总苞所围绕;头状花序单生或数个至多数排列成总状、聚伞状、伞房状或圆锥状;花序托平或凸起,具窝孔或无窝孔,无毛或有毛;具托片或无托片;萼片不发育,通常形成鳞片状、刚毛状或毛状的冠毛;花冠常辐射对称,管状,或左右对称,两唇形,或舌状,头状花序盘状或辐射状,有同形的小花,全部为管状花或舌状花,或有异形小花,即外围为雌花,舌状,中央为两性的管状花;雄蕊4-5个,着生于花冠管上,花药内向,合生成筒状,基部钝,锐尖,戟形或具尾;花柱上端两裂,花柱分枝上端有附器或无附器;子房下位,合生心皮2枚,1室,具1个直立的胚珠;果为不开裂的瘦果;种子无胚乳,具2个,稀1个子叶。
本科约有1000属,25000-30000种,广布于全世界,热带较少。我国约有200余属,2000多种,产于全国各地。
菊科种类繁多,许多种类富于经济价值,如莴苣、莴笋、茼蒿、菊芋等作蔬菜;向日葵、小葵子、苍耳的种子可榨油,供食用或工业用;橡胶草和银胶菊可提取橡胶;艾纳香可蒸馏制取冰片;红花和白花除虫菊为著名的杀虫剂;泽兰、紫菀、旋复花、天名精、菌陈蒿、艾、白术、苍术、牛蒡、红花、蒲公英等为重要的药用植物;此外,菊、翠菊、大丽菊、金光菊、金鸡菊以及许多种类,花美丽鲜艳供观赏,全世界各地庭园均有栽培。
按照头状花序中小花的构造以及植物有无乳汁等特征,本科分为两个亚科和13个族。本卷内容包括管状花亚科 Carduoideae Kitam. 的斑鸡菊族 Vernonieae、泽兰族 Eupatorieae 和紫菀族 Astereae,38个属,共260余种。
The family Asteraceae, alternatively Compositae(菊科), consists of over 32,000 known species of flowering plants in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. Commonly referred to as the aster紫菀属植物, daisy雏菊, composite, or sunflower family, Compositae were first described in the year 1740. The number of species in Asteraceae is rivaled 与…匹敌; 比得上only by the Orchidaceae, and which is the larger family is unclear as the quantity of extant species in each family is unknown.
一、蓍属——Achillea L.
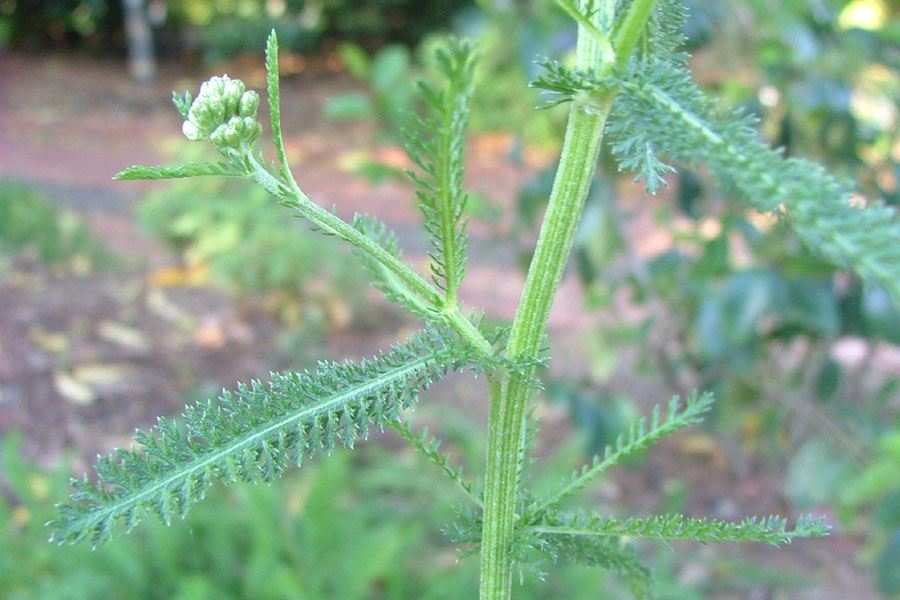
多年生草本。叶互生,羽状浅裂至全裂或不分裂而仅有锯齿,有腺点或无腺点,被柔毛或无毛。头状花序小,异型多花,排成伞房状花序,很少单生;总苞矩圆形、卵形或半球形;总苞片2-3层,覆瓦状排列,边缘膜质,棕色或黄白色;花托凸起或圆锥状,有膜质托片;边花雌性,通常1层,舌状;舌片白色、粉红色、红色或淡黄白色,比总苞短或等长,或超过总苞,偶有变形或缺如;盘花两性,多数,花冠管状5裂,管部收狭,常翅状压扁,基部多少扩大而包围子房顶部。花柱分枝顶端截形,画笔状;花药基部钝,顶端附片披针形。瘦果小,腹背压扁,矩圆形、矩圆状楔形、矩圆状倒卵形或倒披针形,顶端截形,光滑,无冠状冠毛。
本属约200种,广泛分布于北温带。我国产10种。
1.蓍 欧蓍、千叶蓍(东北植物检索表),锯草(华北经济植物志要)
Achillea millefolium L.
俗名:蚰蜒草、千叶蓍
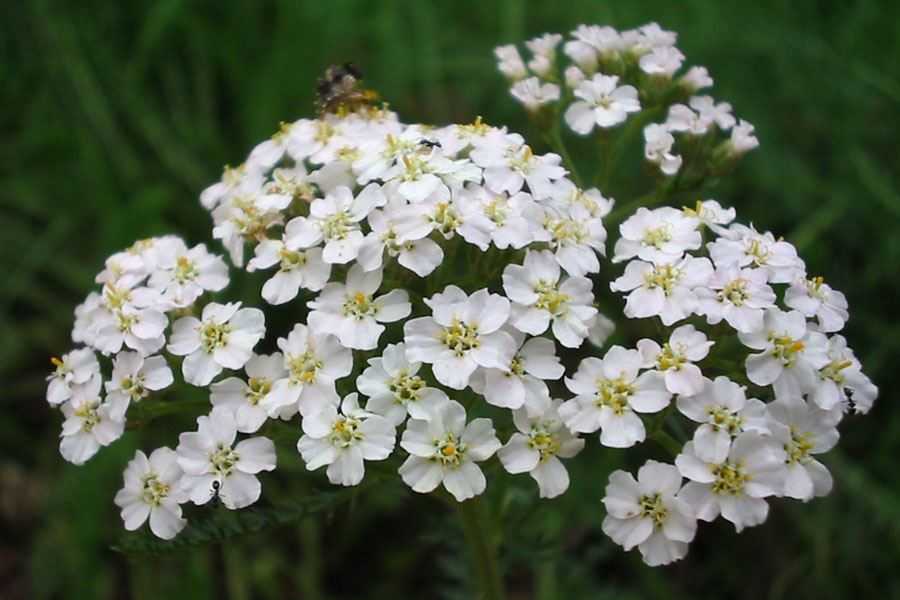
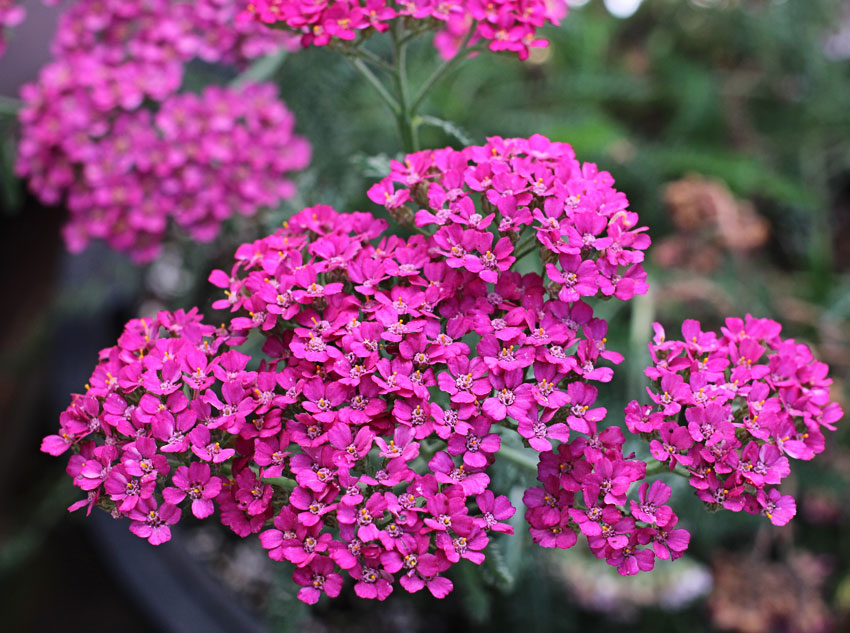
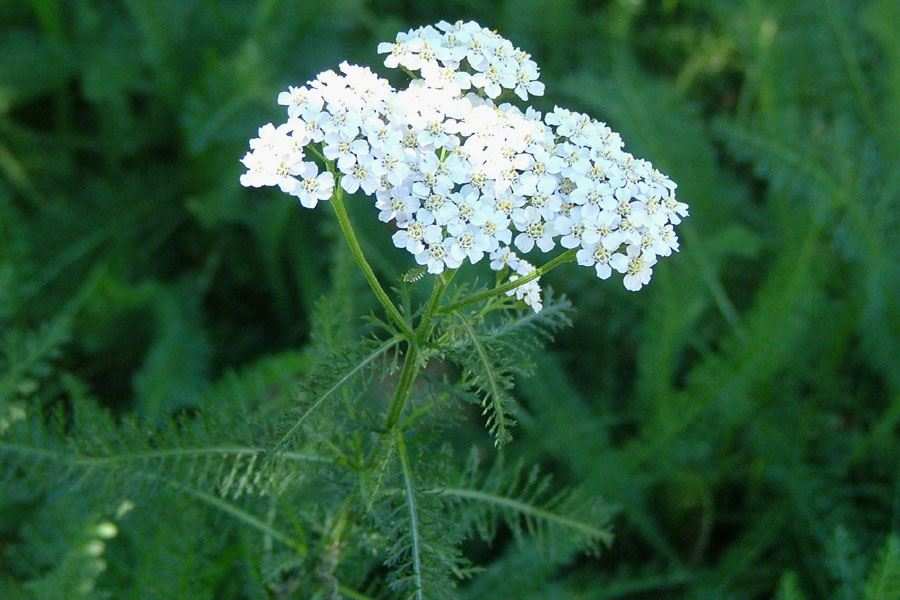
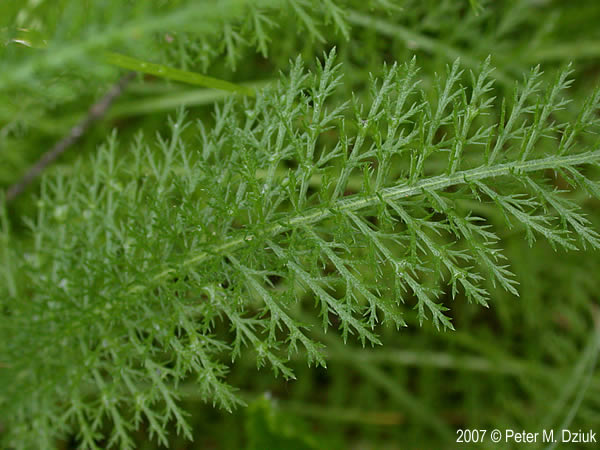
多年生草本,具细的匍匐根茎。茎直立,高40-100厘米,有细条纹,通常被白色长柔毛,上部分枝或不分枝,中部以上叶腋常有缩短的不育枝。叶无柄,披针形、矩圆状披针形或近条形,长5-7厘米,宽1-1.5厘米,(二)至三回羽状全裂,叶轴宽约1.5-2毫米,一回裂片多数,间隔1.5-7毫米,有时基部裂片之间的上部有1中间齿,末回裂片披针形至条形,长0.5-1.5毫米,宽0.3-0.5毫米,顶端具软骨质短尖,上面密生凹入的腺体,多少被毛,下面被较密的贴伏的长柔毛。下部叶和营养枝的叶长10-20厘米,宽1-2.5厘米。头状花序多数,密集成直径2-6厘米的复伞房状;总苞矩圆形或近卵形,长约4毫米,宽约3毫米,疏生柔毛;总苞片3层,覆瓦状排列,椭圆形至矩圆形,长1.5-3毫米,宽1-1.3毫米,背中间绿色,中脉凸起,边缘膜质,棕色或淡黄色;托片矩圆状椭圆形,膜质,背面散生黄色闪亮的腺点,上部被短柔毛。边花5朵;舌片近圆形,白色、粉红色或淡紫红色,长1.5-3毫米,宽2-2.5毫米,顶端2-3齿;盘花两性,管状,黄色,长约2.2-3毫米,5齿裂,外面具腺点。瘦果矩圆形,长约2毫米,淡绿色,有狭的淡白色边肋,无冠状冠毛。花果期7-9月。
我国各地庭园常有栽培,新疆、内蒙古及东北少见野生。广泛分布欧洲、非洲北部、伊朗、蒙古、苏联西伯利亚。在北美广泛归化。生于湿草地、荒地及铁路沿线。叶、花含芳香油,全草又可入药,有发汗、驱风之效。
Achillea millefolium, commonly known as yarrow西洋蓍草 or common yarrow, is a flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere in Asia, Europe, and North America. It has been introduced as a feed for livestock in New Zealand and Australia, where it is a common weed of both wet and dry areas, such as roadsides, meadows, fields and coastal places.
Achillea millefolium
Common Name(s): Common Yarrow、Devil's Nettle、Dog Daisy、Dog Fennel、MilfoilSoldier's Woundwort、Thousandleaf、Westen Yarrow、Yarrow
This plant has low severity poison characteristics.
Description
Yarrow is a perennial in the Asteraceae (daisy) family Introduced to America from Europe in colonial times. This plant prefers well-drained soil and full sun and it is often found naturalizing in fields and along roadsides. It is a wonderful wildlife plant that attracts butterflies. Makes excellent cut or dried arrangements. Very easy to divide. This plant is moderately salt tolerant. Plants can spread aggressively by rhizomes根茎,根状茎 and they self-seed regularly. After initial bloom, it can be dead-headed back to a lateral flower bud to encourage rebloom. Generally considered too weedy to use in borders but works well as a flowering ground cover in meadows, prairies大草原, and naturalized areas. It can even be a lawn alternative in sunny areas with little foot traffic. It can be unattractive by the end of summer after it blooms and can be pruned back severely or mowed with a rotary mower on the highest setting in naturalized areas. Large clumps should be divided as necessary to maintain healthy and vigorous growth and performance and reduce disease. Cultivars cover a range of flower colors including pinks, reds, creams, yellows and bicolor pastels. Hybrid varieties have been bred for stronger stems and a more erect habit.
The finely divided, pinnatifid to decompoundly pinnatifid, leaves give the plant a soft fern-like texture, making it attractive even when the erect flowering branches are not in season; bloom is from mid to late summer, into early fall. It has a tendency to spread in beds.
Quick ID Hints:
Leaves pinnatifid, fern蕨类植物-like in appearance.
Inflorescence terminal, small heads in a dense umbel.
Flower Color:Cream/Tan、Gold/Yellow、Orange、Pink、Purple/Lavender、Red/Burgundy、White
Flower Inflorescence:Corymb伞状花序、Head、Umbel
Flower Value To Gardener:
Good Cut、Good Dried、Long Bloom Season、Long-lasting、Showy
Flower Bloom Time:Summer
Flower Petals:4-5 petals/rays
Flower Size:< 1 inch
Flower Description:June to September numerous long-lasting tiny flowers in corymbs. Minute; ray flowers white, red to pink, yellow; more










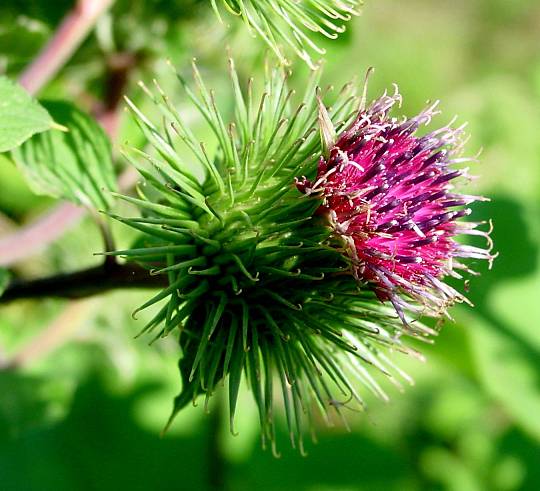
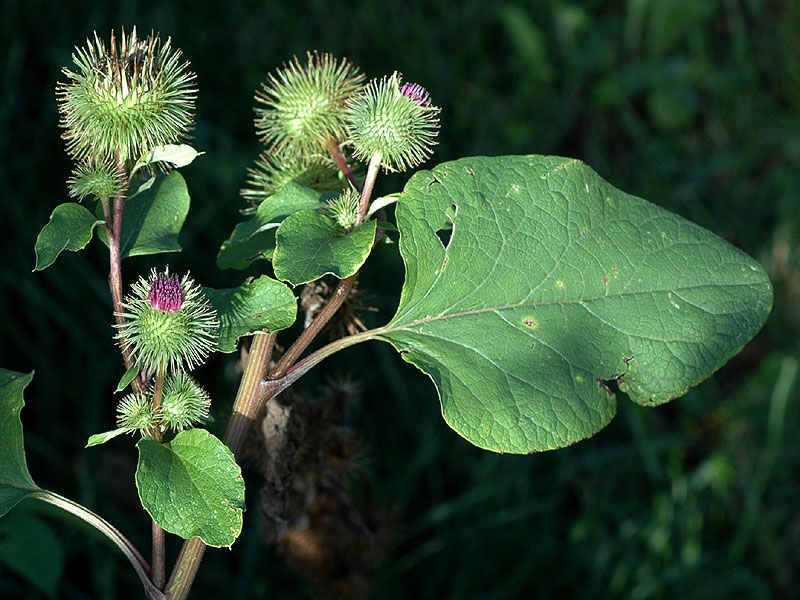
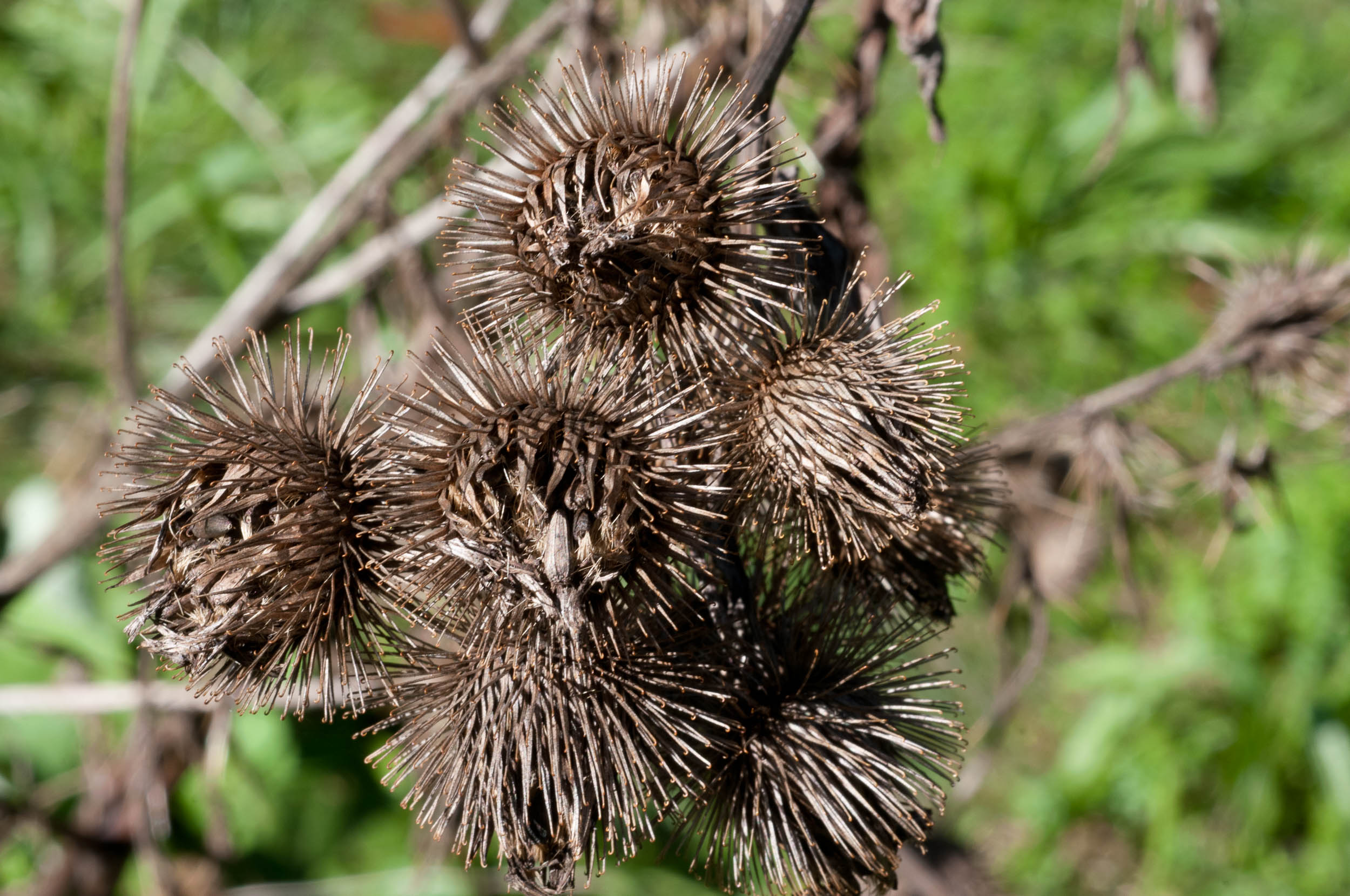
二、牛蒡属——Arctium L.
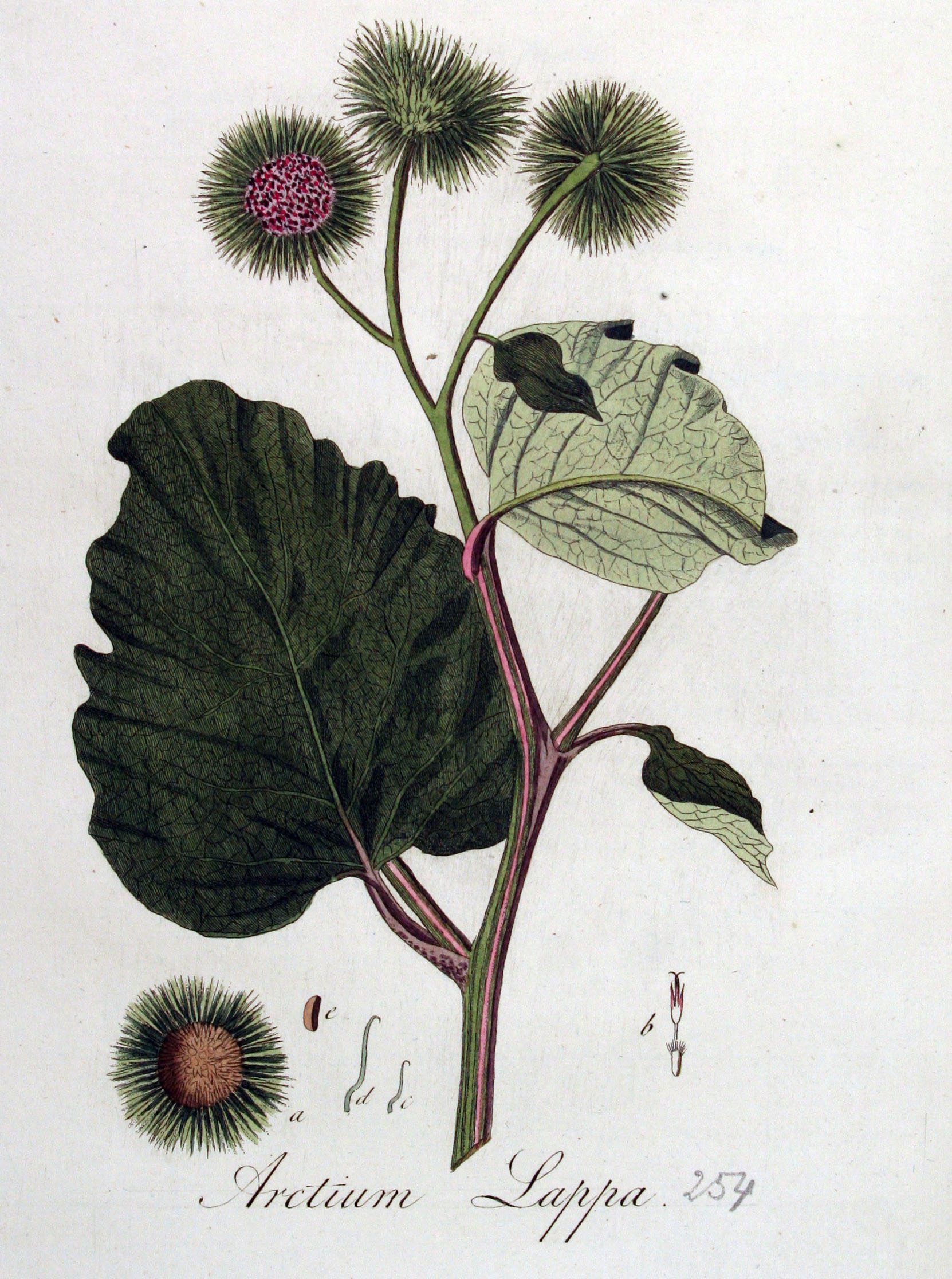
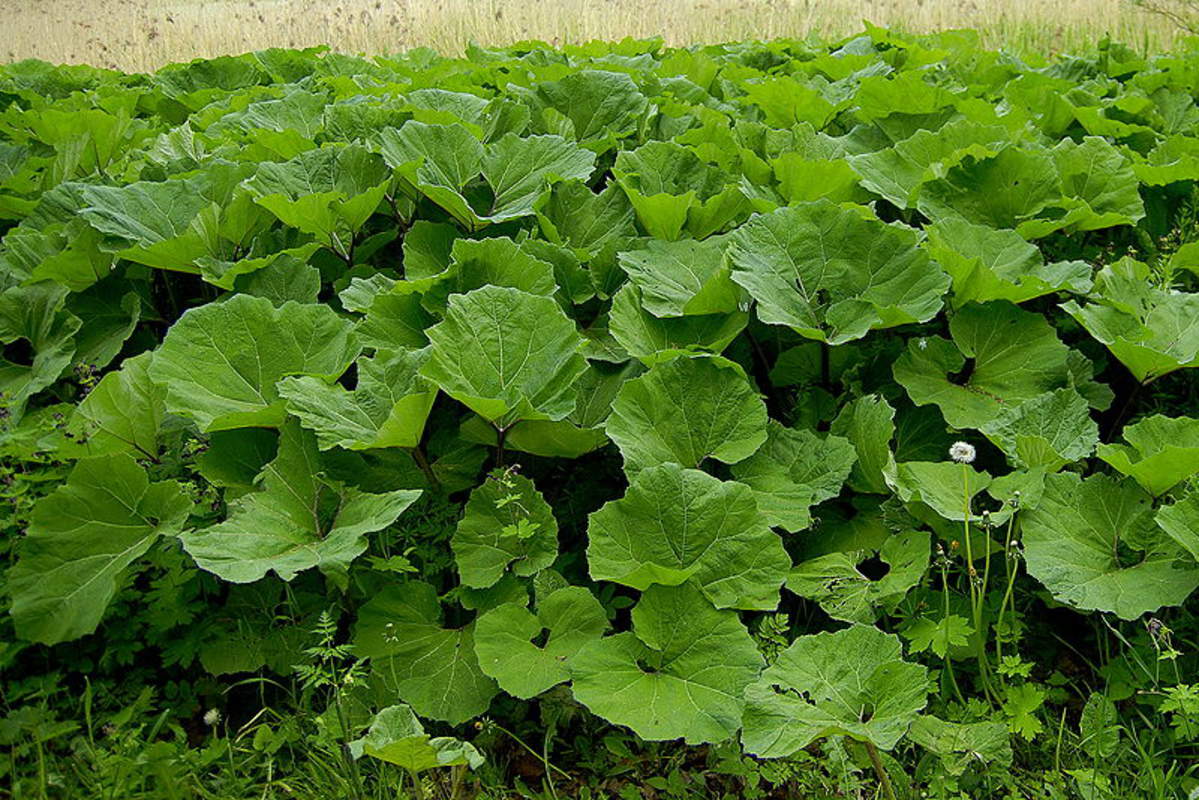
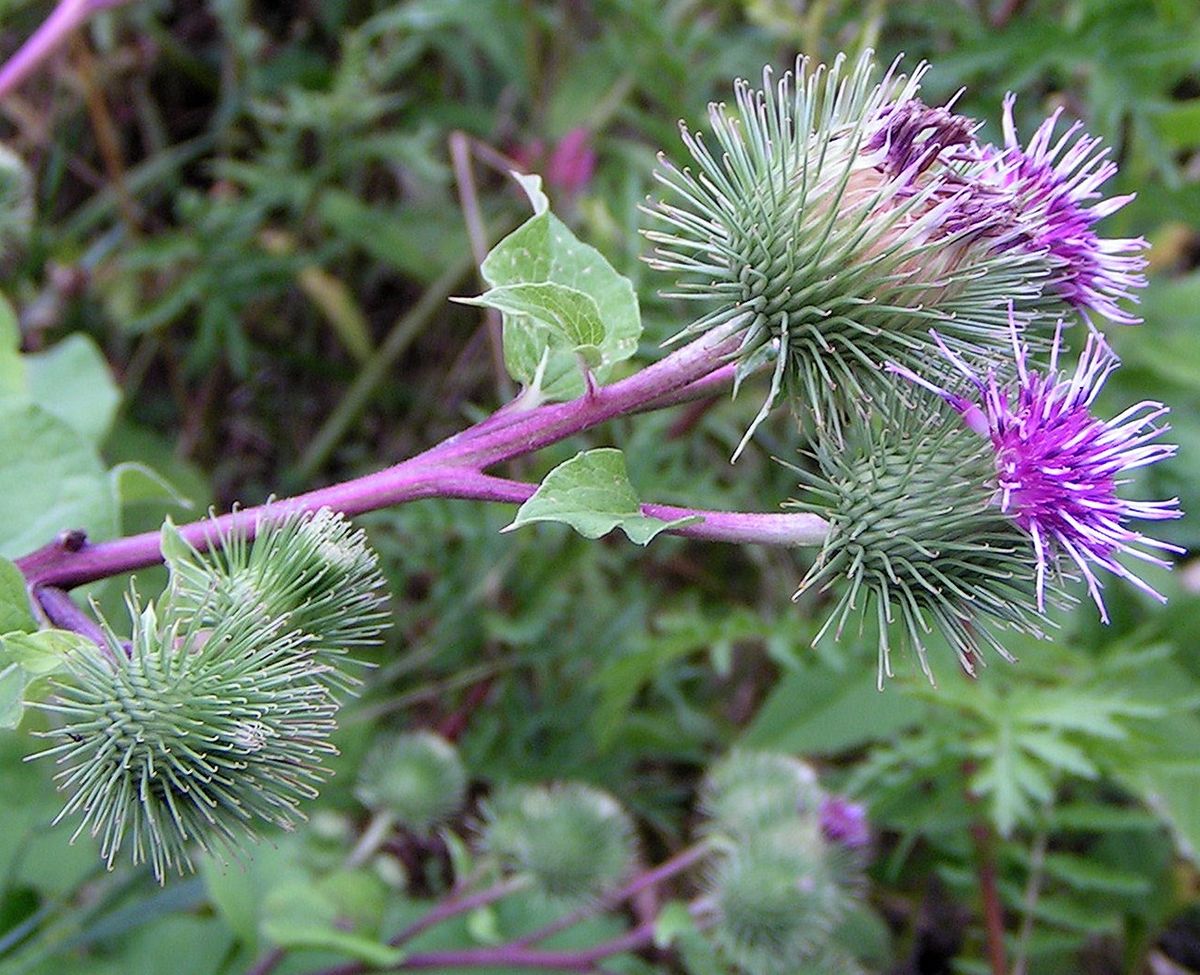
二年生草本。叶互生,通常大型,不分裂,基部通常心形,有叶柄。头状花序中等大小或较大,少数或多数,在茎枝顶端排成伞房状或圆锥状花序,同型,含有多数两性管状花。总苞卵形或卵球形,无毛或有蛛丝毛。总苞片多层,多数,线钻形、披针形,顶端有钩刺。花托平,被稠密的托毛,托毛初时平展,后变扭曲。全部小花结实,花冠5浅裂。花药基部附属物箭形。花丝分离,无毛。花柱分枝线形,外弯,基部有毛环。瘦果压扁,倒卵形或长椭圆形,顶端截形,有多数细脉纹或肋棱,基底着生面,平。冠毛多层,短;冠毛刚毛不等长,糙毛状,基部不连合成环,极易分散脱落。
约10种,分布欧亚温带地区。我国2种。
1.牛蒡 恶实 大力子
Arctium lappa L.
