组合体的阅读 Group reading
(1)刻模型。刻模型的方法适用于初学者,其要点是:利用已知视图的外轮廓先想出大致表示一个什么基本形体,而后利用每个视图的观看方向,边看图边刻模型,直至模型与视图完全对应。
Make models. The way is good for a beginner. The thinking is like that: first, imagine a basic solid based on the given views, and then , cut it based on the details of each view until the three views of the model are same as the given views.
【例 6-5】识读图 6-6(a)所示三视图,刻出该物体的模型。Make model based on given views.
分析 analyze
① 先刻出原体模型。看物体三视图小线框均在大线框内,可以判定该物体是由基本体切割而成的,原体可视为长方体,如图 6-6(b)所示。
Make the original model. One can guess it a box based on given views and as shown in fig 2-6(b).
② 逐步刻出模型的切割处。看左视图在长方体前上方斜切一刀,如图6-6 (c)所示;看主视图在长方体上方左右角各斜切一刀,如图 6-6 (d)所示;看俯视图在前方正中切三刀挖一个槽,如图 6-6 (e)所示。
Cut it and get the required model. First cut a triangular prism away from the left view; subtract two triangular pyramids from the front view; cut a box away from the top view as shown in fig2-6 (e).
③ 将所刻模型与三视图反复对照,直至模型正确。
Compare the model with the three views until the model is correct.
(2)根据两面视图补画第三视图。该练习简称“补视图”或“二补三”,这是一种最常用的练习读图的方
法,它不仅练习读图,同时也练习画图。
Complete the missing view based on given views. It is widely used in training reading and drawing.
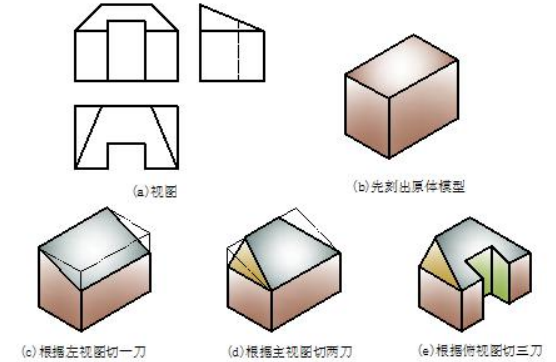
图6-6 读图刻模型示例 Fig 6-6 sample of making model
【例 6-6】识读图 6-7(a)所示两面视图,想象出该物体的空间形状并补出第三视图。
Imagine the solid and complete the missing view based on the given views. Provide the solid based on the given two views and come up with solid and complete the third view.
分析 analyze
Take the two views into account and determine to divide three frames in the front view.Follow the principle of projection rule to find out projection in the top view of the three frames in every case.Think out the shape one by one and assembly(组装) the whole shape.
补视图前应首先根据已给的两面视图,按照前面所述的读图方法想象出物体的立体形状。该物体由两个长方体和一个 U 型柱三部分叠加,叠加后在前后方向又挖一个圆柱通孔,形状如图 6-7(b)所示。根据投影规律,按照前面所述的画图思路,补出第三视图,作图步骤如图 6-7(c)所示。
Step1. Divide the front view into three parts and imagine basic solid one by one based on the basis of reading.
Step2. Combine the superposition solid based on the relative positions among the three basic solids.
Step 3. Complete view of each basic solid and check the solution.
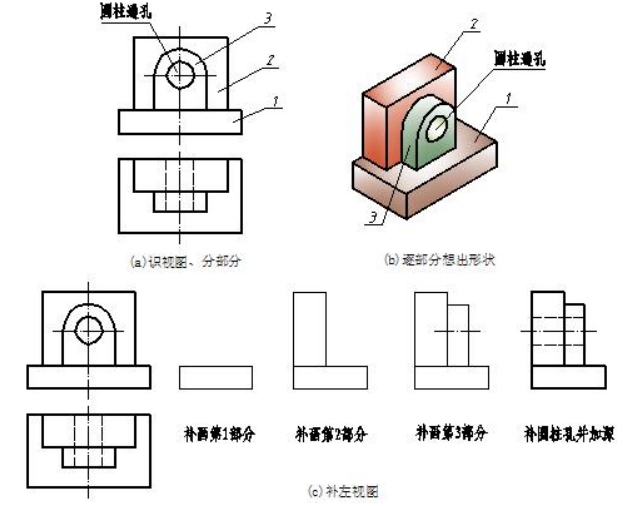
图6-7 补视图示例 fig 6-7 sample of complete missing view


