-
1 Chapter
-
2 Notes
KeyWords and Expressions
feat[fi:t] n. 技艺,功绩,武艺,壮举,技艺表演
consistent[kən'sistənt] a. 一致的,调和的,坚固的,相容的,相符的
manipulate[mə'nipjuleit] v. 操纵,利用,假造; [计算机] 操作
graphical['græfikəl] a. 图解的(绘图的,生动的)
security[si'kjuəriti] n. 安全;保证金,抵押品;债券,证券
virus['vaiərəs] n. 病毒
checkers['tʃekəz] n. 西洋棋
firewall ['faiəwɔ:l] n. 防火墙
potentially[pə'tenʃəli] ad. 潜在的
trojan['trəudʒən] n. 特洛伊人,勤勉的人,勇士 a. 特洛伊的,
特洛伊人的
horse[hɔ:s] n. 马 v. 骑马
malicious[mə'liʃəs] a. 怀恶意的,恶毒的
disastrous [di'zɑ:strəs] a. 灾难性的
unauthorized['ʌn'ɔ:θəraizd] a. 非法的,越权的
assembler[ə'semblə] n. 汇编程序
debugger[di:'bʌgə] n. 调试器,调试程序
convert[kən'və:t] v. 使转变,使…改变信仰,倒置 n. 皈依者,
改变信仰的人
script[skript] n. 原稿,手稿,手迹;脚本
Software around Us
Computers seem to perform amazing feats as they process information and display output almost instantly; but behind the scenes, they are really very simple minded devices.[1]All they do is executing long strings of instructions that were previously written by a clever human programmer.The thing that makes a computer’s performances seems so amazing is that it executes these instructions very,very, very quickly,accurately, and tirelessly. Computers aren’t smart; they are just FAST.
But computers can’t do ANYTHING without step-by-step instructions written out for them. These lists of instructions are called programs. Programs (and the associated data (关联数据))are known as software. Software needs to be installed onto a computer before it can be used. Software is often sold in sets of several programs and associated data called a software package, and typically comes on a CD-ROM or may be downloaded from the Internet. The Microsoft Office Suite is such acollection of programs and data that allows users to manipulate words, numbers,and data.
There are two major categories of software: System software and Application software.
1. System Software
System software controls a computer’soperations and manages a computer’s resources. System software includes theoperating system, utilities (应用程序), and computer programming tools.
The operating system (OS) also includessoftware that provides the user with an operating environment for interactingwith the computer. An operating environment could be a command-line interface(requiring the user to type in commands to control the computer), or it couldbe a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to interact with thecomputer using a mouse to point and click on icons, buttons, menus, etc.[2]
Most PCs today use some versions (版本) of the Microsoft Windows operating system (such as Windows 2000 or Windows XP). Windows includes a GUI user environment. A smaller number of PCs use the Linux operating system (an UNIX-like OS).
System software may also include security software, such as virus checkers and firewalls. A virus checker searches files for potentially harmful programs such as viruses, worms, or trojan horses that are written by malicious programmers. Viruses and similar programs can perform disastrous (损失惨重)activities on your computer system, such as erasing your hard disk. To be safe,you should scan all downloaded files and messages on your PC and never run any e-mail attachments if you don’t know what they are. A firewall, or similar program, protects your computer from unauthorized access over a networkor telecom connection.
System software also includes the tools used to write other programs. These include compilers, assemblers, and debuggers for various computer programming languages. A programming language allows a person to write computer instructions in a language that is easier fora human to understand, but which is then converted into the low-level numerical instruction codes that a computer processor unit can execute. Some programming languages include C, C++, Java, FORTRAN, COBOL, PASCAL, BASIC, Visual Basic(and such scripting languages as JavaScript and Perl).
2. Application Software
Application software runs on top of the operating system and allows the user to perform a specific task, such as word processing a letter, calculating a payroll in a spreadsheet, managing a database of information, reading e-mail messages, or manipulating digitalphotographs.
Some common applications used onpersonal computers include:
A word processor (such as MS Word orWordPerfect) allows you to enter and format text (as well as some graphics) tocreate reports, letters, etc. Formatting options include changing the textsize, font (typeface), line spacing, and page margins. You can also use document templates that contain pre-made formatting, styles,and content to allow you to create a document quickly without repeating workunnecessarily.
Web authoring software (such asDreamweaver or GoLive)allows users to create complex web pages without the user having to know XHTMLor CSS or JavaScript(see Figure 3-1). The user simply inserts text and graphicsinto a WYSIWYG editing window to layout the material as desired, and theapplication software write the necessary web page code in the background.
Presentation software (such as MS PowerPoint) is used to create presentations of slides containing text andgraphics (and also incorporating sound and visual effects). These presentations can be projected from a computer display projection unit, or the slides can be printed out onto transparencies.
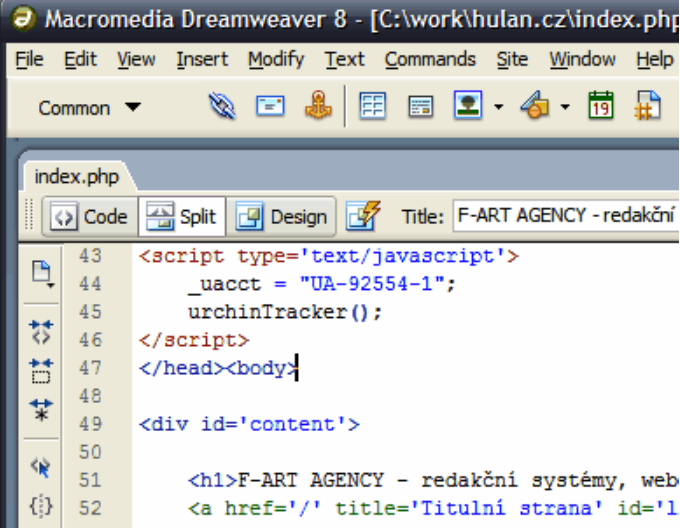
Figure 3-1 Dreamweaver 8.0