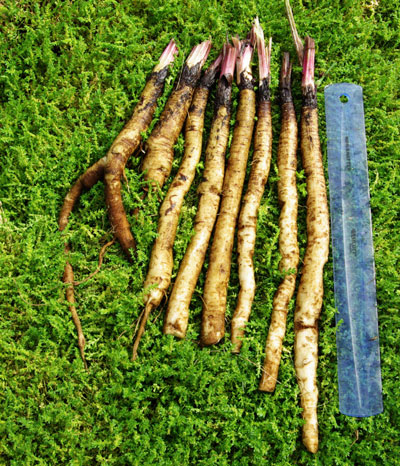
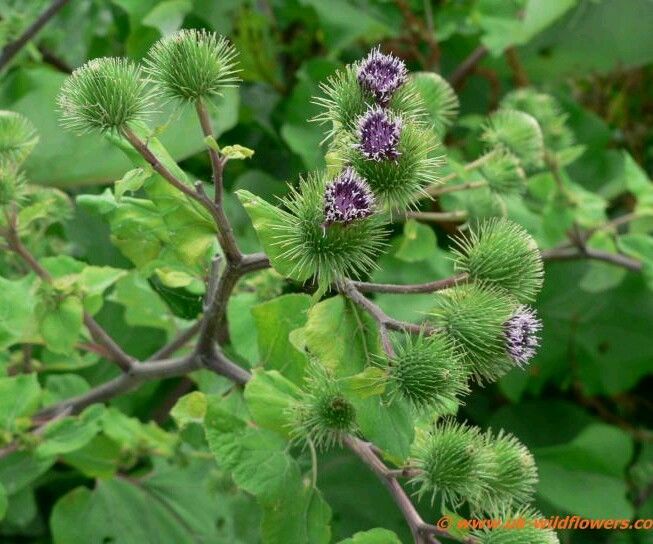
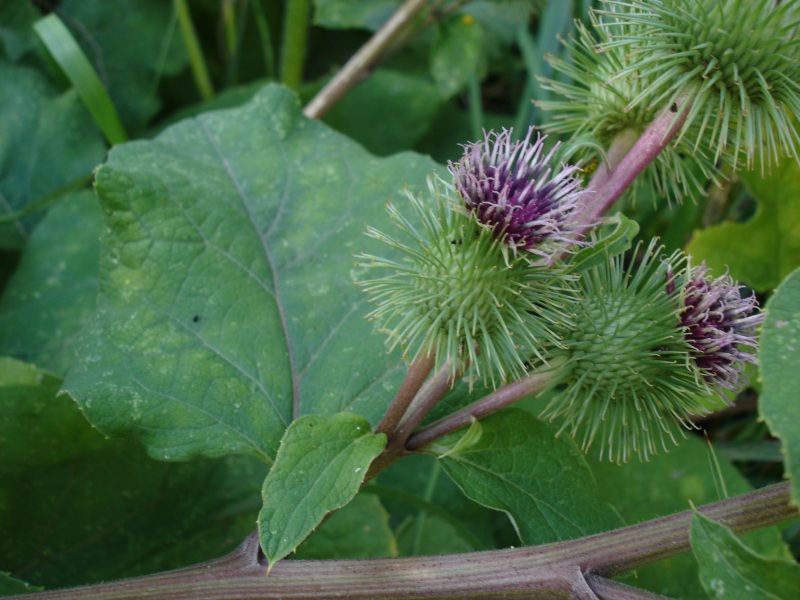
二年生草本,具粗大的肉质直根,长达15厘米,径可达2厘米,有分枝支根。茎直立,高达2米,粗壮,基部直径达2厘米,通常带紫红或淡紫红色,有多数高起的条棱,分枝斜升,多数,全部茎枝被稀疏的乳突状短毛及长蛛丝毛并混杂以棕黄色的小腺点。基生叶宽卵形,长达30厘米,宽达21厘米,边缘稀疏的浅波状凹齿或齿尖,基部心形,有长达32厘米的叶柄,两面异色,上面绿色,有稀疏的短糙毛及黄色小腺点,下面灰白色或淡绿色,被薄绒毛或绒毛稀疏,有黄色小腺点,叶柄灰白色,被稠密的蛛丝状绒毛及黄色小腺点,但中下部常脱毛。茎生叶与基生叶同形或近同形,具等样的及等量的毛被,接花序下部的叶小,基部平截或浅心形。头状花序多数或少数在茎枝顶端排成疏松的伞房花序或圆锥状伞房花序,花序梗粗壮。总苞卵形或卵球形,直径1.5-2厘米。总苞片多层,多数,外层三角状或披针状钻形,宽约1毫米,中内层披针状或线状钻形,宽1.5-3毫米;全部苞近等长,长约1.5厘米,顶端有软骨质钩刺。小花紫红色,花冠长1.4厘米,细管部长8毫米,簷部长6毫米,外面无腺点,花冠裂片长约2毫米。瘦果倒长卵形或偏斜倒长卵形,长5-7毫米,宽2-3毫米,两侧压扁,浅褐色,有多数细脉纹,有深褐色的色斑或无色斑。冠毛多层,浅褐色;冠毛刚毛糙毛状,不等长,长达3.8毫米,基部不连合成环,分散脱落。花果期6-9月。
全国各地普遍分布。生于山坡、山谷、林缘、林中、灌木丛中、河边潮湿地、村庄路旁或荒地,海拔750-3500米。由于瘦果和根入药,各国各地亦有普遍栽培。果实入药,性味辛、苦寒,疏散风热,宜肺透疹、散结解毒;根入药,有清热解毒、疏风利咽之效。广布欧亚大陆。模式标本采自西欧。
Arctium lappa, commonly called greater burdock, gobō, edible burdock, lappa, beggar's buttons, thorny burr, or happy major is a Eurasian species of plants in the Aster family, cultivated in gardens for its root used as a vegetable. It has become an invasive weed of high-nitrogen soils in North America, Australia, and other regions.
Arctium lappa
Common Name(s): Bardane、Beggar's ButtonsBurrdock、Edible Burdock、GoboGreat Burdock、Greater Burdock、LappaSnake's Rhubarb、Thorny Burr
Previously known as: A. lappa major
Description
Great Burdock is a weedy, biennial wildflower belonging to the Aster family. Originating in temperate Eurasia centuries ago, it is now widely distributed in many parts of the world. In North America, it readily naturalizes in disturbed areas, empty lots, parks, roadsides, fields and pastures牧草地. Growth may become invasive and difficult to contain, competing with beneficial native plants. It is extremely difficult to eradicate due to its deep tap roots and copious 丰富的; 大量的;amounts of seed that remain viable for a long while even if plants are destroyed. Its first year's growth forms a short, dense rosette玫瑰花结; 蔷薇花饰; 圆花饰; of leaves. In its second year, it bolts to heights 2-10 feet, develops very large heart-shaped leaves, purple thistle蓟-like flowers, and slender, fleshy, gray-brown tap roots growing to depths of 3 feet. Clusters of purple flowerheads are arranged in flat-headed cymes聚伞花序, with globular bracts terminating in fine, sharp hooks forming burs that aid in seed dispersal by latching onto animals, birds, or hay bales. Burs刺果are very difficult to remove and reportedly have killed small birds and bats that become entangled. Fruits (achenes) within these burs contain sharp, minute bristles (pappas hairs) that easily become windborne and, if exposed to them, can cause severe eye, skin, and respiratory irritation and/or infection in humans, dogs, horses or other livestock. It prefers full sun locations with moist, well drained soil rich in organic matter and nitrogen. In Asia and other parts of the world, Great Burdock has been cultivated for for its edible roots and medicinal uses. Cultivated plants are sowns套种 from seed in summer and first-year roots are harvested by late autumn before becoming too fibrous.
Flower Description:
Purple globular flowerheads are arranged on stalks in flat-headed cymes approximately 1-1.5 inches in size. Flowerheads are comprised of many disk florets and needle-thin bracts苞片 that terminate in a sharp tip with a hook at the end. There are no ray florets on the flowerhead. After flowers whither, bracts turn brown and enclose the flowers, forming a spiked bur covered with looped ends. This design is highly effective in clinging to animal fur, bird feathers or clothing and aids in dispersal of seed. Burs may be very difficult to remove.










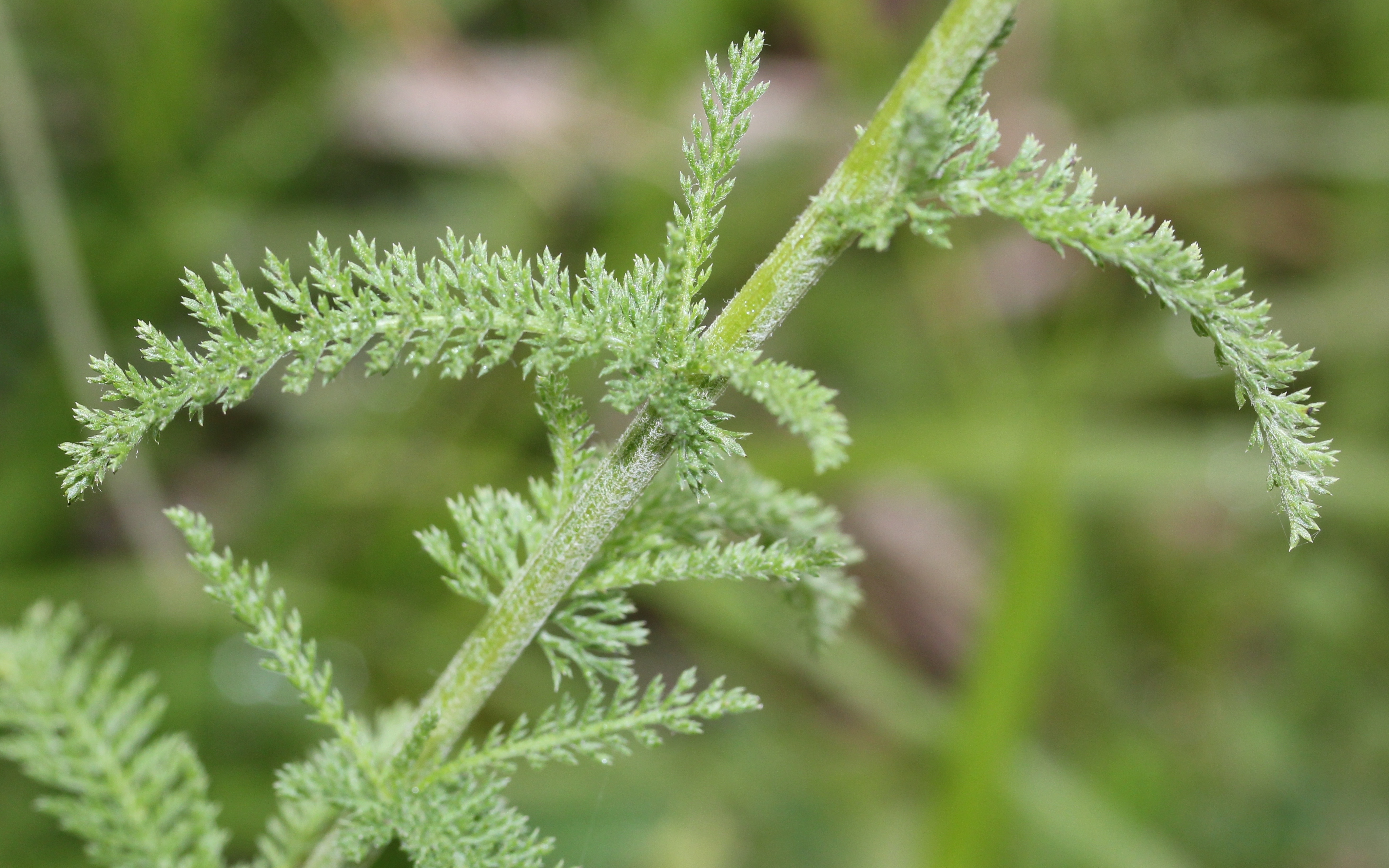
三、蒿属* ——Artemisia Linn. Sensu stricto, excl. Sect. Seriphidium Bess.
一、二年生或多年生草本,少数为半灌木或小灌木;常有浓烈的挥发性香气。根状茎粗或细小,直立、斜上升或旬地,常有营养枝;茎直立,单生,少数或多数,丛生,具明显的纵棱;分枝长或短,稀不分枝;茎、枝、叶及头状花序的总苞片常被蛛丝状的绵毛,或为柔毛、粘质的柔毛、腺毛,稀无毛或部分无毛。叶互生,一至三回,稀四回羽状分裂,或不分裂,稀近掌状分裂,叶缘或裂片边缘有裂齿或锯齿,稀全缘;叶柄长或短,或无柄,常有假托叶。头状花序小,多数或少数,半球形、球形、卵球形、椭圆形、长圆形,具短梗或无梗,基部常有小苞叶,稀无小苞叶,在茎或分枝上排成疏松或密集的穗状花序,或穗状花序式的总状花序或复头状花序,常在茎上再组成开展、中等开展或狭窄的圆锥花序,稀组成伞房花序状的圆锥花序;总苞片(2-)3-4层,卵形、长卵形或椭圆状倒卵形,稀披针形,覆瓦状排列,外、中层总苞片草质,稀半革质,背面常有绿色中肋,边缘膜质,内层总苞片半膜质或膜质,或总苞片全为膜质、且无绿色中肋;花序托半球形或圆锥形,具托毛或无托毛;花异型:边缘花雌性,1(-2)层,10余朵至数朵,稀20余朵,花冠狭圆锥状或狭管状,檐部具2-3(-4)裂齿,稀无裂齿,花柱线形,伸出花冠外,先端2叉,伸长或向外弯曲,叉端尖或钝尖,稀先端不叉开,柱头位于花柱分叉口内侧,子房下位,2心皮,1室,具1枚胚珠;中央花(盘花)两性,数层,孕育、部分孕育或不孕育,多朵或少数,花冠管状,檐部具5裂齿,雄蕊5枚,花药椭圆形或线形,侧边聚合,2室,纵裂,顶端附属物长三角形,基部圆钝或具短尖头,孕育的两性花开花时花柱伸出花冠外,上端2叉,斜向上或略向外弯曲,叉端截形,稀圆钝或为短尖头,柱头具睫毛及小瘤点,稀无睫毛,子房特点同雌花的子房;不孕育两性花的雌蕊退化,花柱极短,先端不叉开,退化子房小或不存在。瘦果小,卵形、倒卵形或长圆状倒卵形,无冠毛,稀具不对称的冠状突起,果壁外具明显或不明显的纵纹,无毛,稀微被疏毛。种子1枚。
本属植物的花粉粒椭圆形或扁球形,具3孔沟,外壁3层明显或稍明显,表面有细刺状或颗粒状纹饰;风媒传粉,稀闭花受粉。染色体多数种n=9,2n=18,少数种2n=36,54,稀2n=34,90。
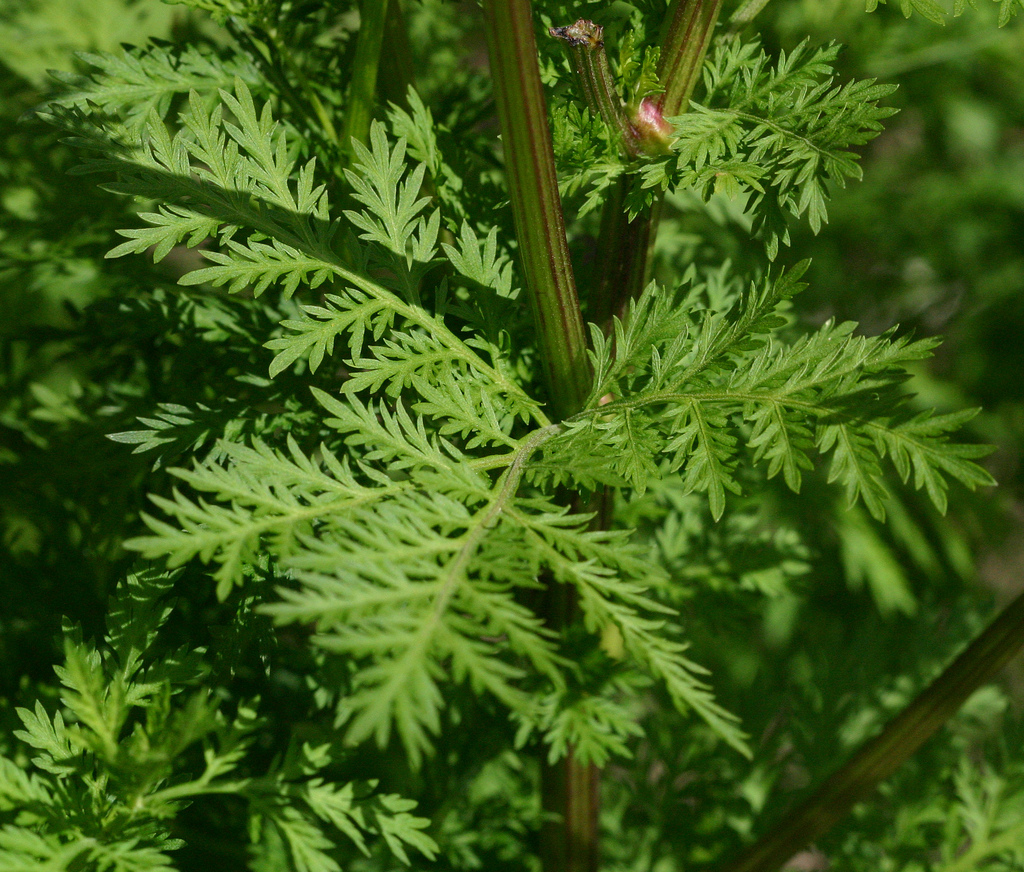
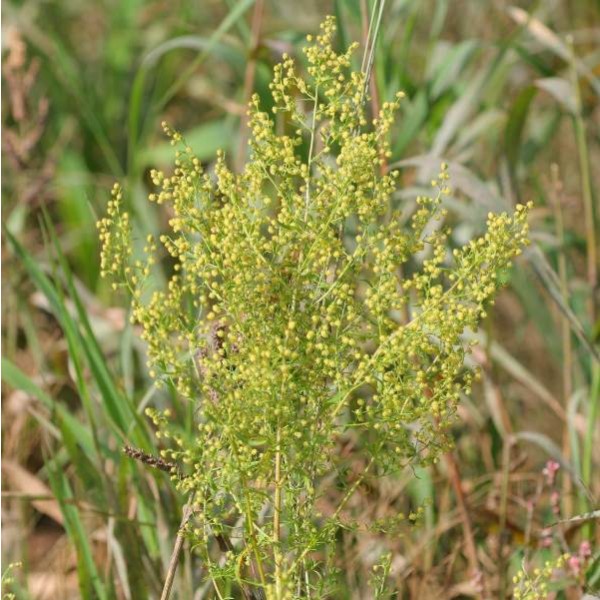
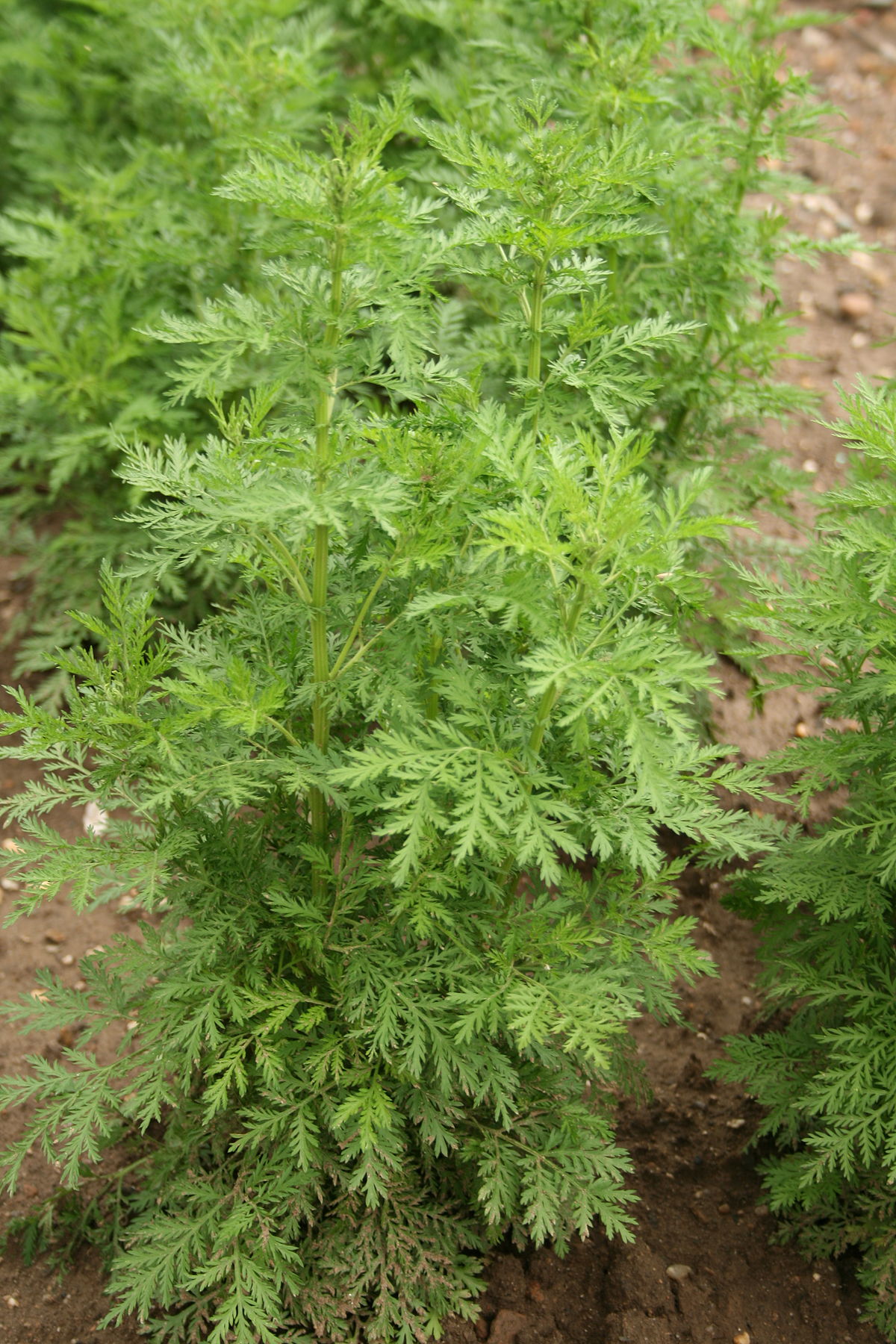
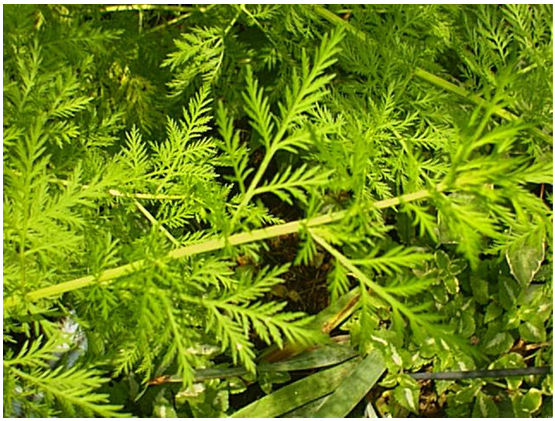
1. 黄花蒿(本草纲目) 草蒿〔神农本草经(部分)],青蒿(神农本草经、中药俗称),臭蒿(日华本草),犱蒿(蜀本草),黄蒿(俗称),臭黄蒿(内蒙古),茼蒿(山西),黄香蒿、野茼蒿(江苏),秋蒿、香苦草、野苦草(上海),鸡虱草(江西),黄色土因呈(湖南),假香菜、香丝草、酒饼草(广东、海南岛),苦蒿(四川、云南),“沙拉翁”、“莫林一沙里尔日”(蒙语名),“好尼一沙里勒吉”(蒙药名),“康帕”(维吾尔语名),“克朗”(藏语名) 图版9: 7-13
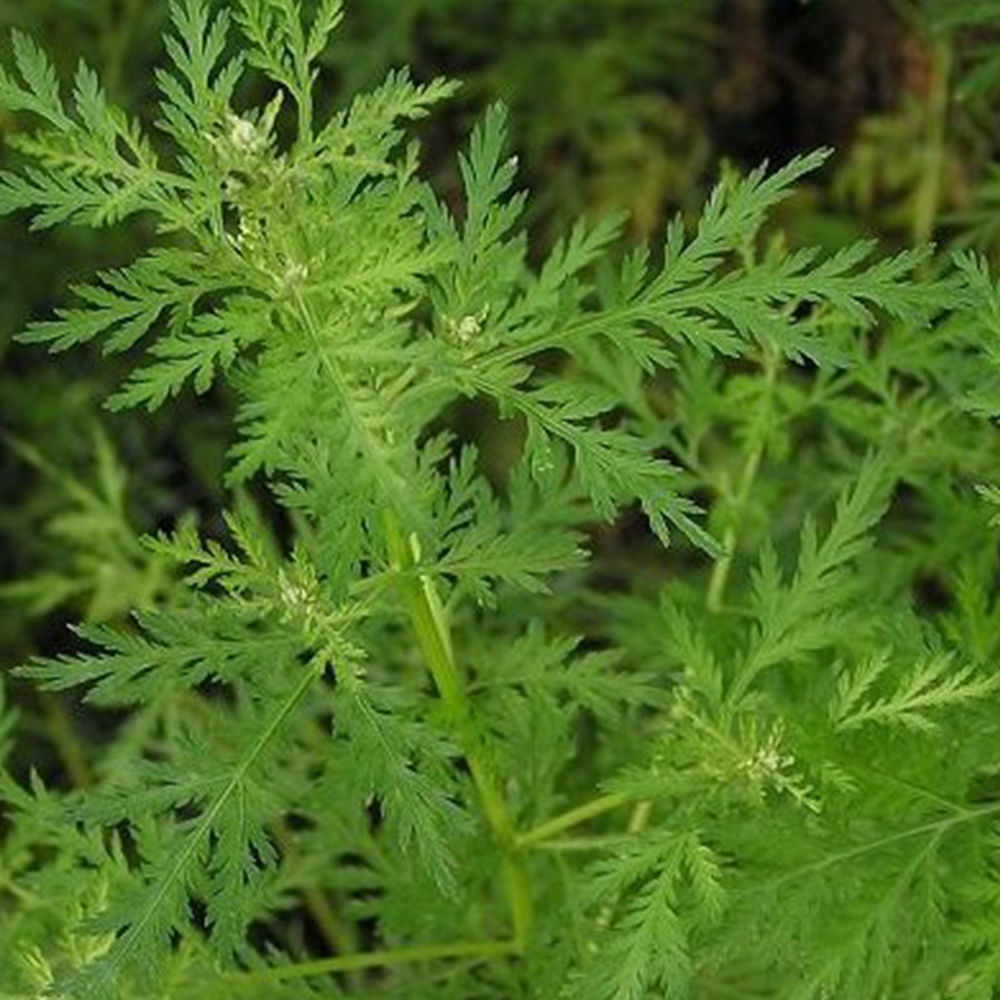
Artemisia annua Linn.
一年生草本;植株有浓烈的挥发性香气。根单生,垂直,狭纺锤形;茎单生,高100-200厘米,基部直径可达1厘米,有纵棱,幼时绿色,后变褐色或红褐色,多分枝;茎、枝、叶两面及总苞片背面无毛或初时背面微有极稀疏短柔毛,后脱落无毛。叶纸质,绿色;茎下部叶宽卵形或三角状卵形,长3-7厘米,宽2-6厘米,绿色,两面具细小脱落性的白色腺点及细小凹点,三(至四)回栉齿状羽状深裂,每侧有裂片5-8(-10)枚,裂片长椭圆状卵形,再次分裂,小裂片边缘具多枚栉齿状三角形或长三角形的深裂齿,裂齿长1-2毫米,宽0.5-1毫米,中肋明显,在叶面上稍隆起,中轴两侧有狭翅而无小栉齿,稀上部有数枚小栉齿,叶柄长1-2厘米,基部有半抱茎的假托叶;中部叶二(至三)回栉齿状的羽状深裂,小裂片栉齿状三角形。稀少为细短狭线形,具短柄;上部叶与苞片叶一(至二)回栉齿状羽状深裂,近无柄。头状花序球形,多数,直径1.5-2.5毫米,有短梗,下垂或倾斜,基部有线形的小苞叶,在分枝上排成总状或复总状花序,并在茎上组成开展、尖塔形的圆锥花序;总苞片3-4层,内、外层近等长,外层总苞片长卵形或狭长椭圆形,中肋绿色,边膜质,中层、内层总苞片宽卵形或卵形,花序托凸起,半球形;花深黄色,雌花10-18朵,花冠狭管状,檐部具2(-3)裂齿,外面有腺点,花柱线形,伸出花冠外,先端2叉,叉端钝尖;两性花10-30朵,结实或中央少数花不结实,花冠管状,花药线形,上端附属物尖,长三角形,基部具短尖头,花柱近与花冠等长,先端2叉,叉端截形,有短睫毛。瘦果小,椭圆状卵形,略扁。花果期8-11月。
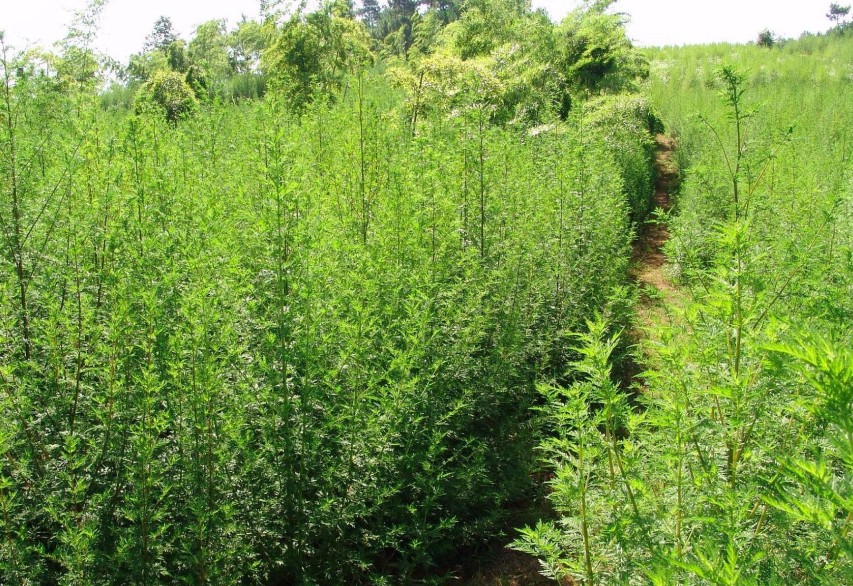
遍及全国;东半部省区分布在海拔1 500米以下地区,西北及西南省区分布在2 000-3 000米地区,西藏分布在3 650米地区;生境适应性强,东部、南部省区生长在路旁、荒地、山坡、林缘等处;其他省区还生长在草原、森林草原、干河谷、半荒漠及砾质坡地等,也见于盐渍化的土壤上,局部地区可成为植物群落的优势种或主要伴生种。广布于欧洲、亚洲的温带、寒温带及亚热带地区,在欧洲的中部、东部、南部及亚洲北部、中部、东部最多,向南延伸分布到地中海及非洲北部,亚洲南部、西南部各国;另外还从亚洲北部迁入北美洲、并广布于加拿大及美国。模式标本采自苏联西伯利亚地区。
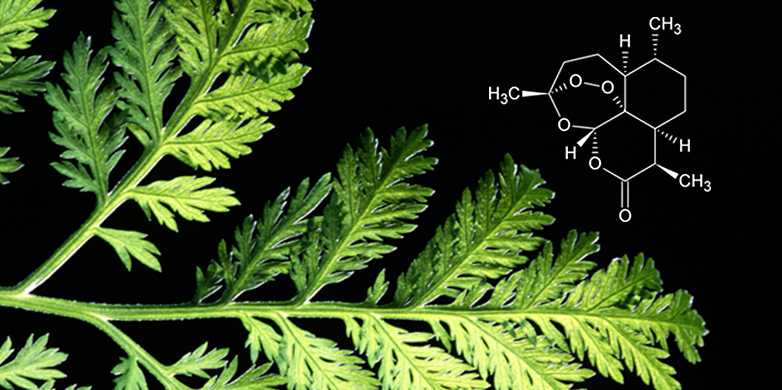
含挥发油,并含青蒿素 (qing hau su C15H2205) 、青蒿内脂I、II (arteannuin I, II) 、a-蒎烯、樟脑、按叶油素、青蒿酮等,此外还含黄酮类化合物;地上部分还含东茛菪内脂类化合物。青蒿素为倍半萜内脂化合物,为抗疟的主要有效成分,治各种类型疟疾,具速效、低毒的优点,对恶性疟及脑疟尤佳。
古本草书记述的“草蒿”(神农本草经)及“青蒿”(除花色淡青、淡黄色者外)与“黄花蒿”(本草纲目)无异,中药习称“青蒿”,而植物学通称为“黄花蒿”A. annur Linn., 该种在不同生态环境中生长,其体态略有变异。入药作清热、解暑、截疟、凉血、利尿、健胃、止盗汗用,此外,还作外用药。南方民间取枝叶制酒饼或作制酱的香料。牧区作牲畜饲料。本种不同于植物学上称的“青蒿”A. carvifolia Buch.-Ham. ex Roxb.,二者药用功能虽然接近,但后者不含“青蒿素”,亦无抗疟作用。
Artemisia annua, also known as sweet wormwood蒿, sweet annie, sweet sagewort, annual mugwort or annual wormwood, is a common type of wormwood native to temperate Asia, but naturalized in many countries including scattered parts of North America.
A 2,000 year force of nature
Artemisia annua is a medicinal plant that originated in Southeast Asia, but is now cultivated all around the world. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for more than 2000 years as a treatment for fevers, but its medicinal properties were rediscovered by modern science in the 1970’s when research revealed that the plant contains more than 10 active substances that act together or in parallel.
Today, one of those substances – artemisinin青蒿素 – is the foundation of all anti-malarial患疟疾的,毒气的; medicine, the discovery of which won Prof. Tu Youyou the Nobel Prize in 2015.
Scientific studies have shown that the components within the leaves of Artemisia annua, which can be ingested in capsules, extracts, or teas, have significant activity against the SARS-coronavirus, as well as against breast and prostate cancer without any serious side effects.
Prevention, as they say, is even better than a cure. Artemisia annua and derivatives are being studied for preventative effects. With no side effects when taken at recommended doses, a regularly-ingested, low-level of leaf material could effectively guard against developing diseases, from infections to cancers.
