一、曲面的形成与表示法 formation and representation of curved faces
曲面是由一条动线在一定约束条件下运动而形成。这根运动的直线或曲线称为母线,母线在曲面上的任意位置时称为素线。
The surface is composed of a dynamic motion under certain conditions. The movement of line or curve is called generatrix 英[ˌdʒenə'reɪtrɪks], generatrix at any position on the surface is called one of generating lines.
母线在运动时所受的约束,称为运动的约束条件。约束条件中,约束母线运动状况的直线或曲线称为导线,约束母线运动状态的平面称为导平面,约束母线运动状态的点称为定点。不同的母线或不同的约束条件,将形成不同的曲面。如图 8-1(a)所示柱面,是直母线 AA1 ,沿曲导线 AB 运动并始终平行于不动的直导线 MN 而形成。
The generatrix follows the constrained condition while moving is called constraint motion. In the movement , a straight line or curve is called guide line, the motion state of the planar constraint is called the guide plane, constraint link motion state is called the point. Different generatrix or different constraint conditions will form different surface.As shown in Figure 8-1 (a).
工程图样中曲面的投影一般包括以下内容:
projection of curved face includes the following points:
(1)曲面边界的投影。如图 8-1(b)中画出的 AA1 、BB1 、ACDB 、A1 C1 D1 B1 的投影。
(2)曲面轮廓素线的投影。如图 8-1(b)中画出的 c'c1、dd1 。由图 8-1(a)可看出,CC1是柱面的正向轮廓素线,只需在正面投影中画出,DD1 是柱面的俯向轮廓素线,只需在水平投影中画出。
(3)若干素线的投影。如图 8-1(b)所示。
Projection of curved face boundary; Projection of contour; Projection of main generating lines.
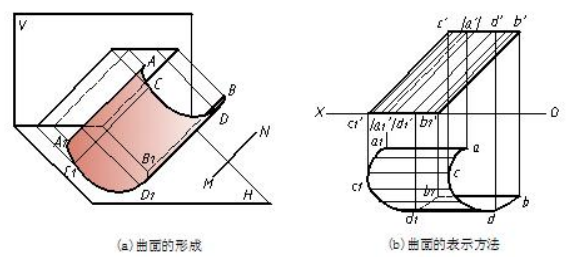
图8-1 曲面的形成和表示法 formation and representation
二、曲面的分类 classification of curved face
曲面按母线的形状可分为直线面和曲线面两类。凡是可以由直母线运动而形成的曲面称为直线面;只能由曲母线运动而形成的曲面称为曲线面。
Surface generatrix shape can be divided into straight line and curve surface. Any face is composed of straight generatrix movement and belongs to linear surface; surface only by the curved generatrix movement is called curve surface.
曲面按母线的运动方式可分为回转面和非回转面两类。由母线绕一轴线旋转而形成的曲面称为回转面;由母线根据其它约束条件运动而形成的曲面称为非回转面。曲面按是否能摊平又可分为可展曲面与不可展曲面。
Curved faces can be divided into revolution and non-revolution surfaces. Revolution face is around an axis to produce and non-revolution surface is following other way to get it. Surface according to whether can flatten out or not, and can be divided into developable and undevelopable curved surface.


