点、直线、平面 Points, lines, planes
一、点的标高投影 Elevation projection of point
基准面以上的高程为正(可省略+),基准面以下的高程为负(-),单位为米。为了表示几何元素间的距离或线段的长度,标高投影中要附以比例尺。用比例尺丈量,即可知A、B、C任意两点间的实际水平距离。见图10-2。
Elevation above the base level is positive (+ can be omitted), elevation below the base level is negative (-), and the unit is meters. To indicate the distance between geometric elements or the length of a line segment, a scale is attached to the elevation projection. The actual horizontal distance between any two points of A, B and C can be known by measuring with A scale.
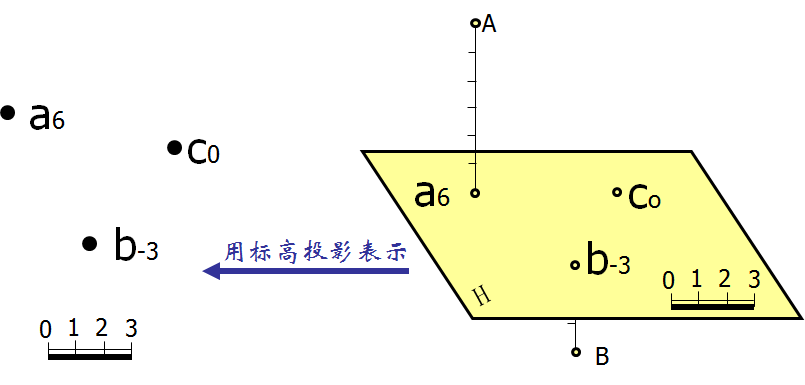
图10-2 点的标高投影 Elevation projection of point
二、直线的标高投影 Elevation projection of lines
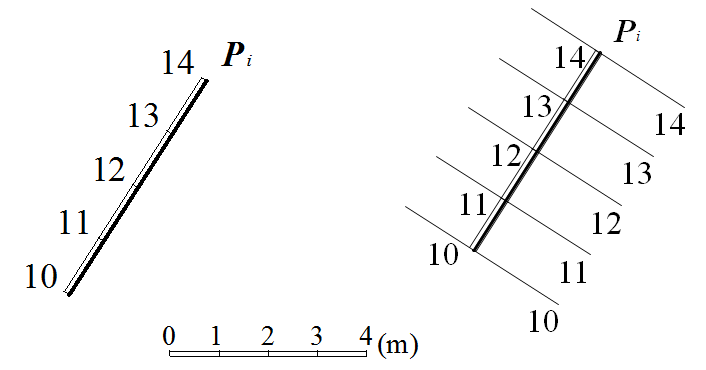
1、直线的水平投影及线上两点的高程,如图10-3。
The horizontal projection of a line and the elevation of two points on the line.
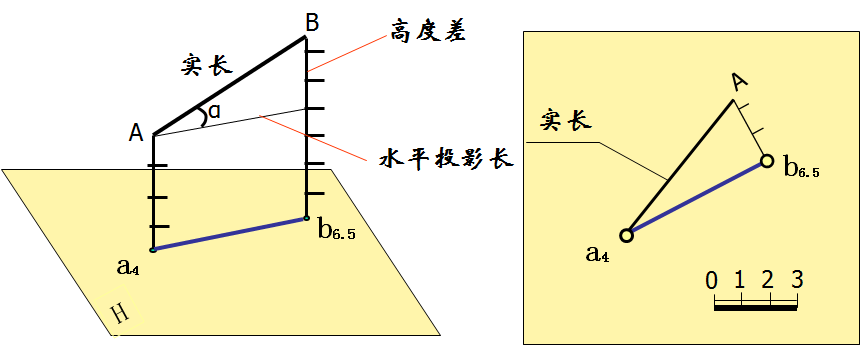
图10-3 直线的水平投影(1)
2、直线的方向及线上一点的高程,如图10-4。
The direction of a line and the elevation of a point on it.
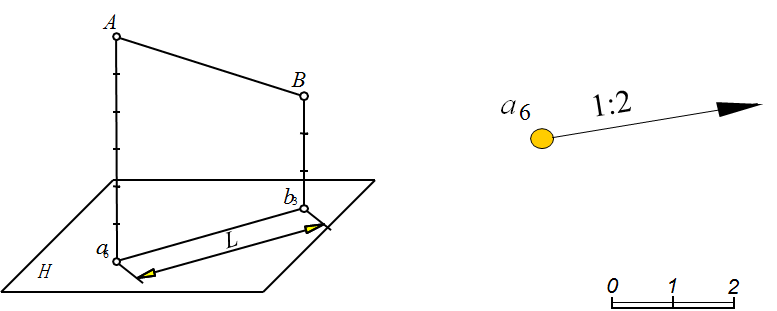
图10-4 直线的水平投影(2)
坡度 Slope —— 直线上任意两点的高差和水平距离之比,用 i 表示。
平距 Horizontal Distance —— 直线上两点的高差为1个单位时两点的水平距离,用 l 表示。
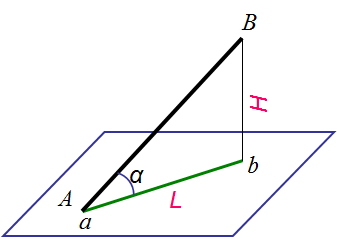
图10-5 坡度与平距
三、平面的标高投影 Elevation projection of planes
平面内的水平线就是等高线,可看作水平面与该平面的交线。 平面上的等高线的特性:等高线是直线;等高线互相平行,其投影也互相平行;等高线的高差相等时,其水平间距也相等。如图10-6(a)。
The horizontal line in the plane is the contour line, which can be regarded as the intersection of the horizontal plane and the plane. Characteristics of contour lines in plane: contour lines are straight lines; The contour lines are parallel to each other and the projections are parallel to each other. When the height difference of contour lines is equal, the horizontal spacing is also equal.