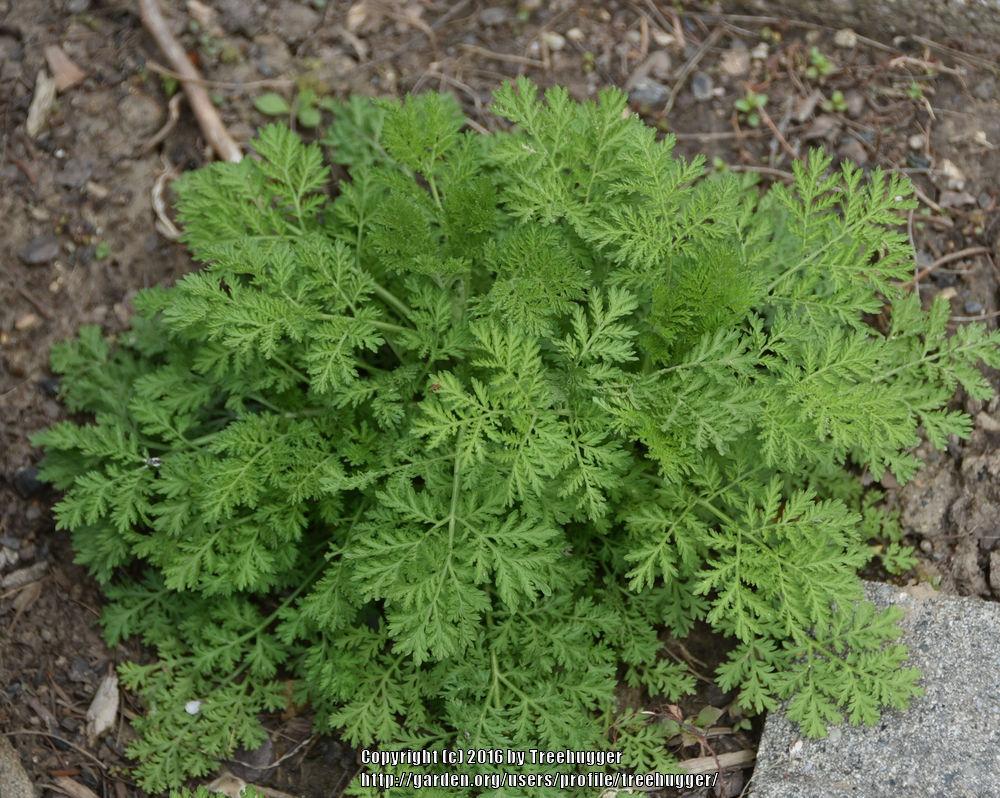








2.青蒿(原变种)
Artemisia carvifolia Buch.-Ham. var. carvifolia
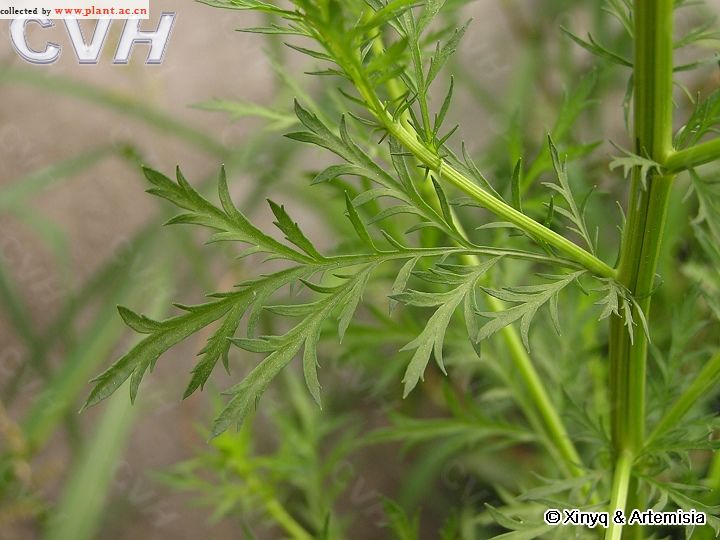
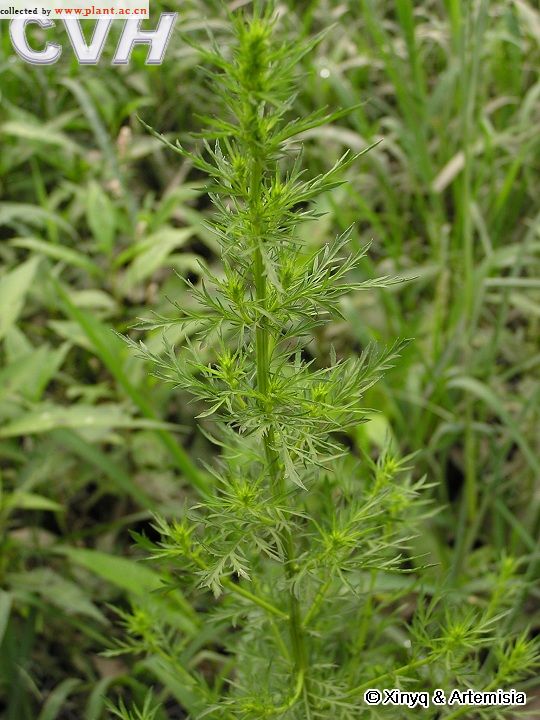
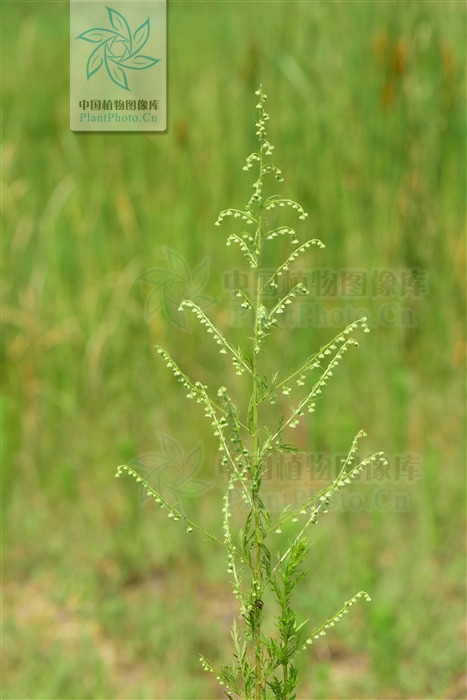
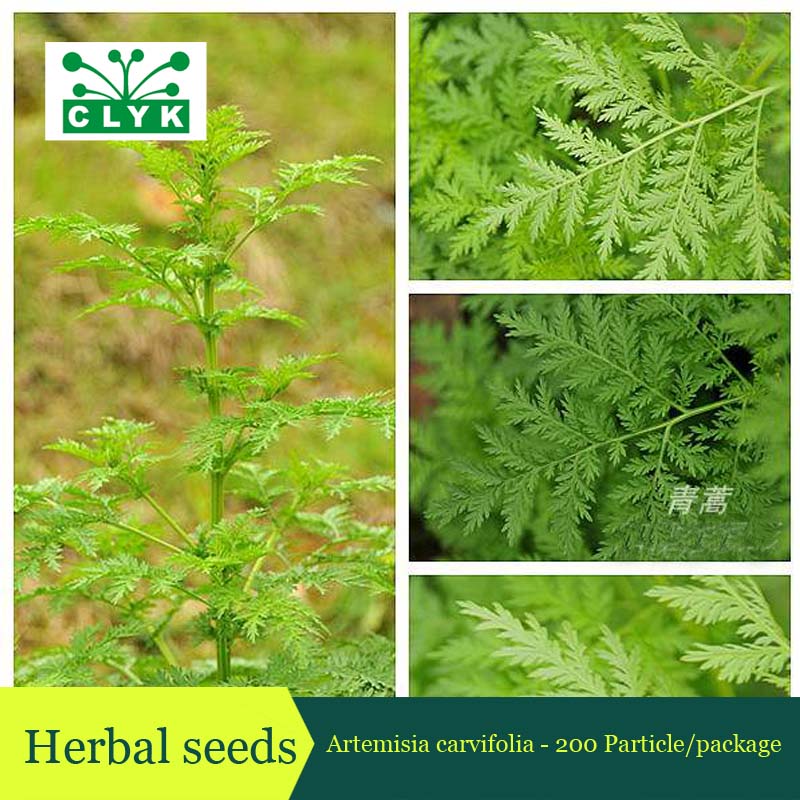
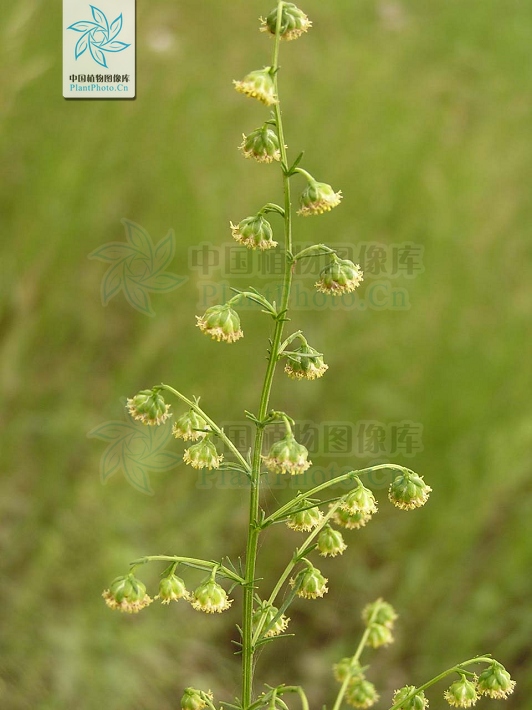
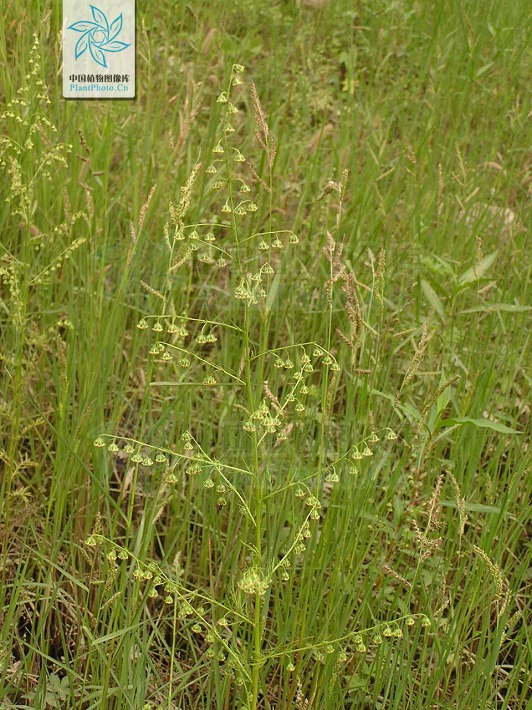
一年生草本;植株有香气。主根单一,垂直,侧根少。茎单生,高30-150厘米,上部多分枝,幼时绿色,有纵纹,下部稍木质化,纤细,无毛。叶两面青绿色或淡绿色,无毛;基生叶与茎下部叶三回栉齿状羽状分裂,有长叶柄,花期叶凋谢;中部叶长圆形、长圆状卵形或椭圆形,长5-15厘米,宽2-5.5厘米,二回栉齿状羽状分裂,第一回全裂,每侧有裂片4-6枚,裂片长圆形,基部楔形,每裂片具多枚长三角形的栉齿或为细小、略呈线状披针形的小裂片,先端锐尖,两侧常有1-3枚小裂齿或无裂齿,中轴与裂片羽轴常有小锯齿,叶柄长0.5-1厘米,基部有小形半抱茎的假托叶;上部叶与苞片叶一(至二)回栉齿状羽状分裂,无柄。头状花序半球形或近半球形,直径3.5-4毫米,具短梗,下垂,基部有线形的小苞叶,在分枝上排成穗状花序式的总状花序,并在茎上组成中等开展的圆锥花序;总苞片3-4层,外层总苞片狭小,长卵形或卵状披针形,背面绿色,无毛,有细小白点,边缘宽膜质,中层总苞片稍大,宽卵形或长卵形,边宽膜质,内层总苞片半膜质或膜质,顶端圆;花序托球形;花淡黄色;雌花10-20朵,花冠狭管状,檐部具2裂齿,花柱伸出花冠管外,先端2叉,叉端尖;两性花30-40朵,孕育或中间若干朵不孕育,花冠管状,花药线形,上端附属物尖,长三角形,基部圆钝,花柱与花冠等长或略长于花冠,顶端2叉,叉端截形,有睫毛。瘦果长圆形至椭圆形。花果期6-9月。
产吉林、辽宁、河北(南部)、陕西(南部)、山东、江苏、安徽、浙江、江西、福建、河南、湖北、湖南、广东、广西、四川(东部)、贵州、云南等省区;常星散生于低海拔、湿润的河岸边砂地、山谷、林缘、路旁等,也见于滨海地区。朝鲜、日本、越南(北部)、缅甸、印度(北部)及尼泊尔等也有。模式标本采自喜马拉雅山脉东南部地区。
Artemisia caruifolia is a ANNUAL growing to 1 m (3ft 3in). It is in flower from June to September, and the seeds ripen from July to September. The species is hermaphrodite雌雄同体 (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Wind.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers dry or moist soil and can tolerate drought.
Although no reports of toxicity have been seen for this species, skin contact with some members of this genus can cause dermatitis皮炎 or other allergic过敏的 reactions in some people.










3. 艾(原变种)
Artemisia argyi Levl. et Van. var. argyi
俗名:金边艾、艾蒿、祈艾、医草、灸草、端阳蒿
多年生草本或略成半灌木状,植株有浓烈香气。主根明显,略粗长,直径达1.5厘米,侧根多;常有横卧地下根状茎及营养枝。茎单生或少数,高80-150(-250)厘米,有明显纵棱,褐色或灰黄褐色,基部稍木质化,上部草质,并有少数短的分枝,枝长3-5厘米;茎、枝均被灰色蛛丝状柔毛。叶厚纸质,上面被灰白色短柔毛,并有白色腺点与小凹点,背面密被灰白色蛛丝状密绒毛;基生叶具长柄,花期萎谢;茎下部叶近圆形或宽卵形,羽状深裂,每侧具裂片2-3枚,裂片椭圆形或倒卵状长椭圆形,每裂片有2-3枚小裂齿,干后背面主、侧脉多为深褐色或锈色,叶柄长0.5-0.8厘米;中部叶卵形、三角状卵形或近菱形,长5-8厘米,宽4-7厘米,一(至二)回羽状深裂至半裂,每侧裂片2-3枚,裂片卵形、卵状披针形或披针形,长2.5-5厘米,宽1.5-2厘米,不再分裂或每侧有1-2枚缺齿,叶基部宽楔形渐狭成短柄,叶脉明显,在背面凸起,干时锈色,叶柄长0.2-0.5厘米,基部通常无假托叶或极小的假托叶;上部叶与苞片叶羽状半裂、浅裂或3深裂或3浅裂,或不分裂,而为椭圆形、长椭圆状披针形、披针形或线状披针形。头状花序椭圆形,直径2.5-3(-3.5)毫米,无梗或近无梗,每数枚至10余枚在分枝上排成小型的穗状花序或复穗状花序,并在茎上通常再组成狭窄、尖塔形的圆锥花序,花后头状花序下倾;总苞片3-4层,覆瓦状排列,外层总苞片小,草质,卵形或狭卵形,背面密被灰白色蛛丝状绵毛,边缘膜质,中层总苞片较外层长,长卵形,背面被蛛丝状绵毛,内层总苞片质薄,背面近无毛;花序托小;雌花6-10朵,花冠狭管状,檐部具2裂齿,紫色,花柱细长,伸出花冠外甚长,先端2叉;两性花8-12朵,花冠管状或高脚杯状,外面有腺点,檐部紫色,花药狭线形,先端附属物尖,长三角形,基部有不明显的小尖头,花柱与花冠近等长或略长于花冠,先端2叉,花后向外弯曲,叉端截形,并有睫毛。瘦果长卵形或长圆形。花果期7-10月。
分布广,除极干旱与高寒地区外,几遍及全国。生于低海拔至中海拔地区的荒地、路旁河边及山坡等地,也见于森林草原及草原地区,局部地区为植物群落的优势种。蒙古、朝鲜、苏联(远东地区)也有。日本有栽培。模式标本采自中国华北。
本种植物早在《神农本草经》中已有记述,称“白蒿”(一部分),历代古本草书记述的“白蒿”或“白艾”,其陆生种的大部分植物实际上是包括了本种及其近缘种,如宽叶山蒿 A. stolonif era (Maxim.) Komar、湘赣艾 A. gilvescens Miq.、野艾蒿 A. lavandulaefolia DC.、南艾蒿 A. verlotorum Lamotte,白叶蒿 A. leuco phylla (Turcz. ex Bess.) C. B. Clarke、蒙古蒿 A. mongolica (Fisch. ex Bess.) Nakai、红足蒿 A. rubripes Nakai、五月艾 A. indico Willd.、魁蒿 A. princeps Pamp. 及歧茎蒿 A. igniaria Maxim. 等多种“复合种”的名称。
Artemisia argyi, commonly known as silvery wormwood or Chinese mugwort, is a herbaceous perennial plant with a creeping rhizome. It is native to China, Korea, Mongolia, Japan, and the Russian Far East. It is known in Chinese as àicǎo or ài yè or ài hao and in Japanese as gaiyou. It is used in herbal medicine for conditions of the liver, spleen and kidney. It is a common flavoring and colorant in the Chinese dish qīng tuán.
Artemisia Argyi is a perennial herb .It is a common plant in south China. In Guilin, Guangxi, it is eaten with the leaves of Artemisia annua wrapped in rice. Artemisia Argyi has a history of thousands of years to prevent plague瘟疫; 灾害.
Characteristics of Artemisia Argyi
The underground rhizome根茎,根状茎 is particularly branched. And Artemisia Argyi was upright stems, round tube with gray hair, stem more than in the middle of the branch. The height of the entire plant can grow to about 15 to 120 cm, blade is oval and other shapes, lobes elliptic, lanceolate, margin is serrated, positive for the dark green, sparsely white fur, Sage green, on the back with gray hairs, leaves will wither枯萎,凋谢 at flowering. Middle leaves irregularly alternate with short stalks; Upper leaves are sessile(花、叶等)无柄的, apical leaves entire, lanceolate or striate, capitate头状花序的;, densely growing on receptacle by many small flowers (or only one flower), forming a capitate, shaped like a large flower, flowers sessile, mostly densely racemose, involucre densely covered with white wool; Marginal flowers female, about 7 to 12, often undeveloped, corolla slender; The center is bisexual flower, 10 ~ 12.Color and color differ somewhat because of breed, have a variety of colors such as red, flaky yellow. The achene瘦果 is oblong, some cloth with fine hairs and some glabrous.
Distribution of Artemisia Argyi
Artemisia Argyi is widely distributed in northeast, North, East, South, southwest and northwest China. China's most provinces are distributed, mostly wild, but also a small number of cultivation, can be a year. artemisia argyi is highly adaptable, but it is best to grow in moist and fertile sandy loam. Wild Artemisia argyi can often be found near ponds, villages and small Bridges.
Artemisia Argyi Habits
Artemisia Argyi is found in wastelands, roadsides and hillsides from low to medium elevations. It is also found in forest steppe干草原 and steppe areas. In some areas, it is the dominant plant community. Artemisia Argyi is very easy to reproduce and grow, and has strong adaptability to climate and soil. It is hardy and drought tolerant, and prefers a warm and humid climate, with moist and fertile soil growing better. Artificial cultivation in hilly and low zhongshan areas, the growth period is 24-30℃, when the temperature is higher than 30℃, the stem is easy to age, branching, disease and insect pest aggravation. In winter, when the low temperature is less than -3℃, the growth of the growing roots is not good.
Artemisia Argyi Uses
Artemisia Argyi has a history of thousands of years for the prevention of plague, and Chinese herbal medicines can be obtained from local sources. Pharmacological药理学的 studies of modern medicine show that Artemisia Argyi is a broad-spectrum范围; 系列; antibacterial and antiviral drug, which has inhibitory and killing effects on many viruses and bacteria, and has certain prevention and treatment effects on respiratory 呼吸的diseases.
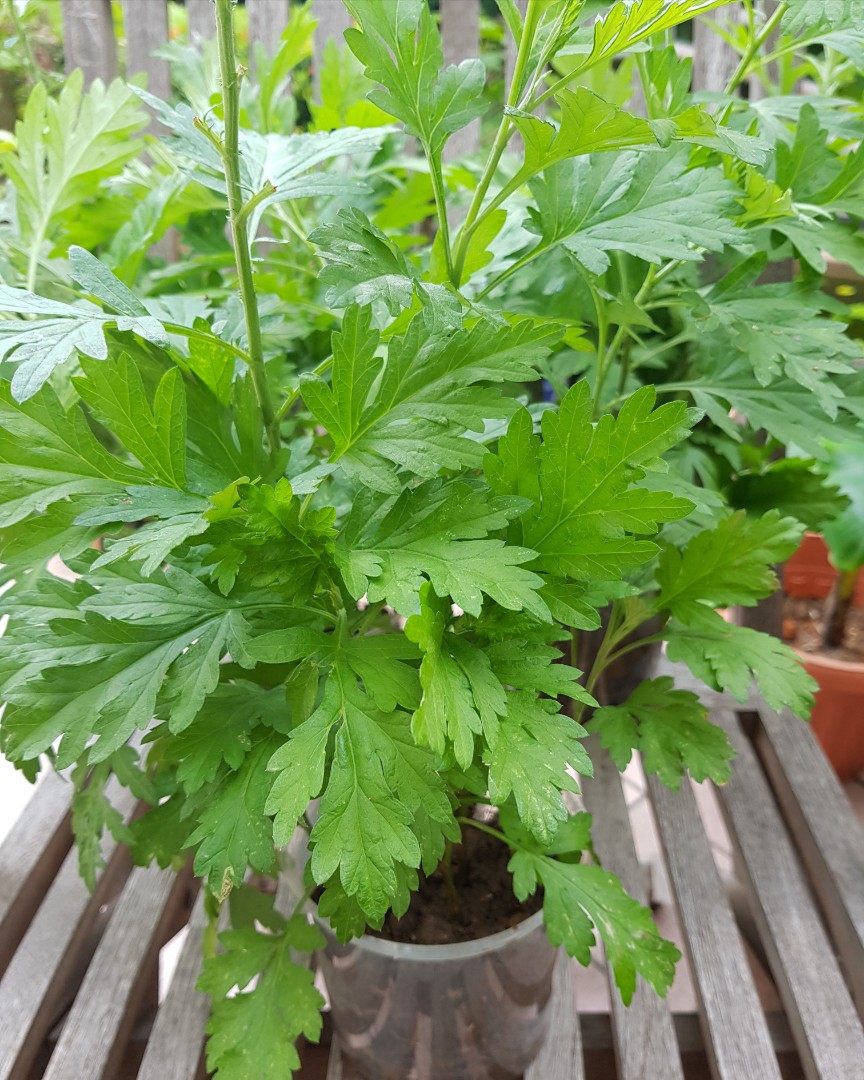
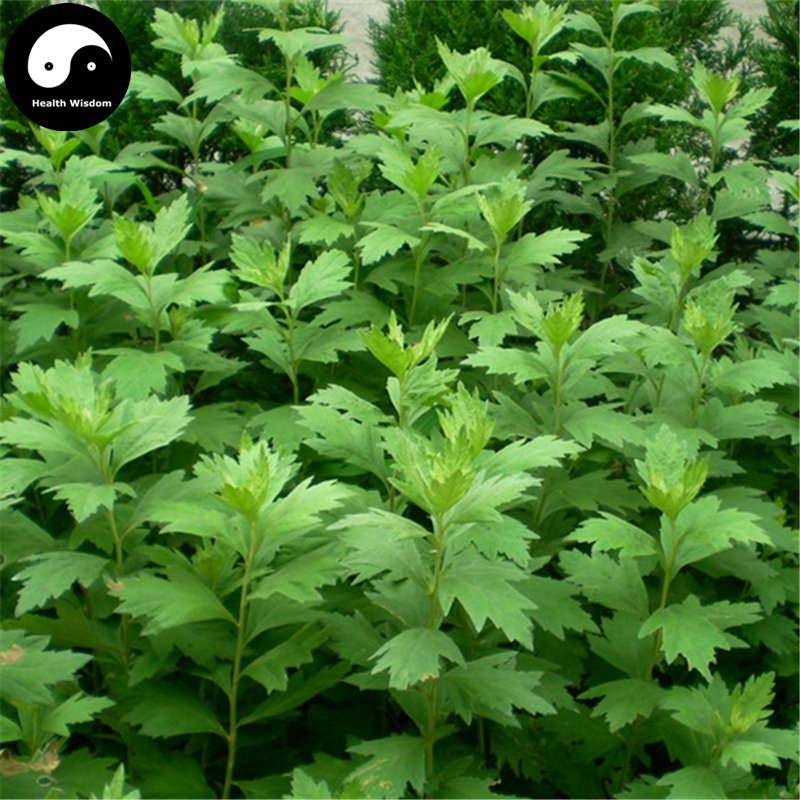







四、鬼针草属——Bidens L.
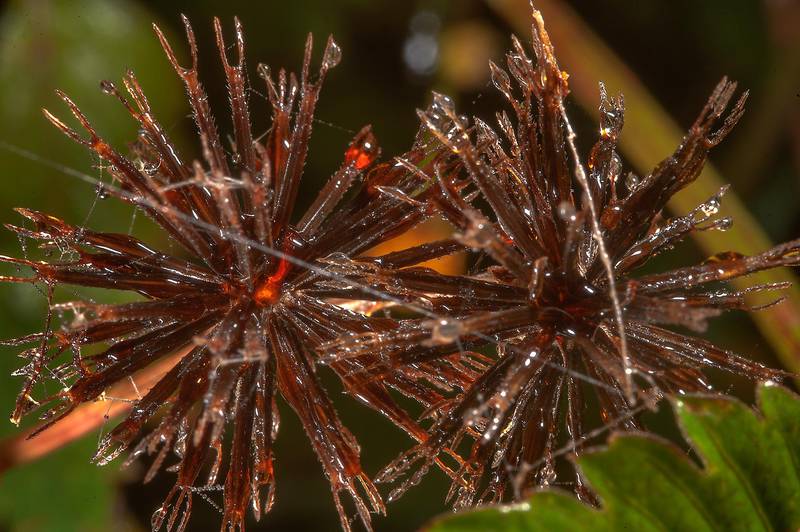
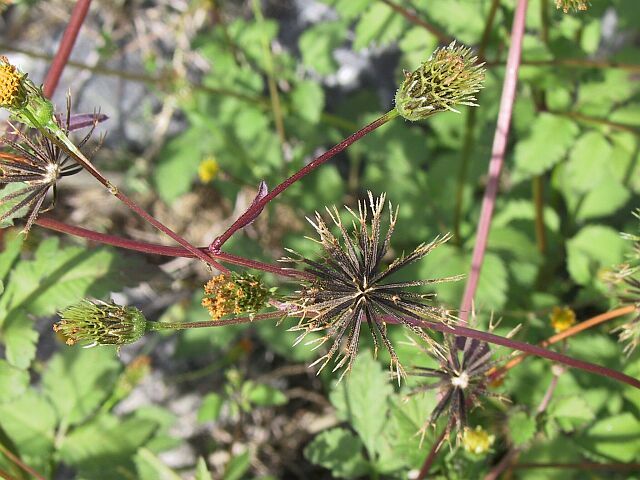
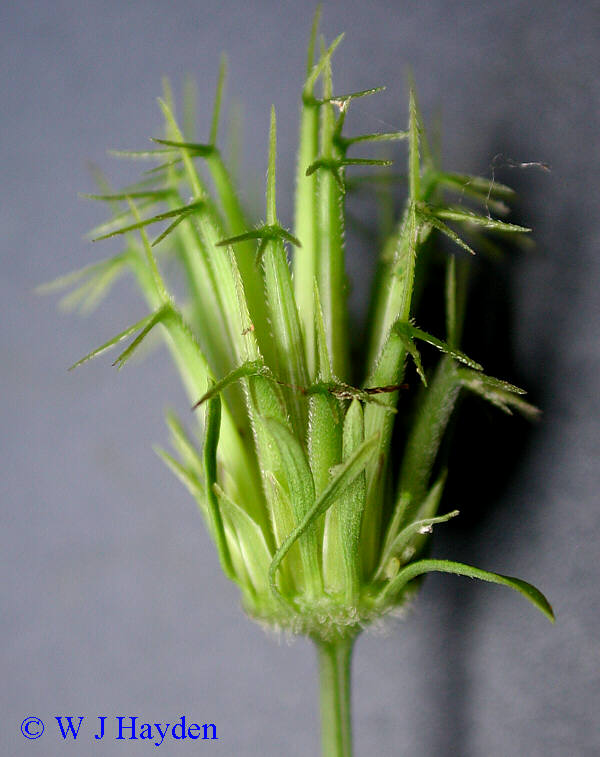
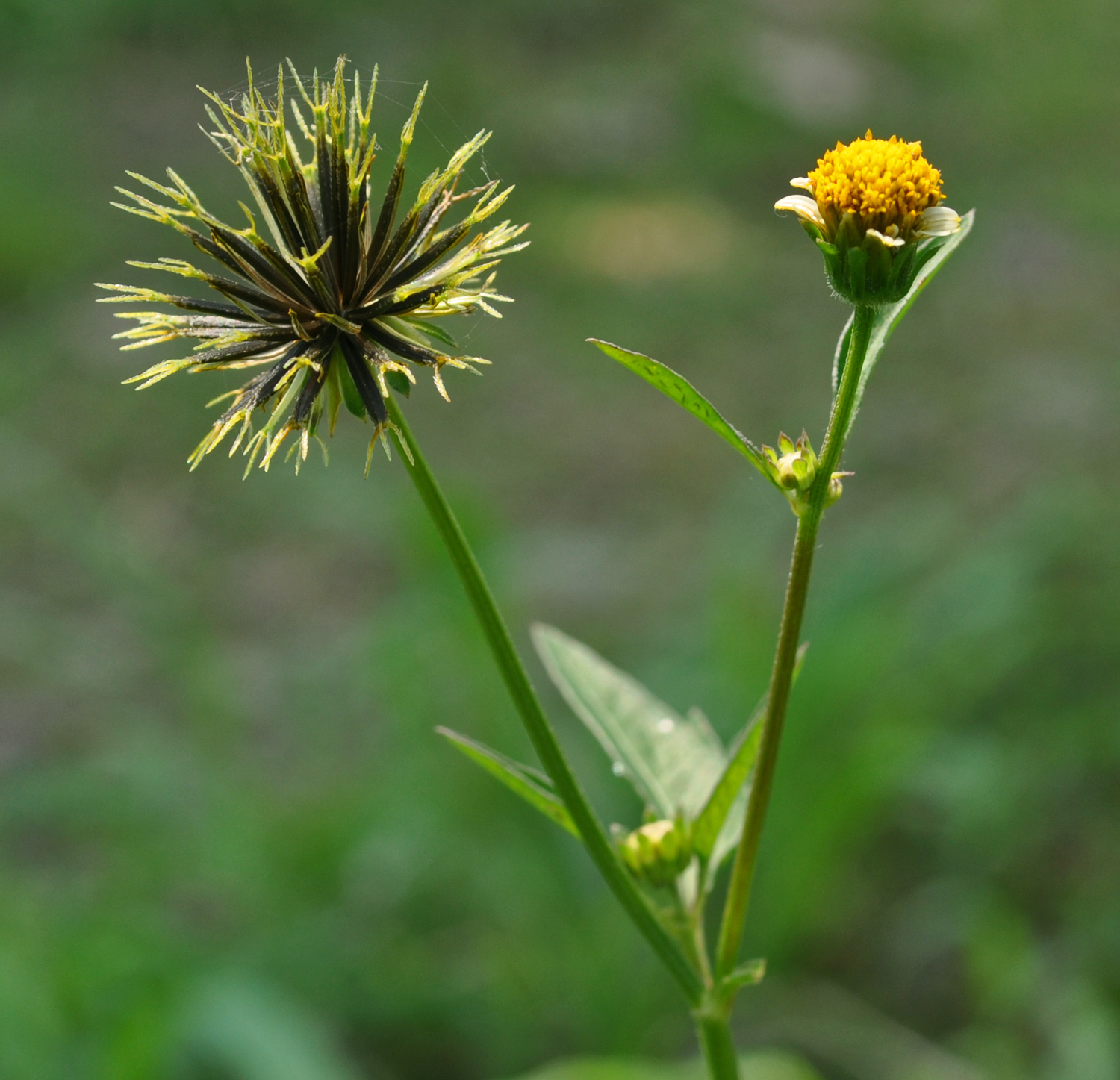
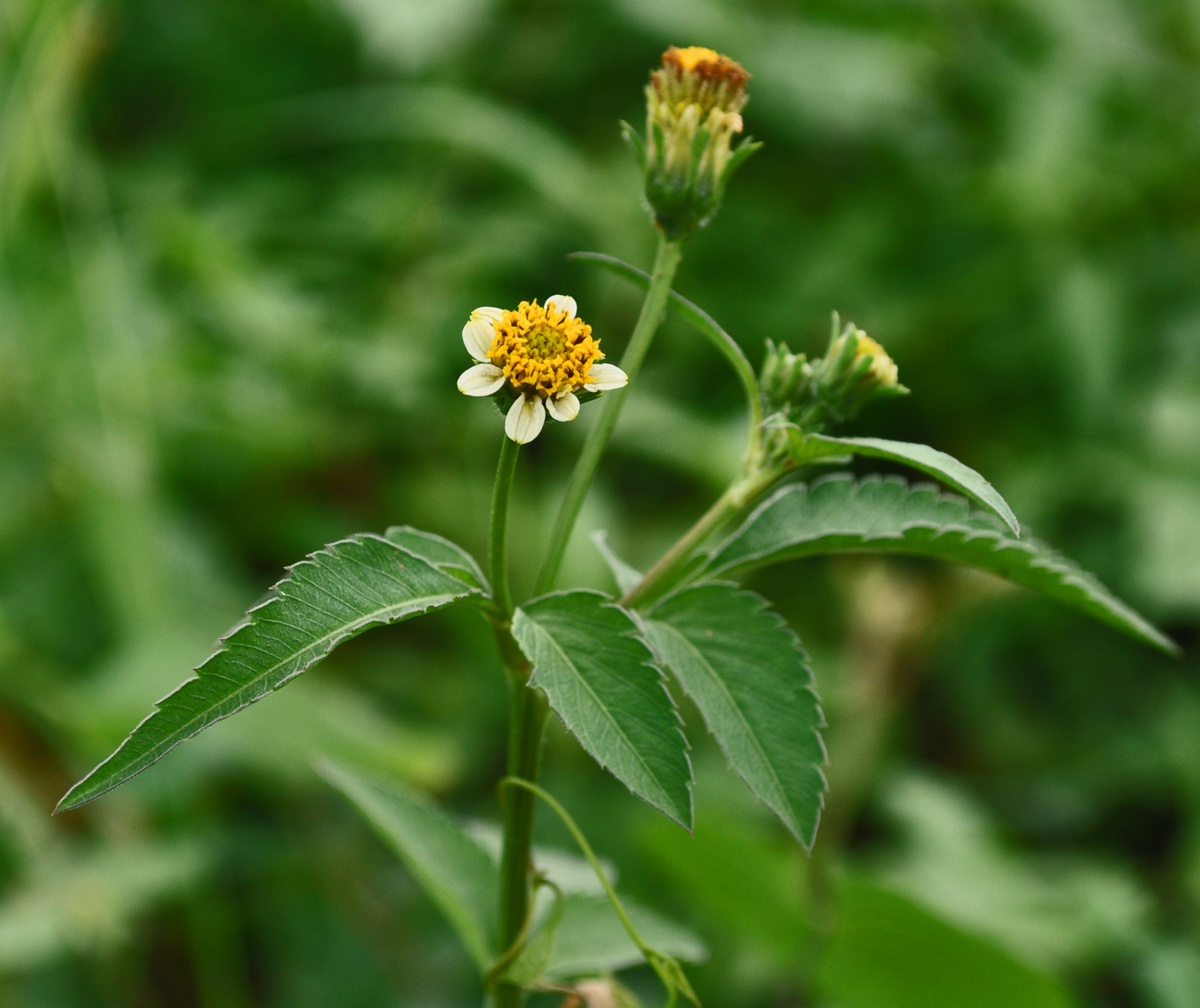
一年生或多年生草本。茎直立或匍匐,通常有纵条纹。叶对生或有时在茎上部互生,很少三枚轮生,全缘或具齿牙、缺刻,或一至三回三出或羽状分裂。头状花序单生茎、枝端或多数排成不规则的伞房状圆锥花序丛。总苞钟状或近半球形;苞片通常1-2层,基部常合生,外层草质,短或伸长为叶状,内层通常膜质,具透明或黄色的边缘;托片狭,近扁平,干膜质。花杂性,外围一层为舌状花,或无舌状花而全为筒状花,舌状花中性,稀为雌性,通常白色或黄色,稀为红色,舌片全缘或有齿;盘花筒状,两性,可育,冠檐壶状,整齐,4-5裂。花药基部钝或近箭形;花柱分枝扁,顶端有三角形锐尖或渐尖的附器,被细硬毛。瘦果扁平或具四棱,倒卵状椭圆形、楔形或条形,顶端截形或渐狭,无明显的喙,有芒刺2-4枚,其上有倒刺状刚毛。果体褐色或黑色,光滑或有刚毛。
本属约230余种,广布于全球热带及温带地区,尤以美洲种类最为丰富。我国有9种,2变种,几遍布全国各地,多为荒野杂草。有数种供药用,为民间常用草药。
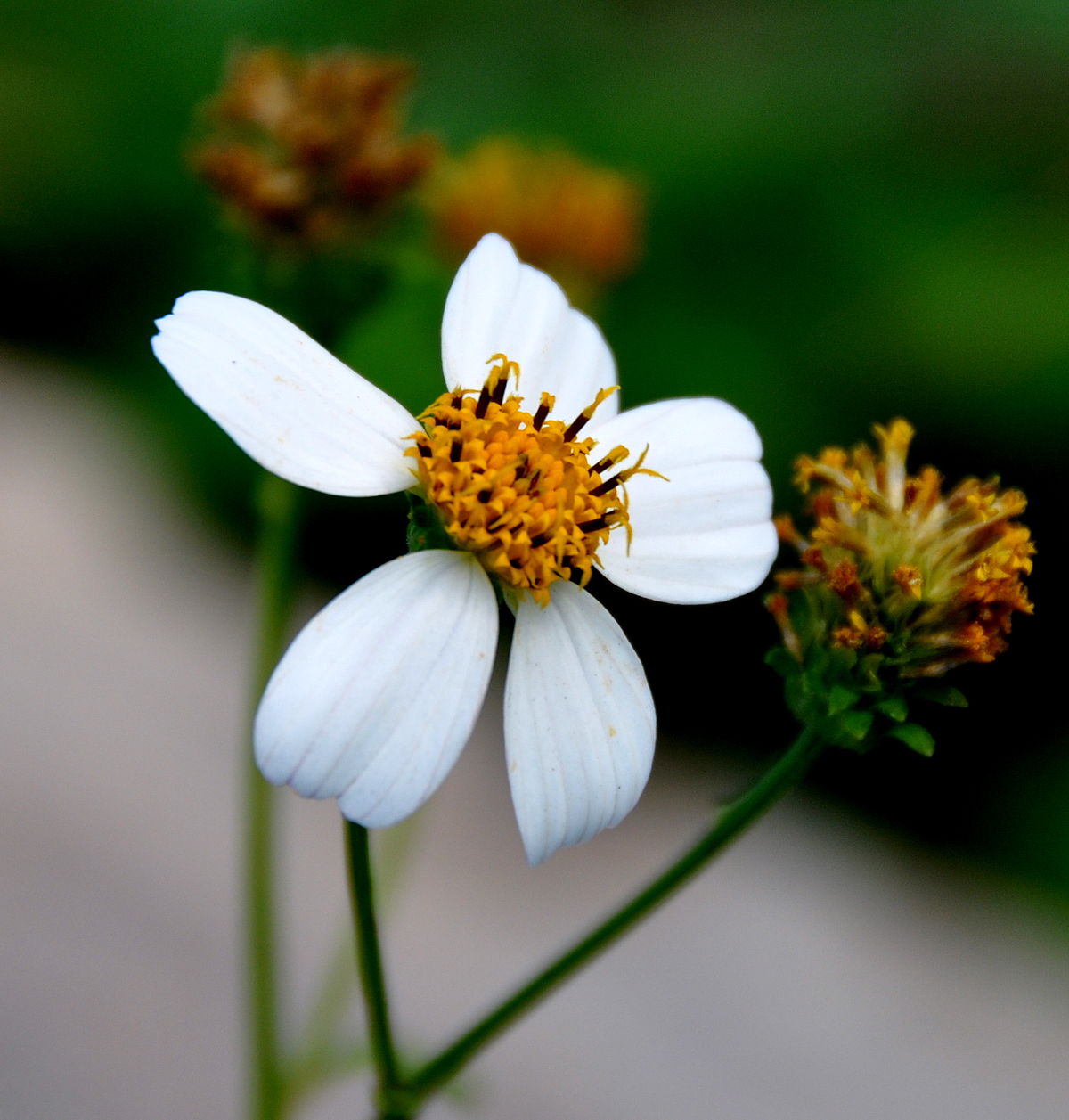
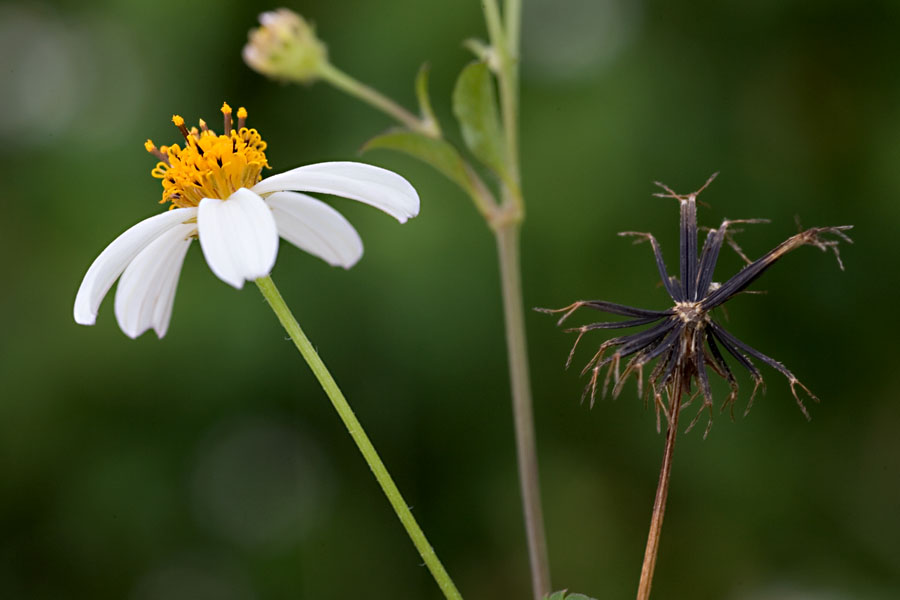
1. 鬼针草(本草拾遗,图考)三叶鬼针草、虾钳草、蟹钳草(广东、广西),对叉草、粘人草、粘连子(云南),一包针、引线包(江苏、浙江),豆渣草、豆渣菜(四川、陕西),盲肠草(福建、广东、广西)
Bidens pilosa L.
