-
1 chapter
-
2 Notes
-
3 Materials
Key Words and Expressions
hardware['hɑ:dwɛə] n. 硬件
peripheral[pə'rifərəl] devices 外部设备
motherboard['mʌðəbɔ:d] n. 主板
main circuit ['sə:kit] board 主电路板,集成板
circuitry['sə:kitri] n. 电路学;电路系统;电路图
expansion slots [iks'pænʃən] [slɔt] 扩展槽
configuration[kənfigju'reiʃən] n. 配置,结构
architecture['ɑ:kitektʃə] n. 建筑,结构
specification[spesifi'keiʃən] n. 规格,详述,详细说明书
terminology[tə:mi‘nɔlədʒi] n. 用辞,术语
CPU(Central Processing Unit) n. 中央处理器
system clock 系统时钟
I/O ports 输入/输出端口
RAM(Random Access Memory) 随机存取存储器
ROM(Read Only Memory) 只读存储器
CMOS(ComplementaryMetal Oxide Semiconductor) n. 互补型金属氧化物半导体
System Unit
The term hardware refers to the physical components of the computer system (as opposed to the software). Your computer hardware will consist of the devices within the case of the computer itself, and any peripheral devices that are connected to the computer (such as the mouse and keyboard).
The primary component of the computer is the motherboard (also called the main circuit board,main logic board, mainboard, or systemboard). The motherboard is a large printed circuit board with microchips, connectors, and other components mounted on it, and with copper circuitry traces that connect the components together.[1]
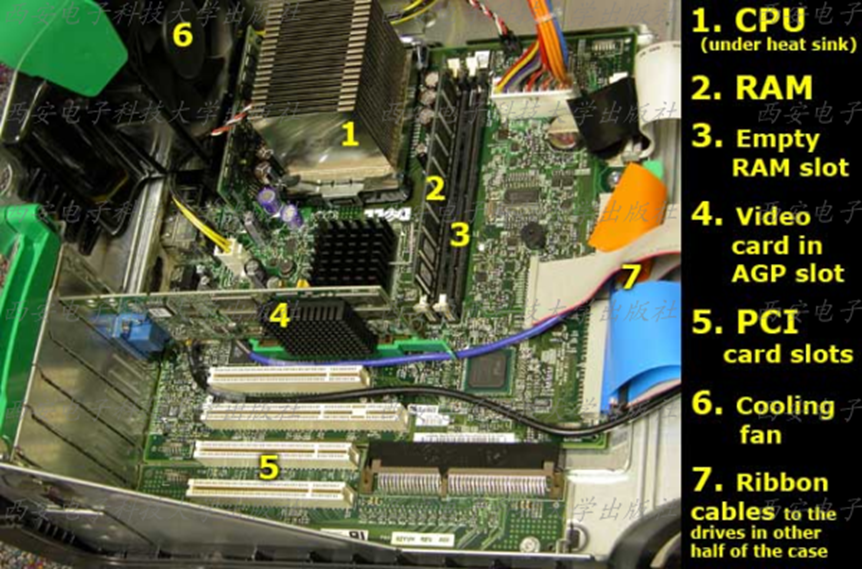
1. The Components of a Motherboard
A motherboard typically holds thefollowing items:
= CPU (Central Processing Unit) (where the actual
processing of data takes place).
= System clock circuitry (that keeps all of the
digital chips in lock step).
= Other controller chips that act as traffic cops directing data
flow along the system busses (the circuitry connecting the chips to the CPU) and I/O ports.
= RAM (the main memory, plus additional slots for adding
more memory).
= ROM (containing the BIOS).
= CMOS memory.
= Expansion slots(for adding expansion cards such
as video cards and sound cards).
Additional information about the parts listed above can be found in the other sections of this tutorial. Along with the motherboard, the case of your computer typically contains a power supply(to convert the AC line current from the wall outlet to the low-voltage DC current used by the computer) and several storage devices located in the expansion bays of the case (such as: hard drives, floppy drives, and CD drives,and DVD drives).[2]