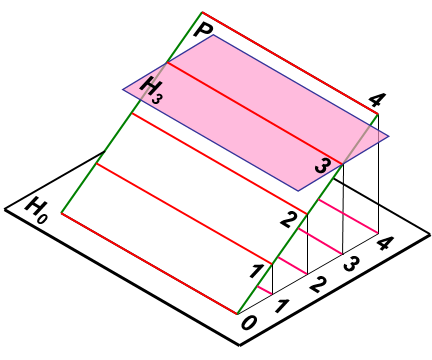
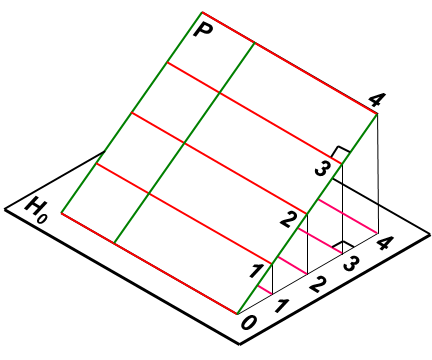
(a) (b)
图10-6 平面的标高投影
坡度线是平面内对 H 面的最大斜度线。平面上的坡度线的特性:坡度线与等高线互相垂直,其水平投影也互相垂直;坡度线的坡度代表了平面的坡度。如图10-6(b)。
Slope line is the maximum slope line of plane H. Characteristics of slope lines on the plane: slope lines and contour lines are perpendicular to each other, and their horizontal projections are also perpendicular to each other. The slope of a slope line represents the slope of a plane.
1、用一条等高线和平面的坡度表示平面,如图10-7。
The plane is represented by a contour line and the slope of the plane.
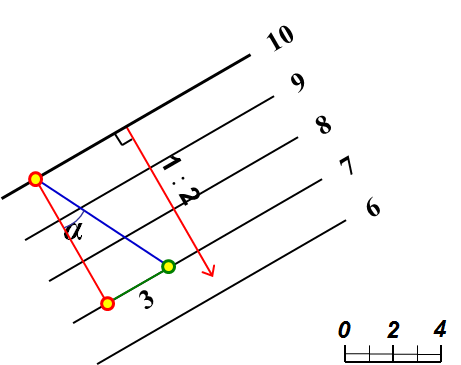
图10-7 平面的投影(1)
2、用平面上的一条倾斜线和平面的坡度表示平面,如图10-8。
A plane is indicated by an inclined line and the slope of the plane.

图10-8 平面的投影(2)
示坡线画法:方向平行于坡度线(即垂直于等高线),长短相间的细实线,短划为长划的1/3~1/2。如图10-9。
Slope line drawing method: the direction is parallel to the slope line (that is, perpendicular to the contour line), and the fine solid lines with long and short sections are 1/3 ~ 1/2 of the long section.
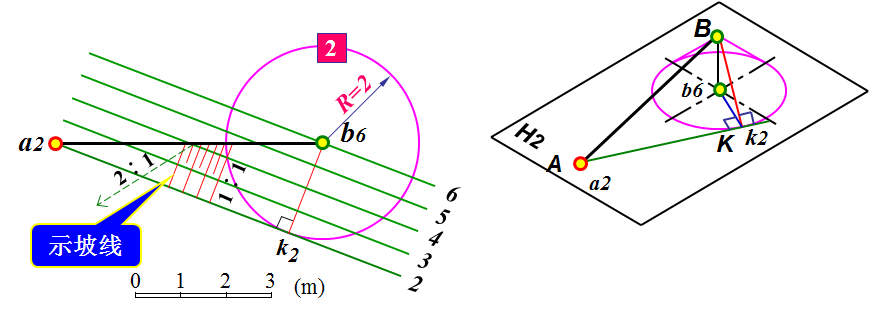
图10-9 示坡线的画法
3、用坡度比例尺表示平面,见图10-10。用坡度比例尺表示平面时,一定要画出标高投影的比例尺。
The plane is represented by a slope scale.When using the slope scale to represent a plane, be sure to draw the scale of the elevation projection.