鬼针草(原变种)
var. pilosa
一年生草本,茎直立,高30-100厘米,钝四棱形,无毛或上部被极稀疏的柔毛,基部直径可达6毫米。茎下部叶较小,3裂或不分裂,通常在开花前枯萎,中部叶具长1.5-5厘米无翅的柄,三出,小叶3枚,很少为具5 (-7) 小叶的羽状复叶,两侧小叶椭圆形或卵状椭圆形,长2-4.5厘米,宽1.5-2.5厘米,先端锐尖,基部近圆形或阔楔形,有时偏斜,不对称,具短柄,边缘有锯齿、顶生小叶较大,长椭圆形或卵状长圆形,长3.5-7厘米,先端渐尖,基部渐狭或近圆形,具长1-2厘米的柄,边缘有锯齿,无毛或被极稀疏的短柔毛,上部叶小,3裂或不分裂,条状披针形。头状花序直径8-9毫米,有长1-6(果时长3-10)厘米的花序梗。总苞基部被短柔毛,苞片7-8枚,条状匙形,上部稍宽,开花时长3-4毫米,果时长至5毫米,草质,边缘疏被短柔毛或几无毛,外层托片披针形,果时长5-6毫米,干膜质,背面褐色,具黄色边缘,内层较狭,条状披针形。无舌状花,盘花筒状,长约4.5毫米,冠檐5齿裂。瘦果黑色,条形,略扁,具棱,长7-13毫米,宽约1毫米,上部具稀疏瘤状突起及刚毛,顶端芒刺3-4枚,长1.5-2.5毫米,具倒刺毛。
产华东、华中、华南、西南各省区。生于村旁、路边及荒地中。广布于亚洲和美洲的热带和亚热带地区。为我国民间常用草药,有清热解毒、散瘀活血的功效,主治上呼吸道感染、咽喉肿痛、急性阑尾炎、急性黄疸型肝炎、胃肠炎、风湿关节疼痛、疟疾,外用治疮疖、毒蛇咬伤、跌打肿痛。
Bidens pilosa is an annual species of herbaceous flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae. Its many common names include hitch hikers, black-jack, beggarticks, farmer’s friends and Spanish needle, but most commonly referred to as cobblers pegs. It is native to the Americas but is widely distributed as an introduced species in other regions worldwide including Eurasia, Africa, Australia, South America and the Pacific Islands.
NOMENCLATURE: From a Western perspective, Bidens (meaning “two teeth”) is a reference to hairy calyx (pappus) of some species. The name “pilosa” means “hairy.” In China the many species and varieties of Bidens are often lumped under the names xian feng cao (“abundant weed”) or gui zhen cao (“demon spike grass” / “ghost needle weed”)cao but each species (see “similarly used species” above) will sometimes have a different Chinese common name. (“demon spike grass” or “ghost needle weed”) In Taiwan Bidens species are called “ham hong chho.”
Many common names of Bidens are a reference to the fruits that are aggravating hitchhikers. Hence the names “demon魔鬼; 恶魔 spike grass” and “ghost needle weed.” Beggars tick is a reference to the fact that hobos流浪者; 漂泊者 would gather these on their clothing as they walked along railroad tracks. • Some Chinese will use Bidens interchangeably with Desmodium spp, as they are thought to be almost therapeutically在治疗上 identical. In China they even share the same name: “nian shen cao.” In South America Bidens is also used interchangeably with Desmodium spp. and there they also share a local common name: “amor seco.” • On a clinical note, current research has shown both plants to be liver protective.
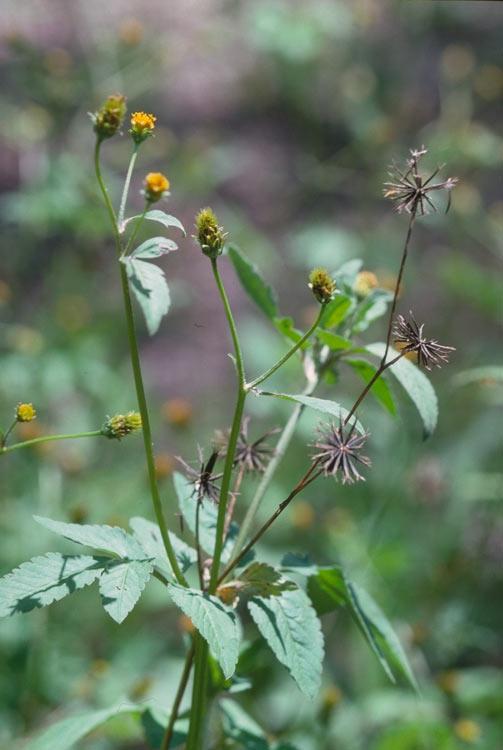










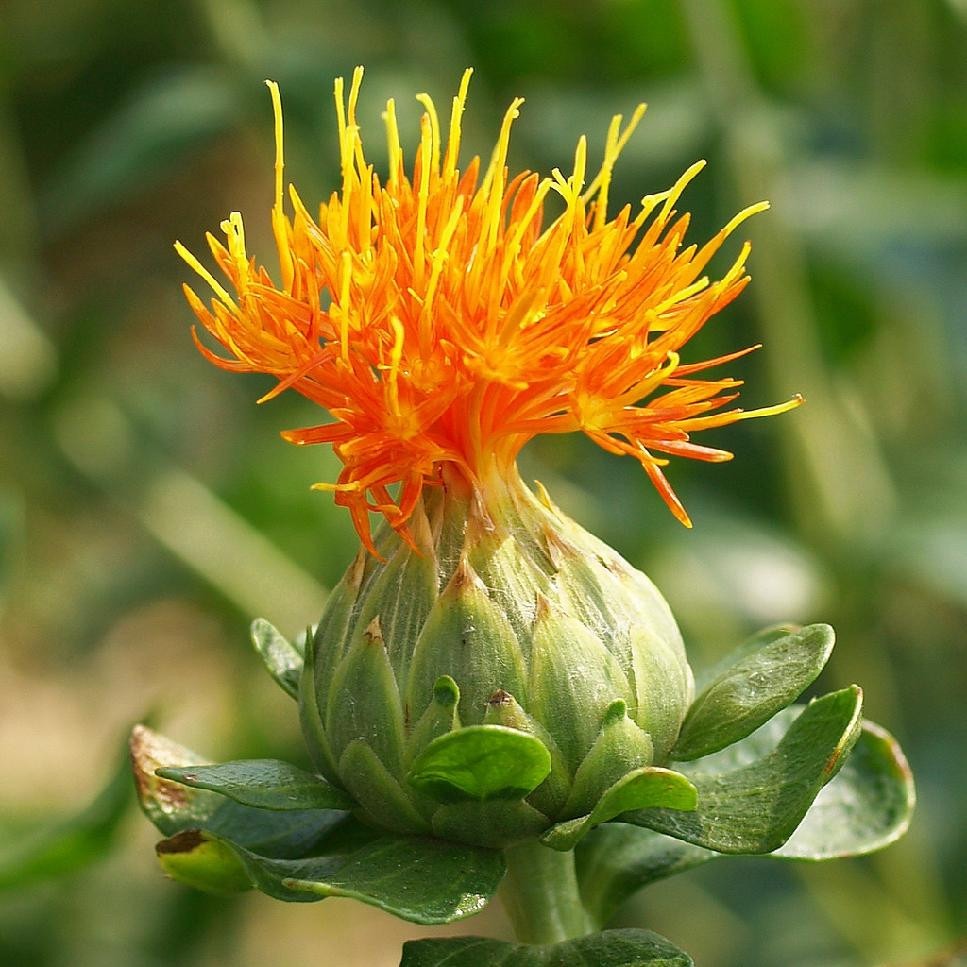
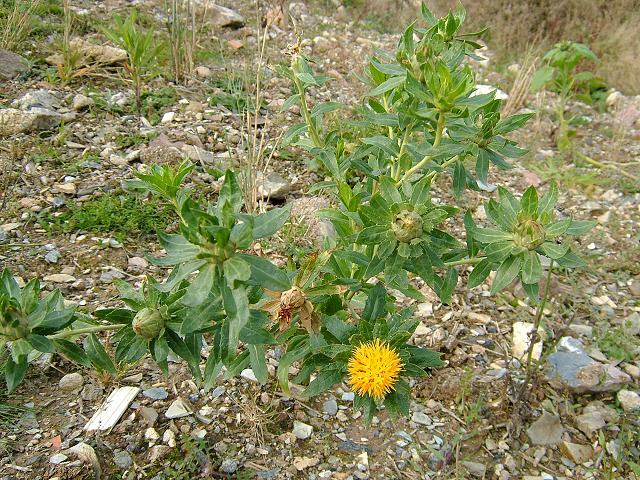
五、红花属——Carthamus L.
一年生草本,极少为二年生或多年生草本。茎直立,上部分枝,全部茎枝坚硬,淡白色,上部通常被柔毛,蛛丝状,多细胞节毛或粗毛。叶互生,无柄,半抱茎或有时全抱茎,革质,羽状分裂或不裂,无毛或被毛,通常有腺点。头状花序同型,为头状花序外围苞叶包绕,含多数小花,多数或少数在茎枝顶端排成伞房花序,极少有单生茎顶的。总苞球形、卵形或长椭圆状。总苞片多层,中层或中外层顶端有卵形、卵状披针形或披针形而边缘有刺齿少无刺齿的革质绿色叶质附属物。花托平,常有托毛或无托毛。全部小花两性,管状,极少外层小花为无性,花冠黄色、杏黄色、红色或紫色,极少有白色的。花丝短,分离,无毛或有毛。花柱分枝短,贴合。瘦果4 棱形,卵形,倒披针形或宽楔形,乳白色,有光泽,果棱伸出成果缘,侧生着生面。冠毛多层或无冠毛,或仅边缘小花的瘦果无冠毛。如有冠毛,则冠毛刚毛膜片状,不等长,最内层膜片极短,中层较长,全部膜片边缘锯齿状。
约18-20种,分布中亚、西南亚及地中海区。我国有两种。
1. 红花(植物名实图考) 红蓝花 刺红花
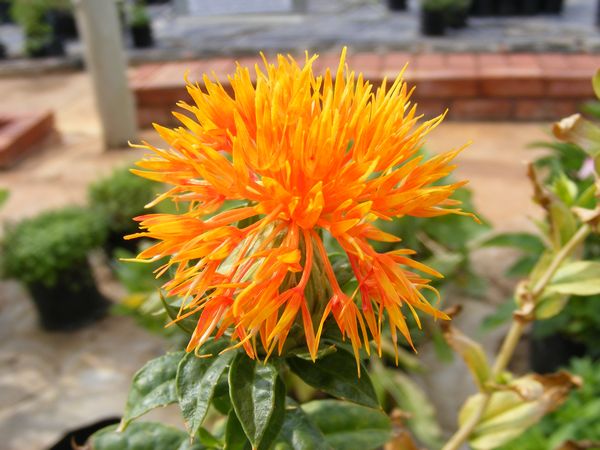
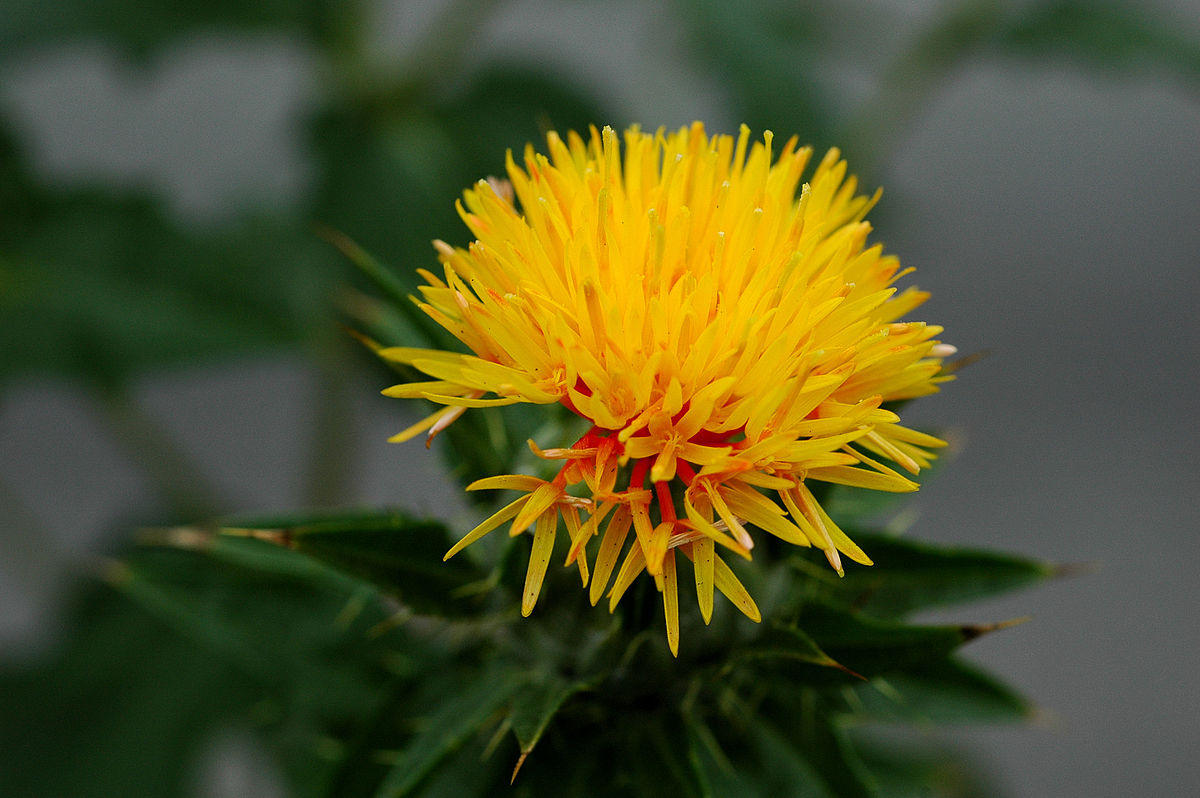
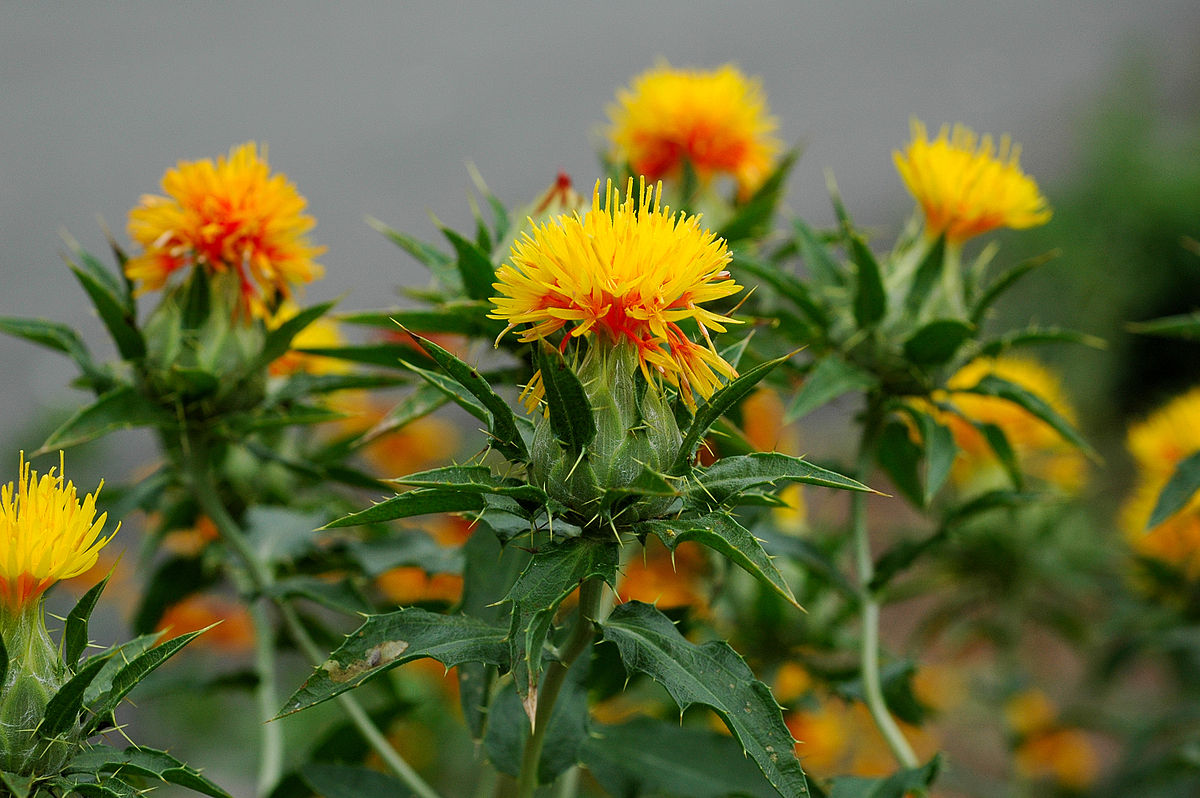
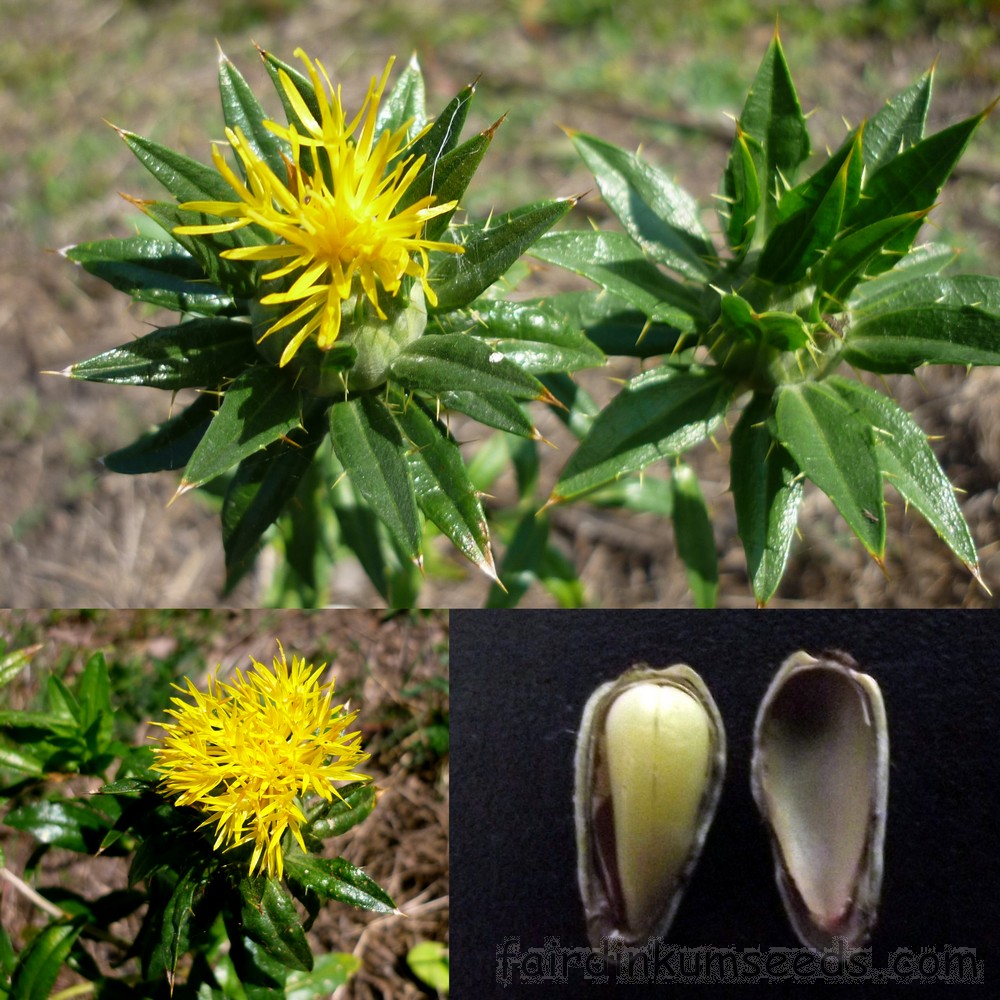
Carthamus tinctorius L.
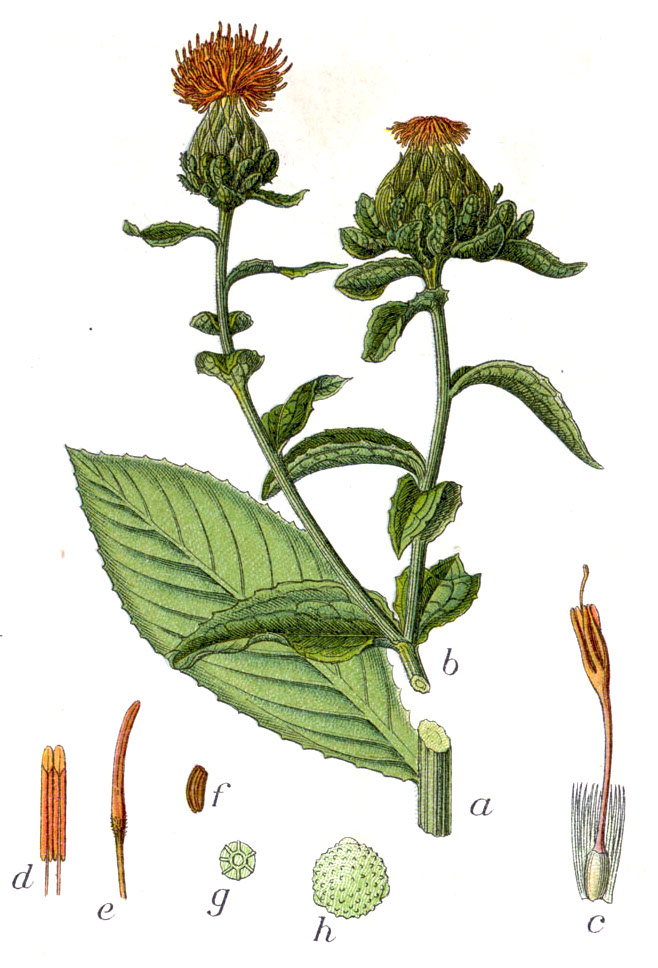
一年生草本。高 (20)50-100(150) 厘米。茎直立,上部分枝,全部茎枝白色或淡白色,光滑,无毛。中下部茎叶披针形、披状披针形或长椭圆形,长7-15厘米,宽2.5-6厘米,边缘大锯齿、重锯齿、小锯齿以至无锯齿而全缘,极少有羽状深裂的,齿顶有针刺,针刺长1-1.5毫米,向上的叶渐小,披针形,边缘有锯齿,齿顶针刺较长,长达3毫米。全部叶质地坚硬,革质,两面无毛无腺点,有光泽,基部无柄,半抱茎。头状花序多数,在茎枝顶端排成伞房花序,为苞叶所围绕,苞片椭圆形或卵状披针形,包括顶端针刺长2.5-3厘米,边缘有针刺,针刺长1-3毫米,或无针刺,顶端渐长,有篦齿状针刺,针刺长2毫米。总苞卵形,直径2.5厘米。总苞片4 层,外层竖琴状,中部或下部有收溢,收缢以上叶质,绿色,边缘无针刺或有篦齿状针刺,针刺长达3毫米,顶端渐尖,有长1-2毫米,收溢以下黄白色;中内层硬膜质,倒披针状椭圆形至长倒披针形,长达2.2厘米,顶端渐尖。全部苞片无毛无腺点。小花红色、桔红色,全部为两性,花冠长2.8厘米,细管部长2厘米,花冠裂片几达檐部基部。瘦果倒卵形,长5.5毫米,宽5毫米,乳白色,有4 棱,棱在果顶伸出,侧生着生面。无冠毛。花果期5-8月。
原产中亚地区。苏联有野生也有栽培,日本、朝鲜广有栽培。现时黑龙江、辽宁、吉林、河北、山西、内蒙古、陕西、甘肃、青海、山东、浙江、贵州、四川、西藏,特别是新疆都广有栽培。我国在上述地区有引种栽培外,山西、甘肃、四川亦见有逸生者。
红花的花入药,通经、活血,主治妇女病。花含红色素,也是我国古代用以提供红色染织物的色素原料。红花中含有红色素与黄色素两种色素,黄色素溶于水,而红色素溶于碱性水液中,明代宋应星的《天工开物》一书中就已经记载了由花中提纯红色素的全过程,足见我国古代印染业之发达。红花也是一种多用途的综合资源植物。种子含油率极高,一般在34-55%之间,多属不饱和脂肪酸油类,极适合作食用油,有降低人体胆固醇和血脂的作用。
Safflower红花, Carthamus tinctorius, is a highly branched, herbaceous, thistle-like annual plant in the sunflower family Asteraceae. It is commercially cultivated for vegetable oil extracted from the seeds and was used by the early Spanish colonies along the Rio Grande as a substitute for saffron藏红花(色的),番红花. Plants are 30 to 150 cm tall with globular flower heads having yellow, orange, or red flowers. Each branch will usually have from one to five flower heads containing 15 to 20 seeds per head. Safflower is native to arid environments having seasonal rain. It grows a deep taproot which enables it to thrive in such environments.
Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) has been grown for centuries, primarily for its colorful petals to use as a food coloring and flavoring agent for vegetable oils and also for preparing textile dye in the Far East, Central, and Northern Asia and European Caucasian高加索人; 白种人; (Gecgel et al., 2007). Safflower is most commonly known as “kusum” (India), derived from the Sanskrit, “kusumbha,” and as “honghua” (red flower) in China. Its use as a less costly substitute for saffron is indicated by the names false saffron, thistle蓟 saffron, and dyer’s saffron (Weiss, 1983). Safflower (C. tinctorius L.), which belongs to the family Compositae, is cultivated in several parts of the world due to its adaptability to different environmental conditions. The world production of safflower seeds in 2013 amounted to 718,161 tons. With a production value of 174,900 tons, Kazakhstan was the leading producer of this crop in the world in the same year. The production of safflower in Kazakhstan accounted for 24% of the total global safflower production. India and the United States ranked second and third in safflower production in 2013 with production values of 109,000 and 95,360 tons, respectively (Sen Nag, 2017). Safflower production in India is mostly confined to rain-fed conditions during winter. It is highly branched, herbaceous, thistle-like annual or winter annual, usually with many long sharp spines刺on the leaves.








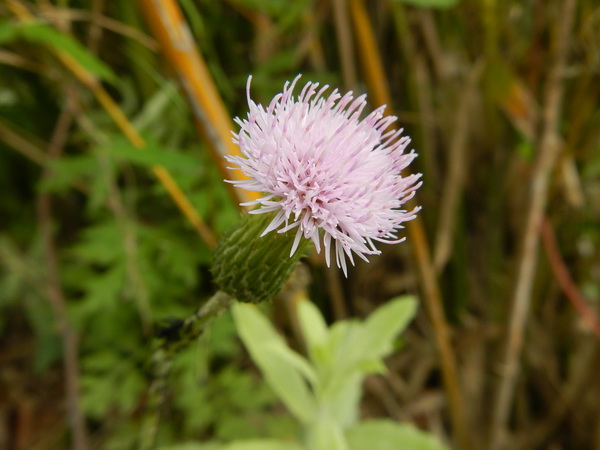
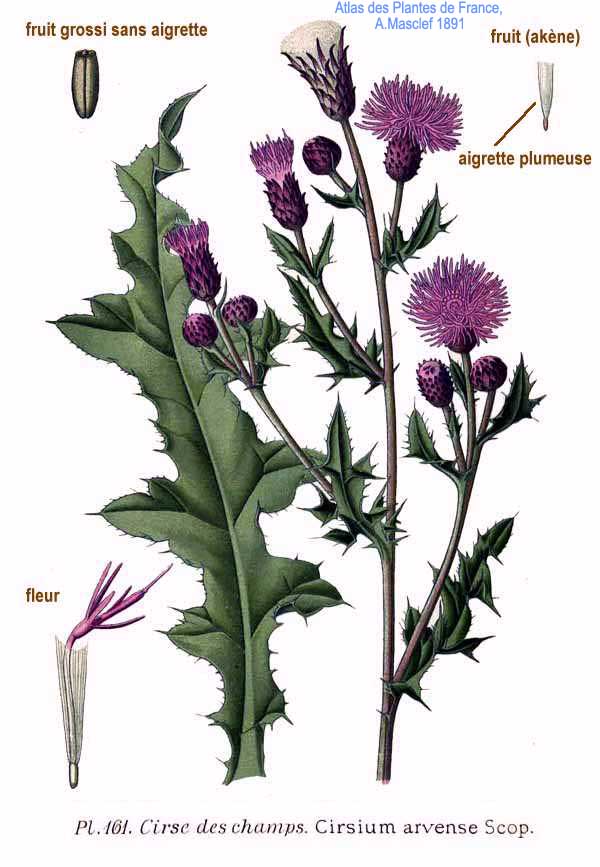
六、蓟属——Cirsium Mill. emend. Scop.
