-
1 chapter
-
2 Notes
-
3 Materials
Key Words and Expressions
substantial [səb'stænʃəl] a. 坚固的, 真实的, 充实的, 大量的
dedicated ['dedikeitid] a. 专用的
sensor ['sensə] n. 传感器, 感应器
constraint [kən'streint] n. 约束, 限制, 强迫, 制止
characteristic [kærəktə'ristik] n. 特征, 特性, 特色
migrate ['maigreit] vi./vt. 移居, 迁移
instruction [in'strʌkʃən] n. 指令
privilege ['privilidʒ] vt. 享有…特权
allocation [ælə‘keiʃən] n. 分配
mainframe ['meinfreim] n. 大型机
glimpse [glimps] n. 一瞥
module ['mɔdju:l] n. 模块
sophistication [səfisti'keiʃən] n. (科技产品的)复杂, 精密
infinite loops 无限循环
multiprogramming 多道程序设计
time-sharing operating systems 分时操作系统
real-time systems 实时操作系统
multi-processor systems 多处理机系统
job management 作业管理
resource management 资源管理
control of I/O operations I/O操作控制
error recovery 差错排除
memory management 存储管理
The Overview of the Operating System
1. Summary of Operating System
Initially, computers were used from the front console. Software such as assemblers, loaders, and compilers improved on the convenience of programming the system, but also required substantial (大量的) set-up time.[1]
Operating systems(see Figure 4-1) have developed over the past thirty years for two main purposes. First, they provide a convenient environment for the development and execution of programs. Second, operating systems attempt to schedule computational activities to ensure good performance of the computing system. [2]
Figure 4-1 Operating system
2. Characteristics of OS
Operating system techniques are migrating (迁移) down from mainframes to minicomputerand microcomputer systems.[3]
What exactly does an operating system do? Basically, it performs anumber of support functions. For example, picture an application program storedon disk. Before the program can be executed, it must first be copied into mainmemory, because the program that controls a computer must be in main memory.The process of copying a program from disk to memory involves considerablelogic. The source of computer’s logic is software. Thus, if the applicationprogram is to be loaded, there must be a program in memory to control theloading process. That programs the operating system.
An operating system serves as an interface, bridging the gap betweenhardware and application software(Figure4-2). Thus, as we move from hardwareto software, it is appropriate that we consider the operating system first. [4]
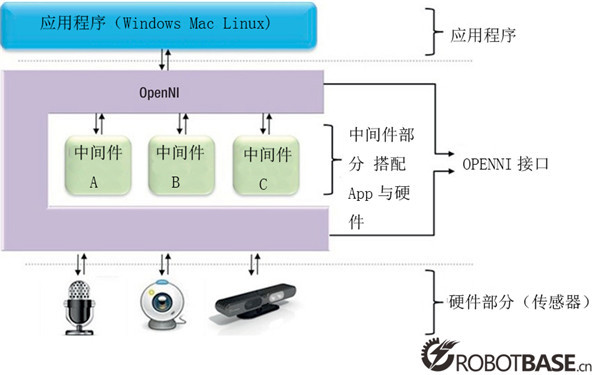
Figure 4-2
The operating system must ensure correct operation of the computersystem. To prevent user programs from interfering with the proper operation ofthe system, the hardware was modified to create two modes: user mode andmonitor mode. Various instructions (指令) (such as I/O instructions and haltinstructions) are privileged (享有…特权) and can only be executed in monitormode.[5] The user must also protect the memory inwhich the monitor resides from modification. A timer prevents infinite loops (无限循环).
3. Function of OS
Though operational software varies with manufacturers, it has similarcharacteristics. Modern hardware, because of its sophistication (精密), requires that operating systems meetcertain specific standards. For example, considering the present state of thefield, an operating system must support some form of online processing.Functions normally associated with operational software are:
(1) Job management (作业管理);
(2) Resource management (资源管理);
(3) Control of I/O operations (I/O操作控制);
(4) Error recovery (差错排除);
(5) Memory management (存储管理).
4. A Glimpse of OS Products
= UNIX
A popular operating system is CP/M, the control program formicrocomputers developed for early 8-bit machines by digital researchincorporated. UNIX, developed by American Telephone and Telegraph(AT&T), showspromise of becoming a new standard, particularly for applications involvingcommunication between two or more computers. Mainframes (大型机) have more complex operating systemswhich, in addition to serving as a hardware/software interface, manage thecomputer’s resources.
= Windows
Windows(Figure 5-3) is a graphical environment that introduces new, morestreamlined ways for you to work with your personal computer. Windows not onlygives you more control. It unleashes your computer so it operates at its fullpower, unhampered by previous memory restrictions. [6]
= DOS
Perhaps the best known microcomputer OS is MS-DOS(Figure 4-3), developedby Microsoft Corporation for the IBM-PC and compatible machines. It has becomeindustry standard.



Figure 4-3
Why is an OS standard so important? At the hardware level, computersmade by different manufacturers are often incompatible. In other words, aprogram written for one won’t work on another. Remember, however, that the OSsits between the hard and the application program. With a common in the middle,it is possible for the same program to run on two quite different machines. [7] Of course the portions of the OS thatcommunicate with the hardware might be very different, but software would see asmooth common interface.
Figure 4-4


