Instruction (导语)
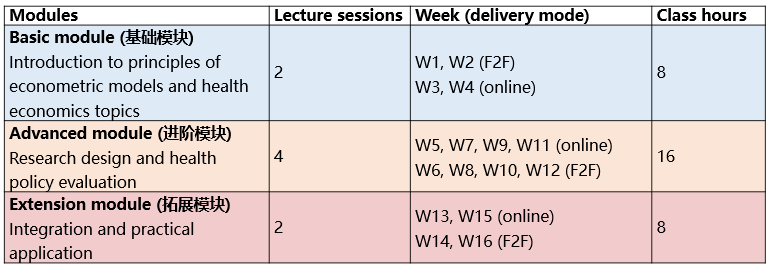
Hello, PHPM110062 fans! Welcome to the course! We will soon embark on a journey to explore how econometric methods can be used to evaluate health policies and healthcare reforms. The course consists of three modules as listed below. The delivery will be hybrid with about half online lecture and half classroom discussions. You may find learning objectives, activities, assignments, slides and case materials on the "instruction page" for each week. Have fun and see you soon in class! (PHPM110062课程的选修学生们,大家好!欢迎来到本课程!我们即将开始一场探索计量经济学方法如何用于评估卫生政策和改革的旅程。课程由下方列出的三个模块组成。教学方式为混合式,一半线上授课一半课堂讨论。在每周的“导语”页面,可以找到当周的学习目标、学习活动以及作业、幻灯片和案例素材等资料。期待在课堂中见到你!)
Learning goals for the basic module (基础模块的教学目标)
The learning goals for the basic module "Introduction to principles of econometric models and health economics topics " include:
1. acquire a firm understanding in the estimation process and related concepts
2. gain the knowledge of interpreting results from classical econometric models
3. obtain a preliminary understanding of the importance of econometric models in health policy evaluation
Instruction for Week 1 (第一周学习导语)
We will meet in class this week. Let's first go through the syllabus together and then have an overview of the course.
Learning objectives (学习目标)
- get familiar with the syllabus and course structure
- understand the importance of exploring causality for health policy
Key knowledge points (核心知识)
- key features of the healthcare market
- differences between causation and correlation
- causation and policy implication
Learning activities (学习活动)
- F2F lecture
- classical case example: Chocolate consumption and innovation [Messerli (NEJM,2012)]
Learning assessment (测评反馈)
- peer collaboration: knowledge points mind map