一年生、二年生或多年生植物,无茎至高大草本,雌雄同株,极少异株。茎分枝或不分枝,叶无毛至有毛,边缘有针刺。头状花序同型,或全部为两性花或全部为雌花,直立,下垂或下倾,小、中等大小或更大,在茎枝顶端排成伞房花序、伞房圆锥花序、总状花序或集成复头状花序,少有单生茎端。总苞卵状、卵圆状、钟状或球形,无毛或被稀疏的蛛丝毛或蛛丝毛极稠密且膨松,或被多细胞的长节毛。总苞片多层,覆瓦状排列或镊合状排列,边缘全缘,无针刺或有缘毛状针刺。花托被稠密的长托毛。小花红色、红紫色,极少为黄色或白色的,檐部与细管部几等长或细管部短,5裂,有时深裂几达檐部的基部。花丝分离,有毛或乳突,极少无毛;花药基部附属物撕裂。花柱分枝基部有毛环。瘦果光滑,压扁,通常有纵条纹,顶端截形或斜截形,有果缘,基底着生面,平。冠毛多层,向内层渐长,全部冠毛刚毛长羽毛状,基部连合成环,整体脱落。
约250-300种,广布欧、亚、北非、北美和中美大陆。我国有50余种,分属8个组中。
1. 刺儿菜 大蓟,小蓟,大小蓟,野红花(浙江),大刺儿菜
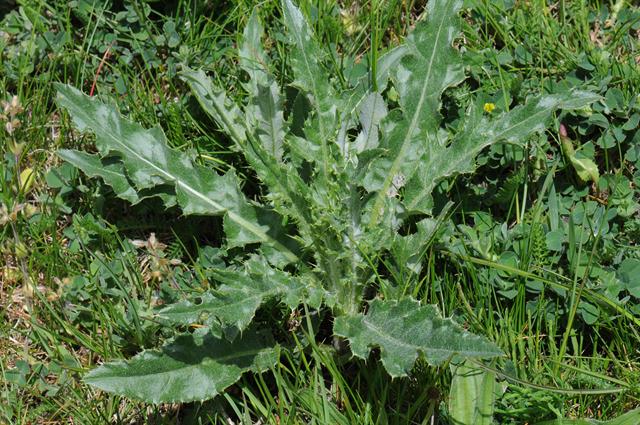
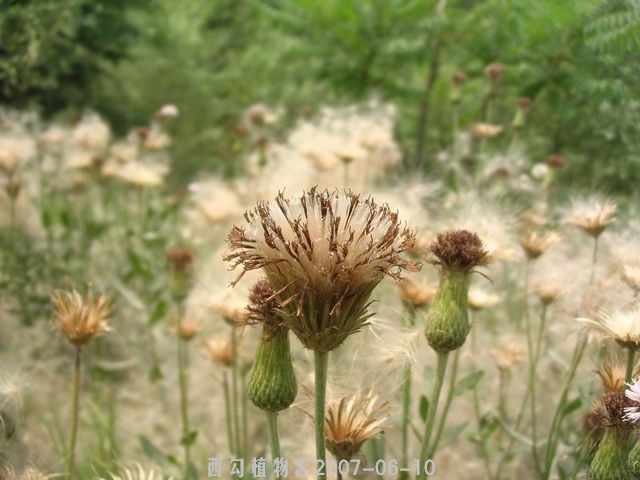
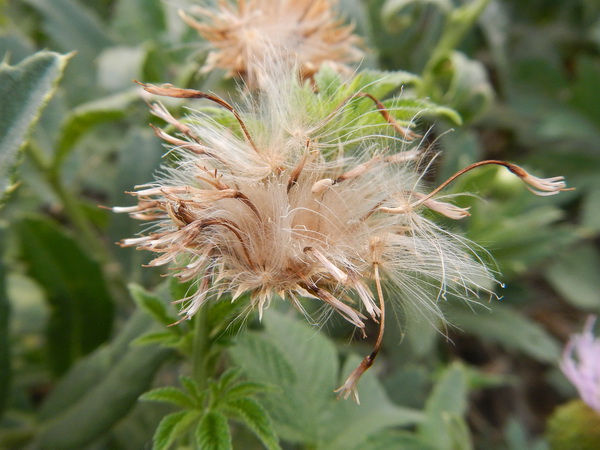
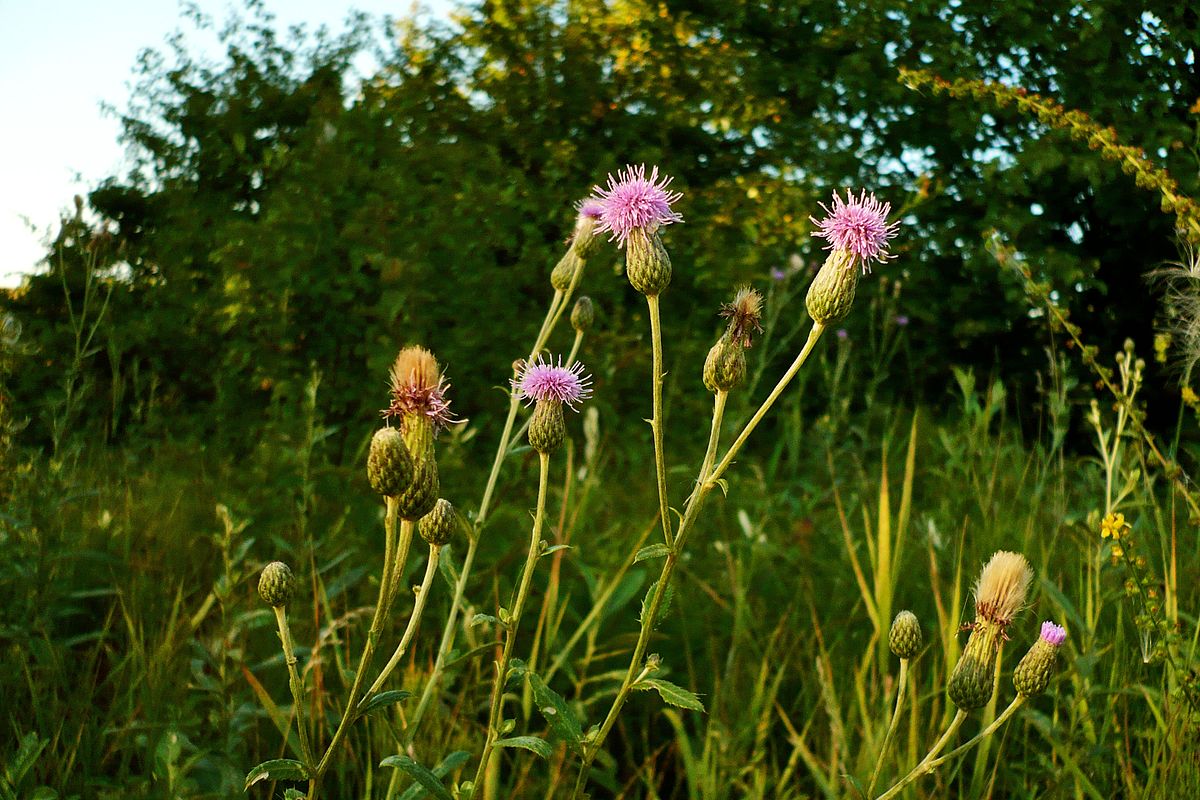
Cirsium setosum (Willd.) MB.
多年生草本。茎直立,高30-80(100-120)厘米,基部直径3-5毫米,有时可达1厘米,上部有分枝,花序分枝无毛或有薄绒毛。基生叶和中部茎叶椭圆形、长椭圆形或椭圆状倒披针形,顶端钝或圆形,基部楔形,有时有极短的叶柄,通常无叶柄,长7-15厘米,宽1.5-10厘米,上部茎叶渐小,椭圆形或披针形或线状披针形,或全部茎叶不分裂,叶缘有细密的针刺,针刺紧贴叶缘。或叶缘有刺齿,齿顶针刺大小不等,针刺长达3.5毫米,或大部茎叶羽状浅裂或半裂或边缘粗大圆锯齿,裂片或锯齿斜三角形,顶端钝,齿顶及裂片顶端有较长的针刺,齿缘及裂片边缘的针刺较短且贴伏。全部茎叶两面同色,绿色或下面色淡,两面无毛,极少两面异色,上面绿色,无毛,下面被稀疏或稠密的绒毛而呈现灰色的,亦极少两面同色,灰绿色,两面被薄绒毛。头状花序单生茎端,或植株含少数或多数头状花序在茎枝顶端排成伞房花序。总苞卵形、长卵形或卵圆形,直径1.5-2厘米。总苞片约6层,覆瓦状排列,向内层渐长,外层与中层宽1.5-2毫米,包括顶端针刺长5-8毫米;内层及最内层长椭圆形至线形,长1.1-2厘米,宽1-1.8毫米;中外层苞片顶端有长不足0.5毫米的短针刺,内层及最内层渐尖,膜质,短针刺。小花紫红色或白色,雌花花冠长2.4厘米,檐部长6毫米,细管部细丝状,长18毫米,两性花花冠长1.8厘米,檐部长6毫米,细管部细丝状,长1.2毫米。瘦果淡黄色,椭圆形或偏斜椭圆形,压扁,长3毫米,宽1.5毫米,顶端斜截形。冠毛污白色,多层,整体脱落;冠毛刚毛长羽毛状,长3.5厘米,顶端渐细。花果期5-9月。
除西藏、云南、广东、广西外,几遍全国各地。分布平原、丘陵和山地。生于山坡、河旁或荒地、田间,海拔170-2650米。欧洲东部、中部、苏联东、西西伯利亚及远东、蒙古、朝鲜、日本广有分布。模式标本采自波兰。
Morphology and biology.
Root system is well developed. It consists of a main stalky root (2-3 m) and numerous horizontal lateral rhizomes, which generate new stalks. Stalk is 50-150 cm in height, upright, ramified, striated or costate, wingless, glabrous or slightly cobwebby pubescent. Phyllotaxy alternate. Leaves are green, sedentary or short-petiolate, oblong or lanceolate, integral or slightly pinnati-lobate, glabrous or cobwebby pubescent from below, 5-15 (20) cm in length and 1-5 cm in width, with dense fine marginal thorns. It is a dioecious plant. Female pistillate flowers are situated in some calathidia, and male staminate flowers in others. Flowers are unisexual owing to insufficient development of either pistils or stamens. Color of flowers is lilac, pink, or purple. Limbus of corolla is pentamerous, with lobes separated from base. The limbus is several times shorter than tube of corolla, viz 2 times shorter in staminate flowers and 4-5 times shorter in pistillate flowers. Anthers at the base have apically jagged appendages; staminal filaments are glabrous. Floral calathidia are small (1-2 cm in diameter), always upright on cobwebby stalks, gathering in corymbose-paniculate inflorescence. Receptacle flat with long bracts. Involucre of staminate calathidia is 1 cm in diameter; the same for involucre of pistillate spherical calathidia. Leaflets of involucre pluriserial, imbricate, rough from outside; cobwebby pubescent, often violet along margins. External leaflets are oblong-ovate, accumbent, thorn-like acuminate; internal ones are lanceolate, thornless. Fruit is an oblong olive-yellowish or brownish hemicarp with indistinct longitudinal grooves. Length of hemicarp is 2.5-4 mm; its thickness is about 1 mm, weight is 2 mg. Pappus is dirty-white, during flowering shorter than nimbus; by the end of flowering it extends almost 3 times longer than nimbus during fruiting. Reproduction occurs by seeds and cloning (root offsprings). The plant grows from April until October, blossoms from May until July. Seeds ripen in September-October.
Distribution.
Cirsium setosum is distributed in all Eurasia; introduced into North America. Described as originating in Europe (Poland). The species is distributed in the entire former USSR, i.e., in the European part, Caucasus, south of Siberia, north of Central Asia (Aral-Caspian floristic area).
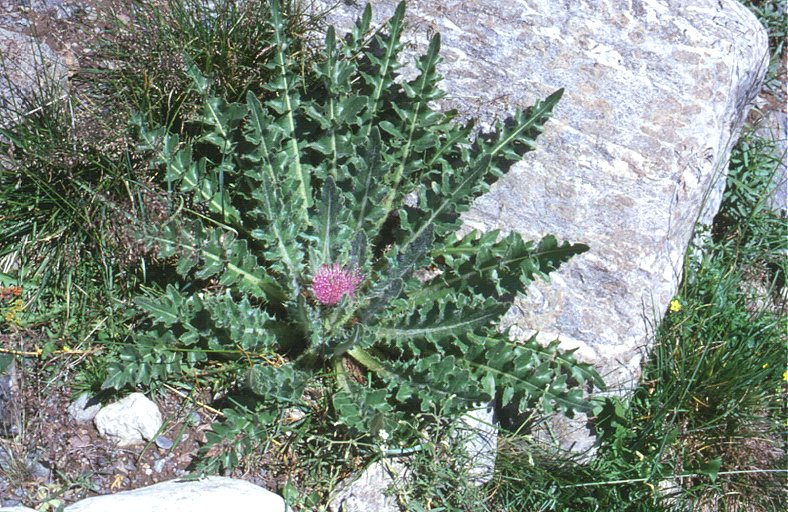
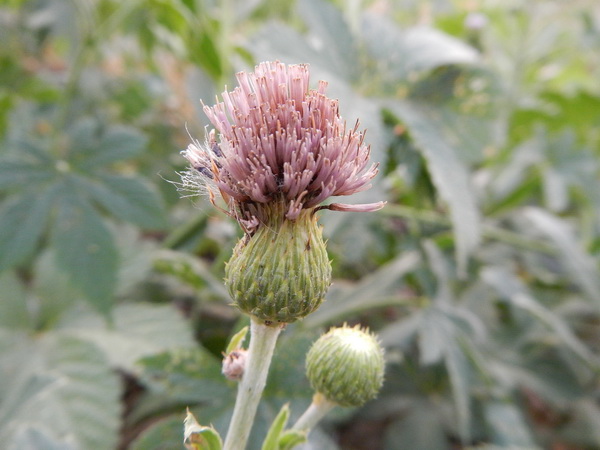










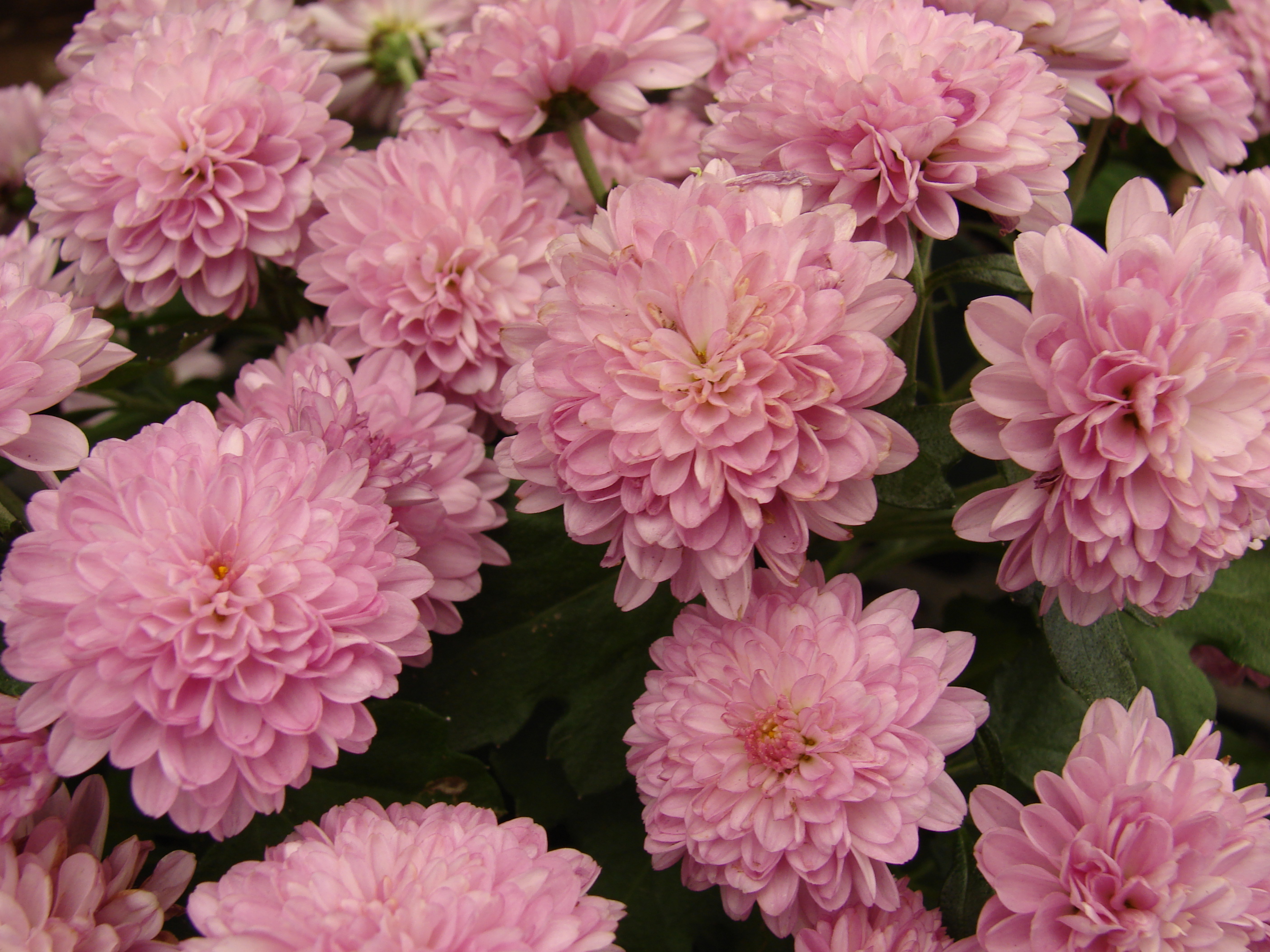
七、菊属——Dendranthema (DC.) Des Moul.
多年生草本。叶不分裂或一回或二回掌状或羽状分裂。头状花序异型,单生茎顶,或少数或较多在茎枝顶端排成伞房或复伞房花序。边缘花雌性,舌状,1层 (在栽培品种中多层) ,中央盘花两性管状。总苞浅碟状,极少为钟状。总苞片4-5层,边缘白色、褐色或黑褐或棕黑色膜质或中外层苞片叶质化而边缘羽状浅裂或半裂。花托突起,半球形,或圆锥状,无托毛。舌状花黄色、白色或红色,舌片长或短,短可至1.5毫米而长可到2.5厘米长或更长。管状花全部黄色,顶端5齿裂。花柱分枝线形,顶端截形。花药基部钝,顶端附片披针状卵形或长椭圆形。全部瘦果同形,近圆柱状而向下部收窄,有5-8条纵脉纹,无冠状冠毛。
本属约近30余种,主要分布我国以及日本、朝鲜、苏联。我国有17种。
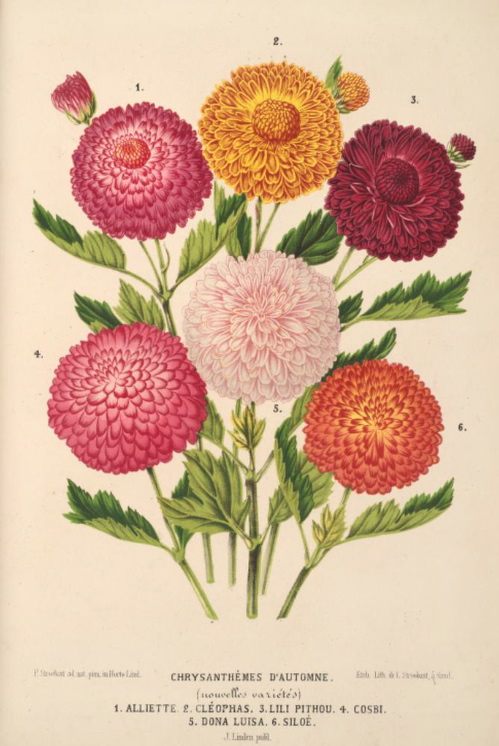
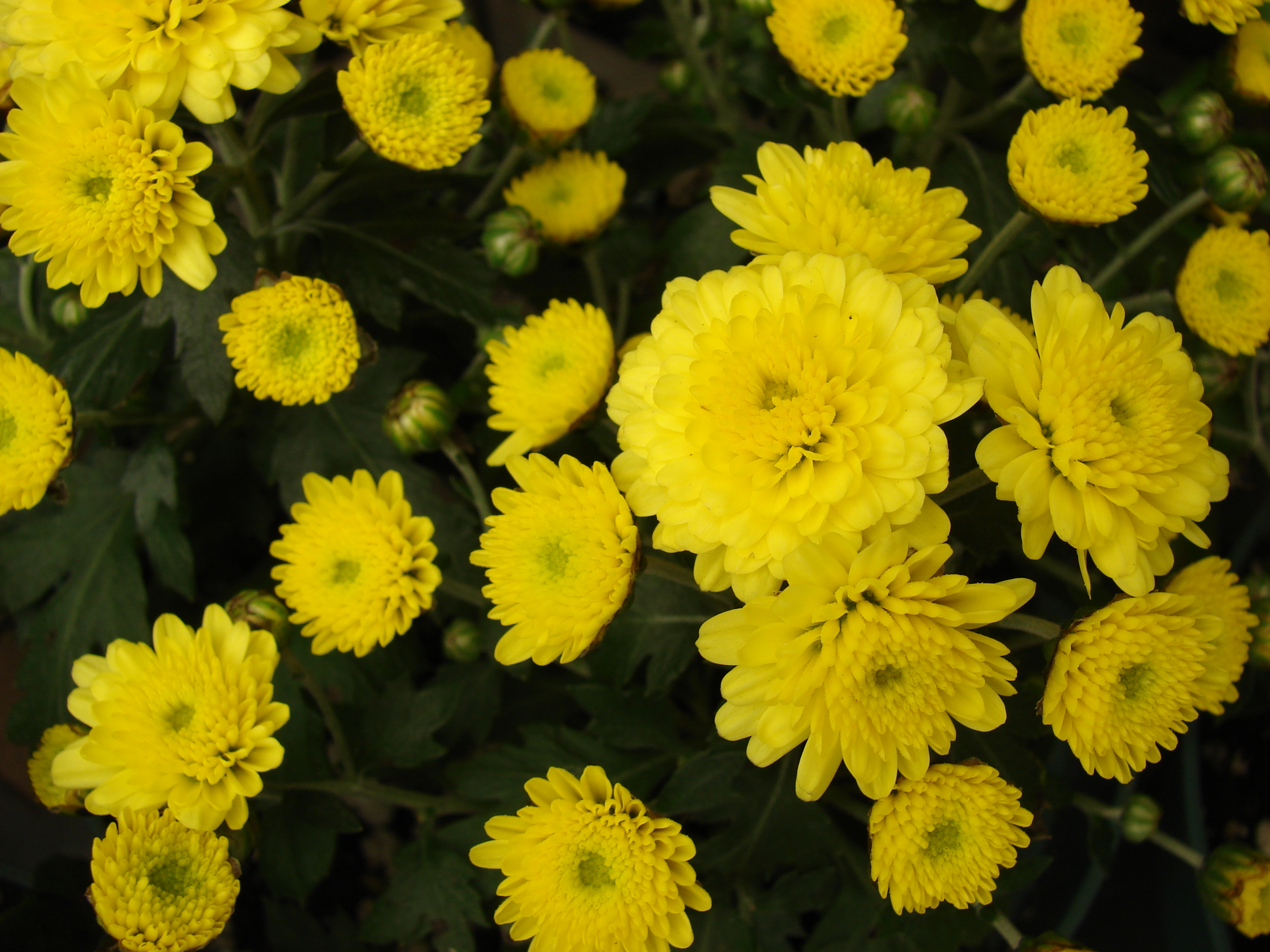
1. 菊花 鞠(尔雅),秋菊(北京)Chrysanthemum × morifolium
Dendranthema morifolium (Ramat.) Tzvel.
俗名:小白菊、小汤黄、杭白菊、滁菊、白菊花、绿牡丹
菊花或称秋菊是自古以来深受我国人民喜爱的一种花卉植物。这不仅仅是由于它的丰富各异的色彩,或白之素洁,或黄而雅淡,或红或紫,沉稳而浑厚。也是由于它的头状花序的奇特姿态,或飘若浮云,或矫若惊龙。所以,我国的历代诗人们,常以菊花为题咏。如唐代李商隐的“暗暗淡淡紫,融融冶冶黄,陶令篱巴色,罗舍宅里香”;宋朝韩琦的“莫嫌老圃秋容淡,犹看黄花分外香”。借菊触景,倚菊抒情,不一而足。
历代的诗人们爱菊、咏菊,可能也偶然成为菊花的栽培者。如晋代陶渊明的“采菊东篱下,悠然见南山。”但是,真正的菊花栽培者是我国的广大劳动群众。我国劳动人民在长.期的历史实践中,不但对菊花的栽培、管理技术方面累积了一套完好的实际经验,而且在培育新品种方面有了一套全面的遗传学知识。我国的菊艺是很发达的。清朝《广群芳谱》所记载的菊花品种,就有300-400种。今天已拥有1000余个菊花品种,成为所有花卉中品种最多的一个种了。作为菊花故乡的我国,由于过去历史上的国际文化交流,也把这一名贵花卉相继传到了国外。相传,唐宋时代,菊花经朝鲜传到日本。十七世纪传到欧洲,然后再传到美洲。今天,我国的菊花已成为世界的名卉了。
Chrysanthemum x morifolium
Common Name(s): ChrysanthemumFlorist's、 ChrysanthemumFlorist's DaisyGarden 、ChrysanthemumGarden Hardy 、ChrysanthemumGarden Mum、Hardy Garden Mum、Mum
Previously known as: Chrysanthemum morifoliumDendranthema x grandiflorum
This plant has low severity poison characteristics.
Description
Chrysanthemum x morifolium is an herbacious perennial which adds a pop of color to your garden when the leaves start to fall and the colder days start to come. Chrysanthemum x morifolium plants will begin to grow in the summer and spring, but it does not flower until the autumn. The aromatic芳香的,有香味的 flowers come in many colors from brownish shades to pastels轻淡柔和的色彩; and vibrant yellows; they can be solid, bi-color, or edged around the petals with another color. The leaves have a curved edge which add to the attractiveness of this plant. It can multiply very fast in your garden beds, making it more than just a potted plant for the autumn. Indeed, you will find this plant next to the scarecrows稻草人 and calling you to make sure that you add it to your garden. The explosion of color will bring a freshness as the summer starts to fade and one thinks of hot cocoa可可饮料; 深褐色 and warm winter fires.
Chrysanthemum x morifolium grows best in areas of your garden with full sun and well-drained soil. To maintain these plants, cut them back three times during the spring and summer– the last cut around August 15– to encourage bushy, compact growth and prevent spring flowering. They can be divided in the spring to further multiply your plants. When buying from a store, remember to plant these chrysanthemums in your garden; these plants do not die off at the end of the season and can come back for you to enjoy for years to come.
Family name Asteraceae (Compositae)
Quick ID Hints:
Leaves variable in size & shape, entire to lobed
Heads of flowers variable in size & shape
Erect, aromatic, perrenial herb forming mounds 1-3' tall.
Blooming late summer to frost; needs to be pinched several times in late spring to early summer to promote a compact mounded form; utilized in massing, edging, borders, cut flowers, pompons; responds well to additional fertilization; not cold hardy in north, must be dug up and overwintered in cold frames. .
Flower Description:
A flower head with many peripheral外围的; 次要的petals of various shapes and colors. Large to gigantic heads, 1-12" diam., solitary or clustered in loose corymbs. Commonly double or semidouble, occasionally as singlescolors variable throughout carotenoid类胡萝卜素 or anthyocyanin pigments; ray flowers conspicuous, variable in size and shape; disc flowers often hidden, yellow.
Edibility:
The petals and flower buds are used to make a sweet drink in Asia and a wine in Korea.
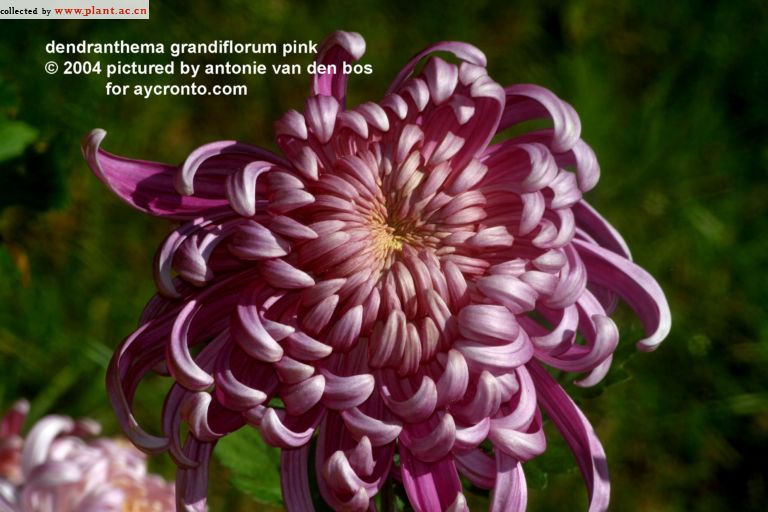
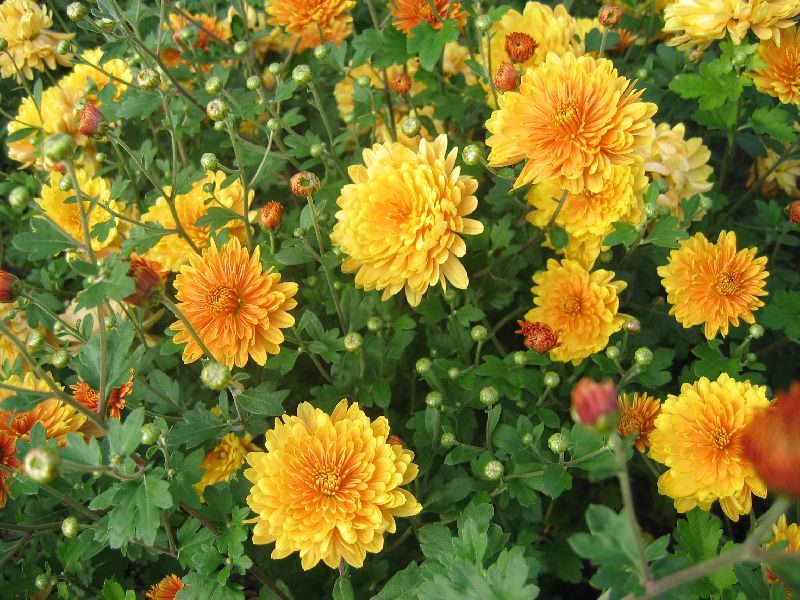










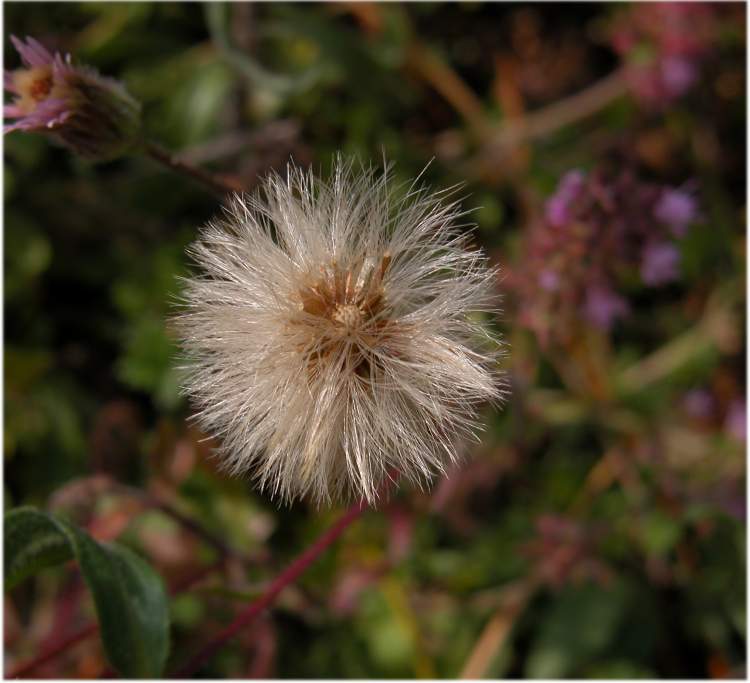
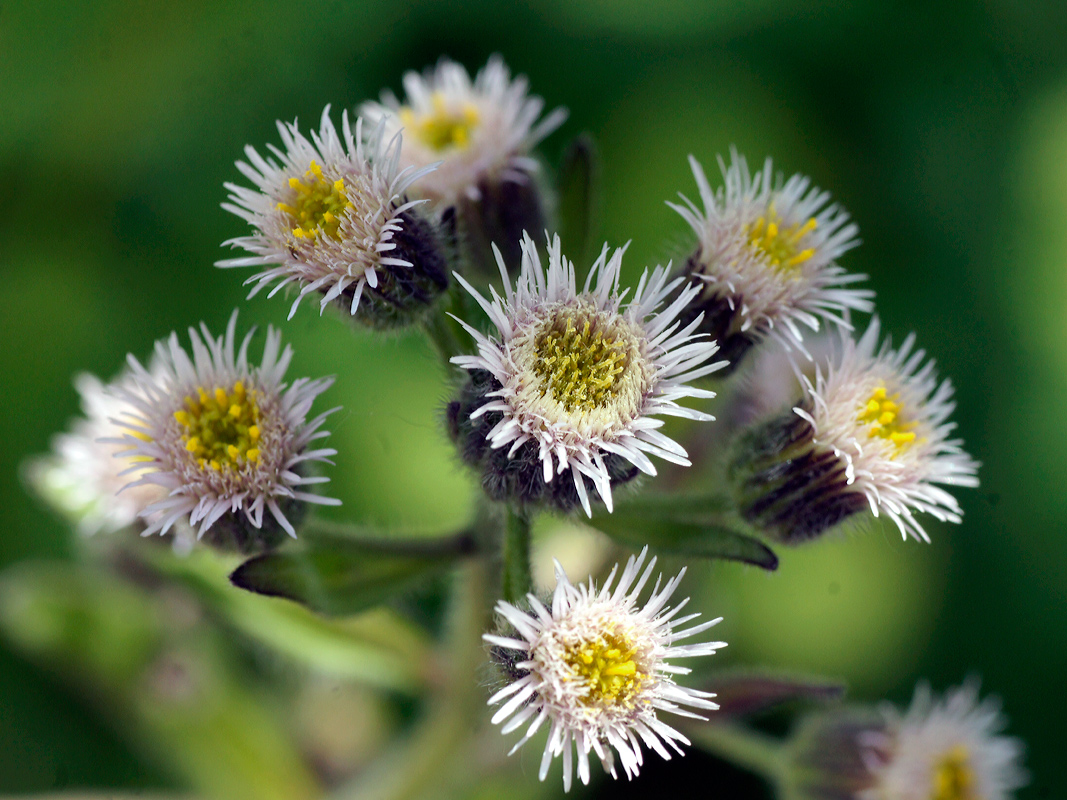
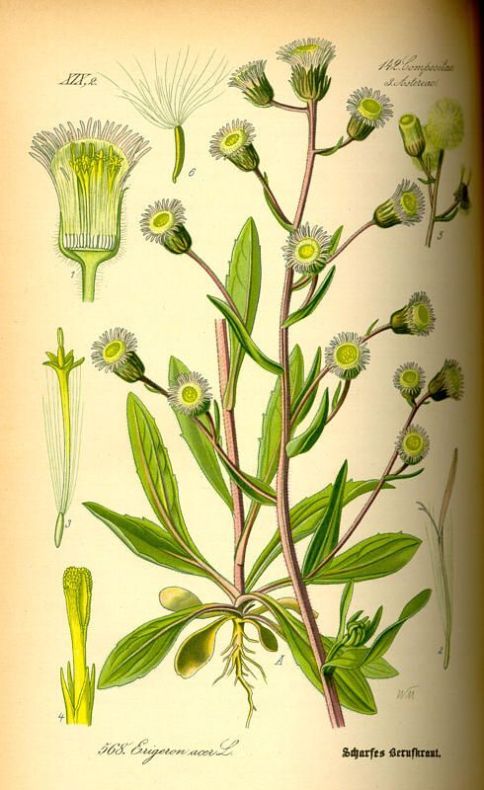
八、飞蓬属——Erigeron L.
多年生,稀一年生或二年生草本,或半灌木。叶互生,全缘或具锯齿。头状花序辐射状,单生或数个,少有多数排列成总状,伞房状或圆锥状花序;总状半球形或钟形,总苞片数层,薄质或草质,边缘和顶端干膜质,具1红褐色中脉,狭长(通常宽0.45-0.6毫米,少有达1.6毫米),近等长,有时外层较短而稍呈覆瓦状,超出或短于花盘;花托平或稍凸起,具窝孔;雌雄同株;花多数,异色;雌花多层,舌状,或内层无舌片,舌片狭小(通常长不超过或稍超过10毫米,宽不超过1毫米),少有稍宽大,紫色,蓝色或白色,少有黄色,多数(通常100个以上),有时较小数;两性花管状,檐部狭,管状至漏斗状(径不超过1毫米),上部具5裂片,花药线状长圆形,基部钝,顶端具卵状披针形附片;花柱分枝附片短(长0.15-0.25毫米),宽三角形,通常钝或稍尖。花全部结实;瘦果长圆状披针形,扁压,常有边脉,少有多脉,被疏或密短毛;冠毛通常2层,内层及外层同形或异形,常有极细而易脆折的刚毛,离生或基部稍连合,外层极短,或等长;有时雌花冠毛退化而成少数鳞片状膜片的小冠。
全属约有200种以上,主要分布于欧洲、亚洲大陆及北美洲,少数也分布于非洲和大洋洲。我国有35种,主要集中于新疆和西南部山区。共分两个亚属:飞蓬亚属 Subgen.Erigeron 及三型花亚属 Subgen. Trimorpha (Cass.) M. Pop.; 这两个亚属又各分2个组和一些亚组和系。
1. 飞蓬(东北植物检索表)
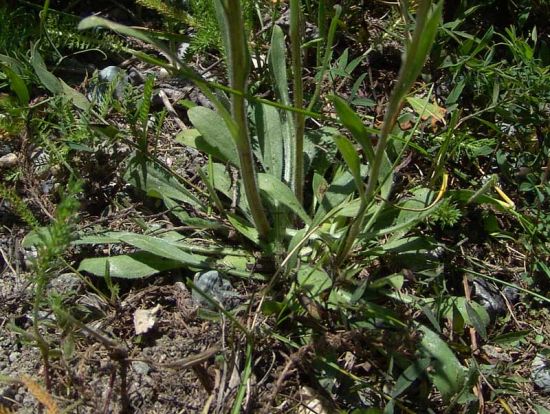
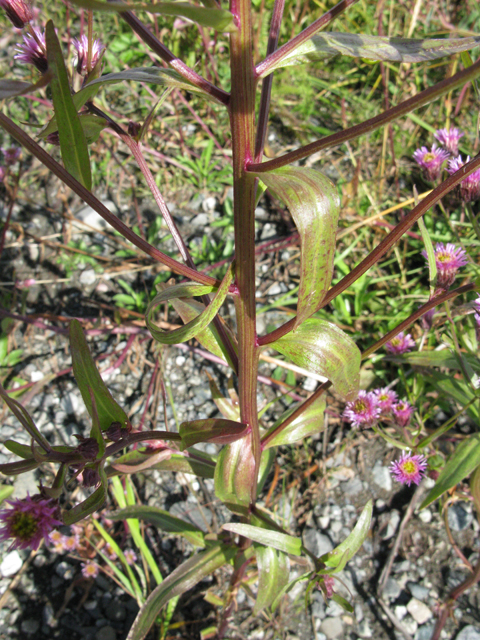
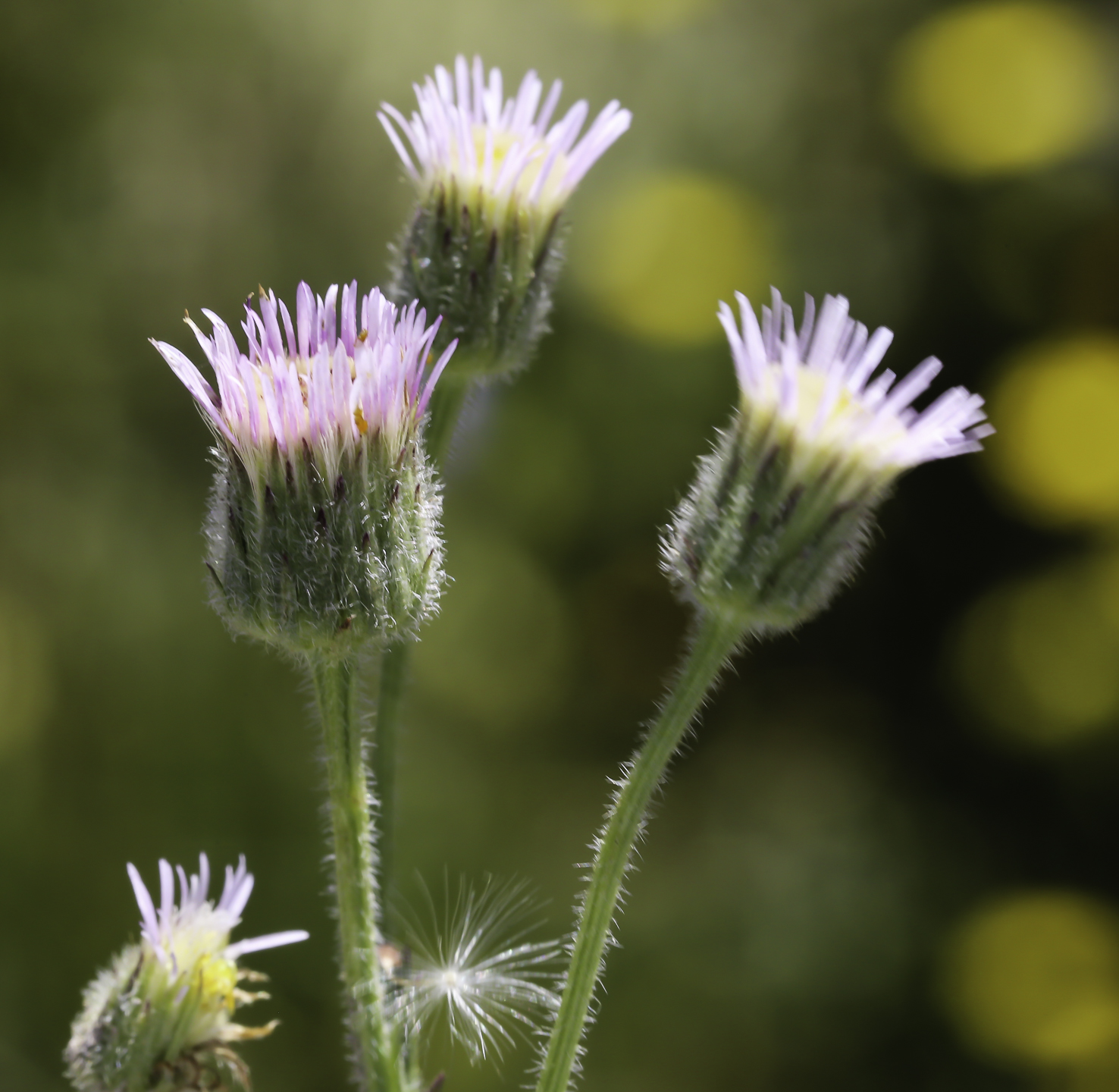
Erigeron acer L.
俗名:狼尾巴棵
二年生草本。茎单生,稀数个,高5-60厘米,基部径1-4毫米,直立,上部或少有下部有分枝,绿色或有时紫色,具明显的条纹,被较密而开展的硬长毛,杂有疏贴短毛,在头状花序下部常被具柄腺毛,或有时近无毛,节间长0.5-2.5厘米;基部叶较密集,花期常生存,倒披针形,长1.5-10厘米,宽0.3-1.2厘米,顶端钝或尖,基部渐狭成长柄,全缘或极少具1至数个小尖齿,具不明显的3脉,中部和上部叶披针形,无柄,长0.5-8厘米,宽0.1-0.8厘米,顶端急尖,最上部和枝上的叶极小,线形,具1脉,全部叶两面被较密或疏开展的硬长毛;头状花序多数,在茎枝端排列成密而窄或少有疏而宽的圆锥花序,或有时头状花序较少数,伞房状排列,长6-10毫米,宽11-21毫米;总苞半球形,总苞片3层,线状披针形,绿色或稀紫色,顶端尖,背面被密或较密的开展的长硬毛,杂有具柄的腺毛,内层常短于花盘,长5-7毫米,宽0.5-0.8毫米,边缘膜质,外层几短于内层的二分之一;雌花外层的舌状,长5-7毫米,管部长2.5-3.5毫米,舌片淡红紫色,少有白色,宽约0.25毫米,较内层的细管状,无色,长3-3.5毫米,花柱与舌片同色,伸出管部1-1.5毫米;中央的两性花管状,黄色,长4-5毫米,管部长1.5-2毫米,上部被疏贴微毛,檐部圆柱形,裂片无毛;瘦果长圆披针形,长约1.8毫米,宽0.4毫米,扁压,被疏贴短毛;冠毛2层,白色,刚毛状,外层极短,内层长5-6毫米。花期7-9月。
产于新疆、内蒙古、吉林、辽宁、河北、山西、陕西、甘肃、宁夏、青海、四川和西藏等省区。苏联高加索、中亚、西伯利亚地区以及蒙古、日本、北美洲也有分布。常生于山坡草地,牧场及林缘,海拔1400-3500米。
此种在我国分布极广,体态及毛茸多变异。据前人记载本种常与其邻种长茎飞蓬 E. elongatus Ledeb., 堪察加飞蓬 E. kamtschaticus DC. 杂交,但它的头状花序较小而多数,常排列成密集的狭圆锥花序;总苞被开展的密长毛,基部叶全缘,与后两种不难区别。
Erigeron acer槭属植物,秋槭 is a widespread herbaceous flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. Common names include bitter fleabane and blue fleabane. The species is native to Canada, colder parts of the United States, northern, central, and southeastern Asia, and most of Europe.
An annual or perennial herb of open, well-drained, skeletal骨骼的,骸骨的 neutral中立的; 中性的 or calcareous soils, often on warm, S.-facing slopes. Habitats include sand dunes, sand-pits, spoil and waste heaps from quarries, railway ballast, industrial waste and cinders. It also grows on rock outcrops, especially of chalk and limestone and on mortared砂浆砌合的 walls. 0-430 m (Banffs.).










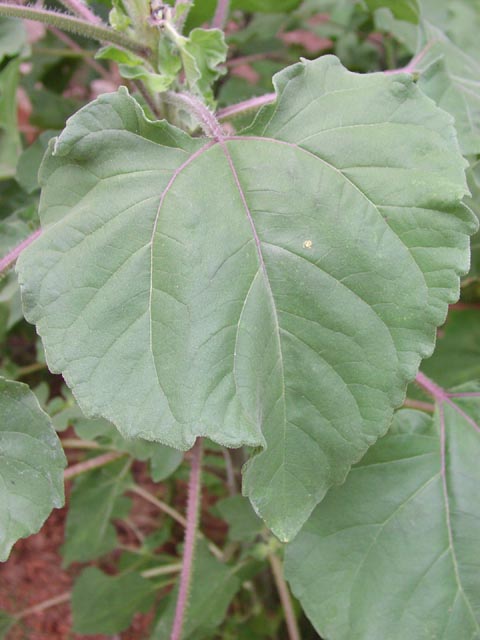
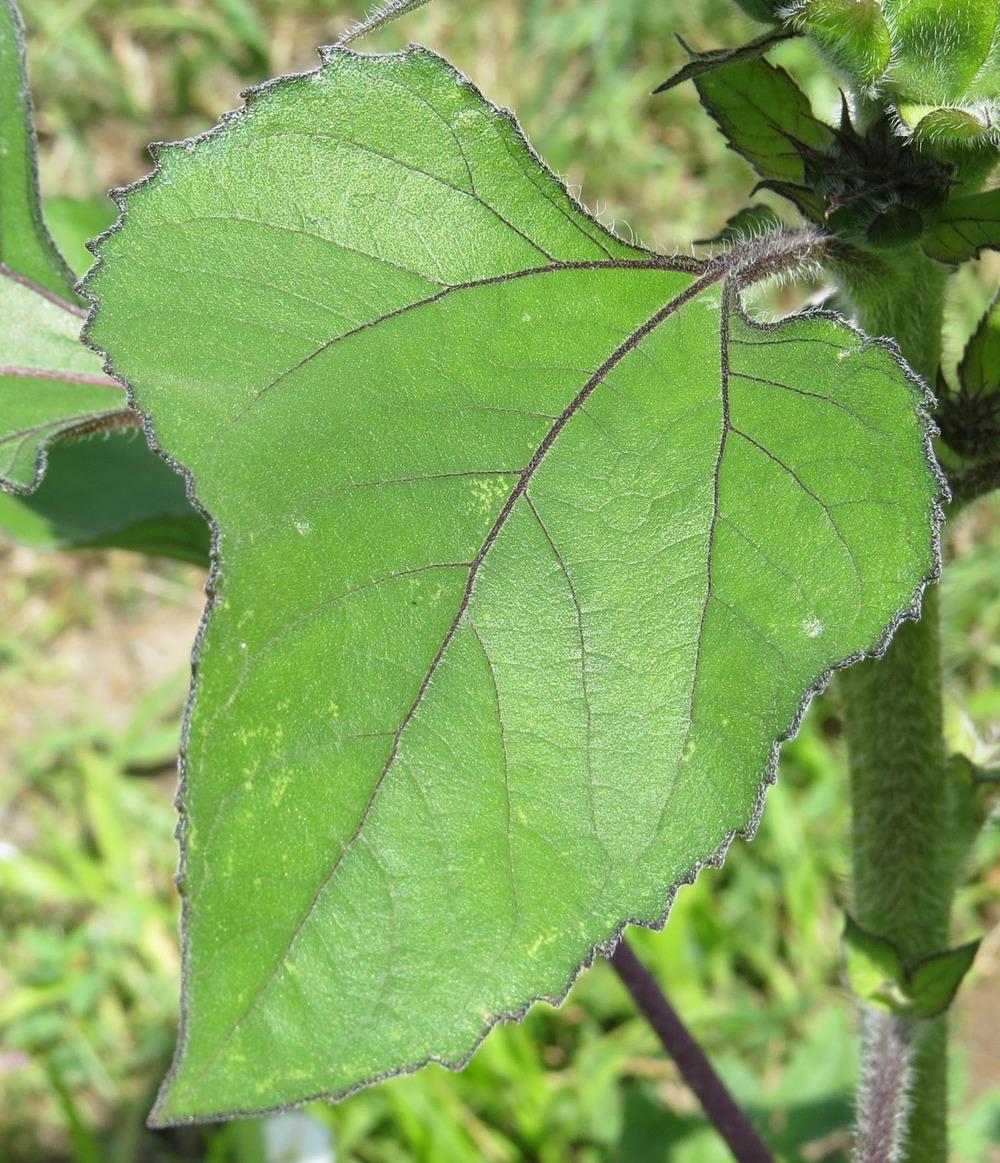
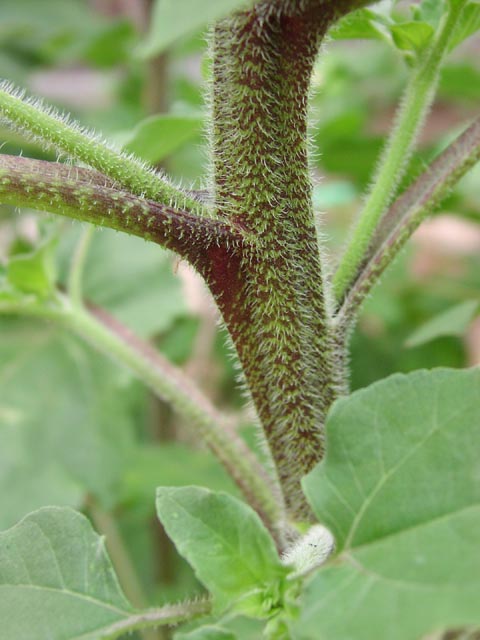
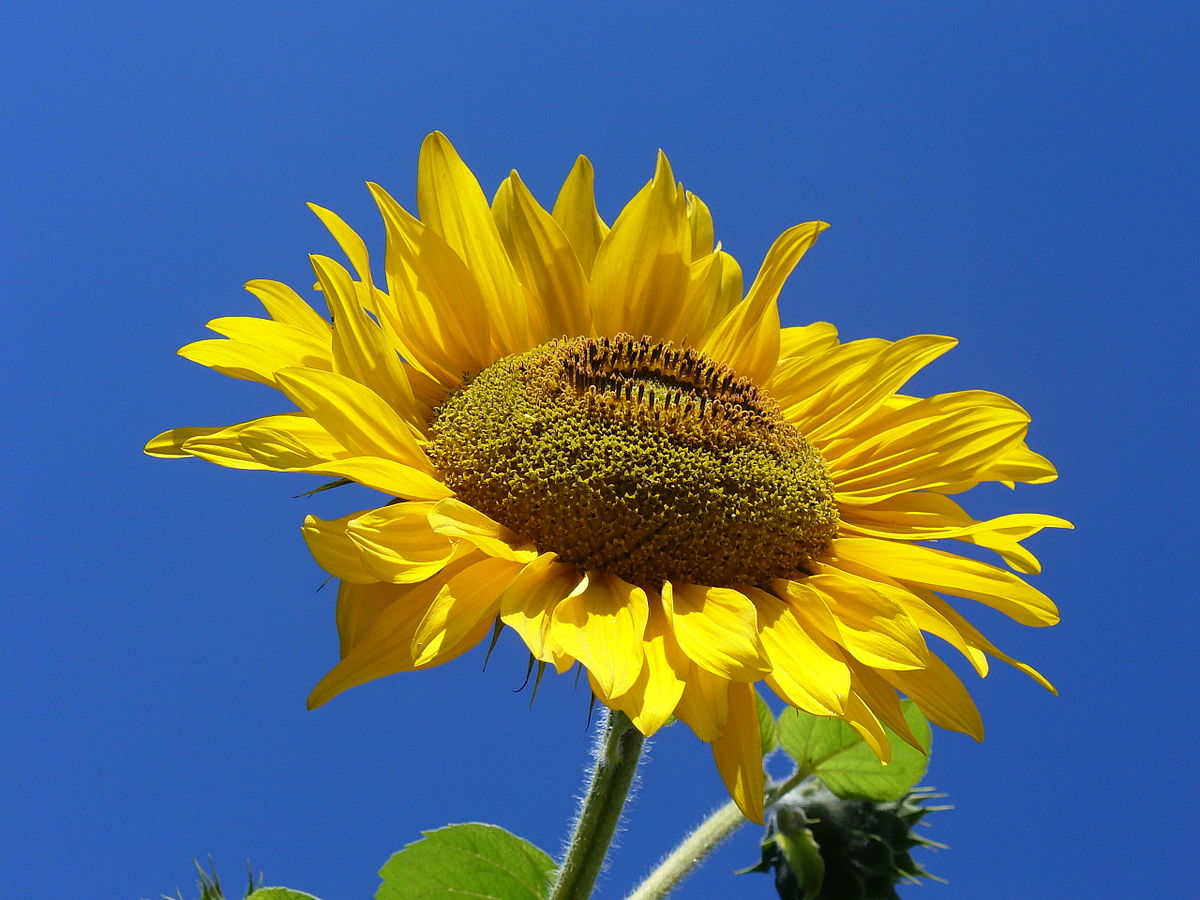
九、向日葵属——Helianthus L.
一年或多年生草本,通常高大,被短糙毛或白色硬毛。叶对生,或上部或全部互生,有柄,常有离基三出脉。头状花序大或较大,单生或排列成伞房状,各有多数异形的小花,外围有一层无性的舌状花,中央有极多数结果实的两性花。总苞盘形或半球形;总苞片2至多层,膜质或叶质。花托平或稍凸起;托片折叠,包围两性花。舌状花的舌片开展,黄色;管状花的管部短,上部钟状,上端黄色、紫色或褐色,有5裂片。瘦果长圆形或倒卵圆形,稍扁或具4厚棱。冠毛膜片状,具2芒、有时附有2-4个较短的芒刺,脱落。
本属约有100种,主要分布于美洲北部,少数分布于南美洲的秘鲁、智利等地,其中一些种在世界各地栽培很广。
1. 向日葵 丈菊(植物名实图考)
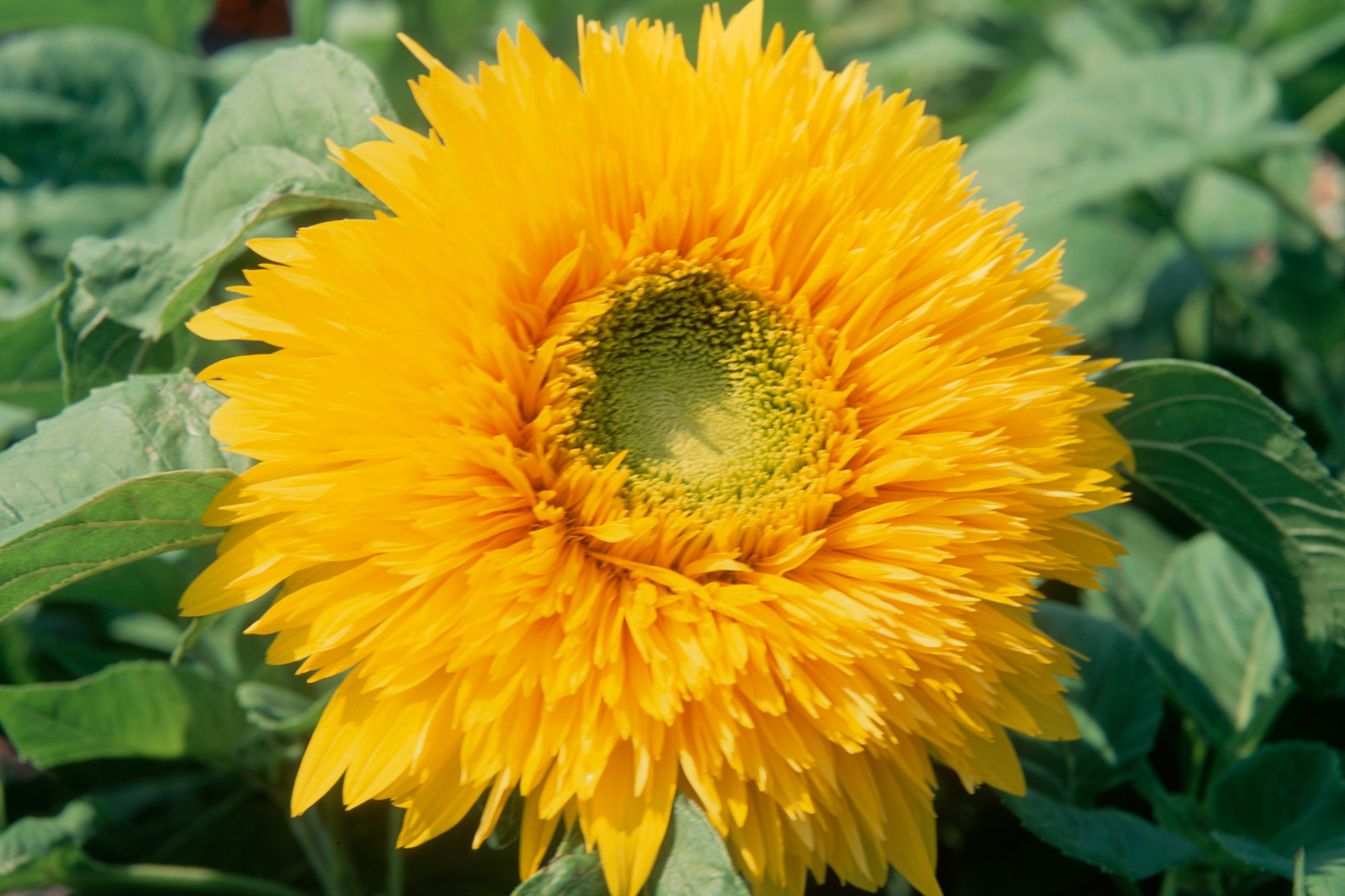
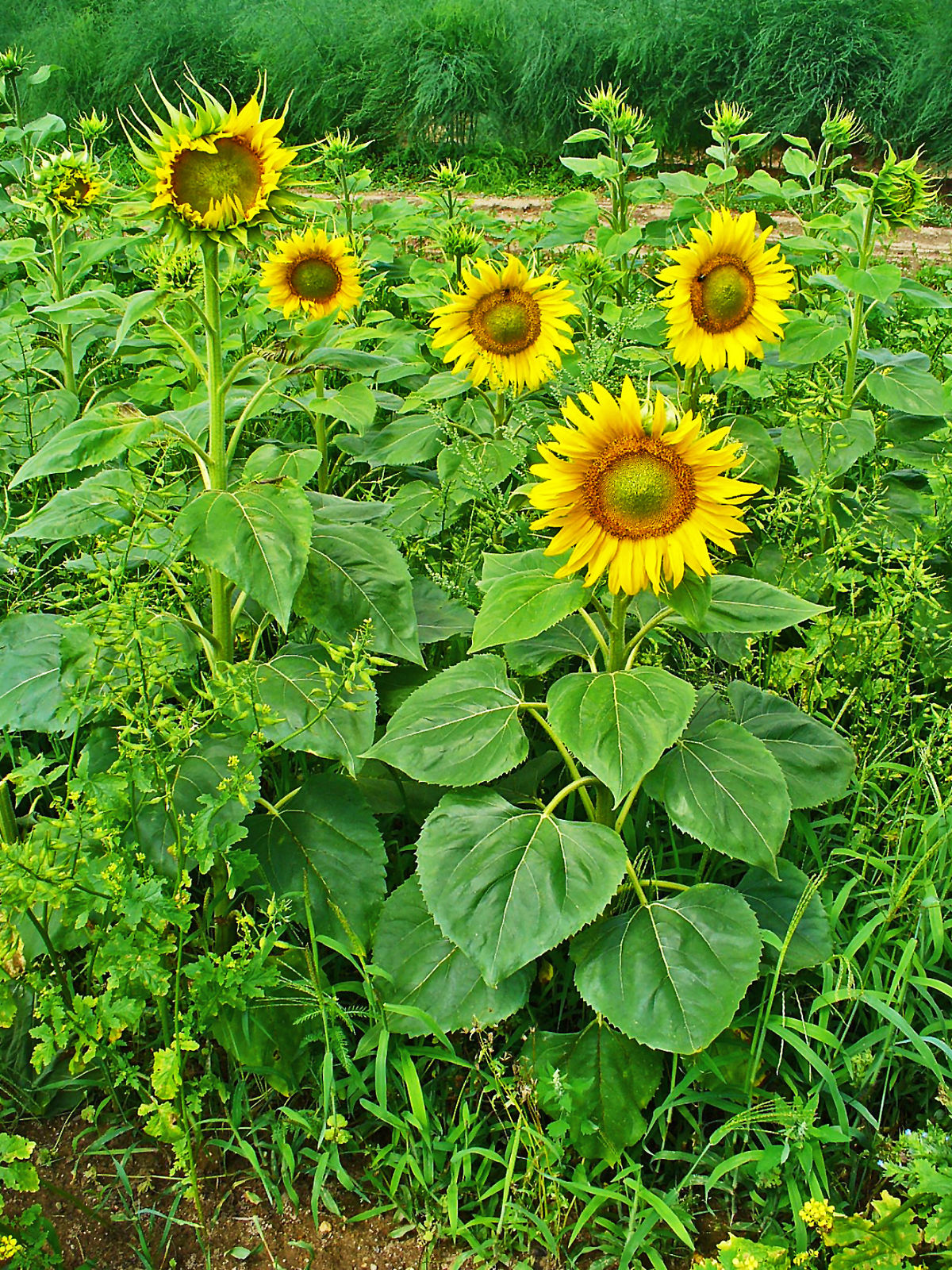
Helianthus annuus L.
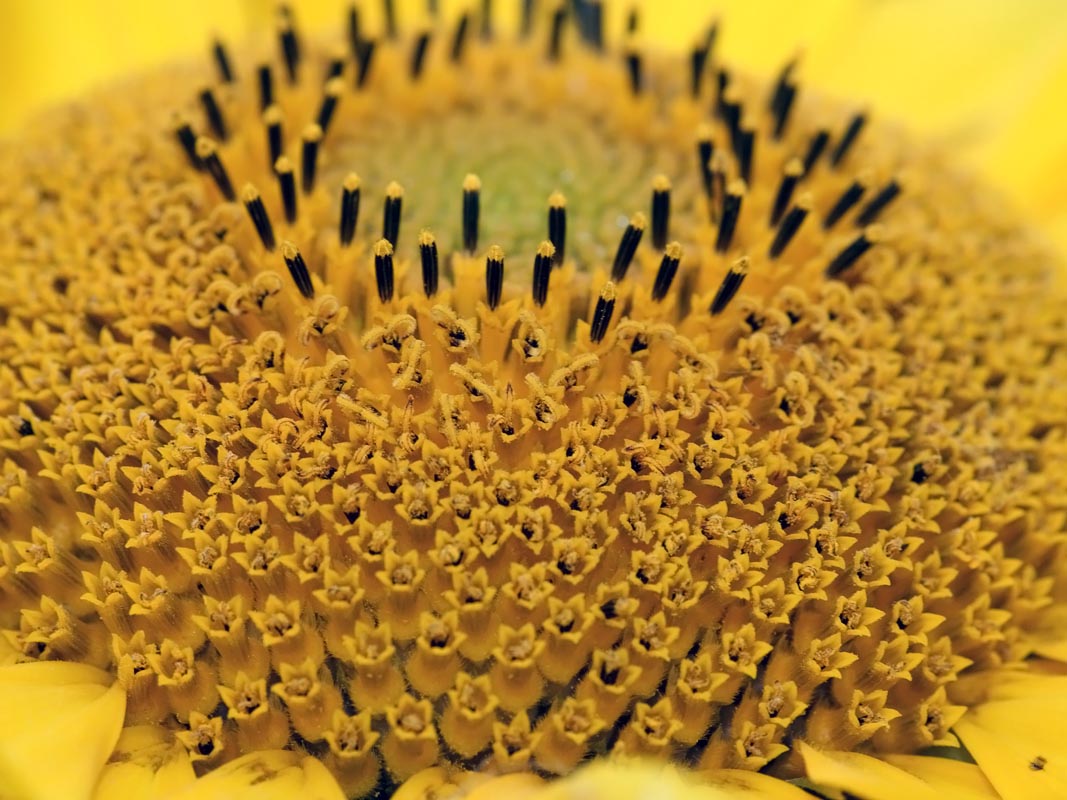
一年生高大草本。茎直立,高1-3米,粗壮,被白色粗硬毛,不分枝或有时上部分枝。叶互生,心状卵圆形或卵圆形,顶端急尖或渐尖,有三基出脉,边缘有粗锯齿,两面被短糙毛,有长柄。头状花序极大,径约10-30厘米,单生于茎端或枝端,常下倾。总苞片多层,叶质,覆瓦状排列,卵形至卵状披针形,顶端尾状渐尖,被长硬毛或纤毛。花托平或稍凸、有半膜质托片。舌状花多数,黄色、舌片开展,长圆状卵形或长圆形,不结实。管状花极多数,棕色或紫色,有披针形裂片,结果实。瘦果倒卵形或卵状长圆形,稍扁压,长10-15毫米,有细肋,常被白色短柔毛,上端有2个膜片状早落的冠毛。花期7-9月,果期8-9月。
原产北美,世界各国均有栽培,通过人工培育,在不同生境上形成许多品种,特别在头状花序的大小色泽及瘦果形态上有许多变异,并为综合利用的最好原料。
种子含油量很高,为半干性油,味香可口,供食用。花穗、种子皮壳及茎秆可作饲料及工业原料,如制人造丝及纸浆等,花穗也供药用。
Helianthus annuus, the common sunflower, is an annual species of sunflower grown as a crop for its edible oil and edible fruits. This species of sunflower is also used as bird food, as livestock forage, and in some industrial applications. The plant was first domesticated in the Americas. Wild Helianthus annuus is a widely branched annual plant with many flower heads. The domestic sunflower, however, possesses a single large inflorescence atop an unbranched stem. The name sunflower may derive from the flower's head's shape, which resembles the sun, or from the false impression that the blooming plant appears to slowly turn its flower towards the sun as the latter moves across the sky on a daily basis. Sunflower seeds were brought to Europe from the Americas in the 16th century, where, along with sunflower oil, they became a widespread cooking ingredient.
Helianthus annuus
Common Name(s): Common Sunflower、Sunflower、Wild Sunflower
Description
Common Sunflower is and annual in the Asteraceae (daisy) family. It ommonly seen growing along roads, fences, fields, and in waste areas west of the Mississippi River and is the state flower of Kansas. Hybridization has produced many cultivars, expanding the range of flowers from the common yellow to red, mahogany, bronze, white and bi-colors.
This plant is grown commercially as food for birds, livestock and humans. Steamed buds have an artichoke flavor.
Uses (Ethnobotany):
Indians ground the seeds into flour and baked into cakes. They applied a poultice of crushed plants to snakebites and also used an infusion of the flowers for chest pains or pulmonary problems.









十、旋覆花属——Inula L.
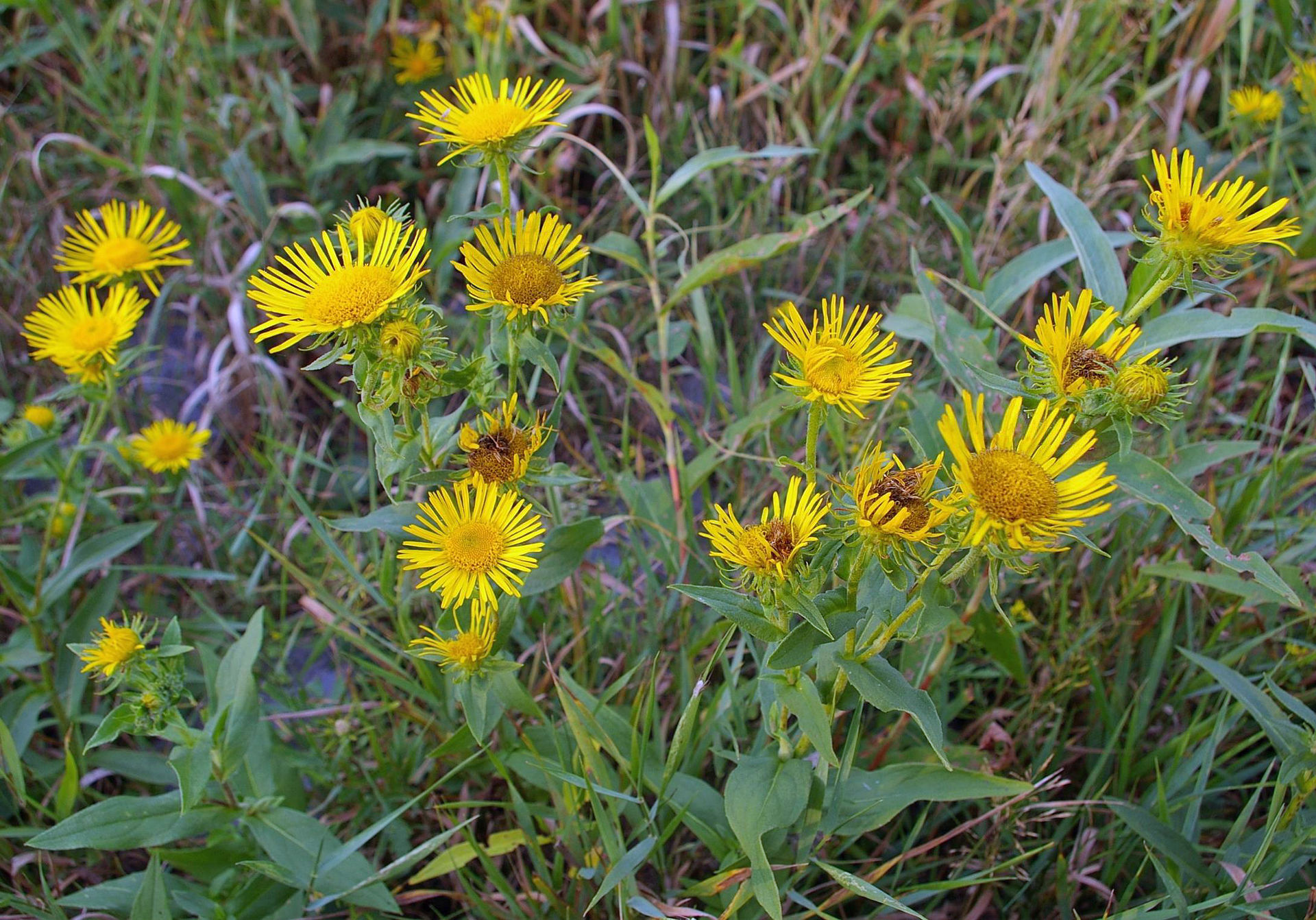
多年生稀一或二年生草本,有直立的茎或无茎,或亚灌木,常有腺,被糙毛、柔毛或茸毛。叶互生或仅生于茎基部,全缘或有齿。头状花序大或稍小,多数,伞房状或圆锥伞房状排列,或单生,或密集于根颈上,各有多数异形稀同形的小花,雌雄同株,外缘有1至数层雌花,稀无雌花;中央有多数两性花。总苞半球状、倒卵圆状或宽钟状;总苞片多层,覆瓦状排列,内层常狭窄,干膜质;外层叶质,革质或干膜质,狭窄或宽阔,渐短或与内层同长;最外层有时较长大,叶质。花托平或稍凸起,有蜂窝状孔或浅窝孔,无托片。雌花花冠舌状,黄色稀白色;舌片长,开展,顶端有3齿,或短小直立而有2-3齿;两性花花冠管状,黄色,上部狭漏斗状,有5个裂片。花药上端圆形或稍尖,基部戟形,有细长渐尖的尾部。花柱分枝稍扁,雌花花柱顶端近圆形,两性花花柱顶端较宽,钝或截形。冠毛1-2层稀较多层,有多数或较少的稍不等长而微糙的细毛。瘦果近圆柱形,有4-5个多少显明的稜或更多的纵肋或细沟,无毛或有短毛或绢毛。
约100种,分布于欧洲、非洲及亚洲,以地中海地区为主。我国有20余种和多数变种,其中一部分是广布种;我国的特有种集中于西部和西南部。
本属有多种植物常供药用。
1. 旋覆花(本经)金佛花,金佛草(江浙),六月菊(河北)
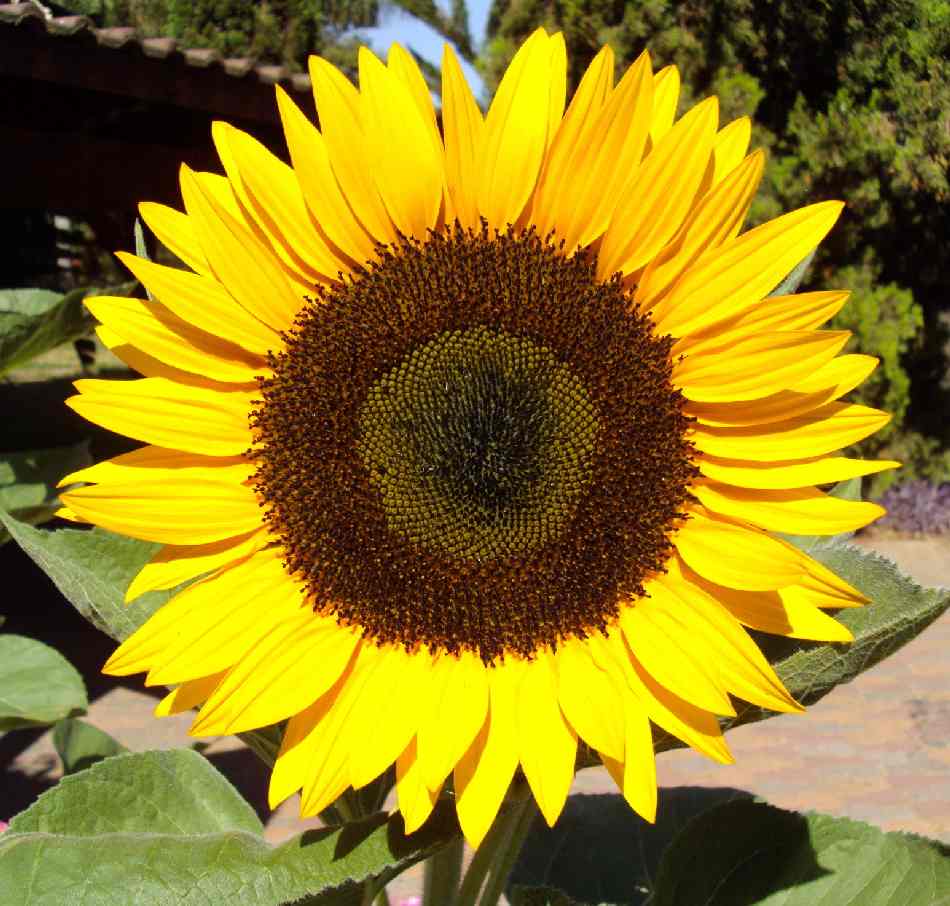
Inula japonica Thunb.
俗名:猫耳朵、六月菊、金佛草、金佛花、金钱花、金沸草、小旋覆花、条叶旋覆花、旋复花多年生草本。根状茎短,横走或斜升,有多少粗壮的须根。茎单生,有时2-3个簇生,直立,高30-70厘米,有时基部具不定根,基部径3-10毫米,有细沟,被长伏毛,或下部有时脱毛,上部有上升或开展的分枝,全部有叶;节间长2-4厘米。基部叶常较小,在花期枯萎;中部叶长圆形,长圆状披针形或披针形,长4-13厘米,宽1.5-3.5稀4厘米,基部多少狭窄,常有圆形半抱茎的小耳,无柄,顶端稍尖或渐尖,边缘有小尖头状疏齿或全缘,上面有疏毛或近无毛,下面有疏伏毛和腺点;中脉和侧脉有较密的长毛;上部叶渐狭小,线状披针形。头状花序径3-4厘米,多数或少数排列成疏散的伞房花序;花序梗细长。总苞半球形,径13-17毫米,长7-8毫米;总苞片约6层,线状披针形,近等长,但最外层常叶质而较长;外层基部革质,上部叶质,背面有伏毛或近无毛,有缘毛;内层除绿色中脉外干膜质,渐尖,有腺点和缘毛。舌状花黄色,较总苞长2-2.5倍;舌片线形,长10-13毫米;管状花花冠长约5毫米,有三角披针形裂片;冠毛1层,白色有20余个微糙毛,与管状花近等长。瘦果长1-1.2毫米,圆柱形,有10条沟,顶端截形,被疏短毛。花期6-10月,果期9-11月。
广产于我国北部、东北部、中部、东部各省,极常见,在四川、贵州、福建、广东也可见到。生于山坡路旁、湿润草地、河岸和田埂上,海拔150-2400米。在蒙古、朝鲜、苏联西伯利亚、日本都有分布。
Characteristics of Inula Japonica
Inula Japonica is a perennial herb with short rhizomes根茎,根状茎, transverse or obliquely斜; 倾斜 ascending and many stout强壮的; 结实的 fibrous roots. Stems are solitary, sometimes 2-3 fascicled, erect, 30 -- 70 cm high, sometimes with adventitious roots at base, 3 -- 10 mm in diameter at base, rill, covered with long hairs, or sometimes depilated below, with ascending or spreading branches distally, all with leaves; The internodes of Inula japonica are 2-4 cm long.
Leaves of Inula Japonica are alternate, elliptic, elliptic lanceolate or narrow long elliptic. Inflorescence head few or many, terminal, was a corymbiform arrangement. Achene is long elliptic, white bristles, white crested hairs.
Basal leaves of Inula Japonica are often smaller, wilted at anthesis; Middle leaves are oblong, oblong-lanceolate or lanceolate, 4-13 cm long, 1.5-3.5 thin 4 cm wide, the base of the number of narrow, often circular semicirculate auricle, sessile, tip slightly pointed or acuminate, the edge of a small pointy head sparsely dentate or the entire margin, above a sparsely hairy or nearly glabrous, below a sparsely overbearing hair and glandular points; Dense long hairs in midvein and lateral veins; Upper leaf of Inula Japonica is tapering, linear-lanceolate.Inflorescences 3-4 cm in diameter, many or few arranged into dispersed corymbs;Peduncle slender.
Involucre of Inula Japonica is hemispherical, 13 -- 17 mm in diameter, 7 -- 8 mm in length; Involucral bracts are ca. 6 layers, linear-lanceolate, subequal, but outermost often leafy and longer; Outer base is leathery, upper leaf leathery, abaxially overlying hairy or subglabrous, ciliate; The inner layer except the green midvein is dry membranous, acuminate, glandular and ciliate. Ligulate flowers of Inula Japonica are yellow, 2-2.5 times longer than the involucre; Tongue linear, 10-13 mm long; Corolla tubular ca. is 5 mm, with triangular lanceolate lobes; Crest 1 layer, white with more than 20 viscose, nearly as long as the tubular flowers. Achene of Inula Japonica is 1-1.2 mm long, cylindrical, with 10 furrows, apex truncate, sparsely short hairy.
Inula Japonica Leaf
Stem of Inula Japonica is longitudinally ribbed, green or slightly purplish red. Leaves are alternate, elliptic, elliptic lanceolate or narrowly long elliptic, 6 ~ 10 cm long, 1 ~ 2.5 cm wide, apex acute, slightly narrow at base, sometimes small ears, semi-branched stem, whole or serrate, green above, sparsely pellucid, light green below, densely pellucid.
Inula Japonica Flowers
Inflorescences have few or many, terminal, corymbiform arrangement, 3 -- 4 cm in diameter; Inflorescence pedicels of Inula Japonica are white-hairy: bracts usually 1-lanceolate near inflorescence, pilose; Involucral bracts are semicircular, 8 -- 10 mm long, 1 -- 1.8 cm in diameter, involucral bracts several layers, outer lanceolate, inner linear-lanceolate or linear, dry membranous, outer hairy or ciliate only; Receptacle is slightly convex; Flowers liguulate 1 layer, yellow, female, corolla apex 3-lobed, base slightly joined on both sides tubular, pistil 1, ovary inferior, angulate, white short bristles, style linear, stigma 2-lobed; Tubular flowers of Inula Japonica are bisexual, at center of inflorescence.
Corolla apex is 5-dentate, lobes ovate-triangular, stamens 5, polymycete, filaments separated and short, pistil 1, style linear, stigma 2-lobed. Achene of Inula Japonica is long elliptic, white bristles, white crested hairs. Inula Japonica was born on hillsides, roads, fields or wetlands near water.
Habits of Inula Japonica
Inula Japonica likes sunlight, has developed roots, and is resistant to diseases and insects, and is resistant to cold, drought and poor soil.
Inula Japonica is born on hillsides, wet grasslands, river banks and ridges at an altitude of 150-2400 m.
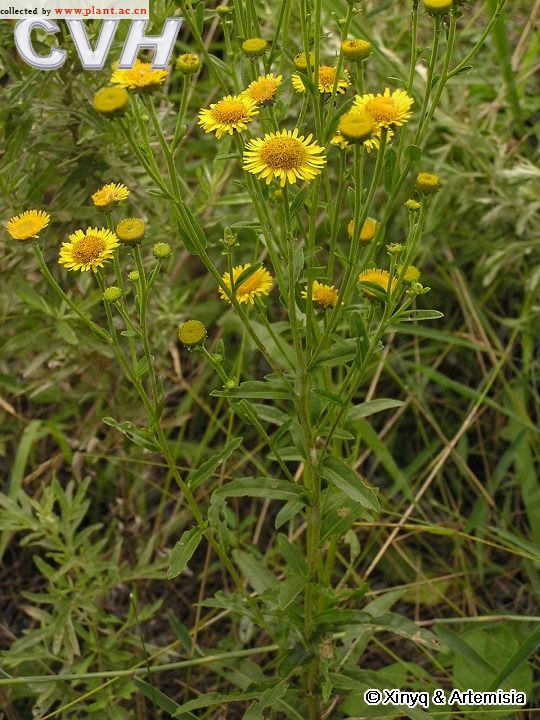
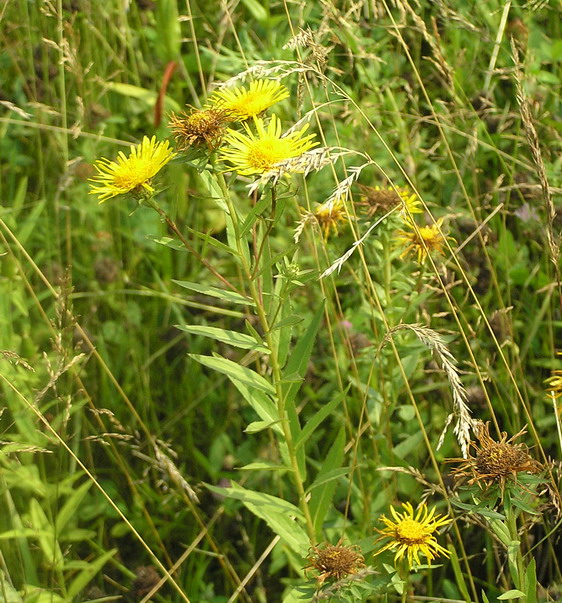
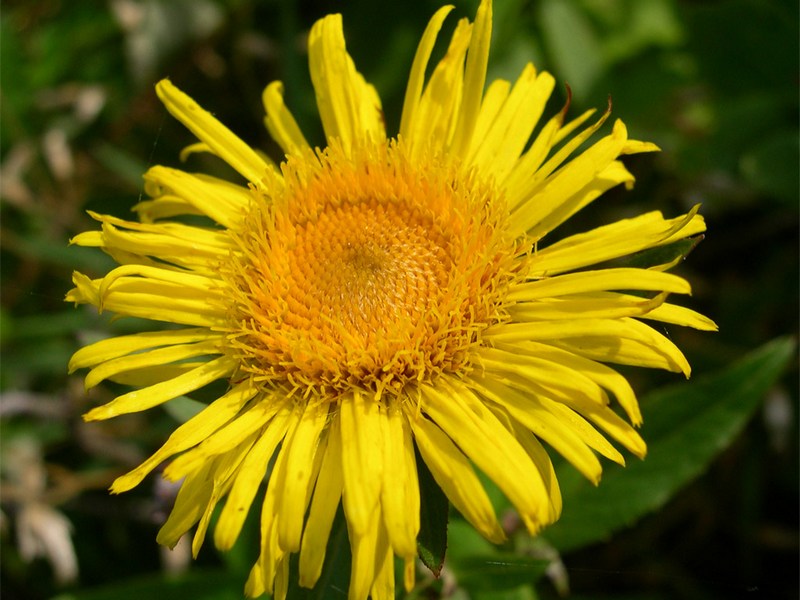
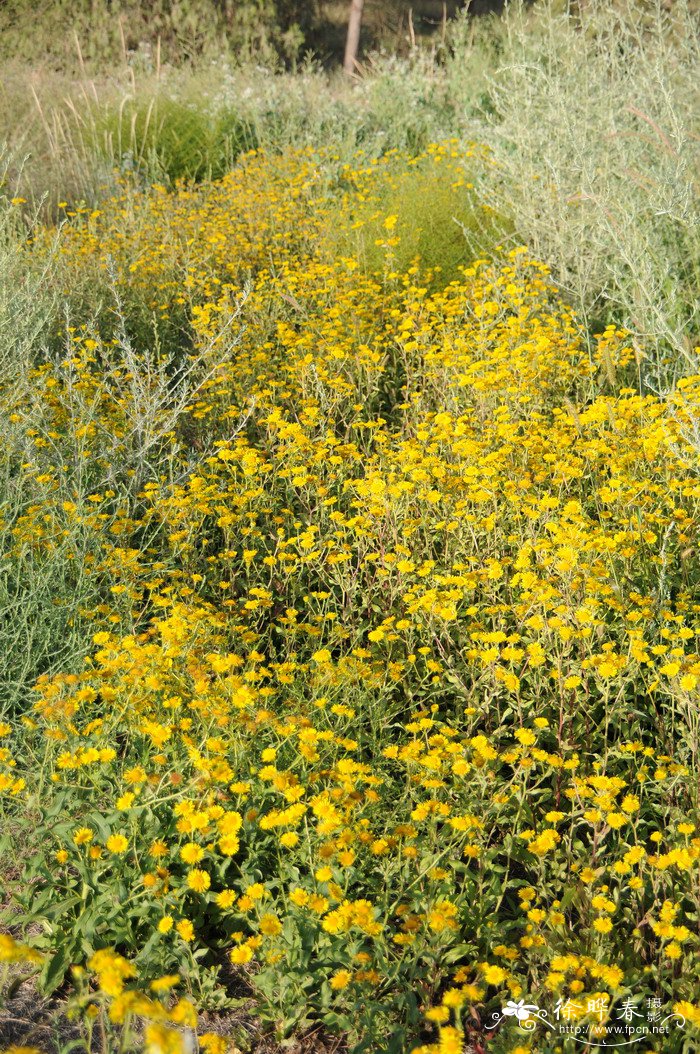
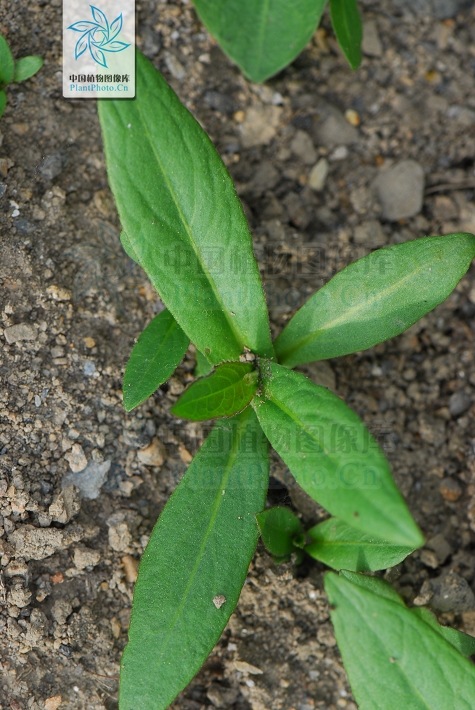









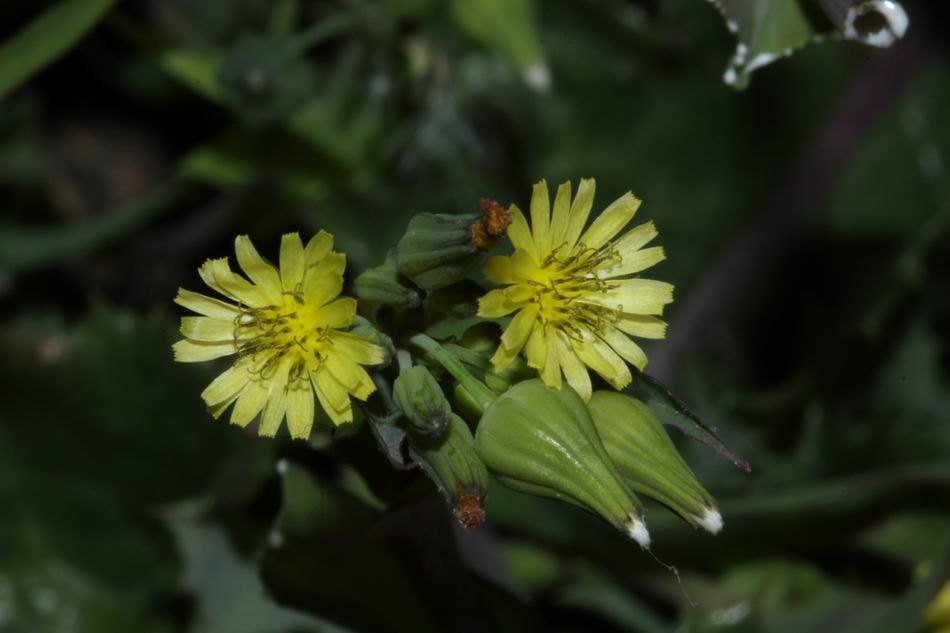
十一、苦荬菜属Ixeris Cass.
一年生或多年生草本。基生叶花期生存。头状花序同型,舌状,含多数舌状小花(10-26枚) ,多数或少数在茎枝顶端排成伞房状花序。总苞花期圆柱状或钟状,果期有时卵球形;总苞片2-3层,外层最短,内层最长。花托平,无托毛。舌状小花黄色,舌片顶端5齿裂。花柱分枝细,花药基部附属物箭头形。瘦果压扁,褐色,纺锤形或椭圆形,无毛,有10条尖翅肋,顶端渐尖成细喙,喙长或短,细丝状,异色。冠毛白色,2层,纤细,不等长,微粗糙,宿存或脱落。
本属约20种,分布东亚和南亚。我国有4种。
Ixeris is a genus of Asian flowering plants in the dandelion family. Concepts of which species should be included in the genus have changed in recent years because of the use of molecular investigations. Numerous species formerly regarded as members of Ixeris have been moved to other genera;. Species remaining in Ixeris or of uncertain affiliations are listed below.
1. 苦荬菜 多头莴苣(广州植物志),多头苦荬菜
Ixeris polycephala Cass.
一年生草本。根垂直直伸,生多数须根。茎直立,高10-80厘米,基部直径2-4毫米,上部伞房花序状分枝,或自基部多分枝或少分枝,分枝弯曲斜升,全部茎枝无毛。基生叶花期生存,线形或线状披针形,包括叶柄长7-12厘米,宽5-8毫米,顶端急尖,基部渐狭成长或短柄;中下部茎叶披针形或线形,长5-15厘米,宽1.5-2厘米,顶端急尖,基部箭头状半抱茎,向上或最上部的叶渐小,与中下部茎叶同形,基部箭头状半抱茎或长椭圆形,基部收窄,但不成箭头状半抱茎;全部叶两面无毛,边缘全缘,极少下部边缘有稀疏的小尖头。头状花序多数,在茎枝顶端排成伞房状花序,花序梗细。总苞圆柱状,长5-7毫米,果期扩大成卵球形;总苞片3层,外层及最外层极小,卵形,长0.5毫米,宽0.2毫米,顶端急尖,内层卵状披针形,长7毫米,宽2-3毫米,顶端急尖或钝,外面近顶端有鸡冠状突起或无鸡冠状突起。舌状小花黄色,极少白色,10-25枚。瘦果压扁,褐色,长椭圆形,长2.5毫米,宽0.8毫米,无毛,有10条高起的尖翅肋,顶端急尖成长1. 5毫米喙,喙细,细丝状。冠毛白色,白色,纤细,微糙,不等长,长达4毫米。花果期3-6月。
分布陕西(华阴、眉县、城固、勉县)、江苏(具体地点不详)、浙江(遂昌、丽水、昌化)、福建(永安)、安徽(各地)、台湾(台东、台北)、江西(南昌)、湖南(具体地点不详)、广东(连平)、广西(百色)、贵州(江口、望谟)、四川(南川)、云南(昆明、大理、丽江)。生于山坡林缘、灌丛、草地、田野路旁,海拔300-2 200米。中南半岛、尼泊尔、印度、锡金、克什米尔地区、孟加拉、日本广有分布。模式标本采自缅甸。
全草入药,具清热解毒、去腐化脓、止血生机功效;可治疗疮、无名肿毒、子宫出血等症。
Ixeris_polycephala is a BIENNIAL growing to 0.3 m (1ft). The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist or wet soil.
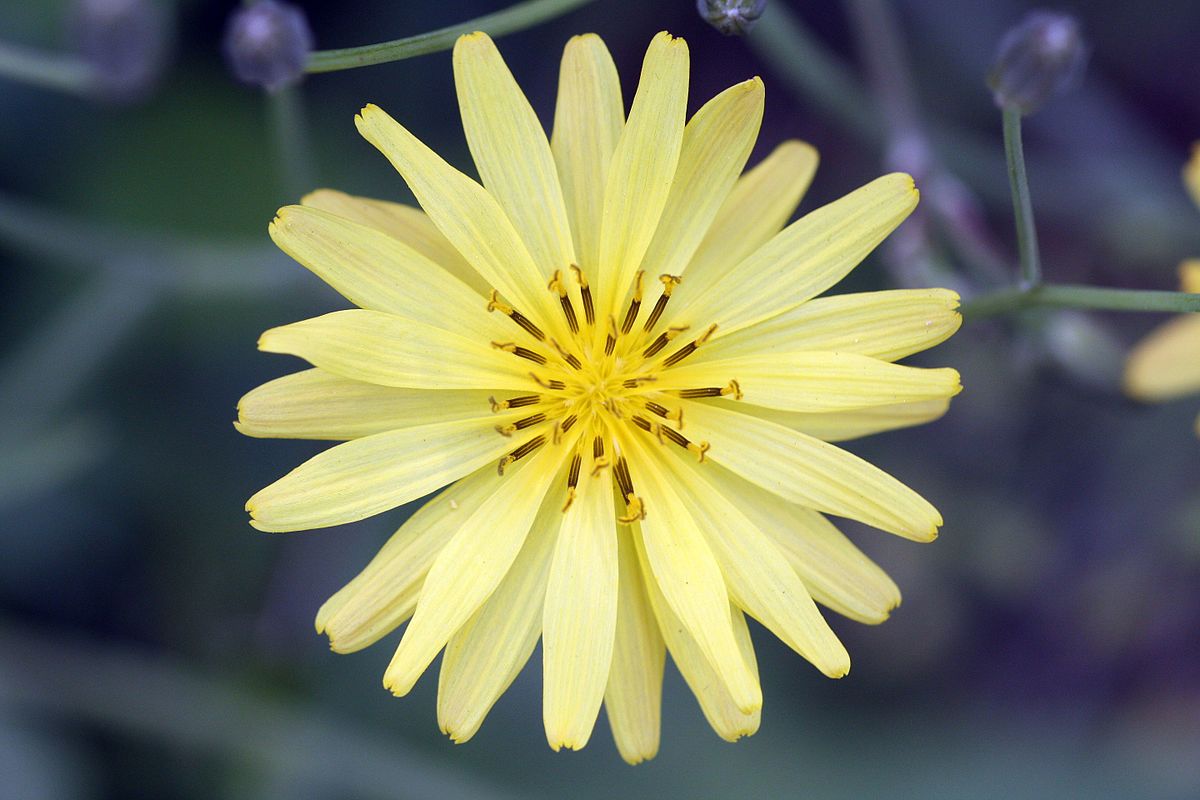
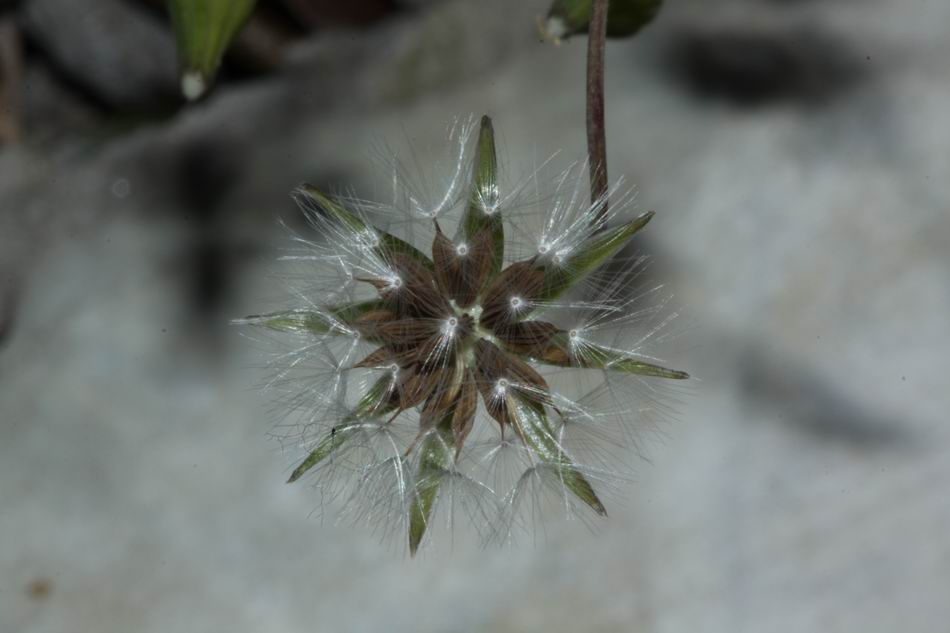
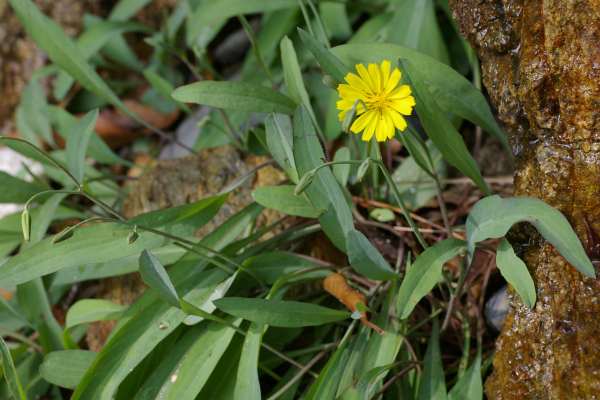
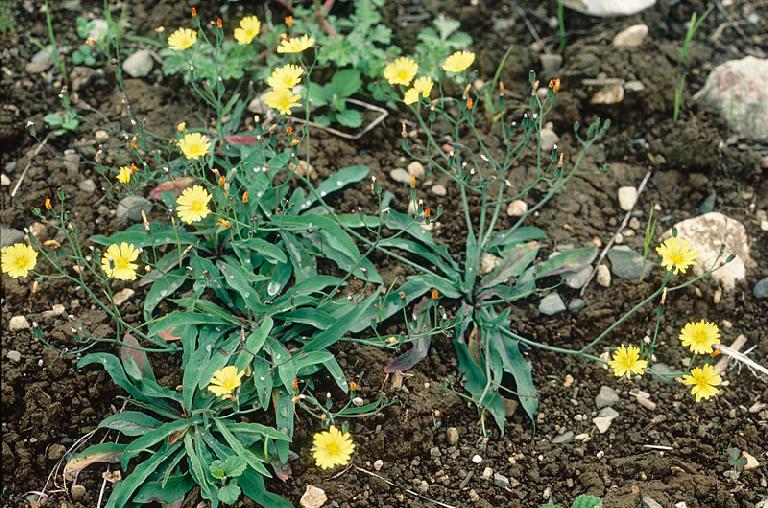
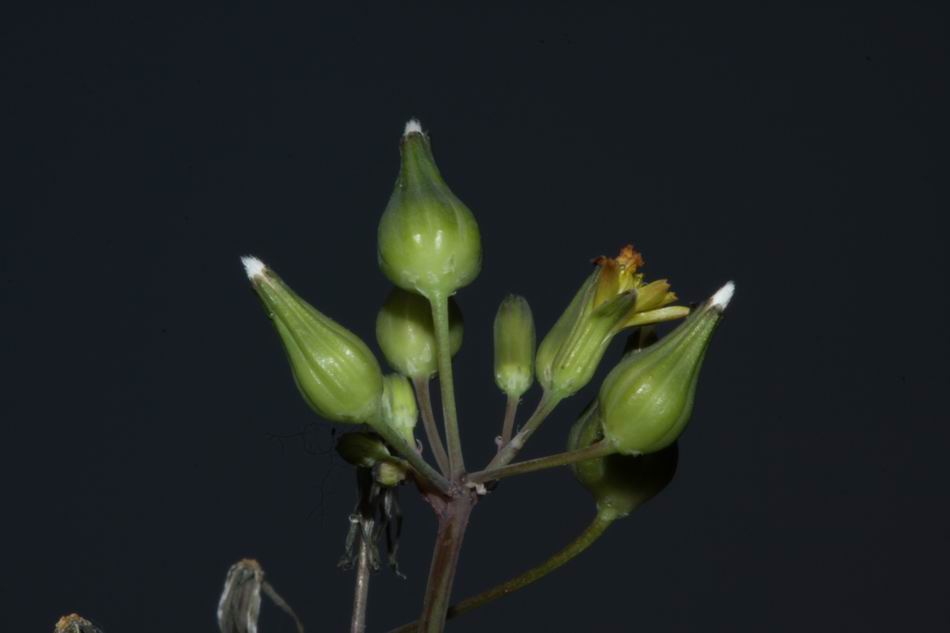
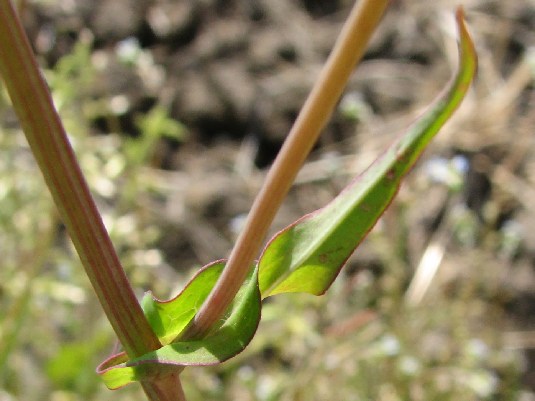









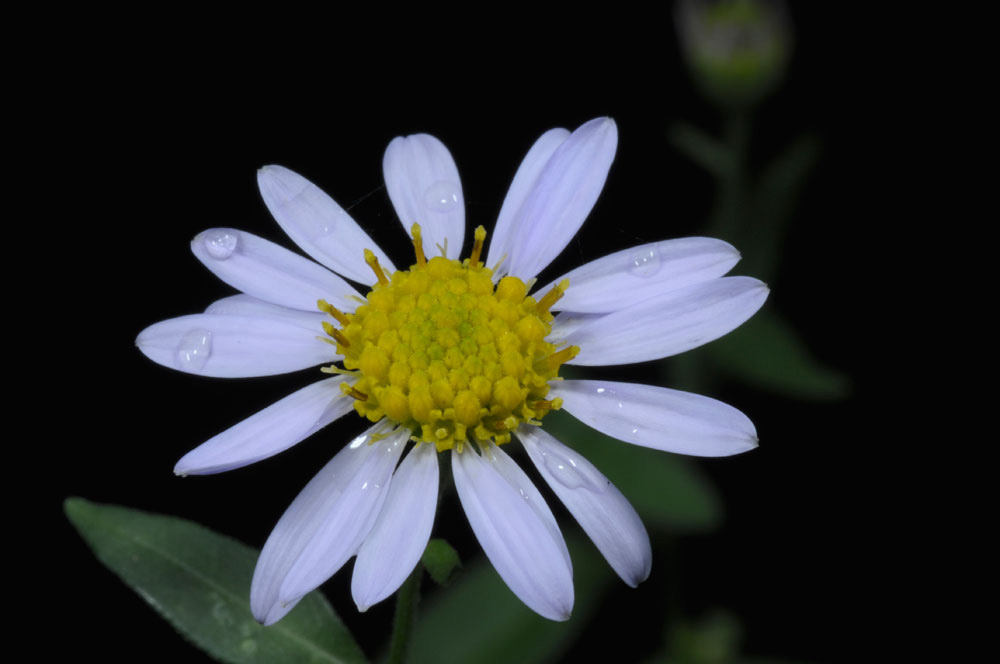
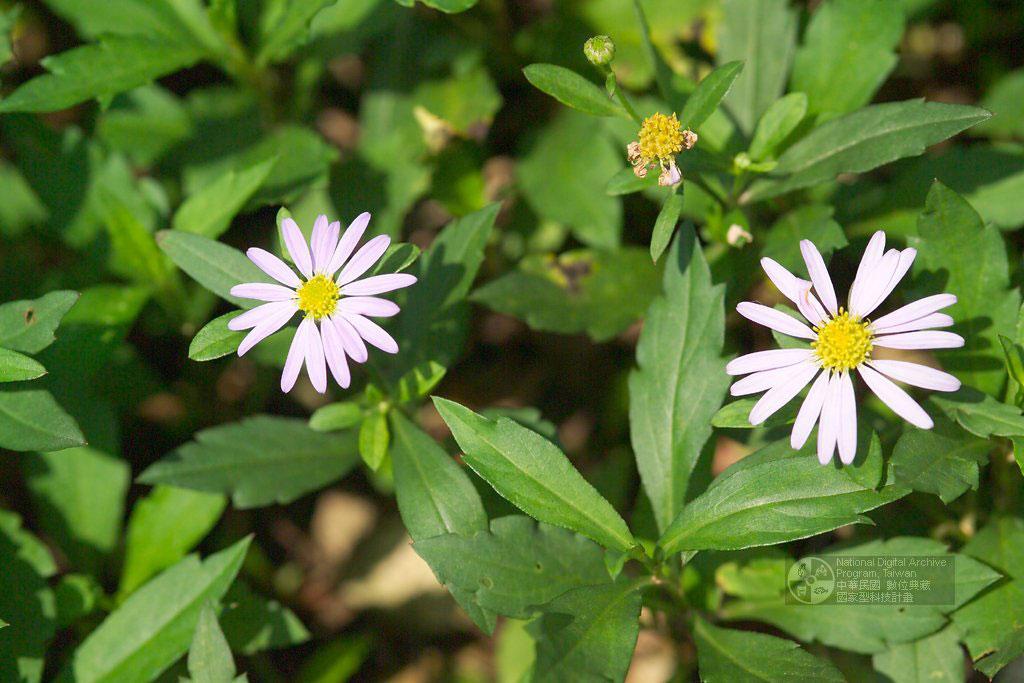
十二、马兰属——Kalimeris Cass.
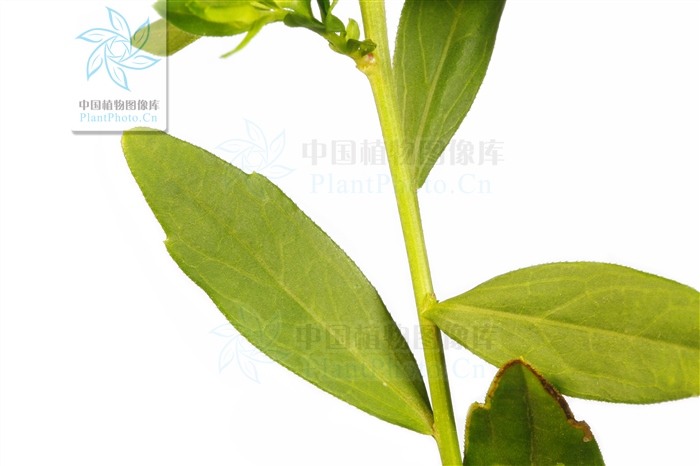
多年生草本。叶互生,全缘或有齿,或羽状分裂。头状花序较小,单生于枝端或疏散伞房状排列,辐射状,外围有1-2层雌花,中央有多数两性花,都结果实。总苞半球形;总苞片2-3层,近等长或外层较短而覆瓦状排列;草质或边缘膜质或革质;花托凸起或圆锥形,蜂窝状。雌花花冠舌状,舌片白色或紫色,顶端有微齿或全缘;两性花花冠钟状,有分裂片;花药基部钝,全缘;花柱分枝附片三角形或披针形。冠毛极短或膜片状,分离或基部结合成杯状。瘦果稍扁,倒卵圆形,边缘有肋,两面无肋或一面有肋,无毛或被疏毛。
约20种,分布于亚洲南部及东部,喜马拉雅地区及西伯利亚东部。我国有7种。
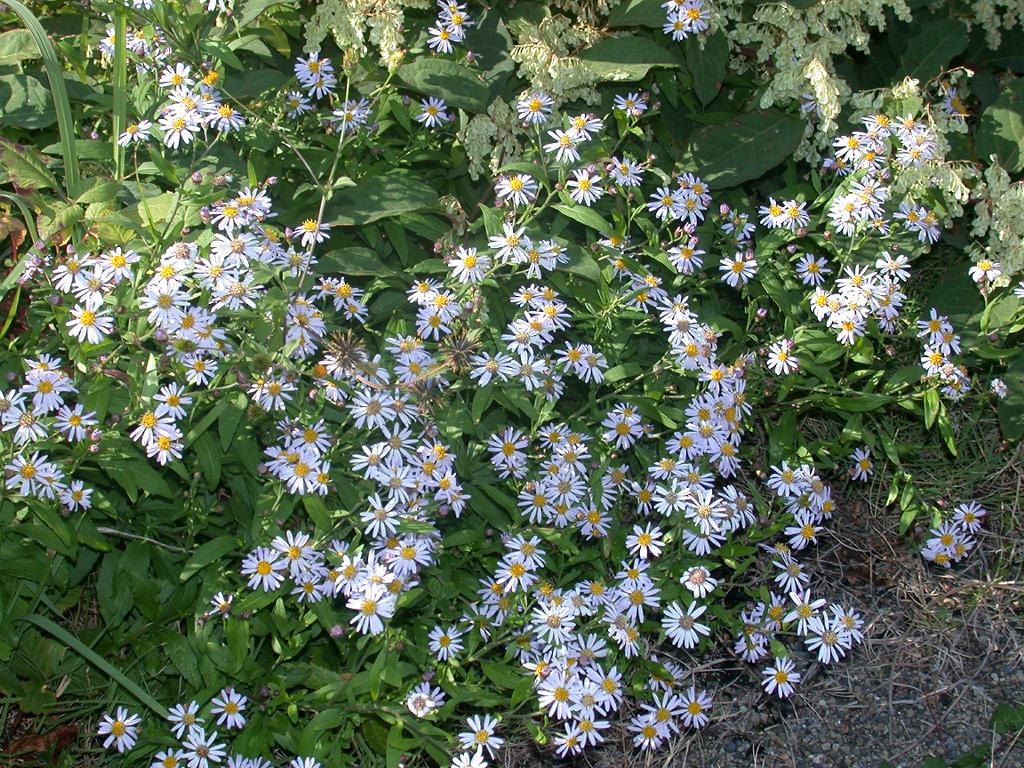
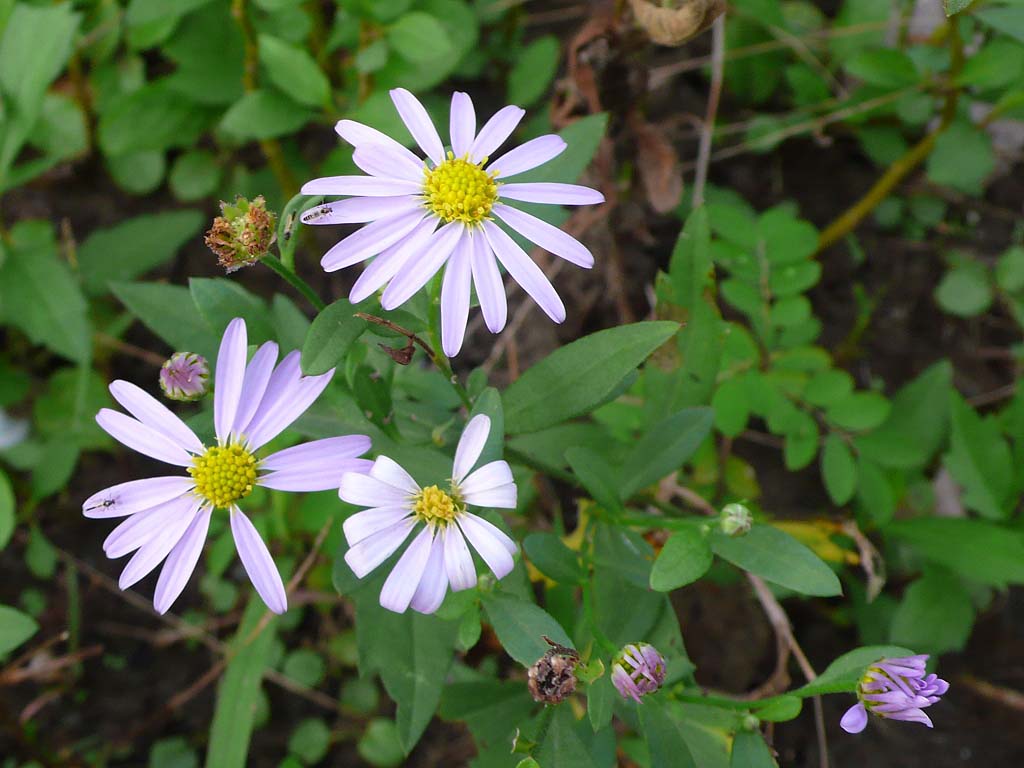
1. 马兰(本草纲目) 马兰头(救荒本草)鸡儿肠(误用名)田边菊 路边菊 鱼鳅串 蓑衣莲
Kalimeris indica (L.) Sch.
根状茎有匍枝,有时具直根。茎直立,高30-70厘米,上部有短毛,上部或从下部起有分枝。基部叶在花期枯萎;茎部叶倒披针形或倒卵状矩圆形,长3-6稀达10厘米,宽0.8-2稀达5厘米,顶端钝或尖,基部渐狭成具翅的长柄,边缘从中部以上具有小尖头的钝或尖齿或有羽状裂片,上部叶小,全缘,基部急狭无柄,全部叶稍薄质,两面或上面有疏微毛或近无毛,边缘及下面沿脉有短粗毛,中脉在下面凸起。头状花序单生于枝端并排列成疏伞房状。总苞半球形,径6-9毫米,长4-5毫米;总苞片2-3层,覆瓦状排列;外层倒披针形,长2毫米,内层倒披针状矩圆形,长达4毫米,顶端钝或稍尖,上部草质,有疏短毛,边缘膜质,有缘毛。花托圆锥形。舌状花1层,15-20个,管部长1.5-1.7毫米;舌片浅紫色,长达10毫米,宽1.5-2毫米;管状花长3.5毫米,管部长1.5毫米,被短密毛。瘦果倒卵状矩圆形,极扁,长1.5-2毫米,宽1毫米,褐色,边缘浅色而有厚肋,上部被腺及短柔毛。冠毛长0.1-0.8毫米,弱而易脱落,不等长。花期5-9月,果期8-10月。
广泛分布于亚洲南部及东部。林奈的原始标本采自中国。
Kalimeris indica, also known as Indian aster紫菀属植物 or Indian Kalimeris, is a flowering herbaceous perennial plant of the family Asteraceae. Kalimeris indica, like other species in the genus of Kalimeris, occurs mainly in eastern Asian countries of China, Korea and Japan, and has been introduced to California and Hawaii.
Kalimeris incisa
Common Name(s): Blue Star Kalimeris、Japanese Aster、Kalimeris
Previously known as: Aster incisus 'Blue Star'
Description
'Blue Star' kalmeris is a clumping blue flowered cultivar in the Asteraceae (daisy) family.
It is somewhat tolerant of part shade, but will be at its best when situated in full sun. The flowers can bloom singly or in flat-topped clusters.
Maturity can take two to five years for a plant to reach. Over time a group of plants will spread to form a colony. At that time, they are also ready to divide.
Its blooms are perfect for your cut flower or dried flower arrangements.
Cutting to the ground or deadheading after flowering may produce an additional fall rebloom.









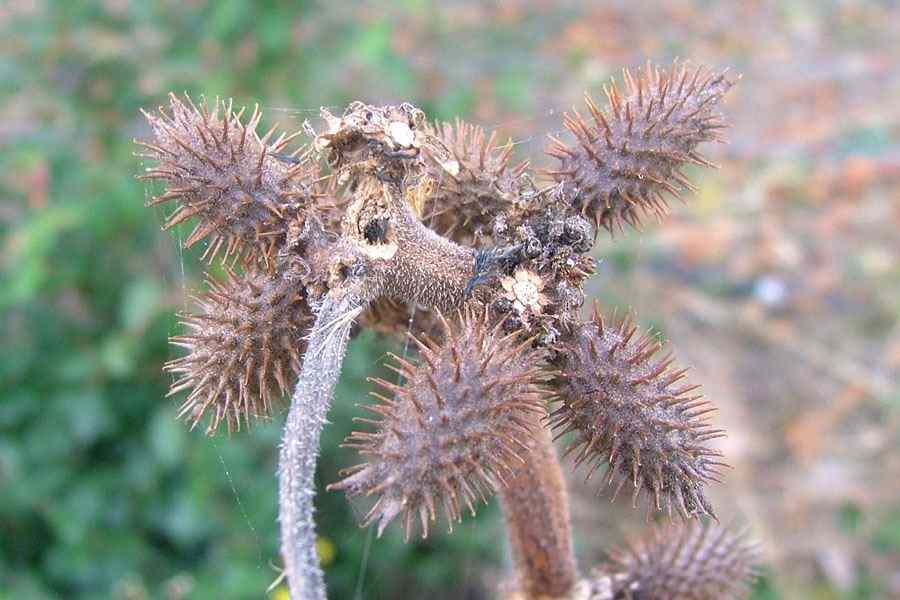
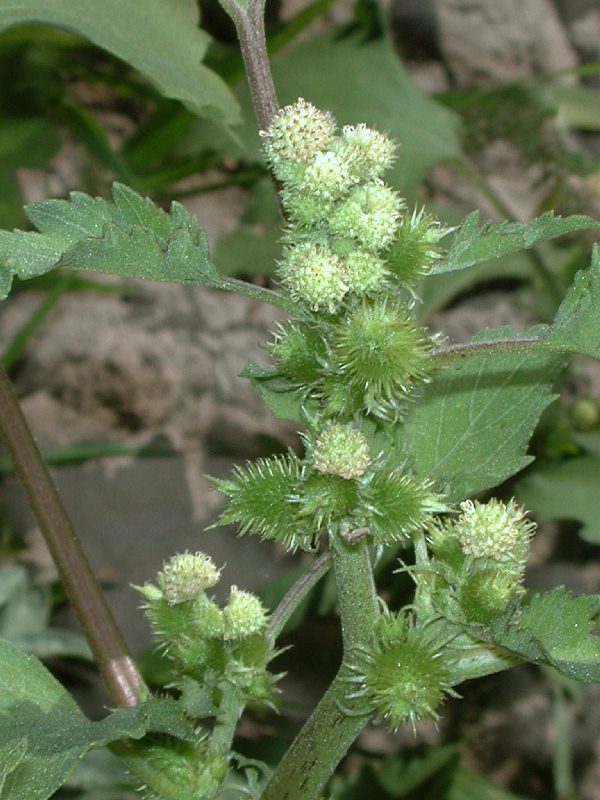
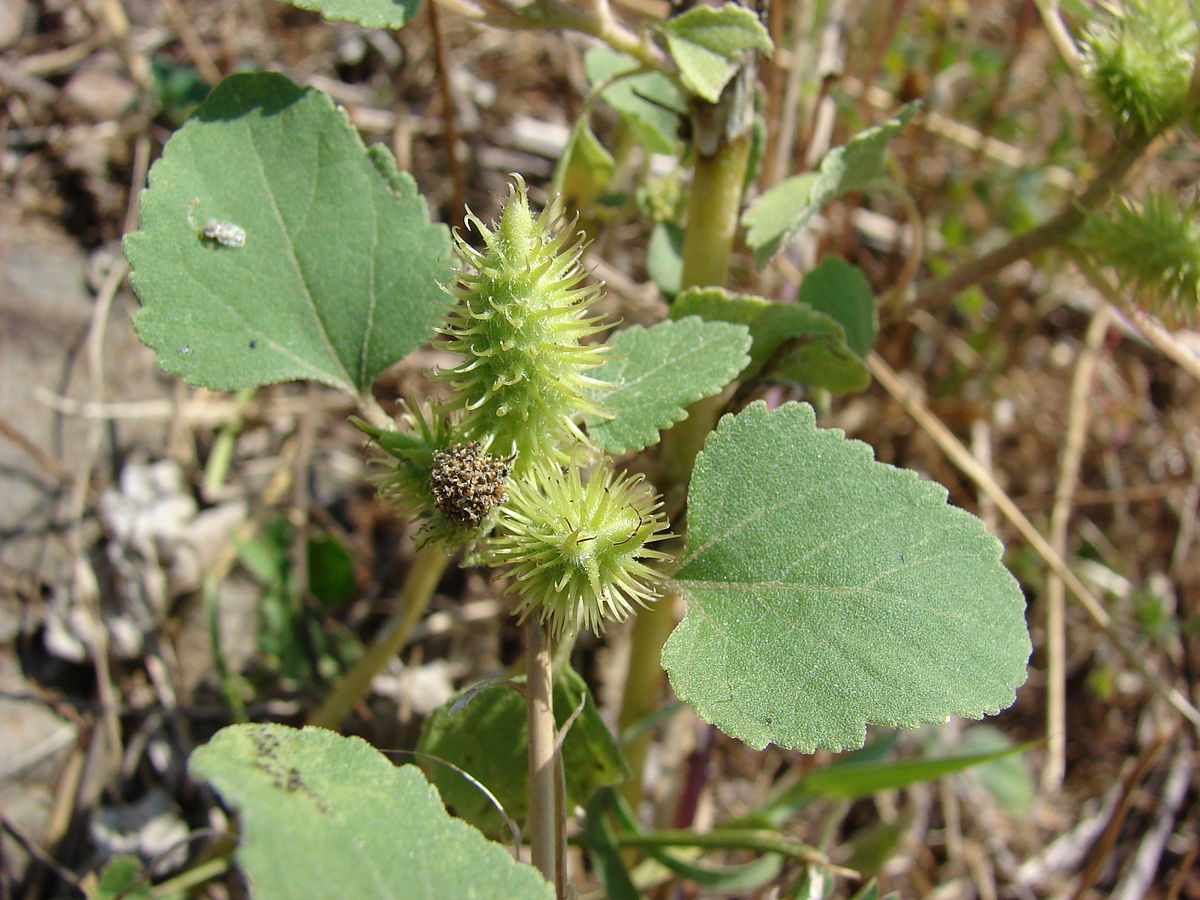
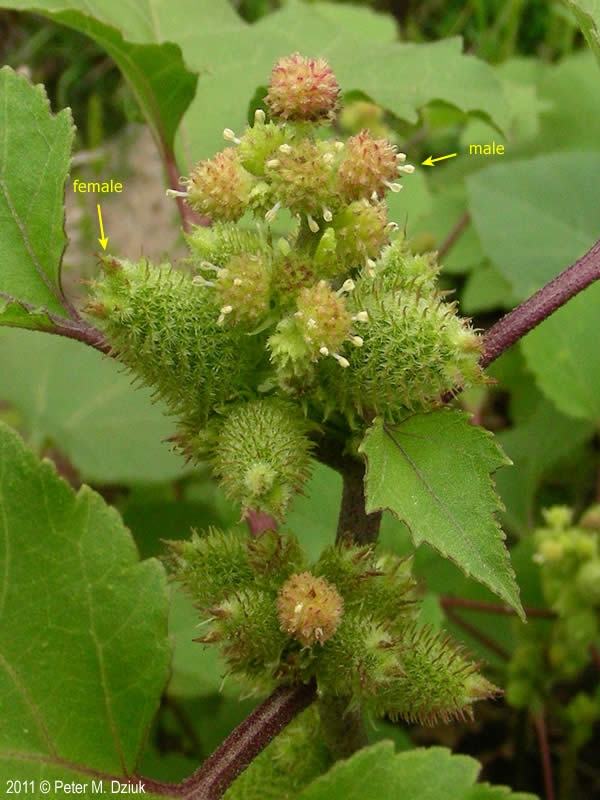
十三、苍耳属——Xanthium L.
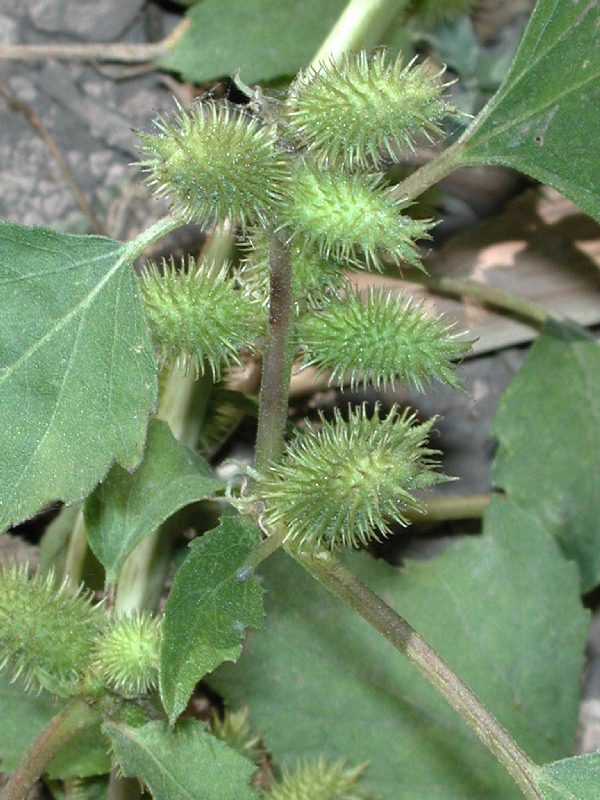
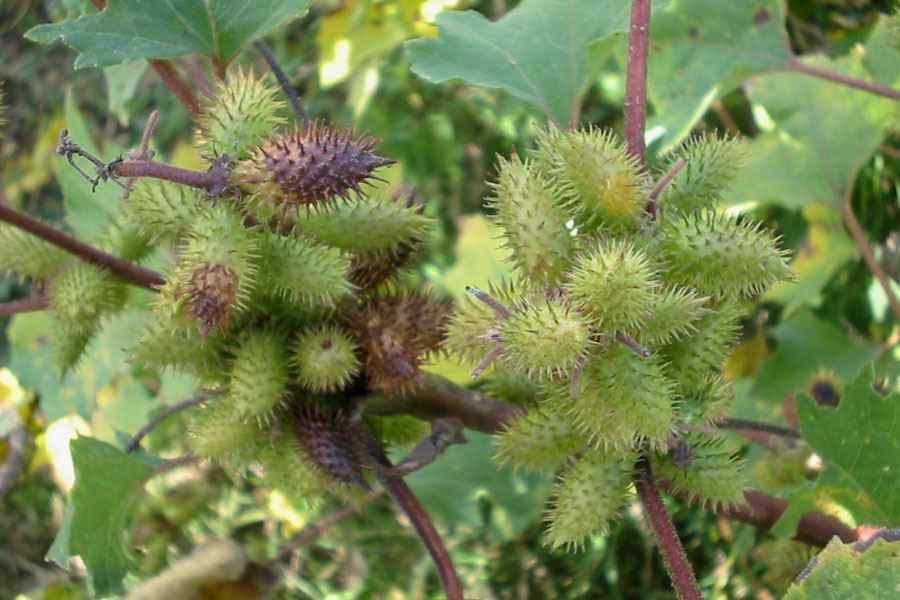
一年生草本,粗壮。根纺锤状或分枝。茎直立,具糙伏毛,柔毛或近无毛,有时具刺,多分枝。叶互生,全缘或多少分裂。有柄。头状花序单性,雌雄同株,无或近无花序梗,在叶腋单生或密集成穗状,或成束聚生于茎枝的顶端。雄头状花序着生于茎枝的上端,球形,具多数不结果实的两性花;总苞宽半球形,总苞片1-2层,分离,椭圆状披针形,革质;花托柱状,托片披针形,无色,包围管状花;花冠管部上端有5宽裂片;花药分离,上端内弯,花丝结合成管状,包围花柱;花柱细小,不分裂,上端稍膨大。雌头状花序单生或密集于茎枝的下部,卵圆形,各有2结果实的小花;总苞片两层,外层小,椭圆状披针形,分离;内层总苞片结合成囊状,卵形,在果实成熟变硬,上端具1-2个坚硬的喙,外面具钩状的刺;2室,各具1小花;雌花无花冠;柱头2深裂,裂片线形,伸出总苞的喙外。瘦果2,倒卵形,藏于总苞内,无冠毛。
本属约有25种,主要分布于美洲的北部和中部、欧洲、亚洲及非洲北部。我国有3种及1变种,都隶属于苍耳组 Sect. Xanthium 的直喙亚组 Subsect. Orthorrhyncha Wallroth.。原产南美洲的刺苍耳 Xanthium spinosum L. 在我国河南郸城县也有栽培,并已归化。
1. 苍耳(尔雅) 别名:葈耳(本草经),粘头婆,虱马头(广州),苍耳子(四川、云南、河南、山东、山西、东北),老苍子(辽宁、江西、河北),野茄子,敝子(东北),道人头,刺八裸(河南),苍浪子,绵苍浪子,羌子裸子,青棘子(江苏),抢子(安徽),痴头婆,胡苍子(湖南),野茄(河北),猪耳,菜耳(甘肃
Xanthium strumarium
俗名:苍子、稀刺苍耳、菜耳、猪耳、野茄、胡苍子、痴头婆、抢子、青棘子、羌子裸子、绵苍浪子、苍浪子、刺八裸、道人头、敝子、野茄子、老苍子、苍耳子、虱马头、粘头婆、怠耳、告发子、刺苍耳、蒙古苍耳、偏基苍耳、近无刺苍耳
苍耳(原变种)
var. sibiricum
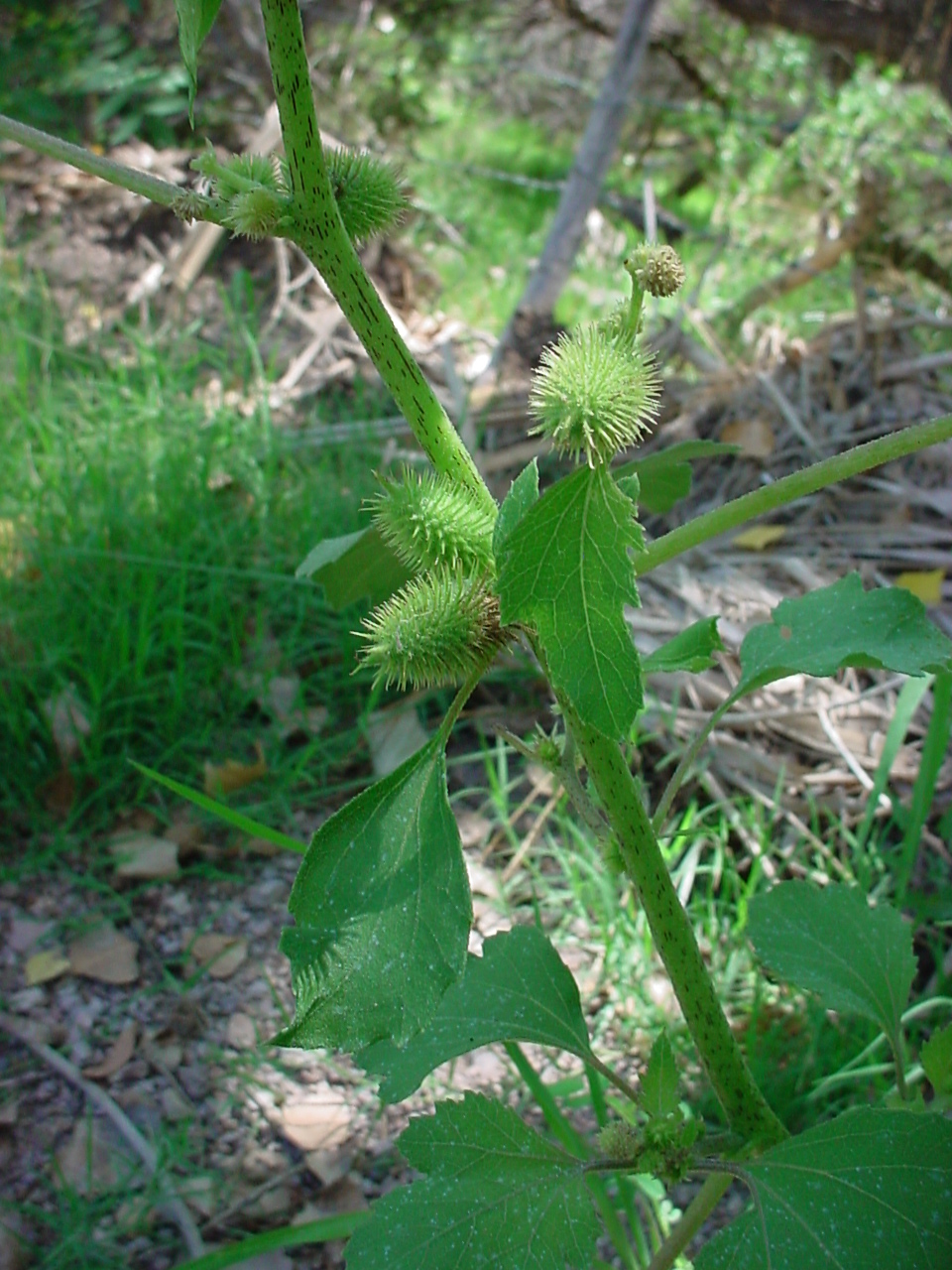
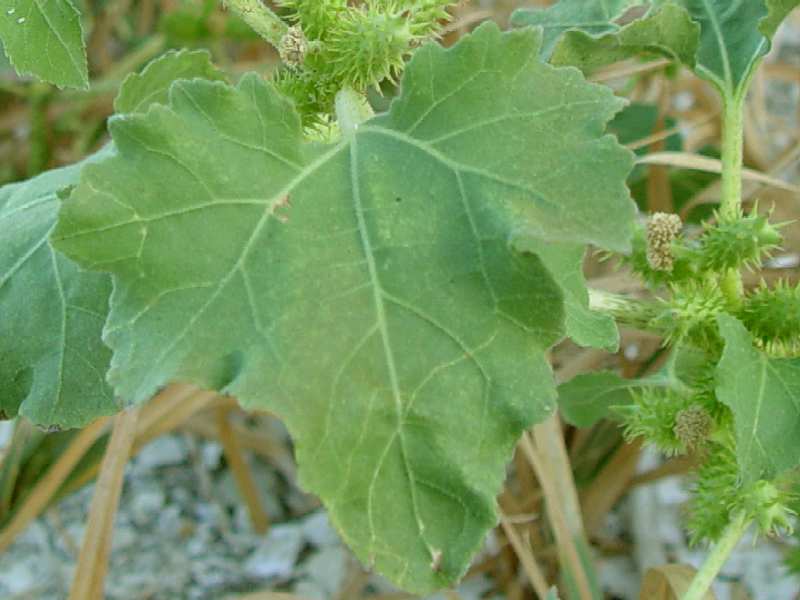
一年生草本,高20-90厘米。根纺锤状,分枝或不分枝。茎直立不枝或少有分枝,下部圆柱形,径4-10毫米,上部有纵沟,被灰白色糙伏毛。叶三角状卵形或心形,长4-9厘米,宽5-10厘米,近全缘,或有3-5不明显浅裂,顶端尖或钝,基部稍心形或截形,与叶柄连接处成相等的楔形,边缘有不规则的粗锯齿,有三基出脉,侧脉弧形,直达叶缘,脉上密被糙伏毛,上面绿色,下面苍白色,被糙伏毛;叶柄长3-11厘米。雄性的头状花序球形,径4-6毫米,有或无花序梗,总苞片长圆状披针形,长1-1.5毫米,被短柔毛,花托柱状,托片倒披针形,长约2毫米,顶端尖,有微毛,有多数的雄花,花冠钟形,管部上端有5宽裂片;花药长圆状线形;雌性的头状花序椭圆形,外层总苞片小,披针形,长约3毫米,被短柔毛,内层总苞片结合成囊状,宽卵形或椭圆形,绿色,淡黄绿色或有时带红褐色,在瘦果成熟时变坚硬,连同喙部长12-15毫米,宽4-7毫米,外面有疏生的具钩状的刺,刺极细而直,基部微增粗或几不增粗,长1-1.5毫米,基部被柔毛,常有腺点,或全部无毛;喙坚硬,锥形,上端略呈镰刀状,长1.5-2.5毫米,常不等长,少有结合而成1个喙。瘦果2,倒卵形。花期7-8月,果期9-10月。
广泛分布于东北、华北、华东、华南、西北及西南各省区。苏联、伊朗、印度、朝鲜和日本也有分布。常生长于平原、丘陵、低山、荒野路边、田边。此植物的总苞具钩状的硬刺,常贴附于家畜和人体上,故易于散布。为一种常见的田间杂草。种子可榨油,苍耳子油与桐油的性质相仿,可掺和桐油制油漆,也可作油墨、肥皂、油毡的原料;又可制硬化油及润滑油;果实供药用。此种有1变种。
Xanthium strumarium is a species of annual plants of the family Asteraceae. It probably originates in southern Europe and Asia, but has been extensively naturalized elsewhere.
Xanthium strumarium
Common Name(s): Clotbur、Cocklebur、Common Cocklebur、Donkeybur、Donkey BurrHeartleaf、Rough Cocklebur、Woolgarie Bur
This plant has high severity poison characteristics.
Description
Cocklebur is a summer annual weed in the daisy family that is native to North America and has naturalized elsewhere. It is found in all areas of NC. They grow 2-4 feet tall and prefer moist to wet sandy loam or loams in full sun to partial shade. It cannot grow in full shade.
They have minimal branching, except for short side stems that develop from the leaf axils. The central stem ends in a spike-like raceme similar to the racemes of the leaf axils. Cocklebur is monoecious, that is having both male and female reproductive organs on a plant. Each raceme produces several male compound flowers along the upper half and several female compound flowers along the lower half. Pollination occurs by wind, reproduction by self-seeding. This often leads to colonies being formed.
The seeds were a food source for the now extinct Carolina Parakeet, which was the only parrot native to eastern North America.
Insects, Diseases, and Other Plant Problems: Their aggressive growth can be a problem for pastures, fields, roadsides, along stream banks, dunes or poorly drained areas. The burs attach to clothing and animal fur for dispersal by short hooked prickles. Young Cocklebur seedlings exude toxic chemicals that can affect germination of surrounding plants, or kill seedlings.












